Binomial distribution
1/21
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Binompdf
Use for exact probabilities (ex. P(x=5)
Binomcdf
Use for more than, less than, at least, or at most questions
1-binomcdf
Use for “at least” probabilities (ex. P(x≥4); x=3 on Calc)
Where “x” is AT LEAST a number; not for “no more than” problems
Binomial distribution
B - Binomial; only TWO possible outcomes “success” or failure
I - Independent; the observations are independent; knowing the result of one observation tells you nothing about the others
N - Number; there is a fixed number “n” observations
S - Same probability; the probability of success “p” is the same for each observation
For binomial distribution, we will look at the probability of getting an event with:
n - total number of trials
x - number of successes
p - probability of success
(1-p) - probability of failure
This is the binomial setting
If x is a binomial random variable, it is said to have a binomial distribution, and is denoted as
B(n,p)
If data is produced in a binomial setting, then random variable x is called a
Binomial Random Variable
Binomial coefficient (also called a combination)
The number of ways to arrange x successes in n observations (read as “n choose x)
Math → PRB → 3 nCr
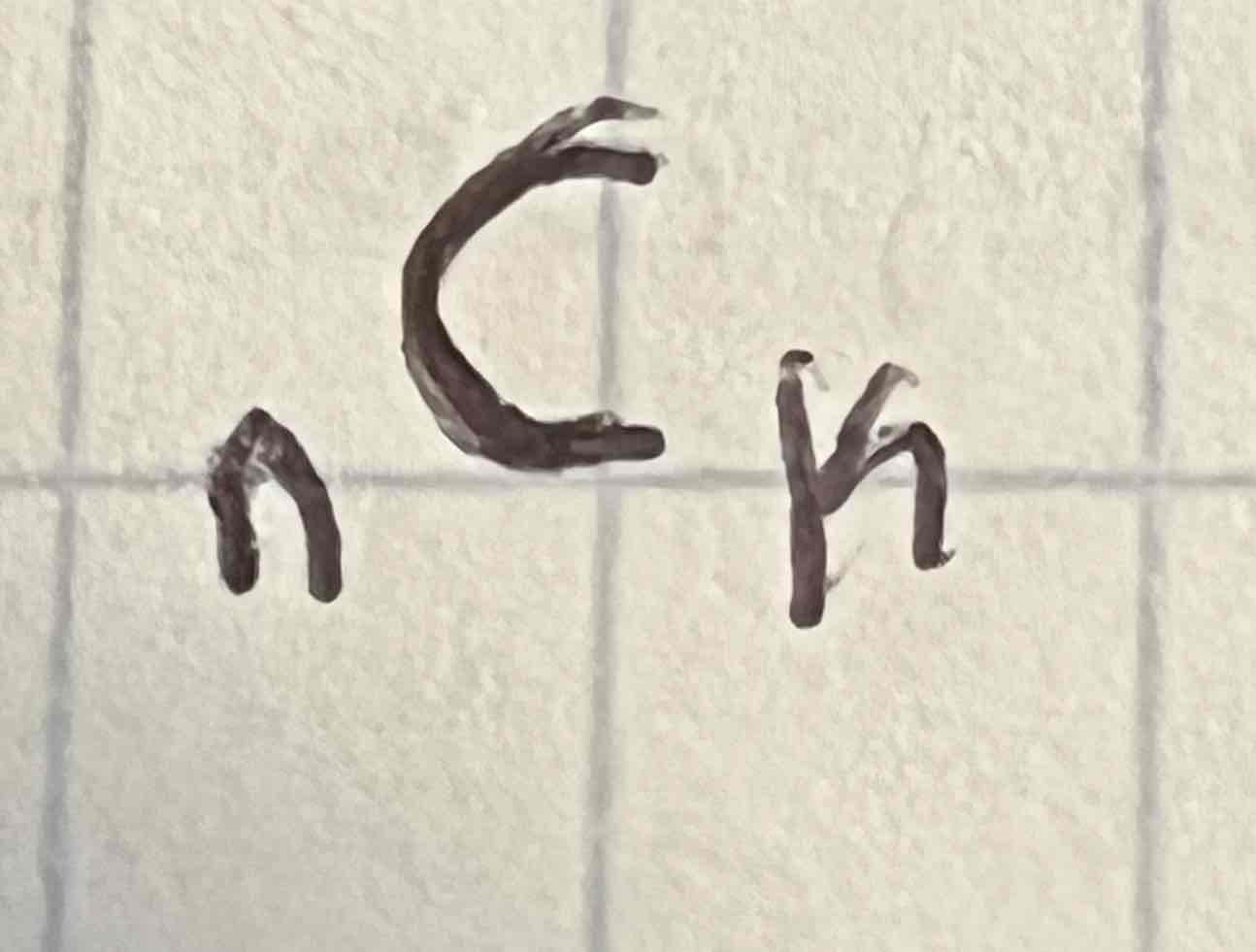
Means are NEVER
Percentages
Population (parameter) mean
µ
Population (parameter) standard deviation
sigma
Population (parameter) proportion
p
Population (parameter) SD of proportion

Sample (statistic) mean

Sample (statistic) standard deviation
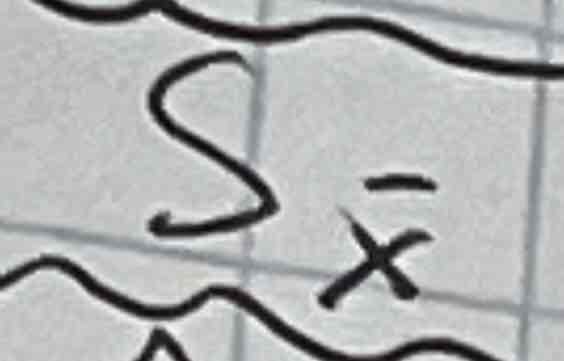
Sample (statistic) proportion

Sample (statistic) SD of proportion
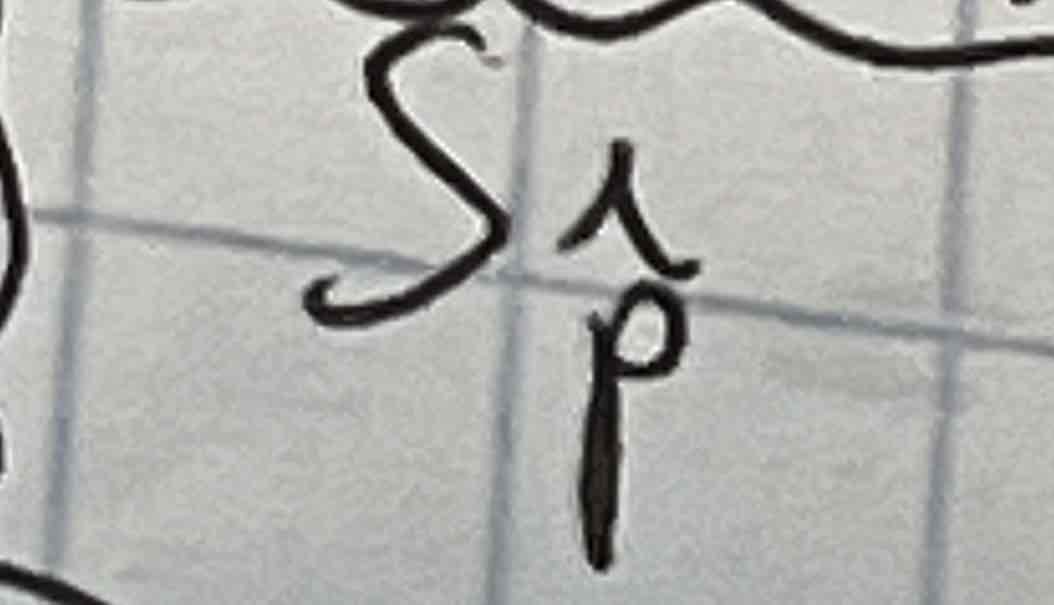
Sample Distribution truths
The distribution is normal regardless of the shape of the population distribution as long as the sample size, n, is large enough
The distribution is normal regardless of the sample size as long as the population distribution is normal
The distribution’s mean is the same as the population mean
The distribution’s standard deviation is smaller than the population’s standard deviation
Geometric Distribution
Only Two outcomes - “success” or failure
The probability of success, p, is the same for each observation (consistent probability)
n observations are independent
TRIALS REPEAT UNTIL YOU GET A SUCCESS
Bins WITHOUT the s - Bint
geometcdf
Use for more than, less than, at least, or at most questions (geometric)
geometpdf
Use for exact probabilities (ex. P(x=5) (geometric)
1-geometcdf
For “at least” problems (geometric)