Biochemistry Exam 1 First Review
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Proteins: Main Agents of Bio Function
~Catalysis?
DNA polymerase (in DNA replication)
RNA polymerase (Transcription)
Proteins: Main Agents of Bio Function
~Transport
hemoglobin (transports O2 in the blood)
myoglobin (storage of O2)
lactose permeate (transports lactose across the cell membrane)
Proteins: Main Agents of Bio Function
~Structure
collagen (connective tissue)
keratin (hair, nails, feathers, horns)
Proteins: Main Agents of Bio Function
~Motion
myosin (muscle tissue)
actin (muscle tissue, cell motility)
Luciferase
Example: light produced by a firefly
Keratin
fingernail, common contaminants in MS assay
example: rhino horn
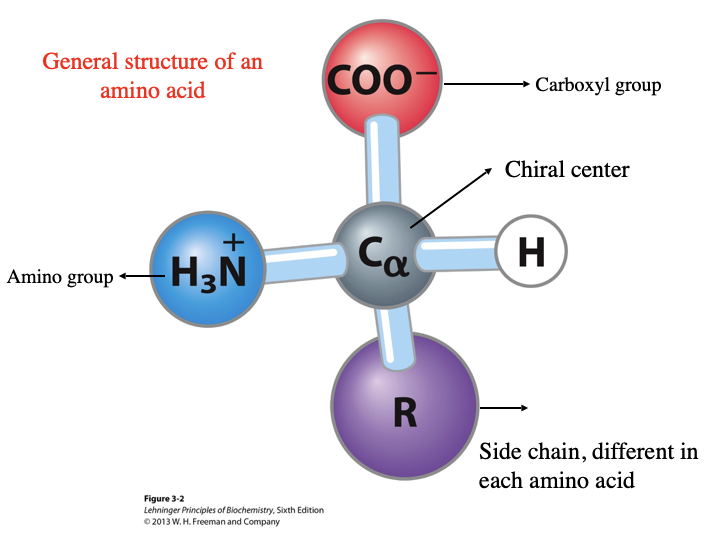
General Structure of an Amino Acid
Contains:
carboxyl group
hydrogen
side chain, different in each amino acid
amino group
chiral center
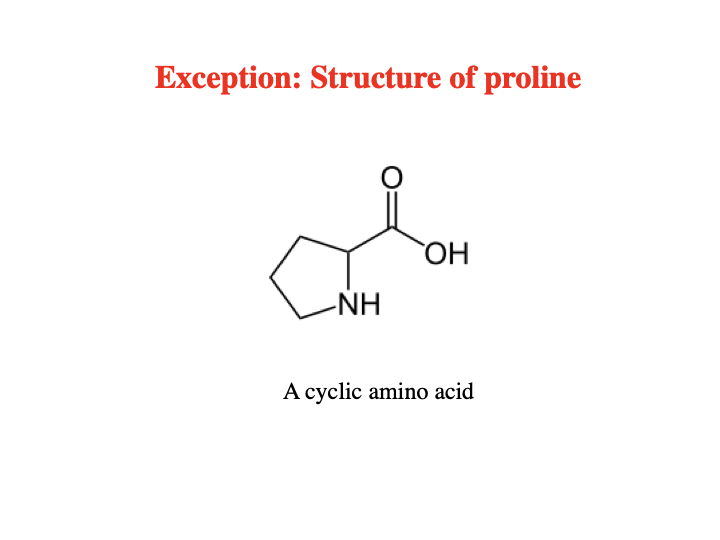
What amino acid is an exception for the general structures of AAs?
Proline ; P ; Pro
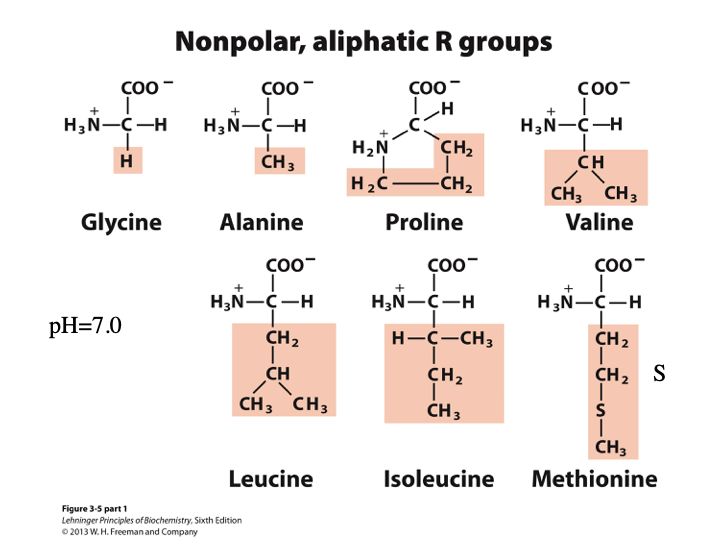
Amino Acids Classification: Nonpolar, aliphatic R Groups
Glycine (G), Alanine (A), Proline (P), Valine (V), Leucine (L), Isoleucine (i), Methionine (M)
AA Classification: Aromatic R groups
Phenylalanine (F), Tyrosine (Y), Tryptophan (W)
Are the Aromatic R groups non-polar or polar? hydrophobic or hydrophilic? Which two absorb more light than the other?
Non-polar
Hydrophobic: normally buried inside the protein core
Y and W absorb UV light more than F
AAs Classification: Polar uncharged R groups
Serine (S), Threonine (T), Cysteine (C), Asparagine (N), Glutamine (Q)
What is the smallest amino acid?
Glycine (G)
What kind of bonds are formed in polar, uncharged R groups?
Hydrogen bonds
What kind of bonds can Cysteine (C) form?
Disulfide bonds
AAs Classification: Positively charged R groups
Lysine (K), Arginine (R), Histidine (H)
Which AA has an imidazole group attached?
Histidine (H)
What are ampholytes?
Substances that have dual acid and base nature
Example of ampholyte?
Alanine (A)
Formation of Peptides: What are peptides? Are they smaller or larger than proteins?
peptides are small condensation products of amino acids. They are smaller than proteins
Where does numbering and naming peptides start from?
Amino terminus
Practice AA code: Serylglycyltyrosylalanylleucine
SGYAL
What is the average molecular weight of AAs?
138 da
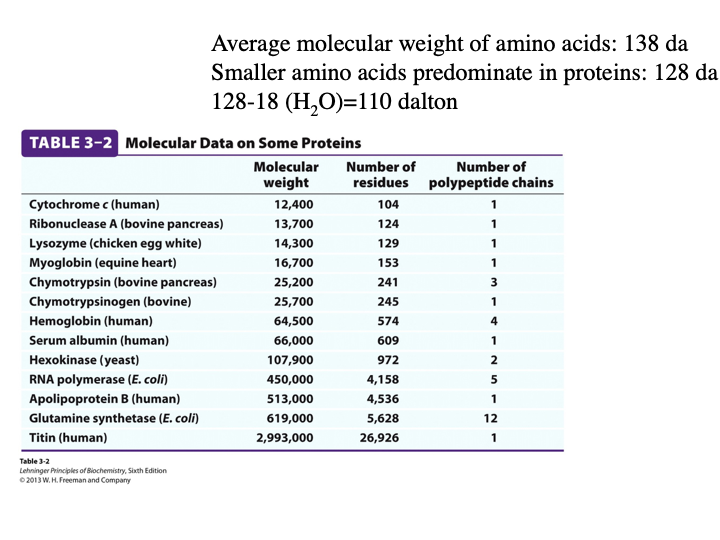
Weight of smaller AAs predominate in proteins?
128 da
Techniques used for protein purification?
Extraction
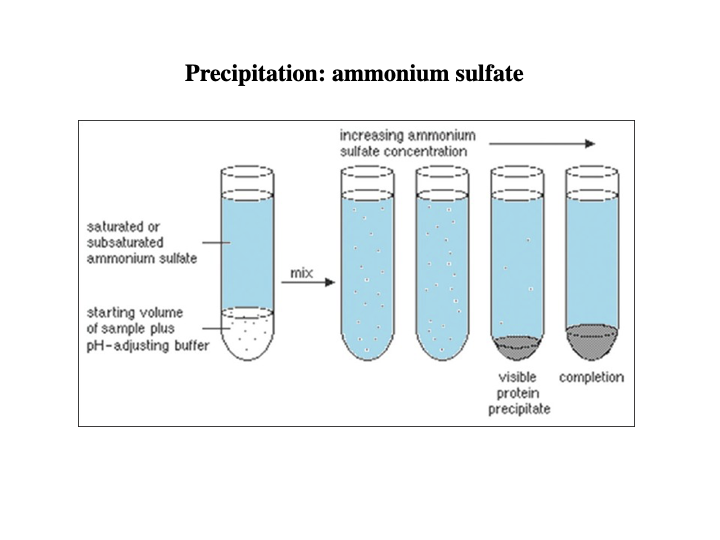
Precipitation: ammonium sulfate
dialysis
ultracentrifugation
size exclusion chromatography
ion exchange chromatography
metal binding
purification of a tagged protein
Techniques used for protein extraction?
Grinding with or without liquid N
Grinding with sand
Bead beater
sonication
French press
buffer with or without mild detergent
Explain what precipitation of ammonium sulfate looks like
What is dialysis used for?
It gets rid of ammonium sulfate
What is SDS? What do its micelles do?
SDS Is sodium dodecyl sulfate - a detergent -
SDS gives all proteins uniformly negative charge
SDS micelles bind to and unfold all the proteins
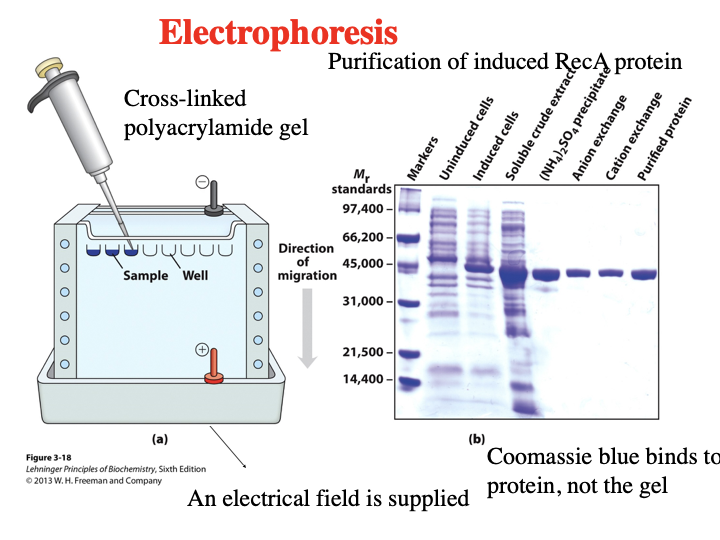
What is Electrophoresis? What is it checking in this image?
(SDS-PAGE) Electrophoresis a method to separate proteins by size using an electric field. It is checking each step of the purification process and shows the purification of induced RecA protein getting purer at each stage.
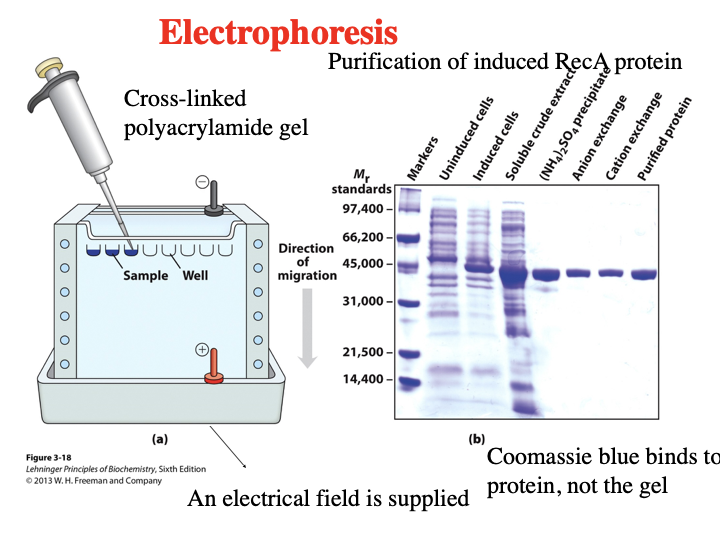
Steps of SDS
a protein will bind to SDS
Bound SDS will contribute to negative charge
unmask intrinsic charge of protein
>all protein will have similar charge to mass ratio
Levels of Structures In Proteins?
Primary - amino acid residues - sequence, peptide bond and disulfide bond
secondary structure - alpha helix - local structure, piece of tertiary structure
tertiary structure - polypeptide chain (three dimensional)
quaternary structure - assembled subunits - a protein has two or more polypeptides
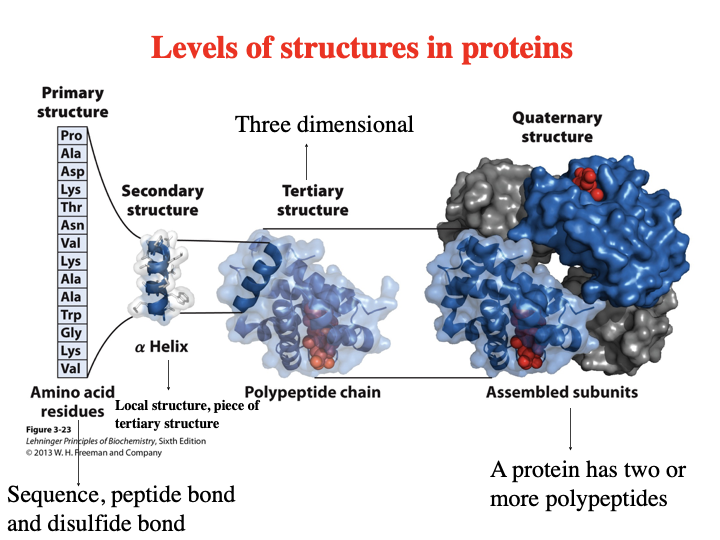
The polypeptide is made up of a series of planes linked at _____ carbons.
alpha
X-ray diffraction showed that C-N bond is shorter than regular C-N bond indicating….? Can partial bonds rotate freely
resonance or sharing of two pairs of electrons. partial double bonds cannot rotate freely.
What are secondary structures?
They refer to a local spatial arrangement of the polypeptide backbone.
What two regular secondary structure arrangements are common and what are they stabilized by?
The alpha helix:
stabilized by hydrogen bonds between nearby residues.
The beta sheet:
stabilized by hydrogen bonds between adjacent segments that may not be nearby
What is a random coil?
irregular arrangement of the polypeptide chain
What is an alpha helix? Are they right or left handed helices? How are peptide bonds aligned with the helical axis? Are side chains pointing out or in? Are they perpendicular with or alongside the helical axis?
helical backbone held together by hydrogen bonds between the backbone amides of an n and n+4 AAs.
right handed
roughly parallel
They point out
They are roughly perpendicular with helical axis
T/F? Sequence affects helix stability
True
Do all polypeptide sequences adopt an alpha helical structure?
No
What small hydrophobic residues AAs are strong helix formers?
Ala (A) and Leu (L)
What two AAs act as helix breakers?
Pro (P) - because rotation around N-C bond is impossible
Gly (G) - because tiny R-groups support other conformations
T/F Parallel or antiparallel orientation of two chains within a sheet are impossible.
False
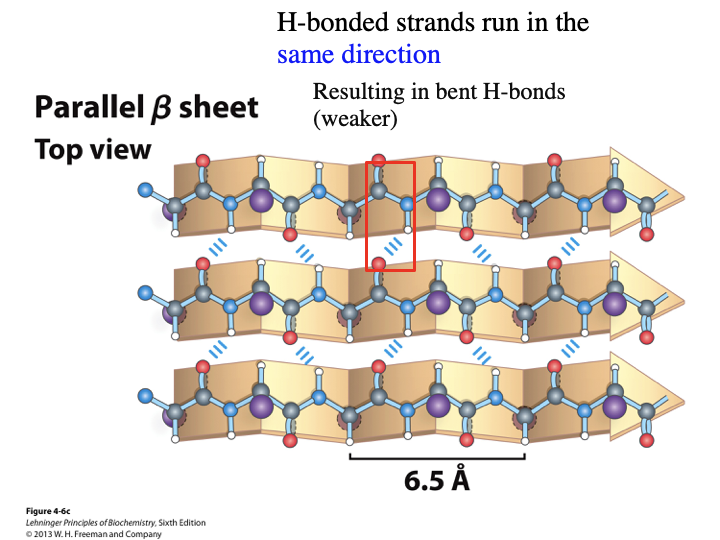
In parallel B sheets, do the H-bonded strands run in the same or opposite directions? Do they result in bent or linear H-bonds? Are they weaker or stronger?
same direction
bent
weaker
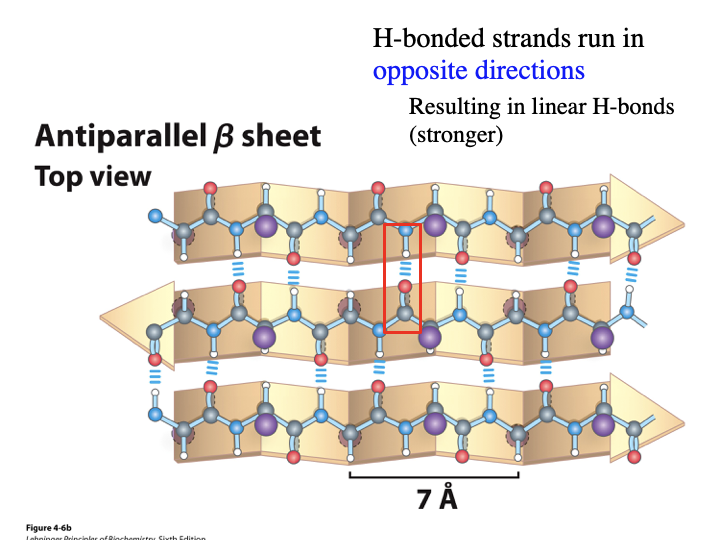
In antiparallel B sheets, do the H-bonded strands run in the same or opposite directions? Do they result in bent or linear H-bonds? Are they weaker or stronger?
opposite
linear
stronger
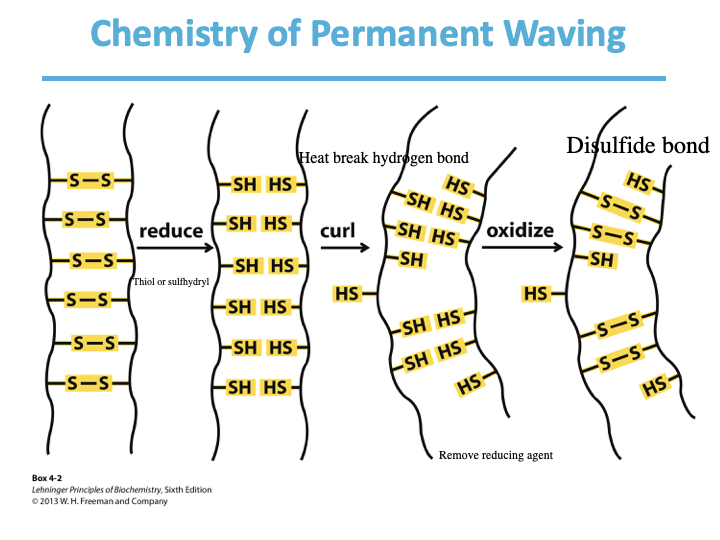
What happens during permanent waving?
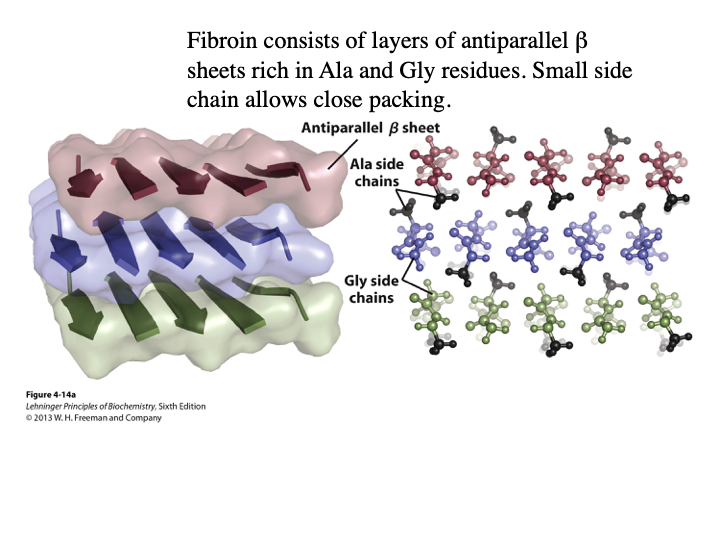
What is fibroin? Does it have antiparallel or parallel beta sheet structure? What AA side chains allow the close packing of sheets? What is the structure stabilized by?
The main protein in silk from mothers and spiders
Antiparallel
A and G
hydrogen bonding within sheets and London dispersion interactions between sheets
What is spider silk used for? Is it a strong or weak material? Is it flexible? How is it a composite material?
used for webs, egg sacks, and wrapping prey
extremely strong material that is stronger than steel and can stretch A LOT
It is composite with crystalline parts and rubber-like stretchy parts
Steps needed for X-ray Crystallography
purify protein
crystallize protein
collect diffraction data
calculate electron density
fit resides into density
Pros and Cons of X-ray Crystallography
Pros:
no size limits
well-establish
Cons:
difficult for membrane proteins
cannot see hydrogens
What does x-ray crystallography do?
it measures the locations and intensities of spots produced by a be a of X-ray.
Steps of Biomolecular NMR:
purify protein
dissolve protein
collect nmr data
assign nmr signals
calculate structure
Pros and Cons of Biomolecular NMR
Pros:
no need to crystallize protein
can see many hydrogens
Cons:
difficult for insoluble proteins
works best with small proteins
What is NMR (nucleic magnetic resonance)? What happens when static magnetic field is applied?
manifestation of nuclear spin angular momentum
nuclear spin generates dipoles
A proteins function depend on its ____.
3D structure
What is denaturation?
Loss of structural integrity with accompanying loss of activity
How can proteins be denatured?
heat or cold
pH extremes
organic solvents
chaotropic agents: urea and guanidinium
What do chaperones prevent? What do they facilitate?
Misfolding
folding
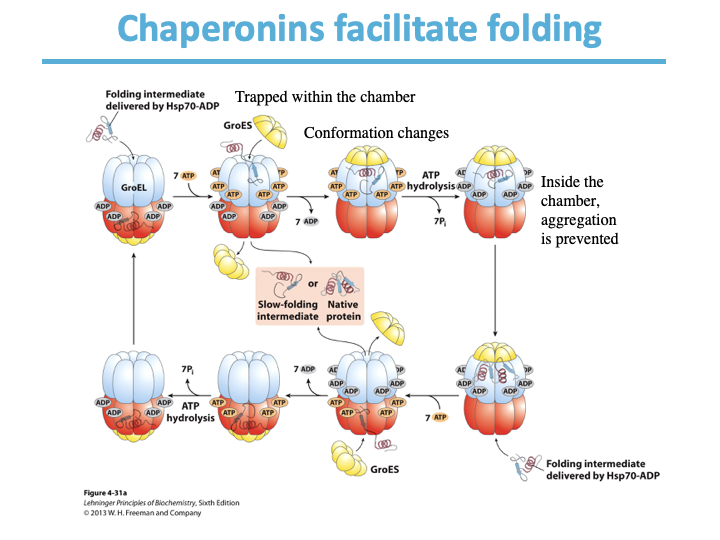
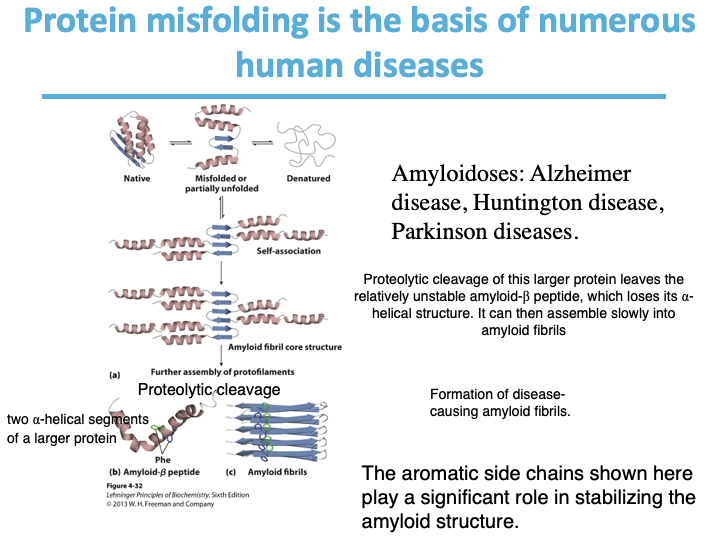
What kind of human diseases are the basis of protein folding?
Amyloidoses: Alzheimer disease, Huntington disease,
Parkinson diseases