BIOL 3320 Lab 3
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
Nervous Tissue
Recieves and transmits stimuli, communication/coordination/control and sends electrical impulses to the brain and spinal cord
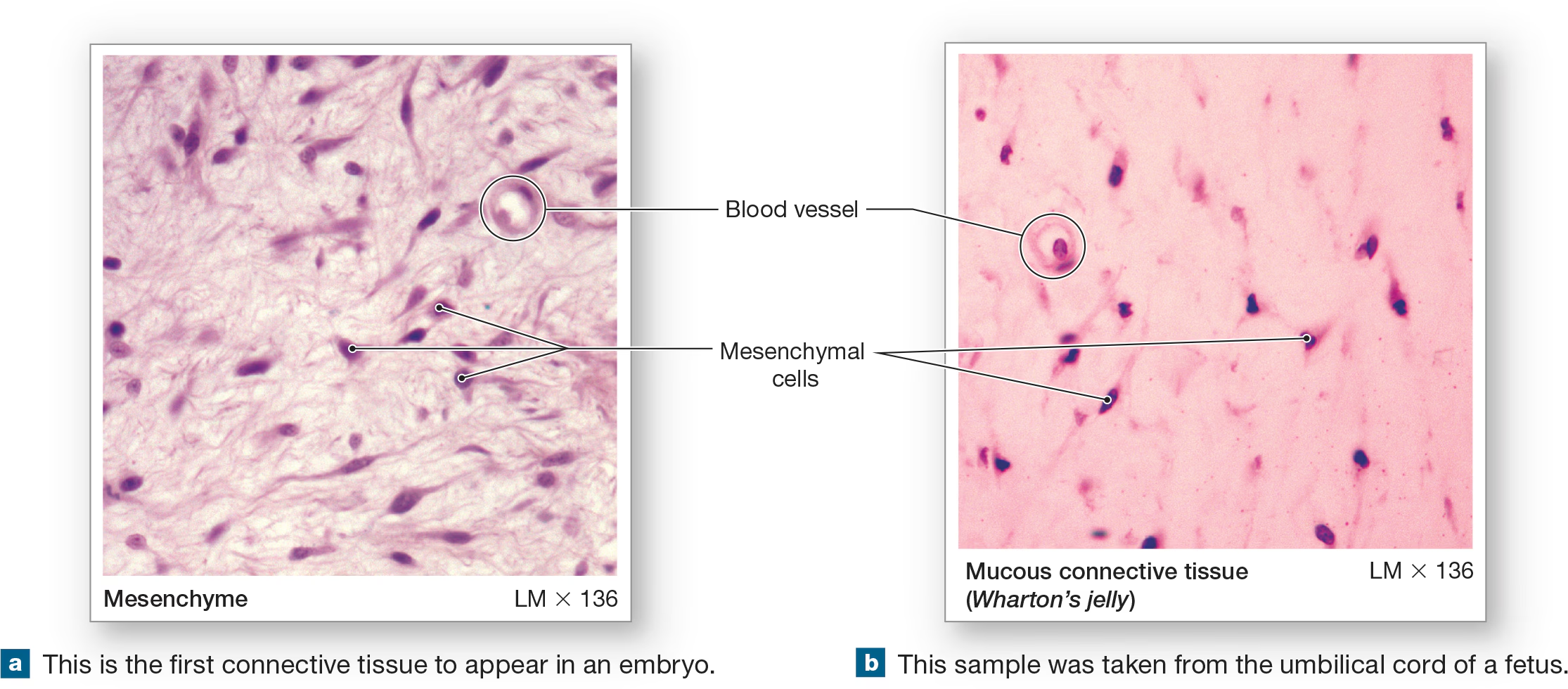
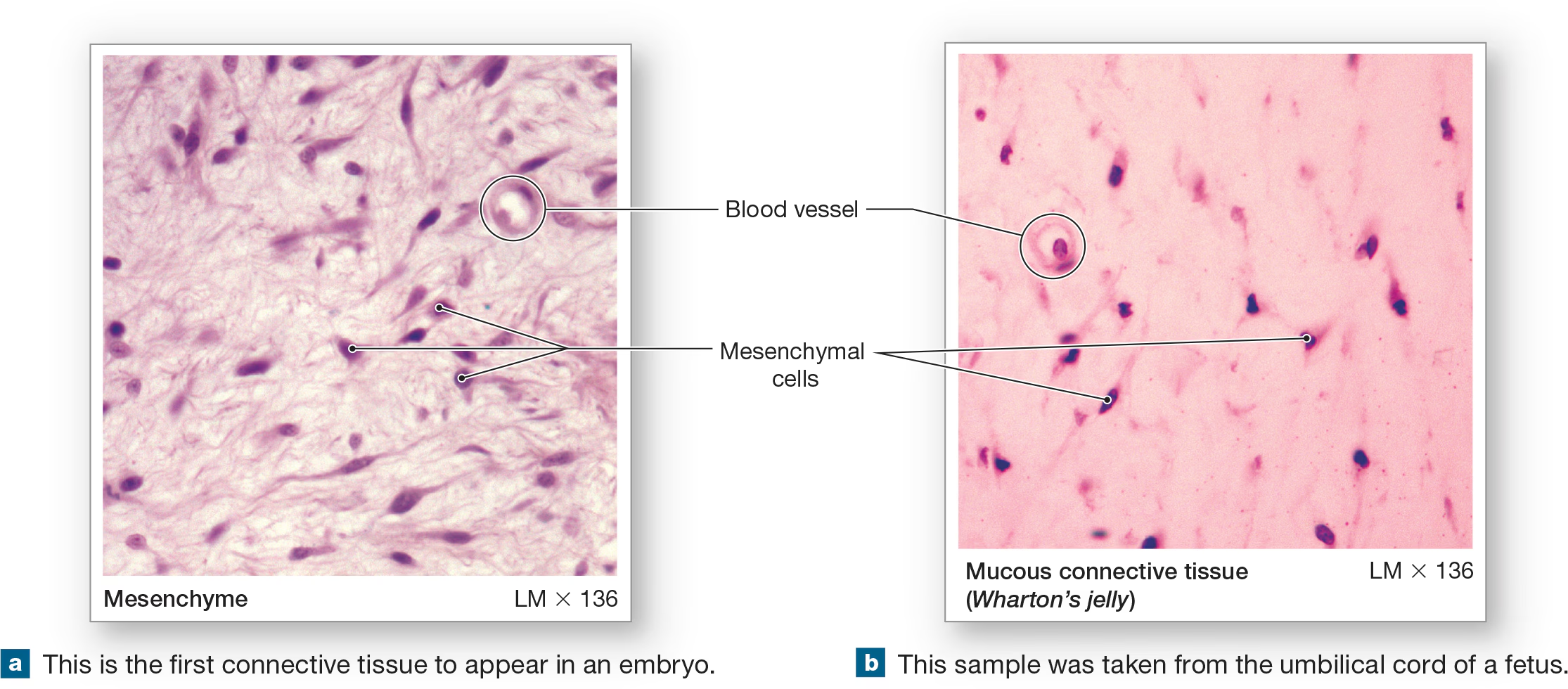
Mesenchyme
embryonic tissue from which all connective tissues stem from
Connective Tissue Proper
the most widely distributed class of connective tissues in the body
Fibroblasts
scattered cells in the connective tissue proper that secrete ECM filled with different protein fibers and is highly vascular.
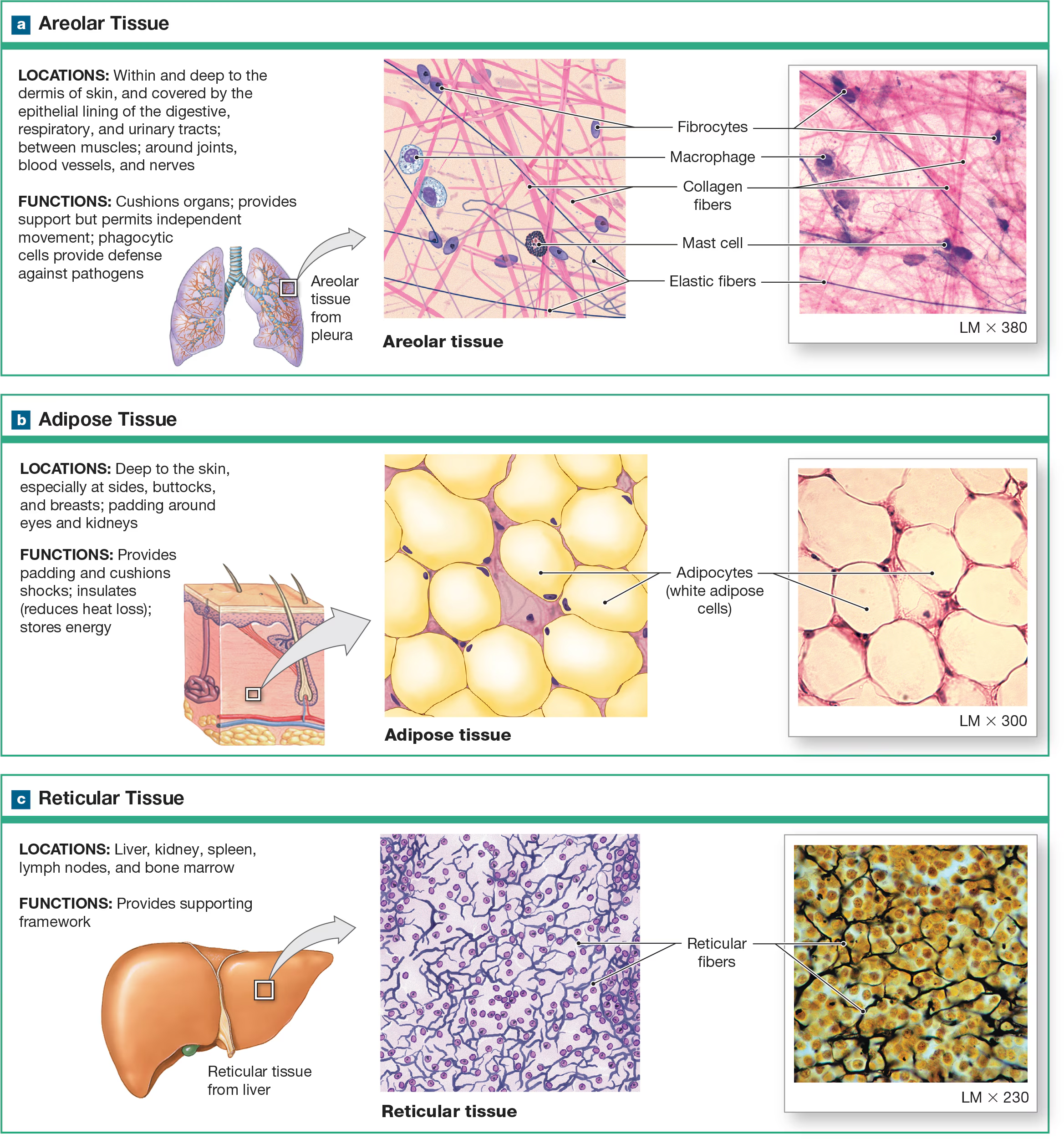
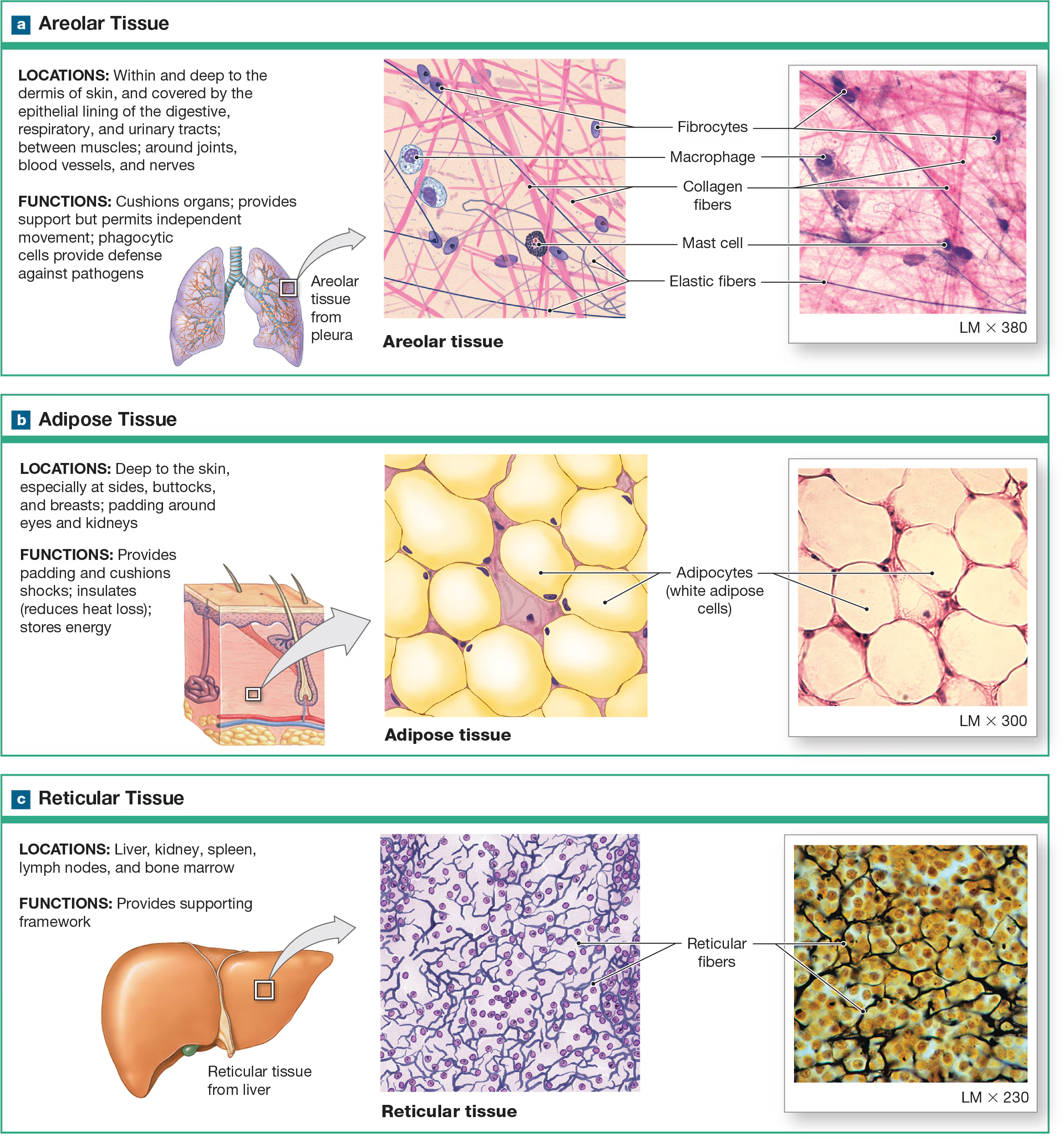
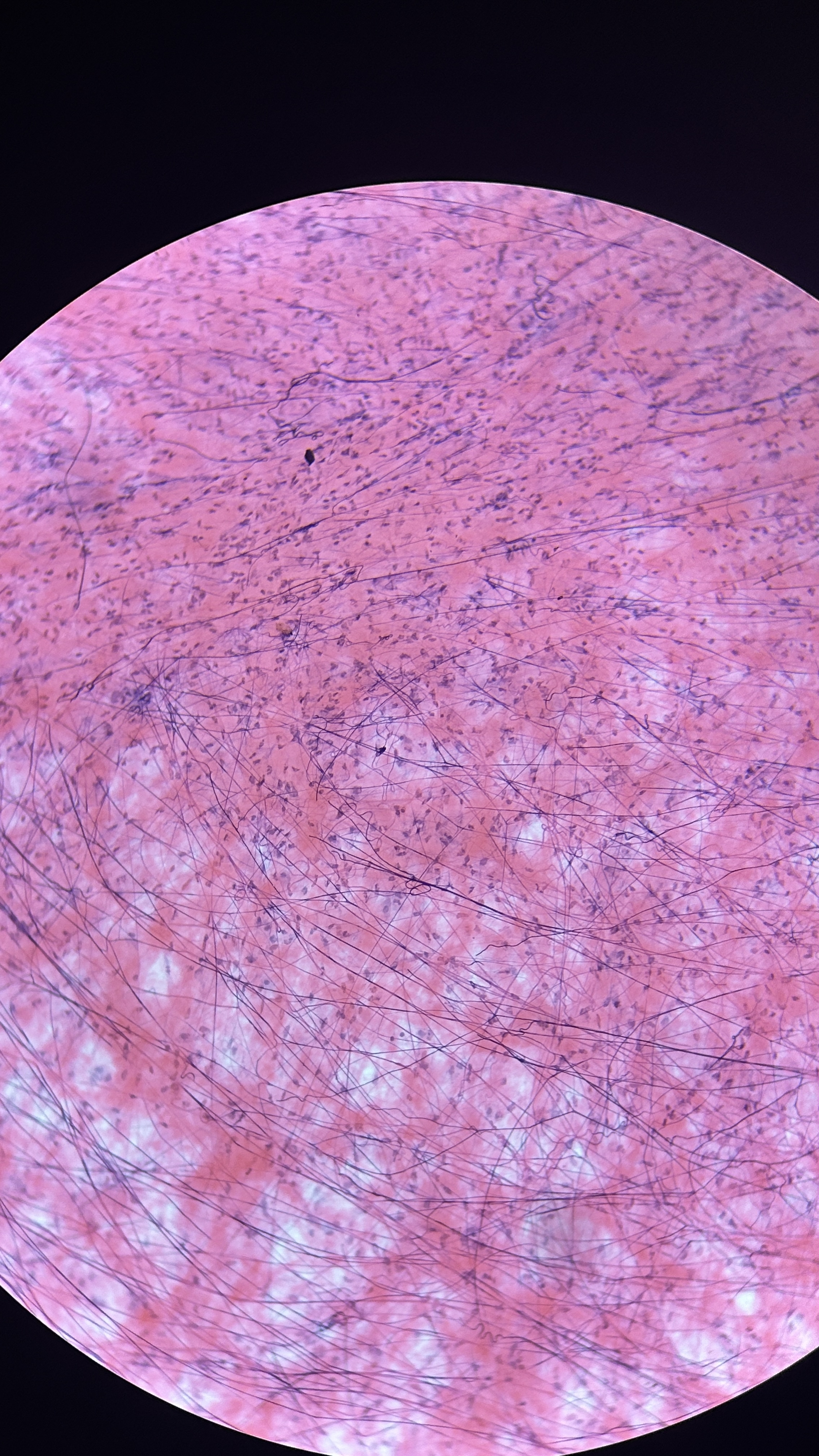
Loose (areolar) CT
viscous ground substance, which looks loose on the slide, which includes all 3 types of protein fibers, but slides are usually stained with collagen and elastin fibers. Its apart of the basement membrane and in the walls of hollow organs (glue). least specialized, open framework, holds capillary beds like under skin (subcutaneous layer)
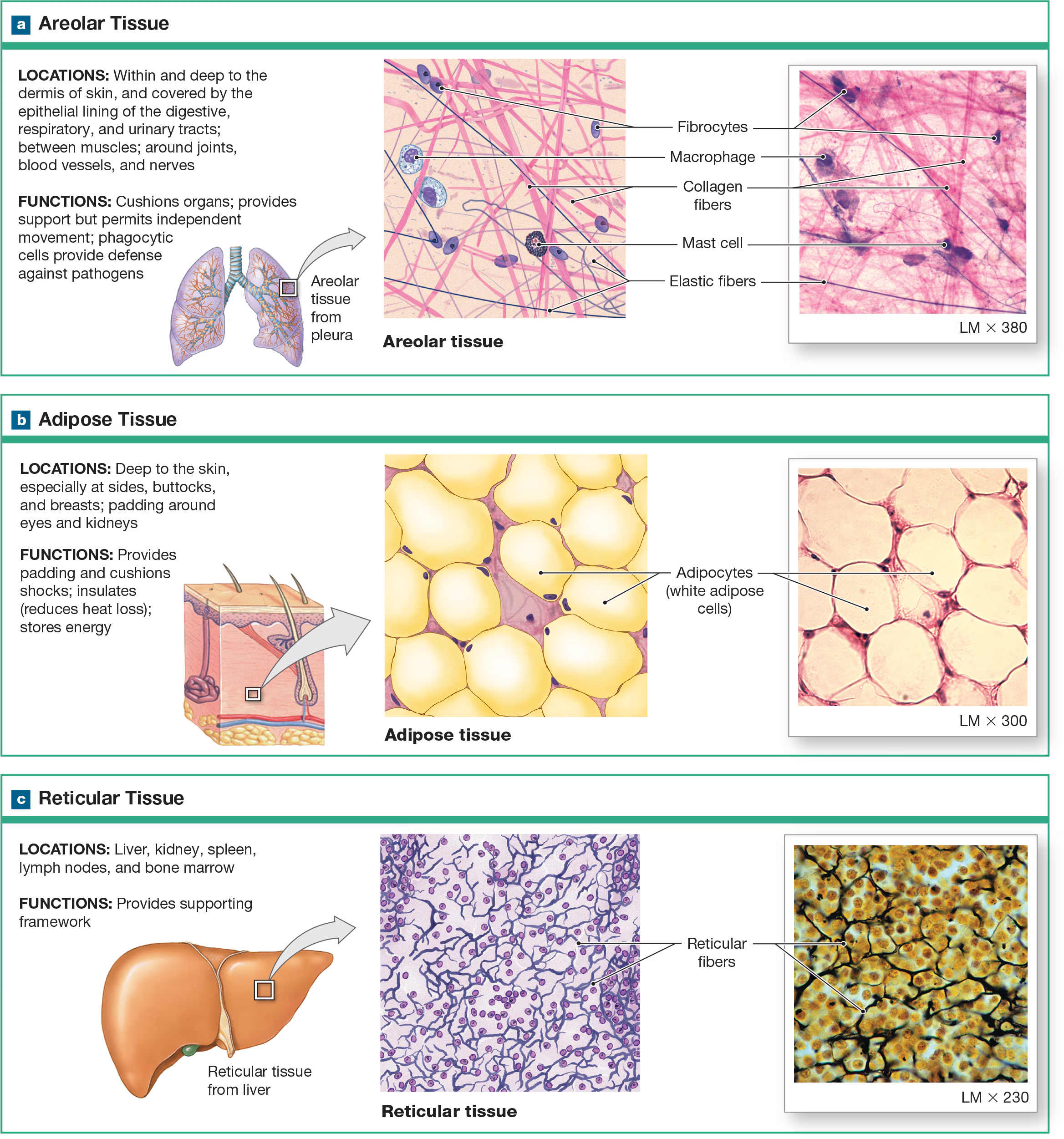
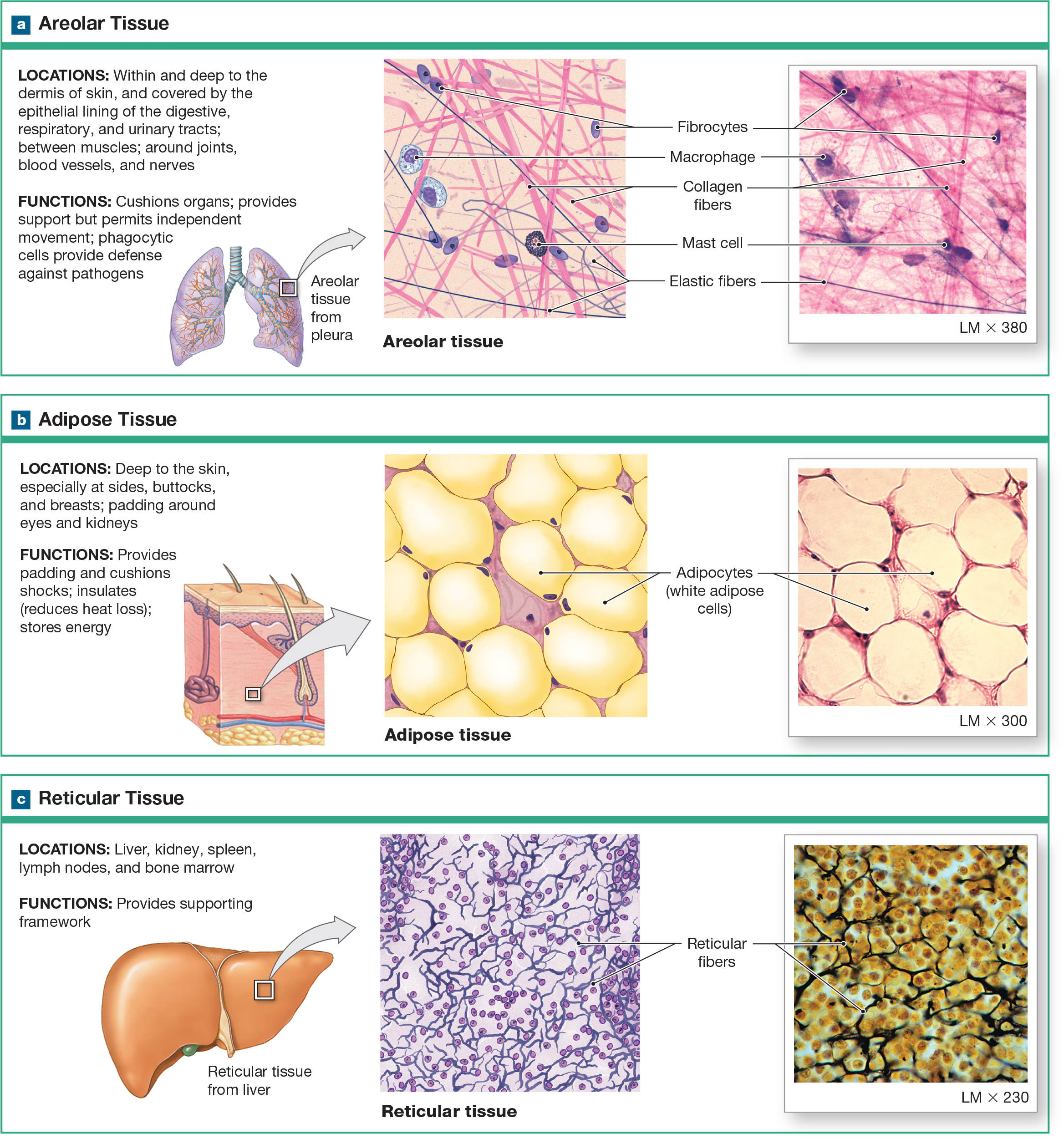
Reticular CT
made of many fibers produced by reticular cells and is located in the spleen and lymph nodes, where the fibers can weave nets to trap pathogens and foreign cells. It is also located near blood vessels and nerves, where it forms supportive networks.
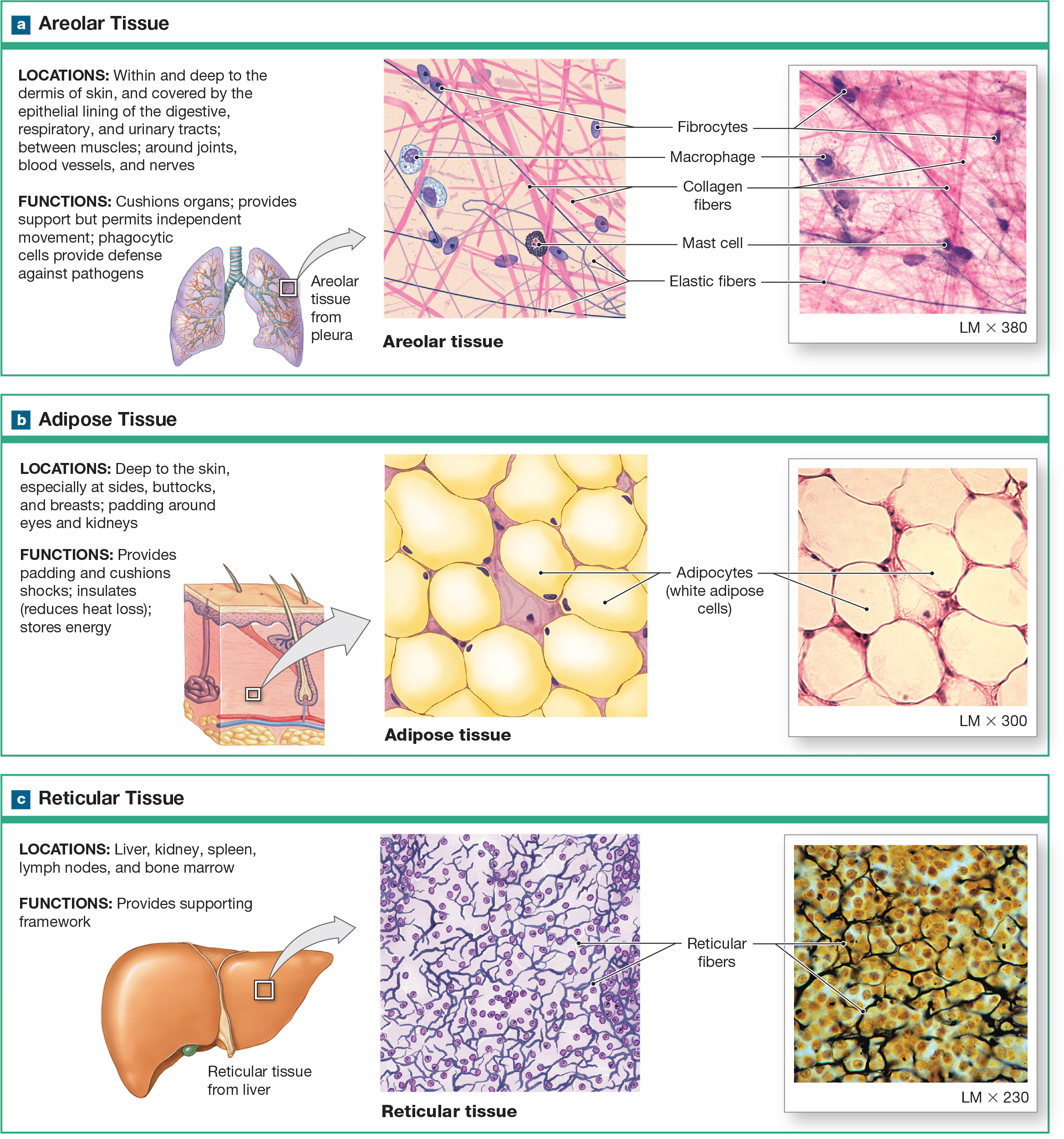
Adipose Tissue
Consists of adipocytes with collagen fibers in the ECM. Mesenchymal cells divide and differentiate to produce more fat cells when more storage is needed and can be removed through liposuction.
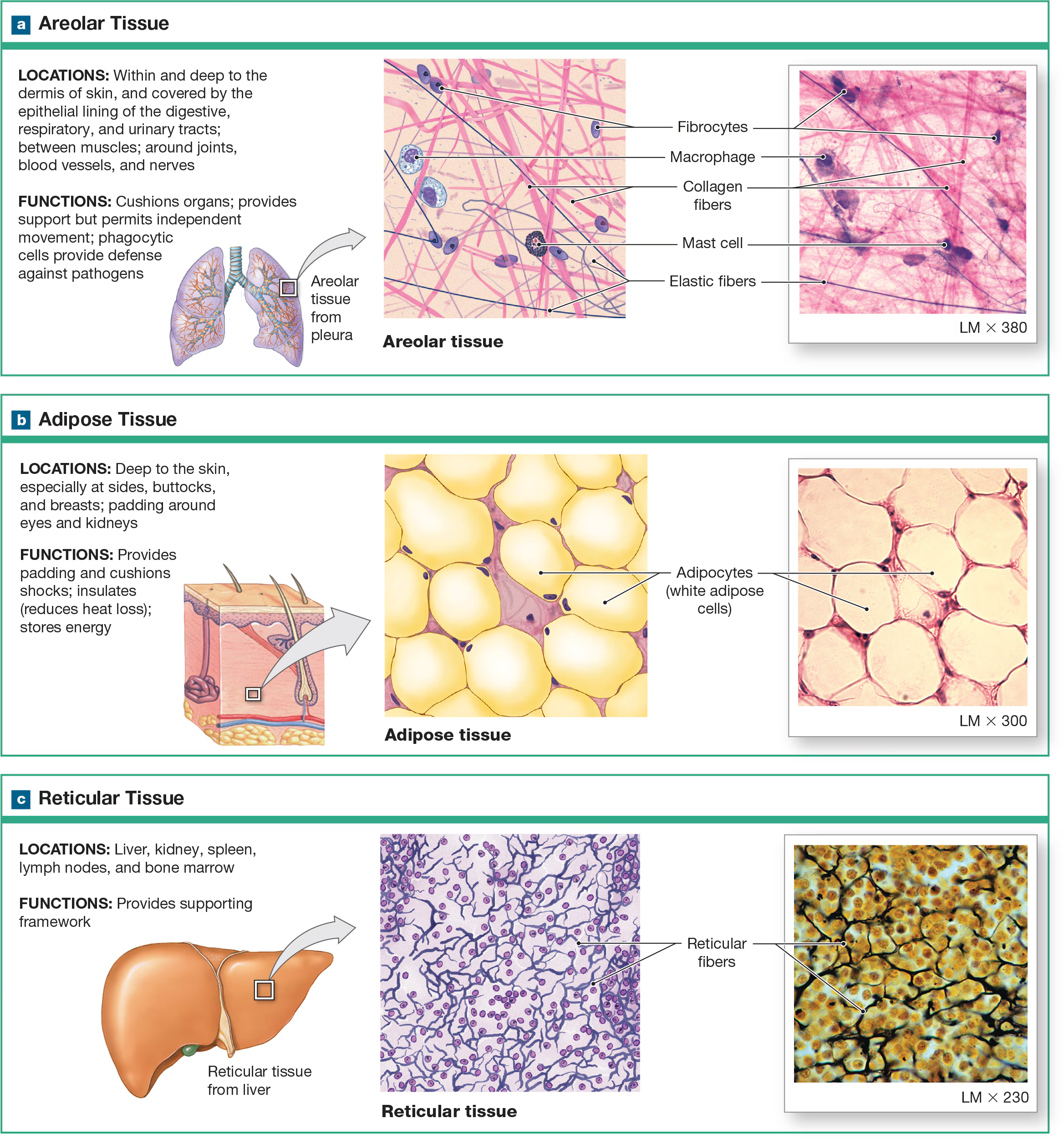
Adipocytes
Huge cells in the adipose tissue contain a large lipid droplet that occupies most of their cytoplasm. Adipocytes are distributed throughout the body, under the skin, and around organs. Adipocytes push the nucleus and other organelles to the periphery of the cell against the plasma membrane.
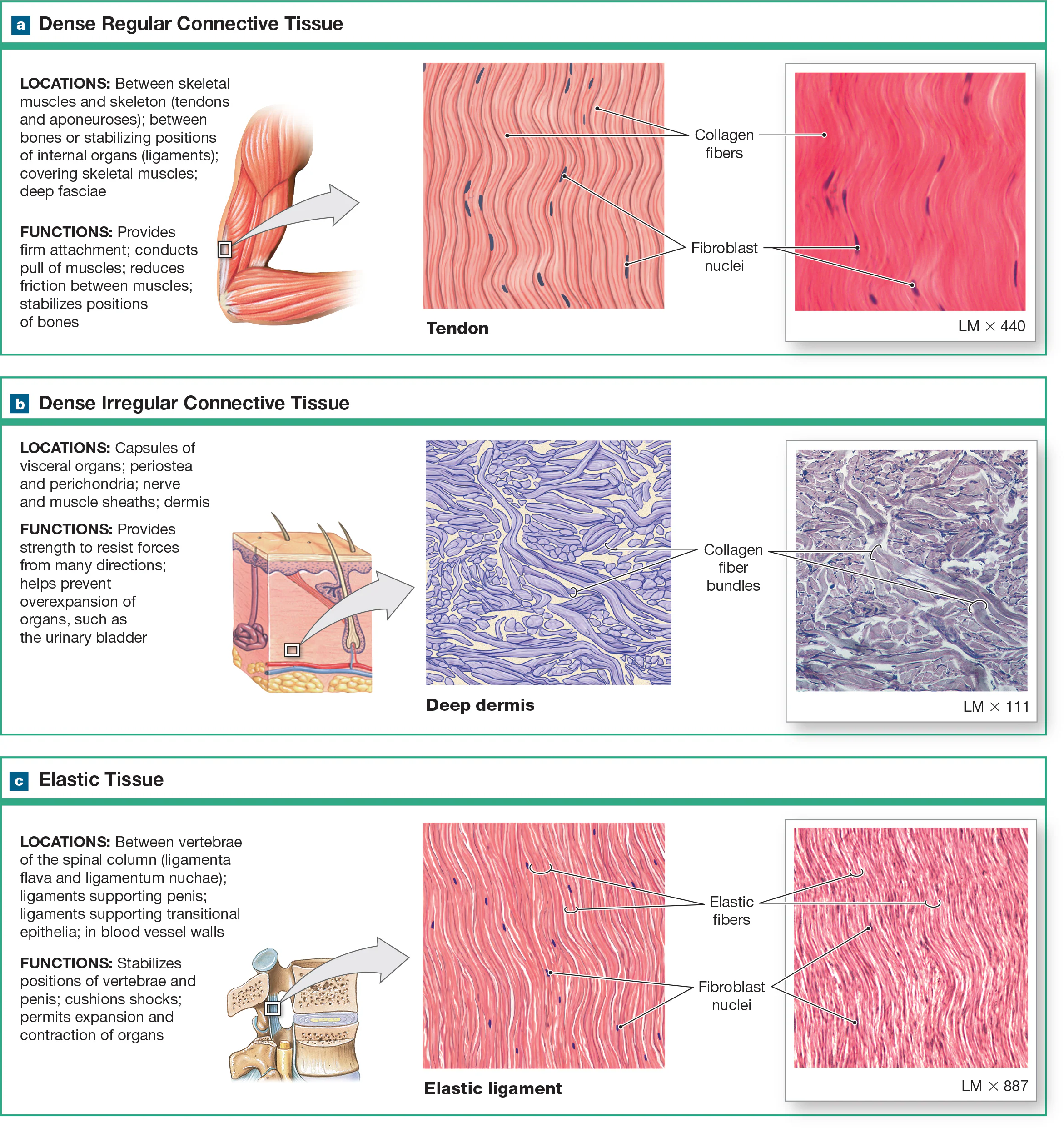
Dense regular collagenous CT
consists of collagen fibers arranged in parallel bundles with little ground substance and few cells. It’s very strong and its structure requires tensile strength in a single plane, like tendons and ligaments. Tightly packed parallel collagen fibers
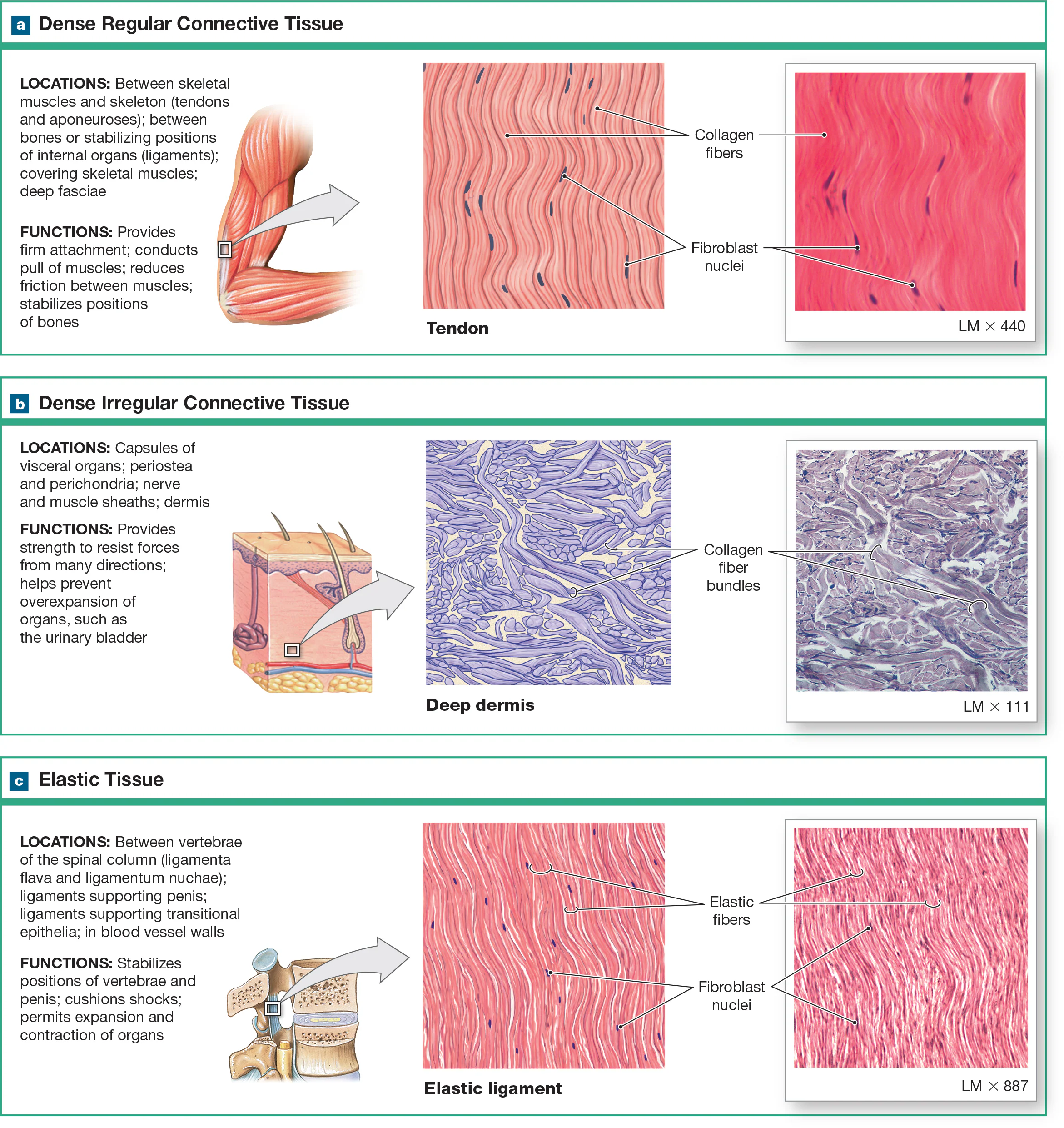
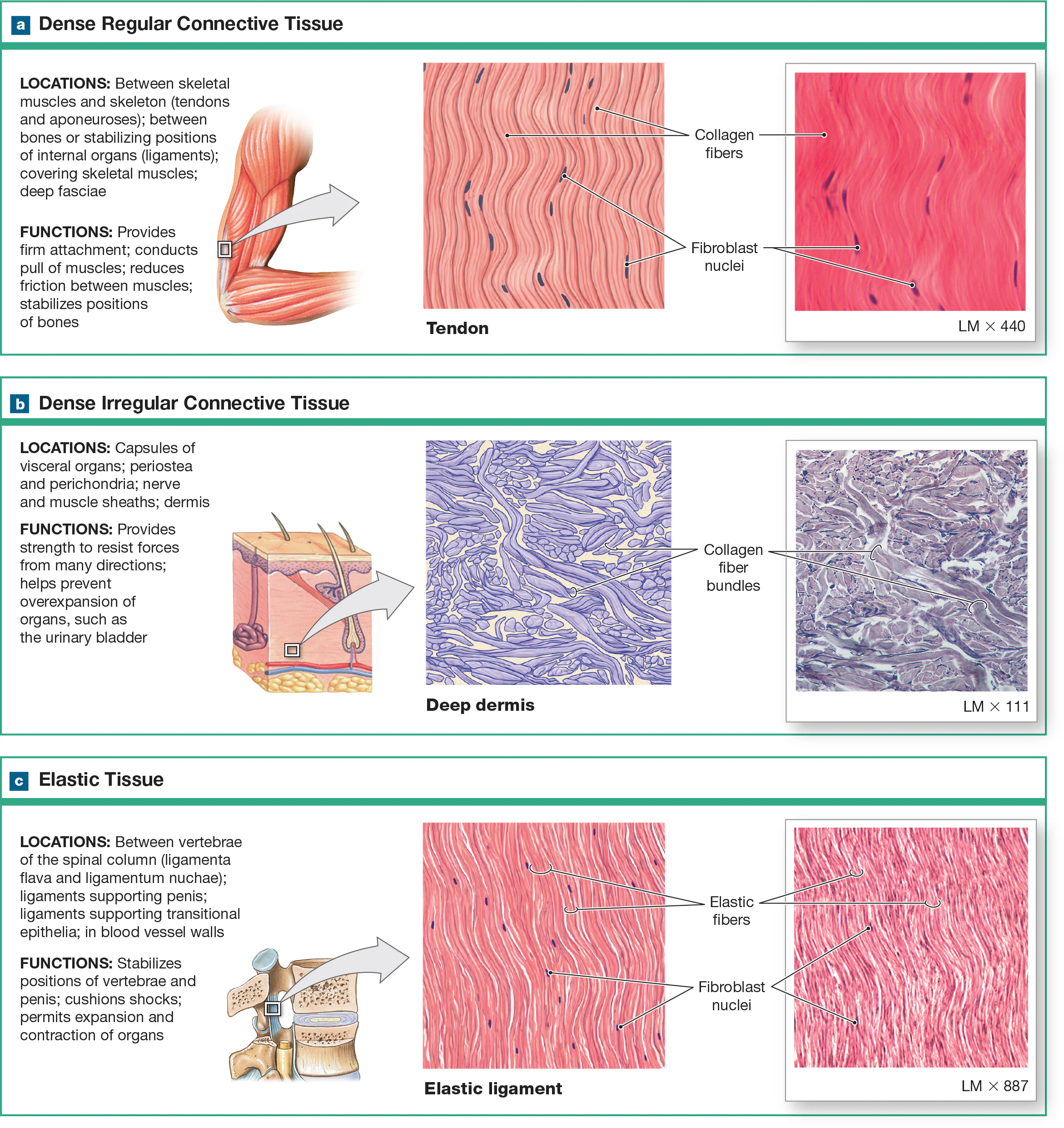
Dense irregular CT
Collagen fibers are arranged in an irregular, haphazard fashion without a consistent pattern. It’s strong, but its arrangement makes it well-suited to support multiple planes like the dermis, joints, and organ capsules (liver, kidneys, and spleen). Forms sheath around cartilages (perichondrium) and bones (periosteum).
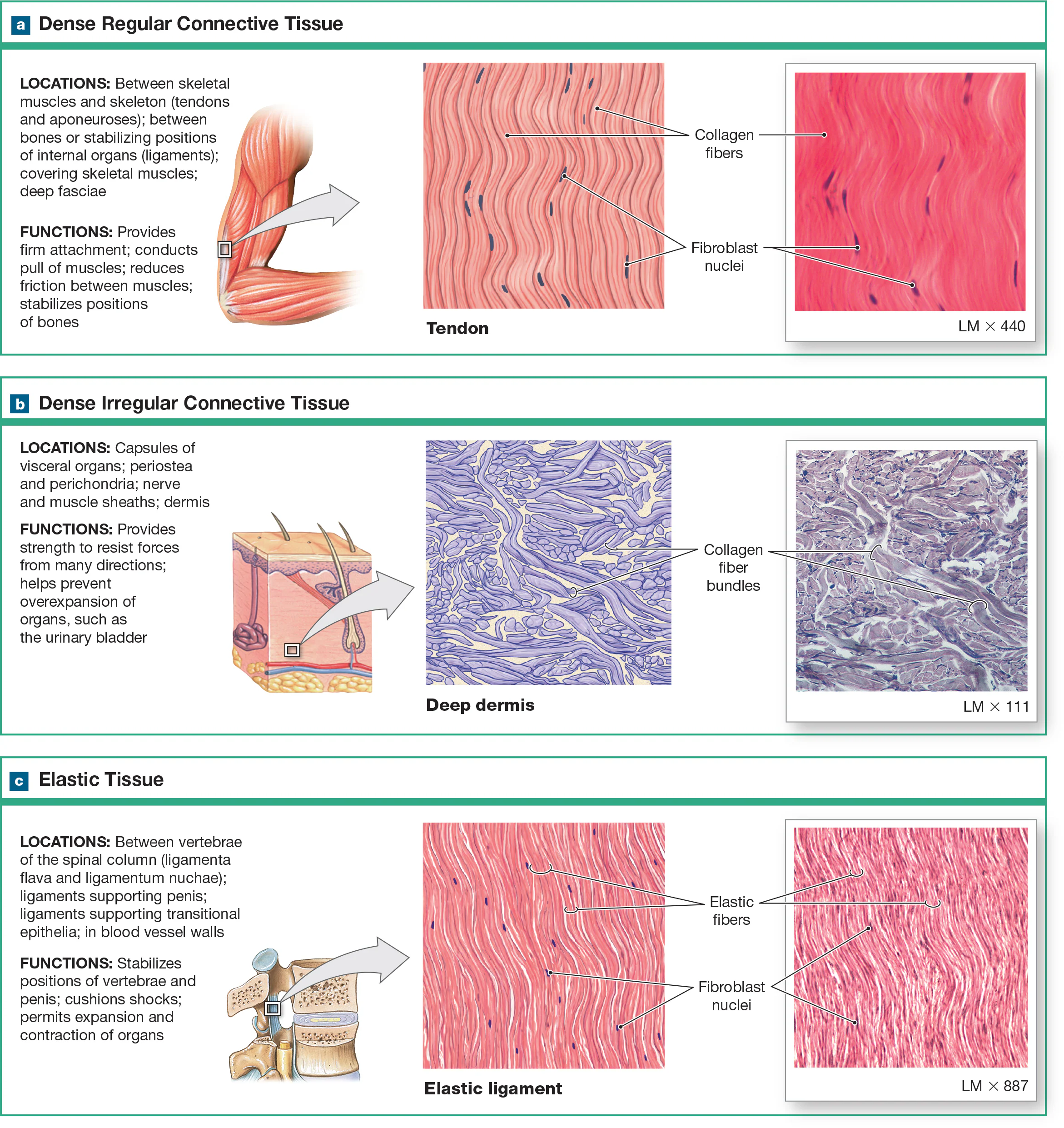

Dense regular elastic CT
contains elastic fibers arranged in parallel bundles, which are found in organs that need both distensible and elastic like large blood vessels and ligaments, to allow adherence to pressure changes and stretchiness.

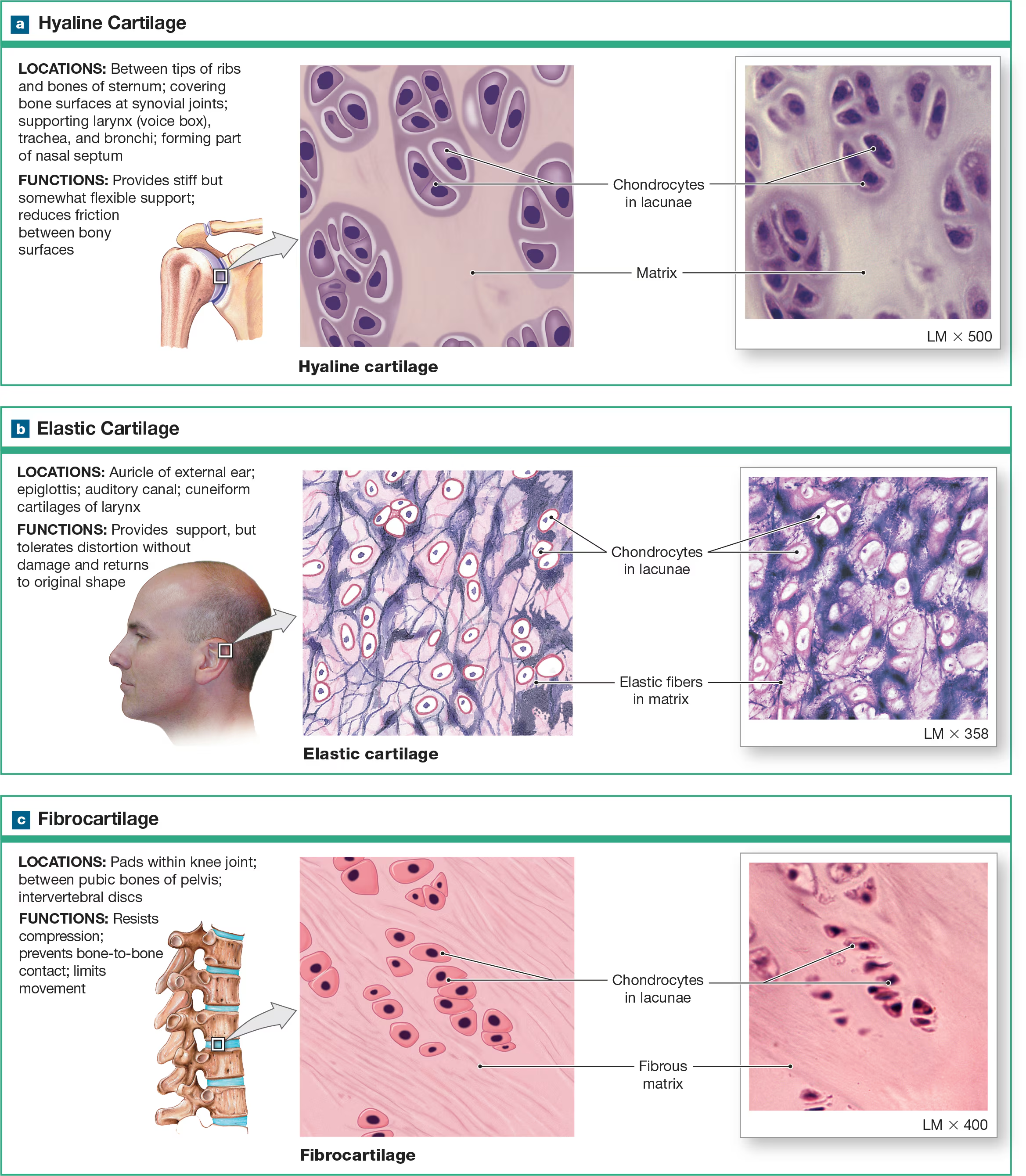
Cartilage
tough but flexible tissue that is resistant to tension. twisting and compressive forces, composed of chondrocytes cells, and avascular, plus each type of cartilage (total 3) has a different ECM composition. Matrix is a firm gel
Chondrocytes
Cartilage cells that are embedded in the ECM lacunae cavities/chambers.
Lacunae
small cavities in the ECM that house chondrocytes.
What are the three types of cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage
elastic cartilage
fibrocartilage
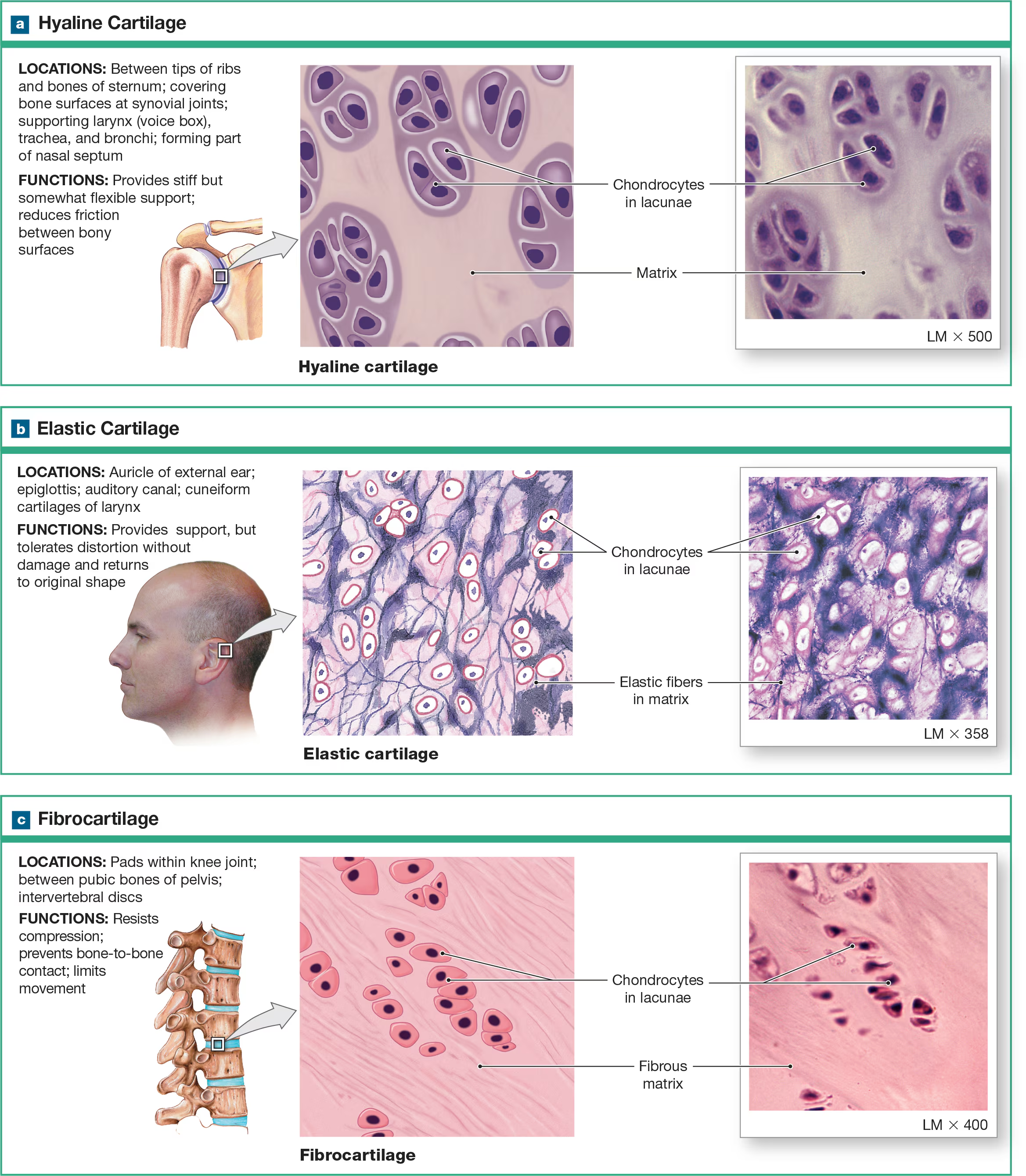
Hyaline cartilage (glass)
contains chronodrocytes scattered in ground substance with a few visible protein fibers. Has a glassy smooth apperace which makes it ideal to cover the ends of bones by the joint connecting other bones and provides a frictionless surface. Connecting the ribs to the sternum, lines respiratory passageways, and forms the framework for the nose.
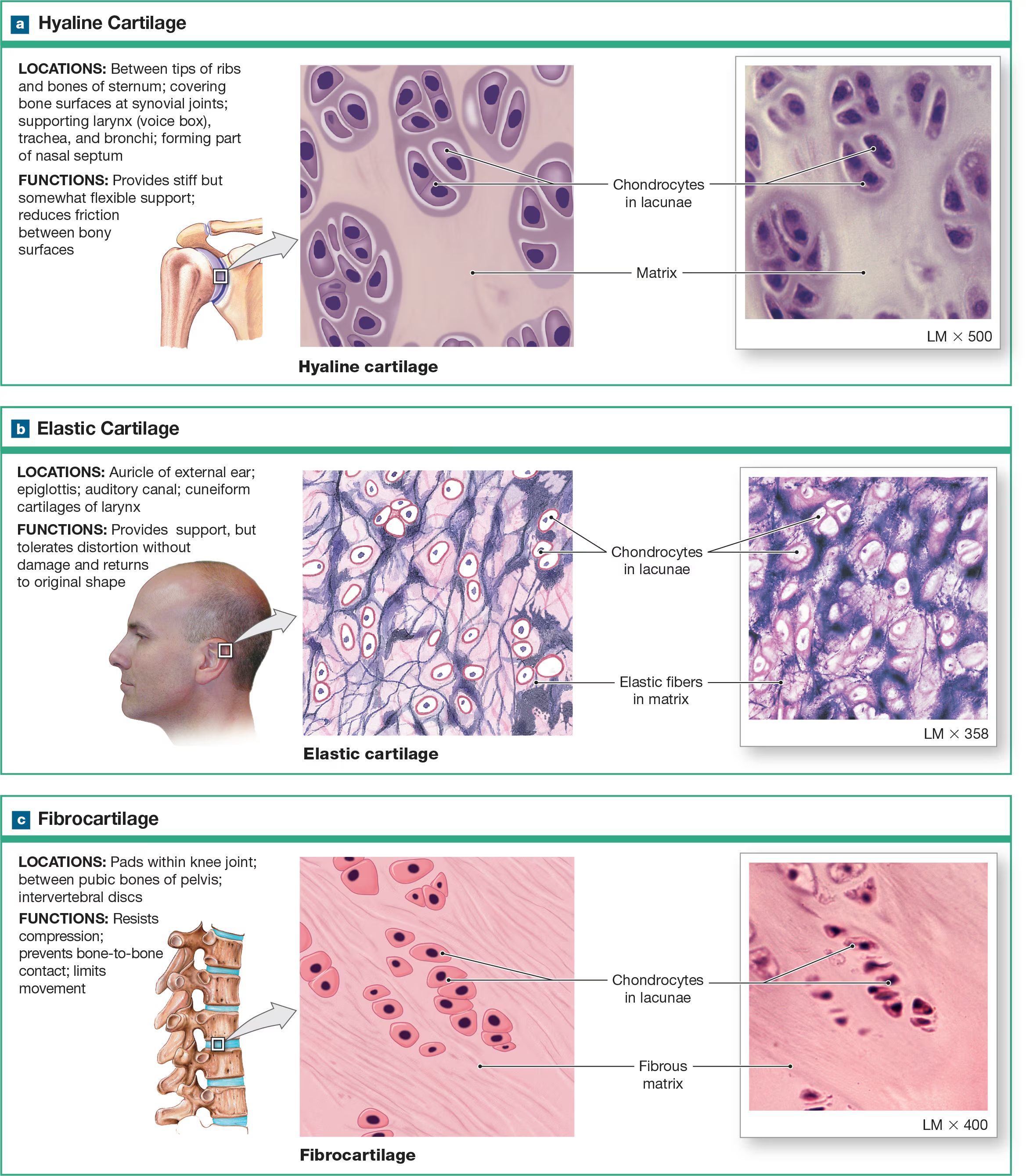
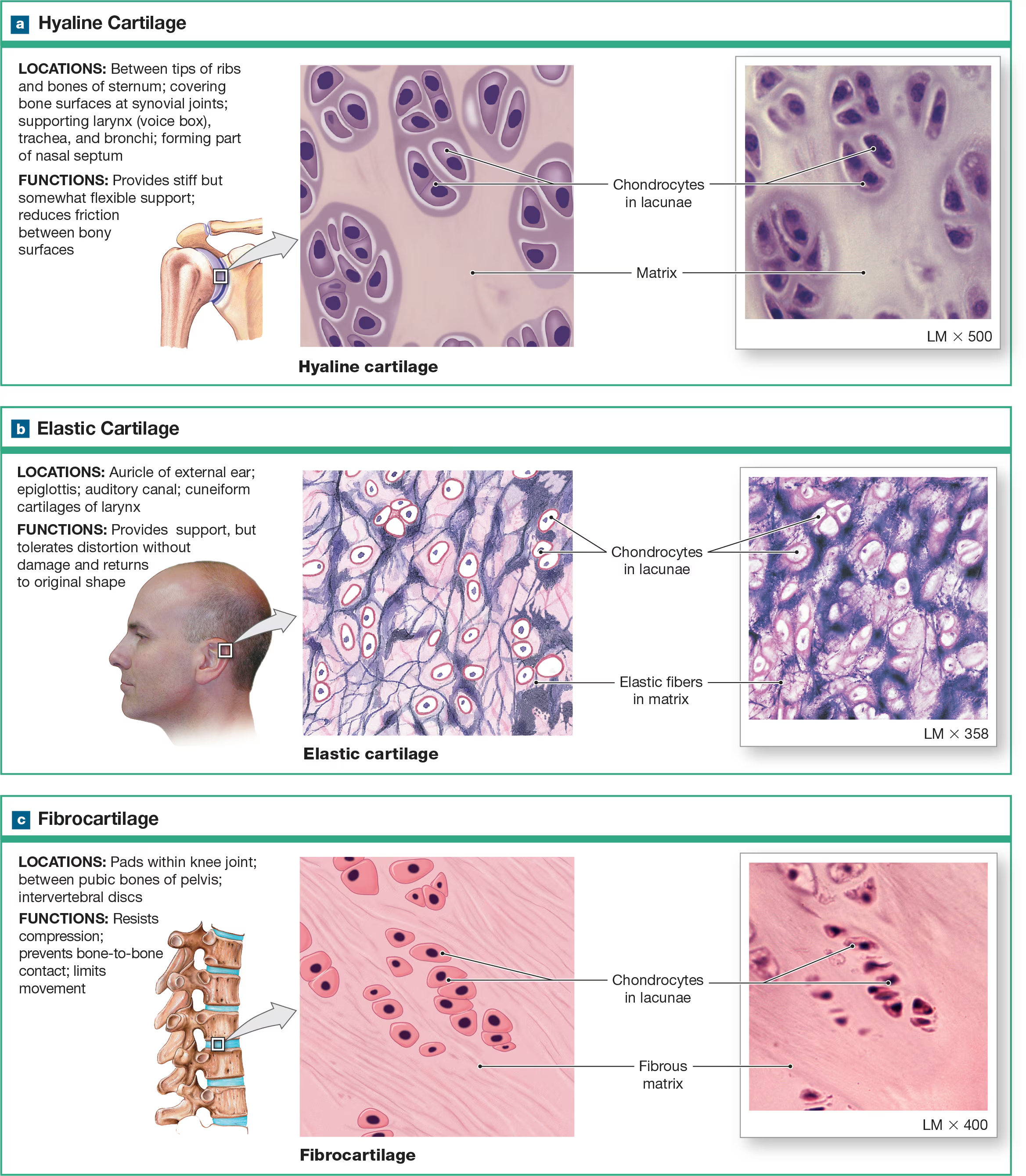
Fibrocartilage
ECM is full of collagen fibers that are extremely strong but not smooth. It’s like a flannel sheet, with cotton fibers representing the protein fibers. Does not form cartilage but reinforces ligaments and forms articular/intervertebral discs.
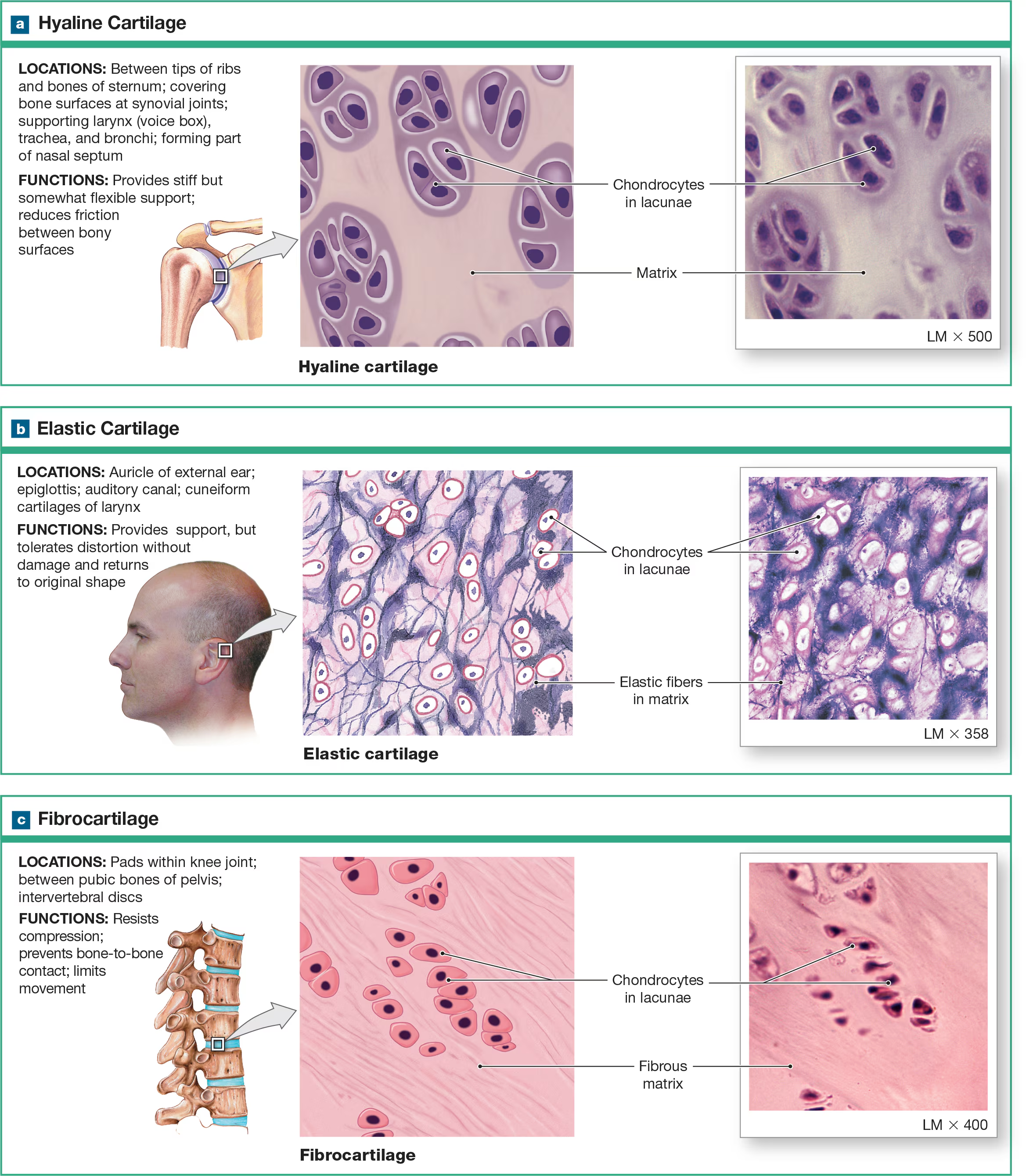
Articular discs
tough structures that improve the fit of two bones.
Intervertebral discs
Structures between two vertebrae that help to support the weight of the vertebral column and absorb shock.
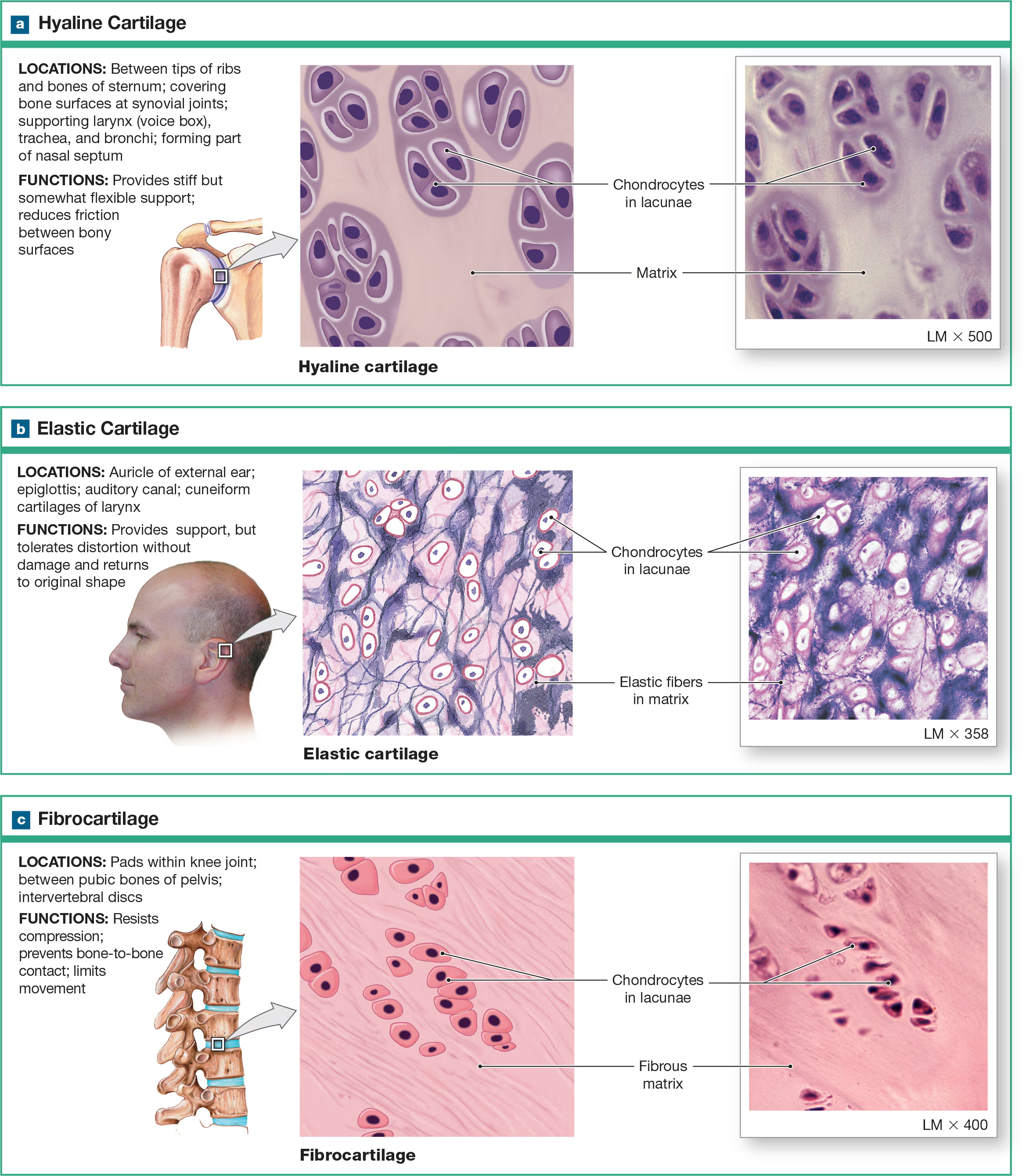
Elastic Cartilage
ECM filled with elastin fibers that allow it to stretch and recoil, which is found in the ear and epiglottis.
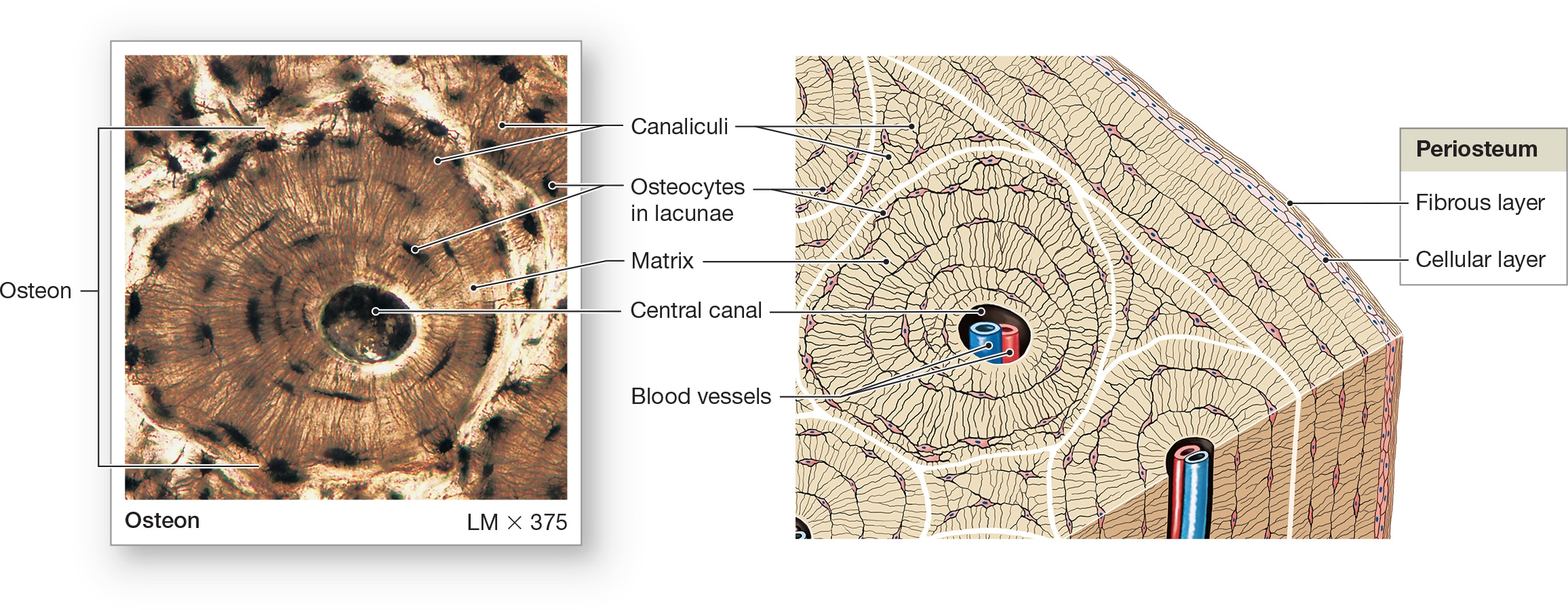
Osseous Tissue
Bone tissue:
weight support
Calcified (made rigid by calcium salts)
Resists shattering (flexible collagen fibers)
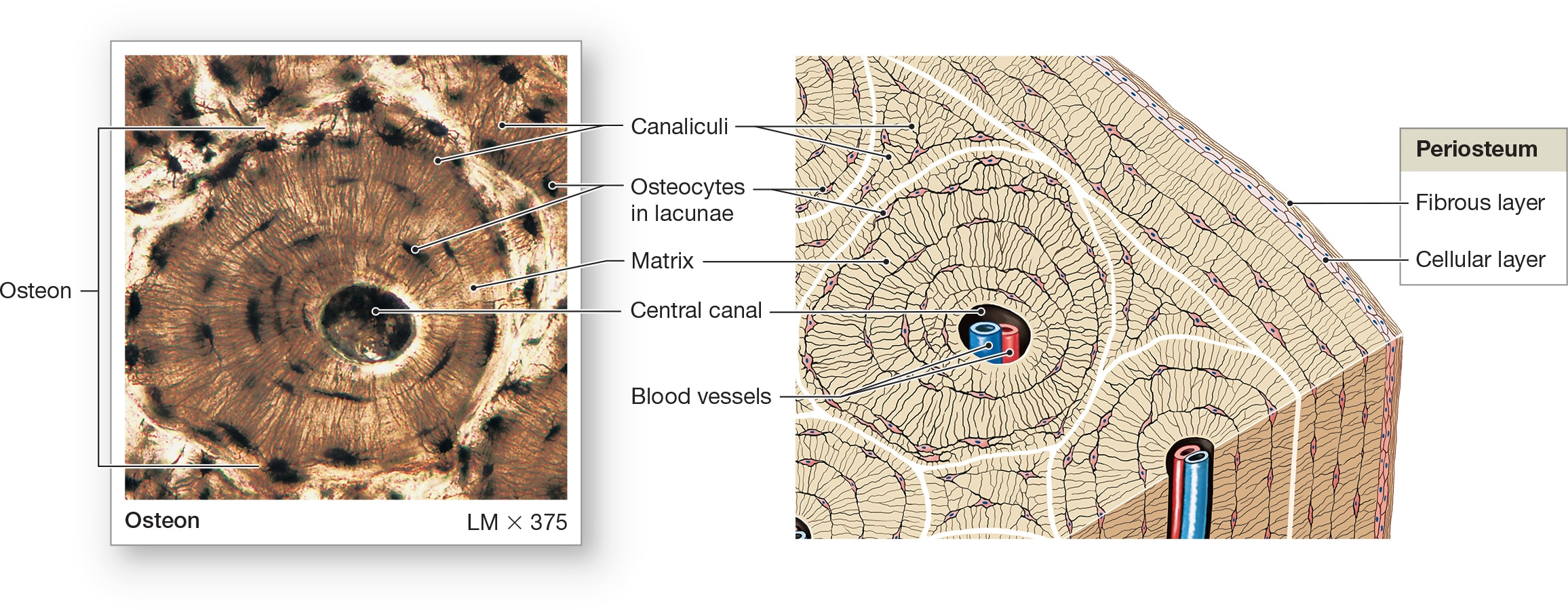
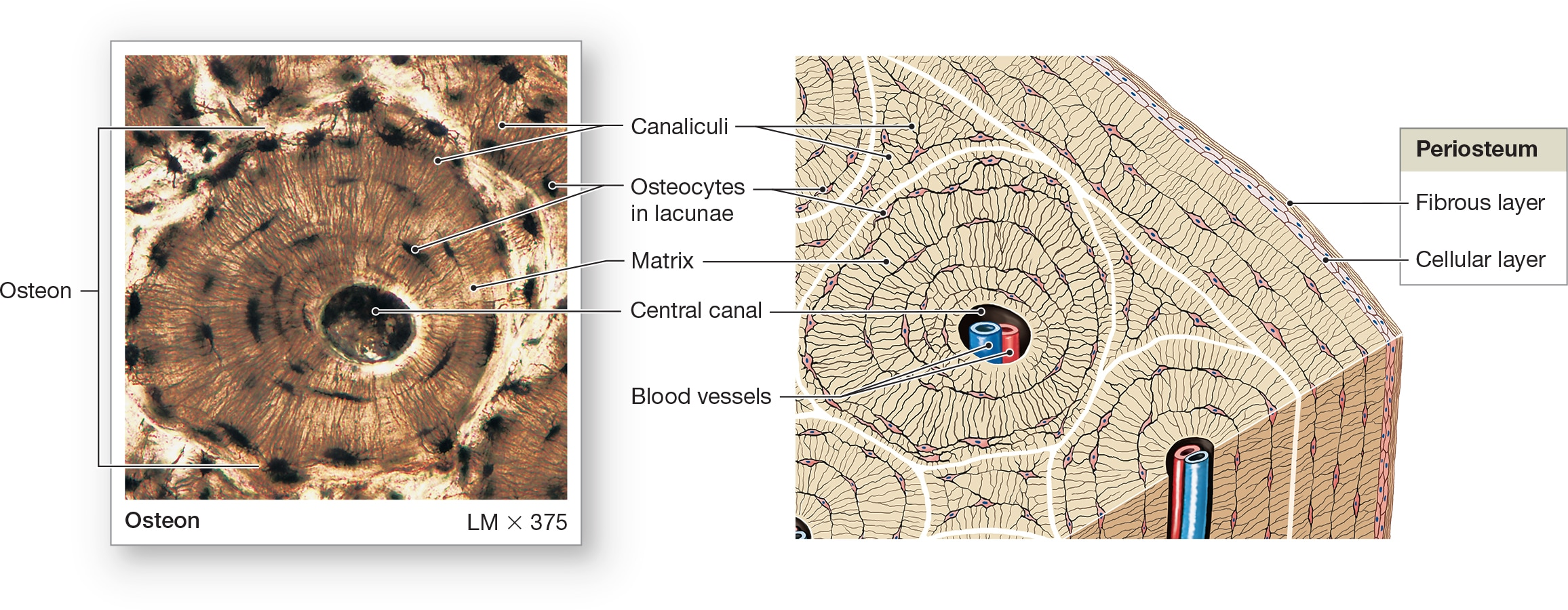
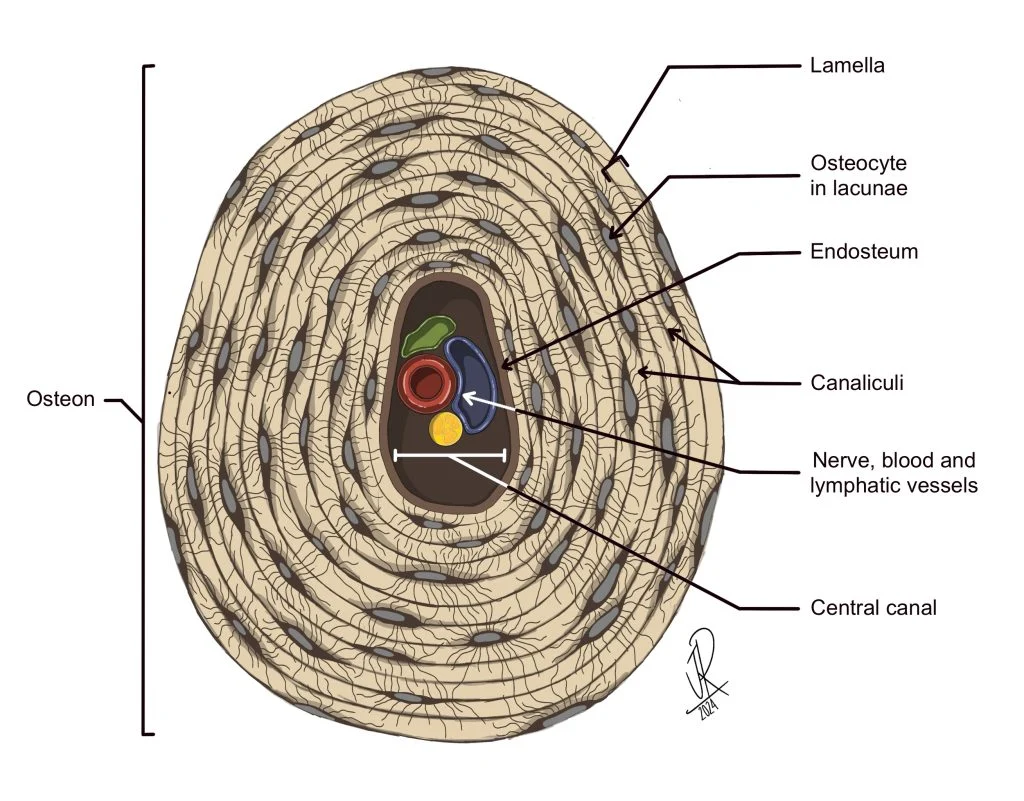
Osteocytes
bone cells encased in ECM that contains collagen fibers and calcium hydroxyapatite crystals in lacunae. Arranged around central canals within matrix and Small channels through matrix (canaliculi) allow for exchange of materials with blood.
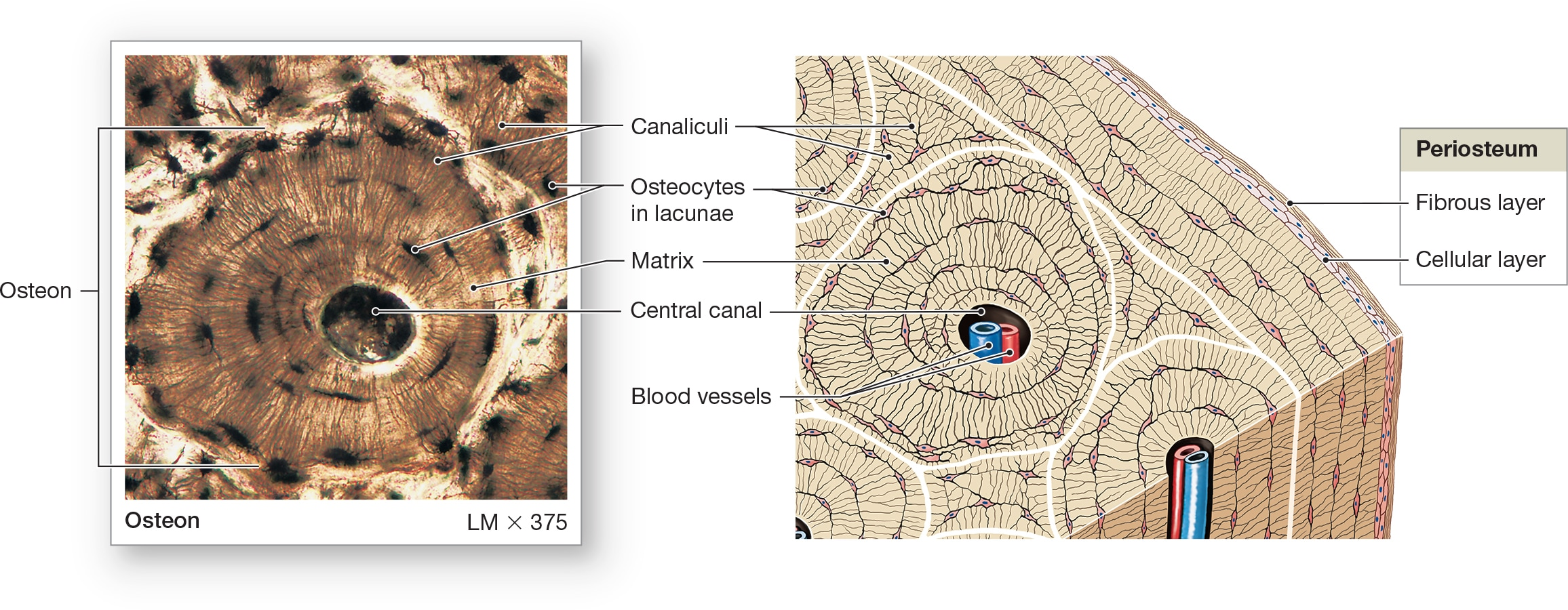
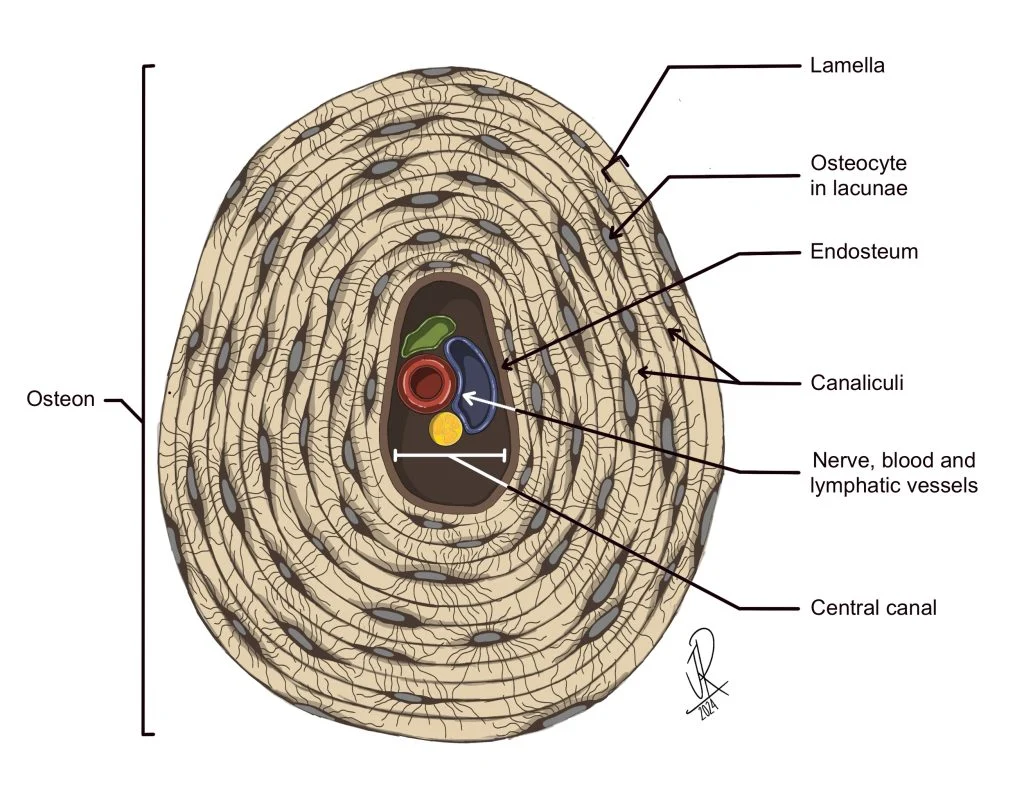
Lamellae
centric layers of the ECM with osteocytes sandwiched in between them, making bones the hardest tissue in the human body and most resistant to mechanical stresses.
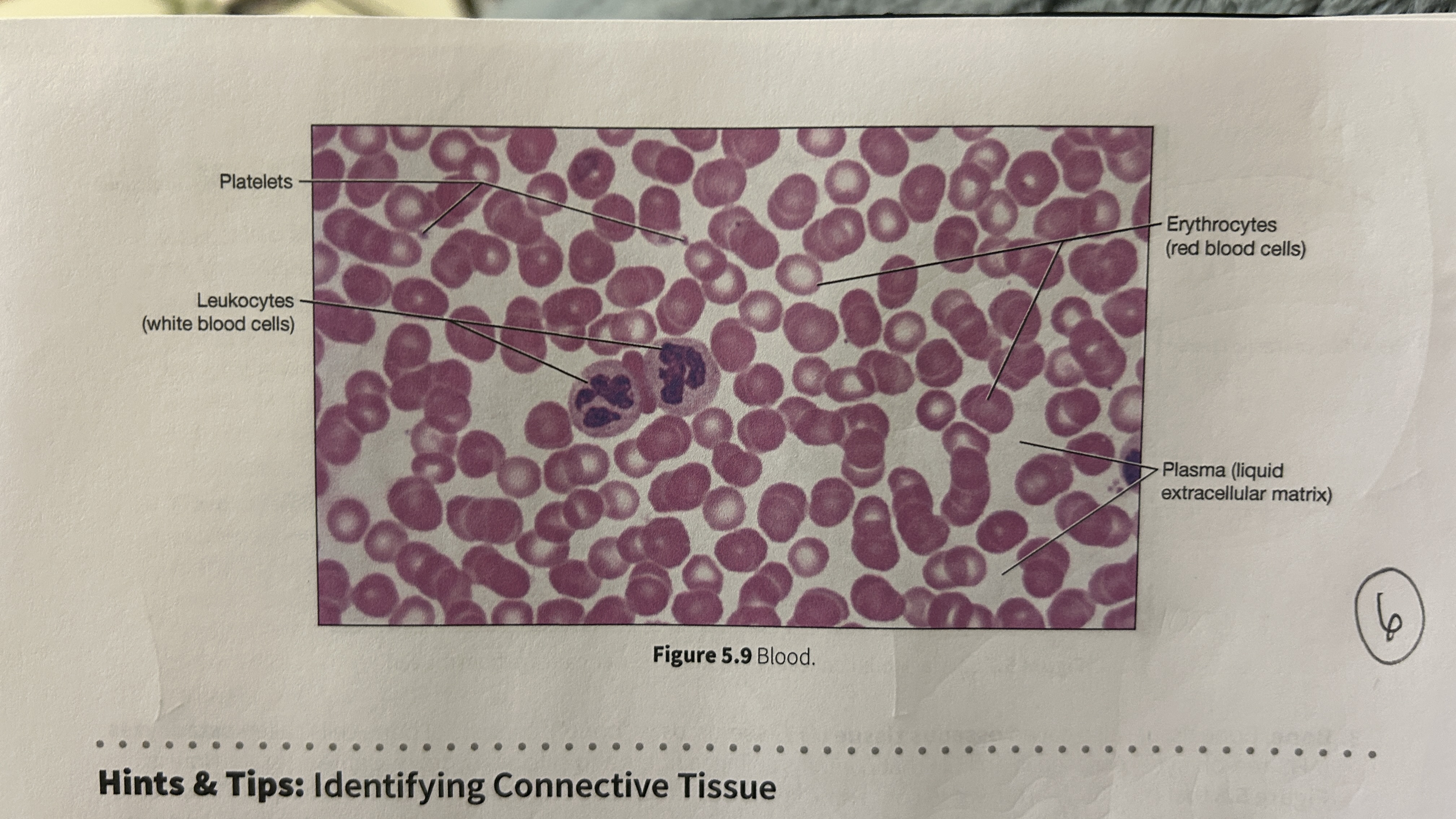
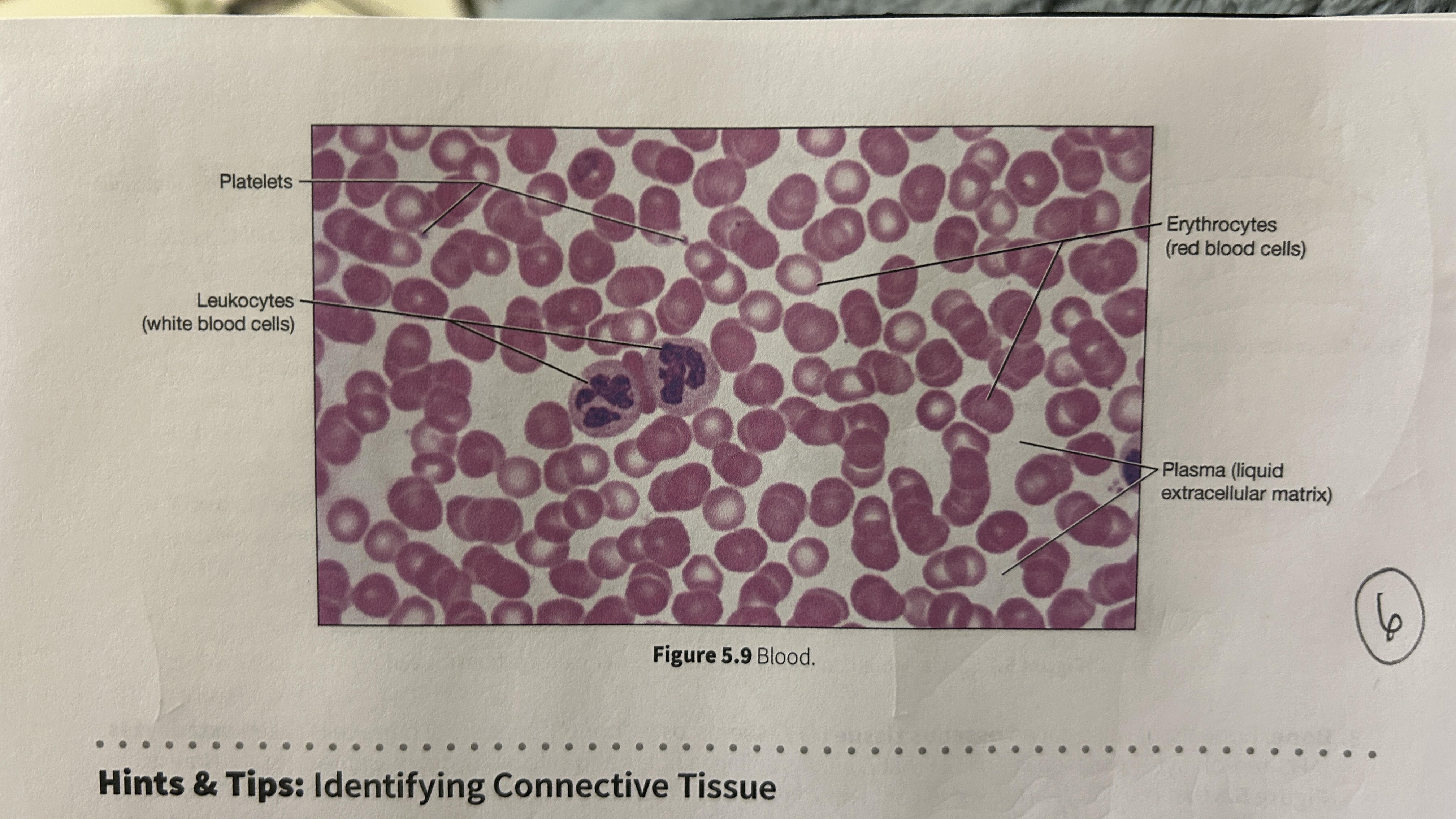
Plasma
blood that consists of liquid ECM
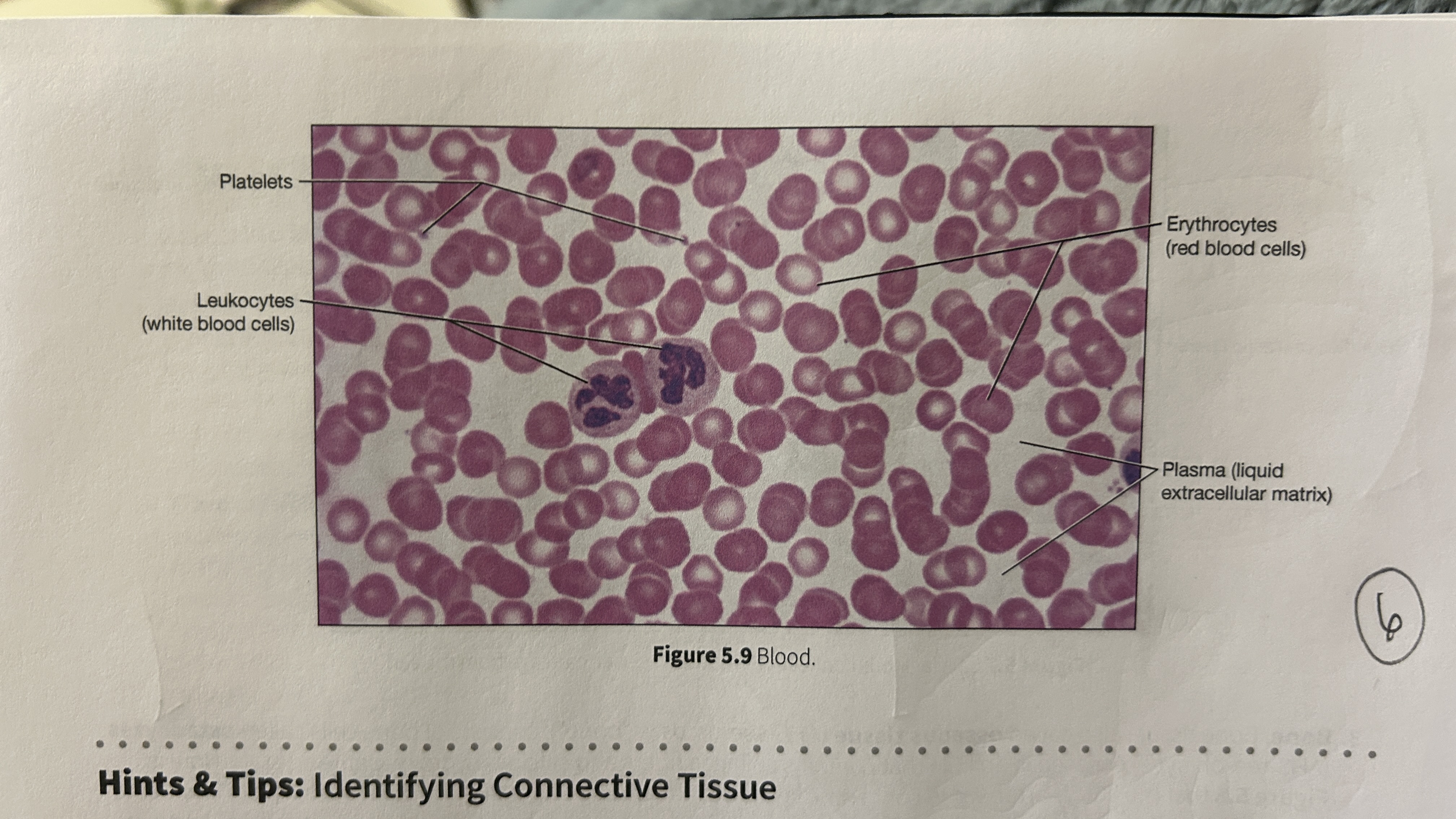
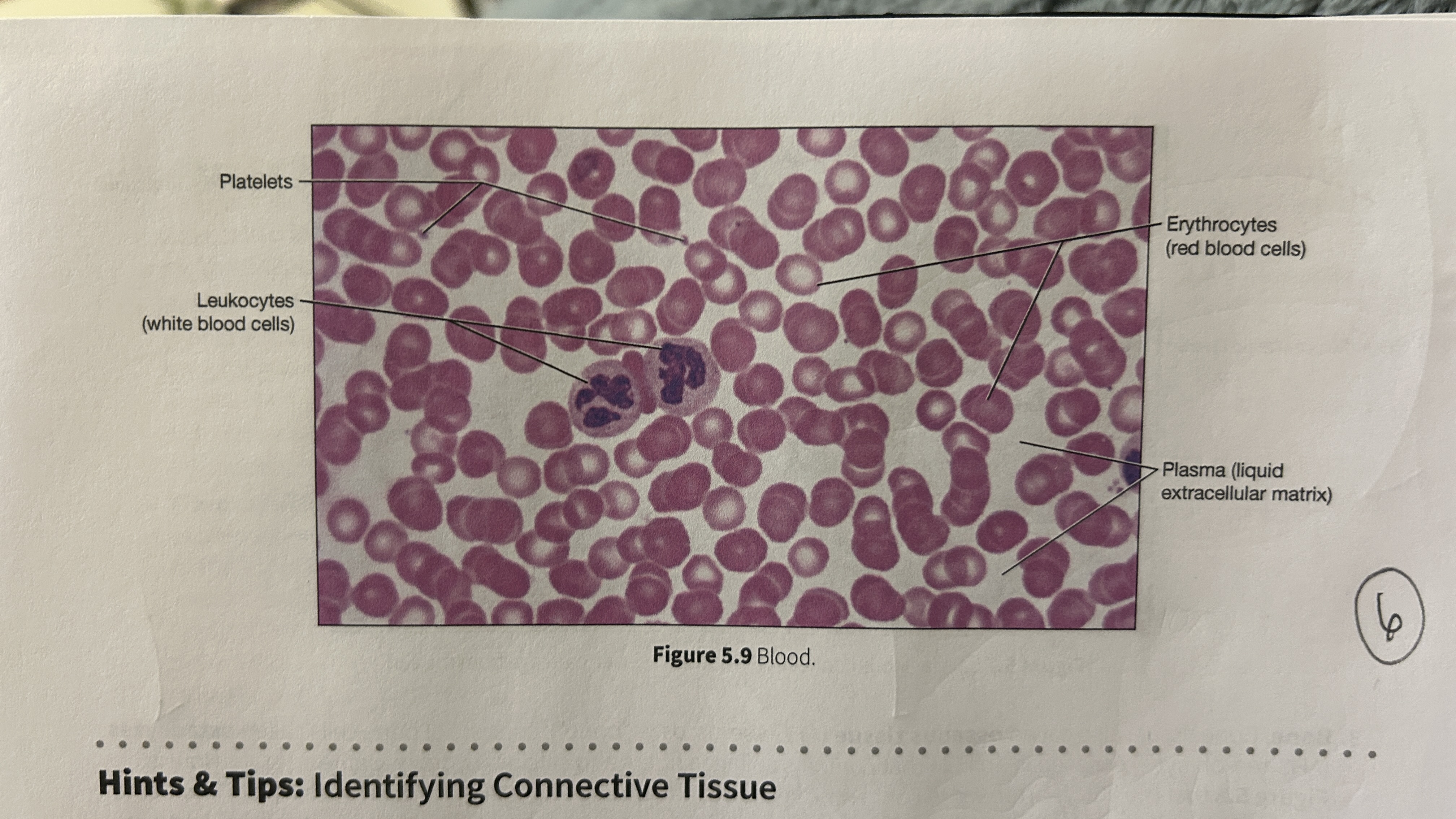
Erythocytes
red blood cells
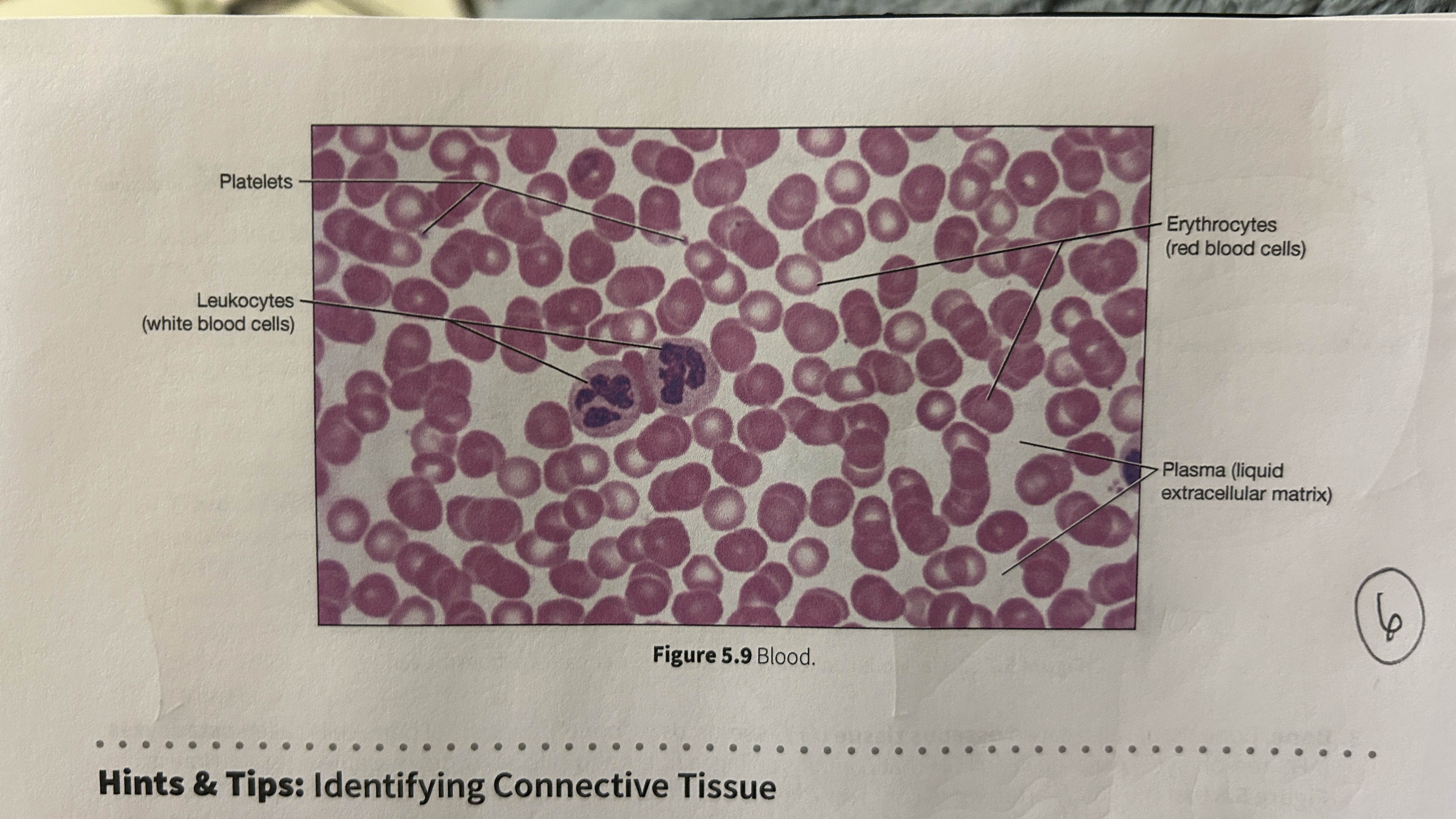
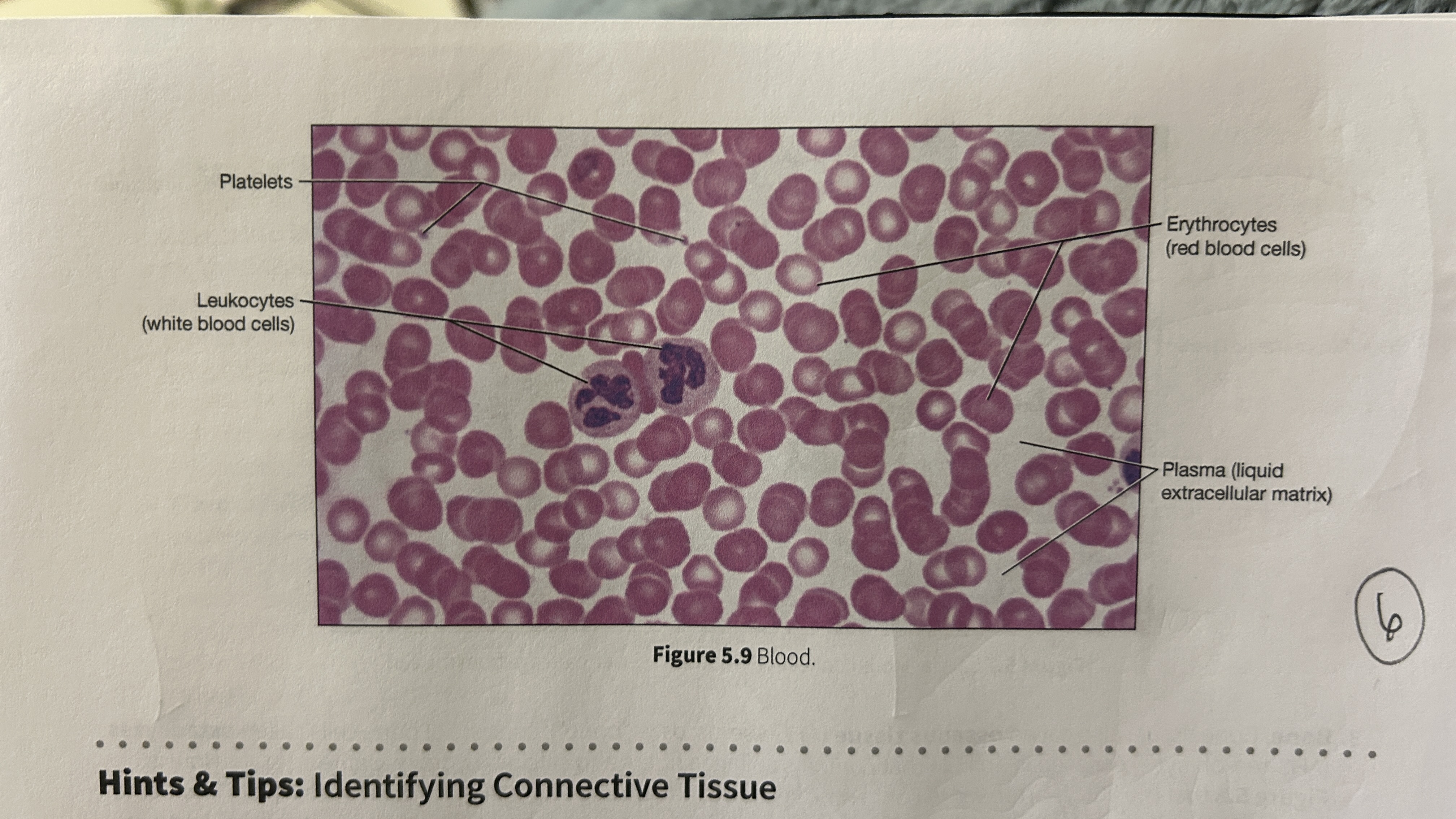
Leukocytes
white blood cells
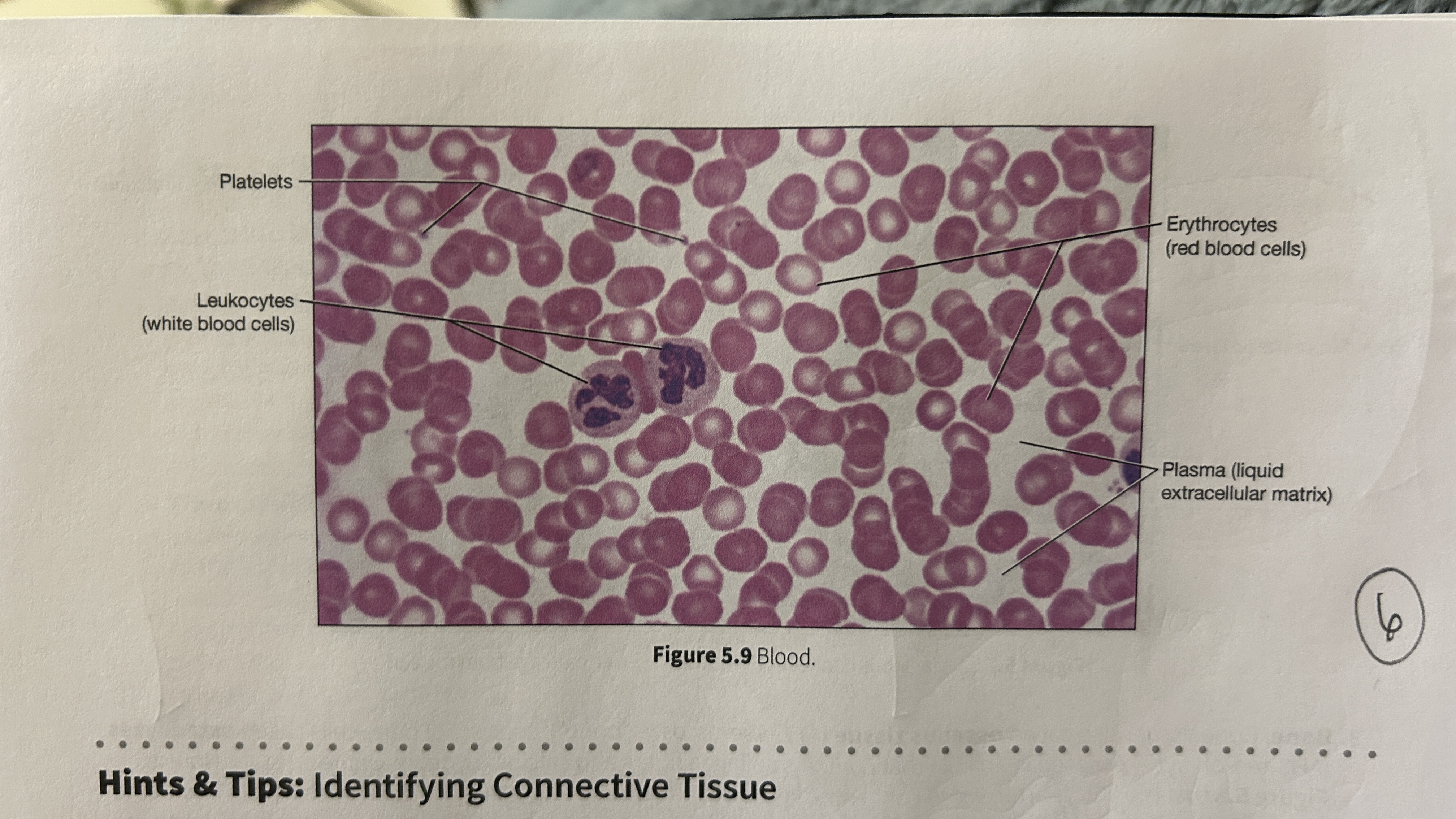
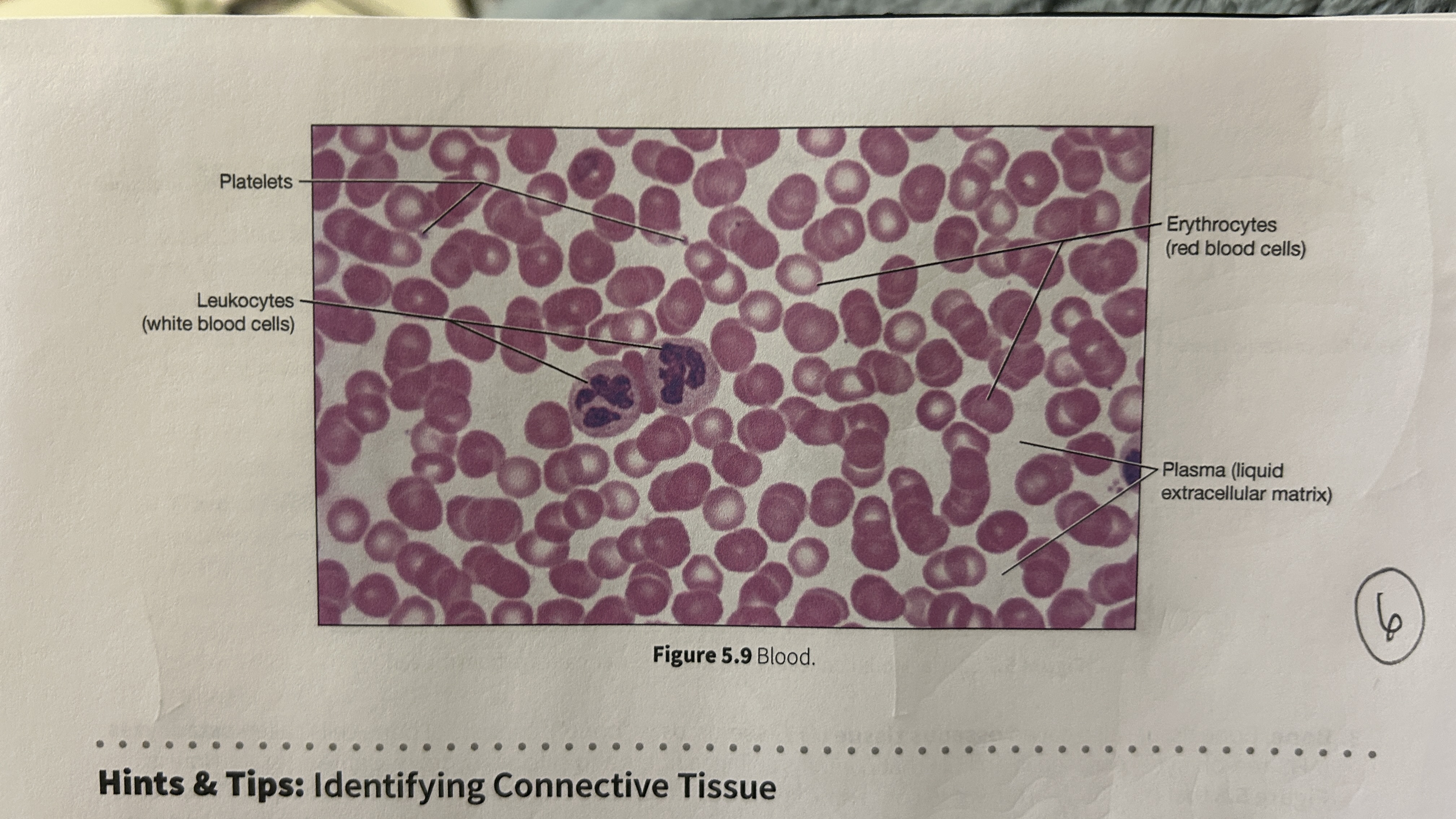
Platelets
blood cellular fragments
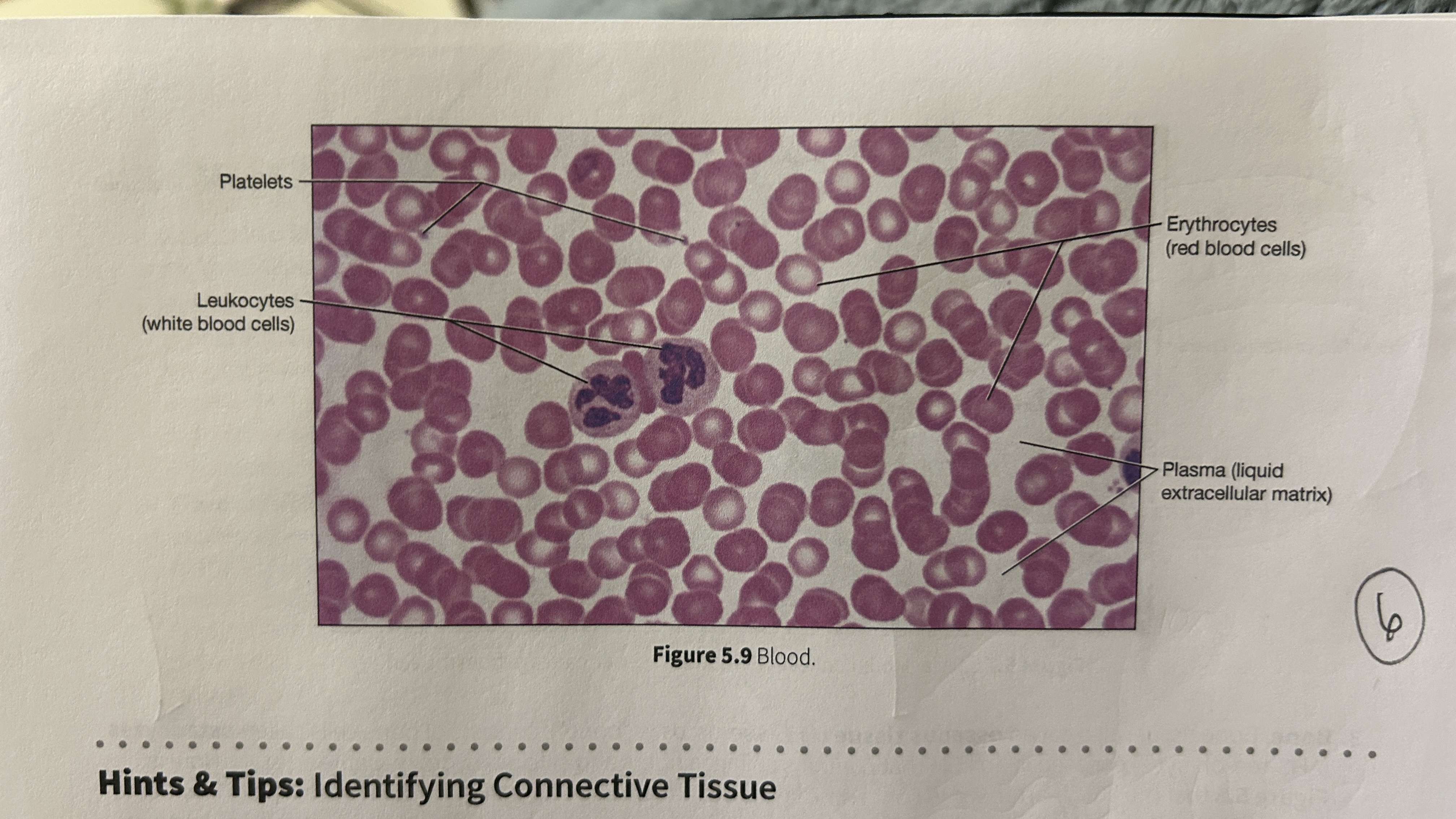
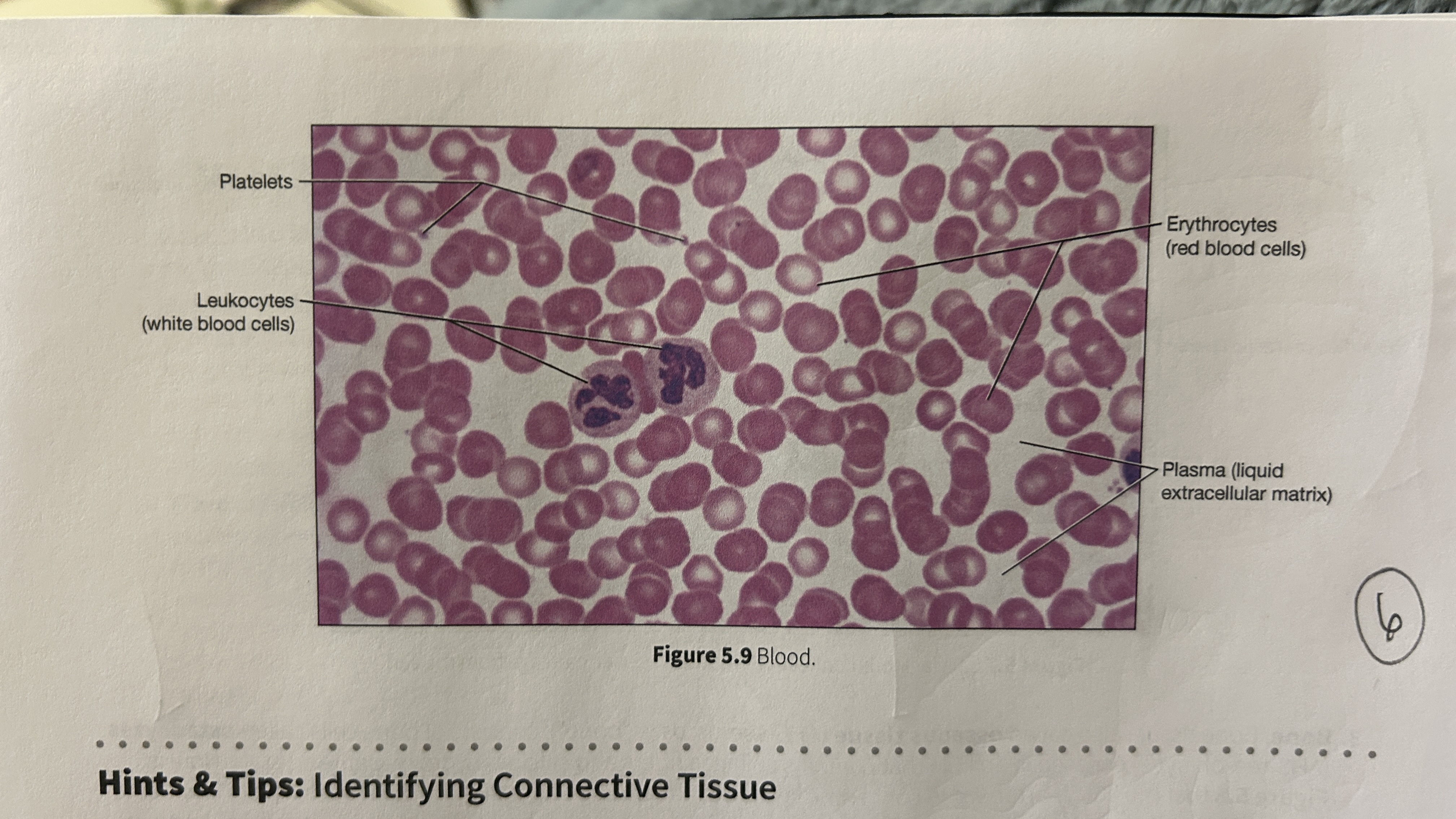
What is the main role of blood?
Transport oxygen, nutrients, electrolytes, wastes, and other substances through the body. Blood is the only cell type without a nucleus (mature erythrocyte).
What is the magnification level of the Loose (areolar) CT?
4x
What is the magnification level of the Loose (areolar) CT?
10x
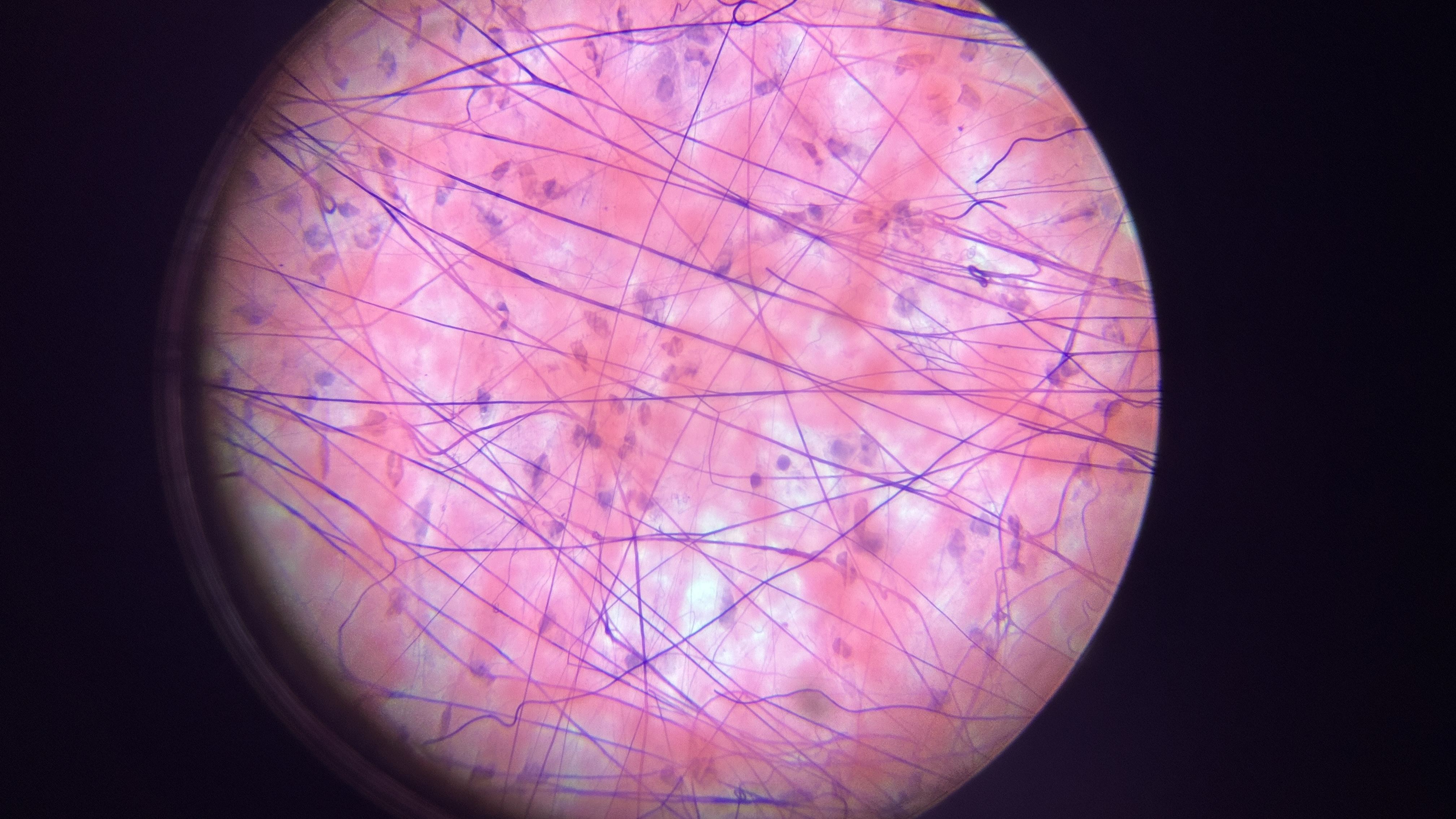
What is the magnification level of the Loose (areolar) CT?
40x
What is the magnification level of the Reticular CT?
4x
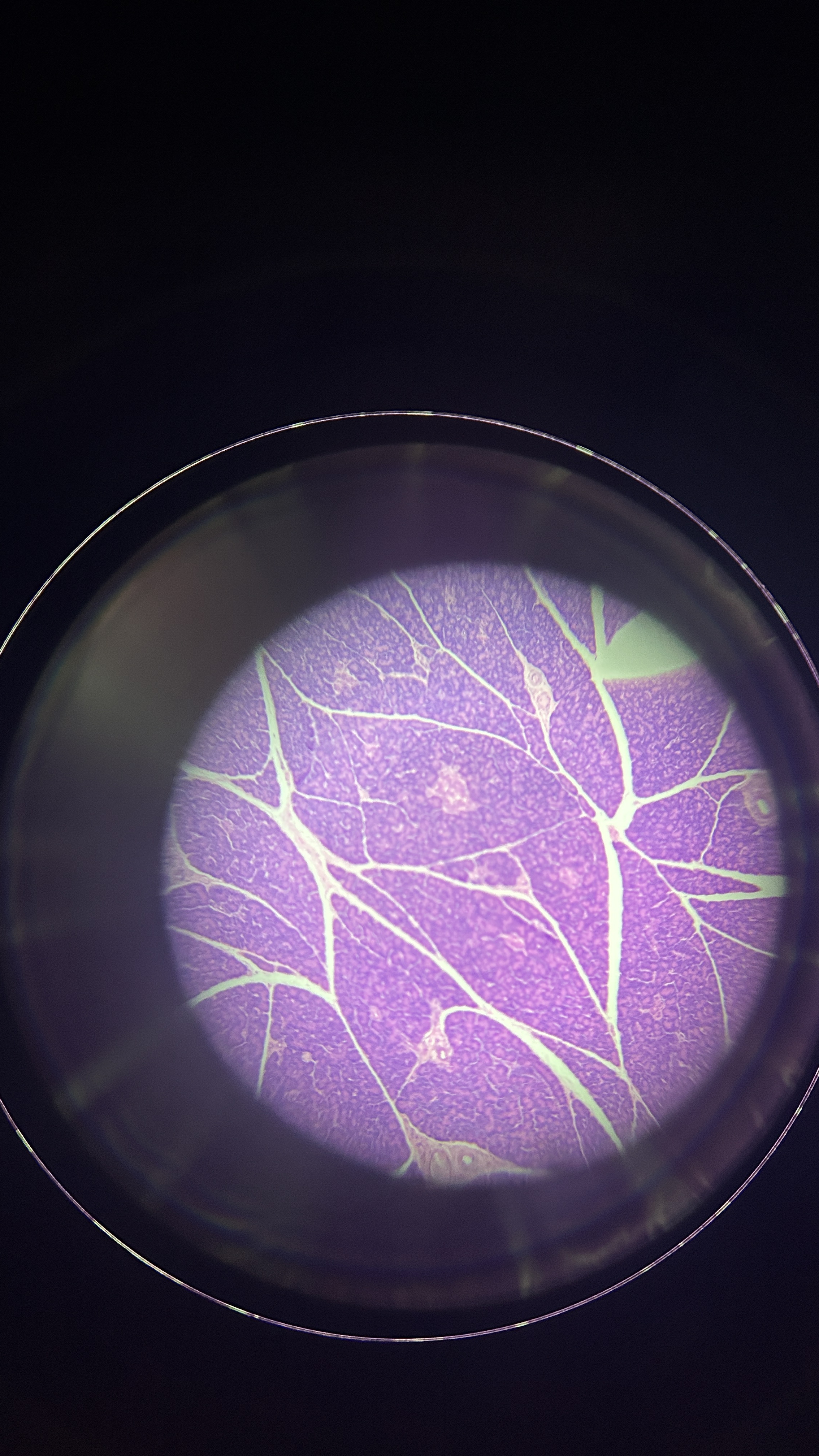
What is the magnification level of the Reticular CT?
10x
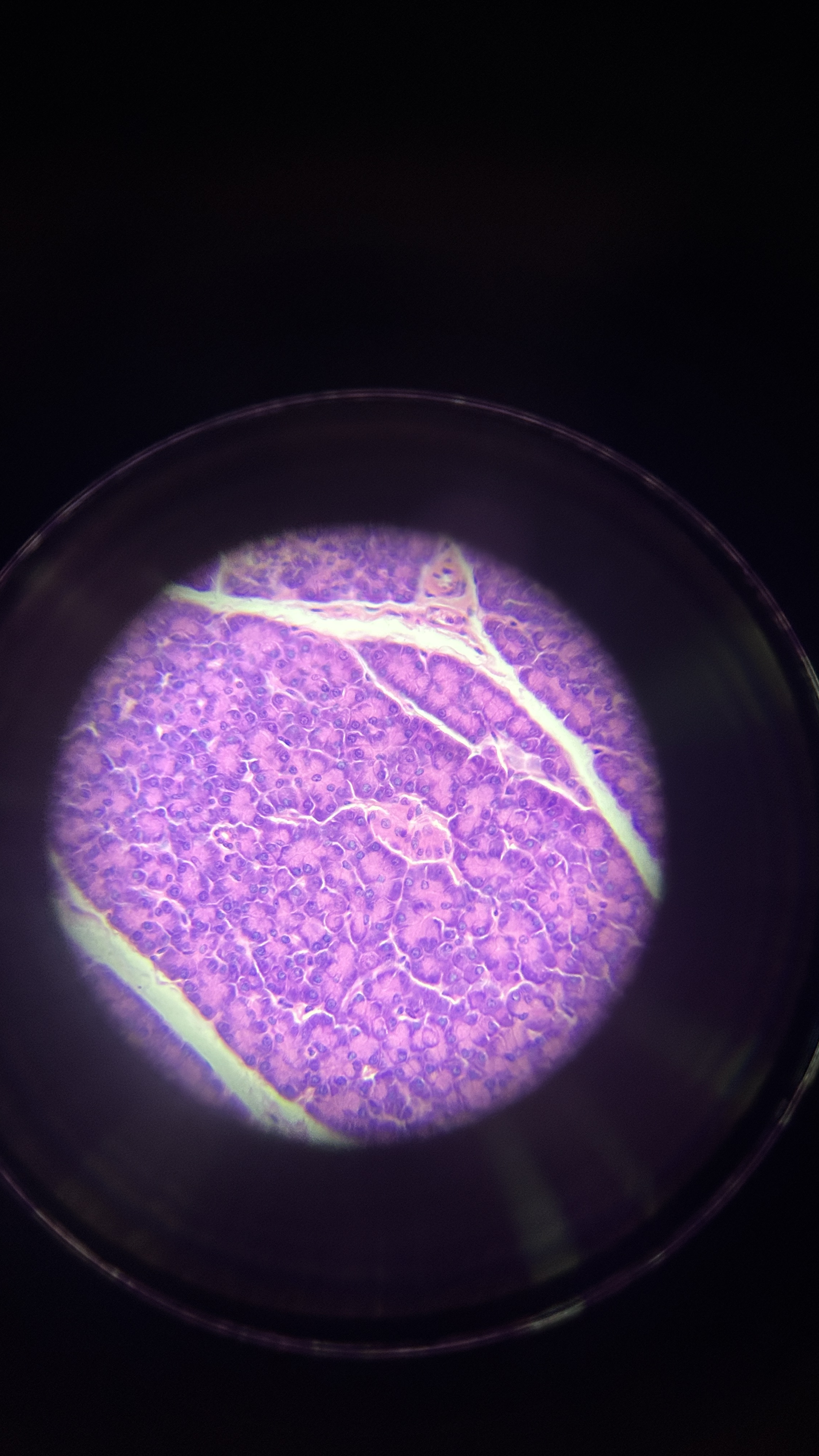
What is the magnification level of the Reticular CT?
40x
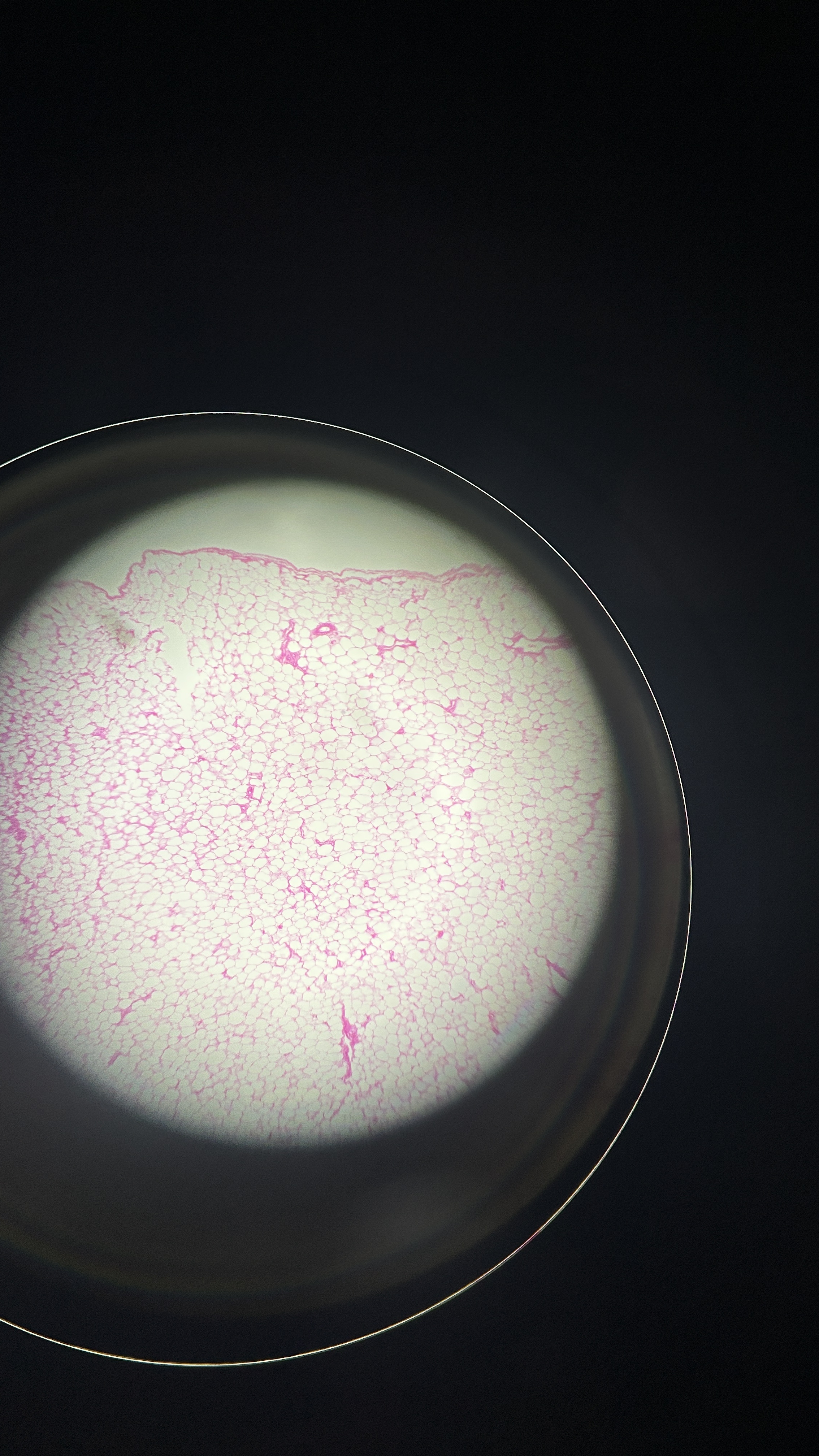
What is the magnification level of the Adipose Tissue?
4x
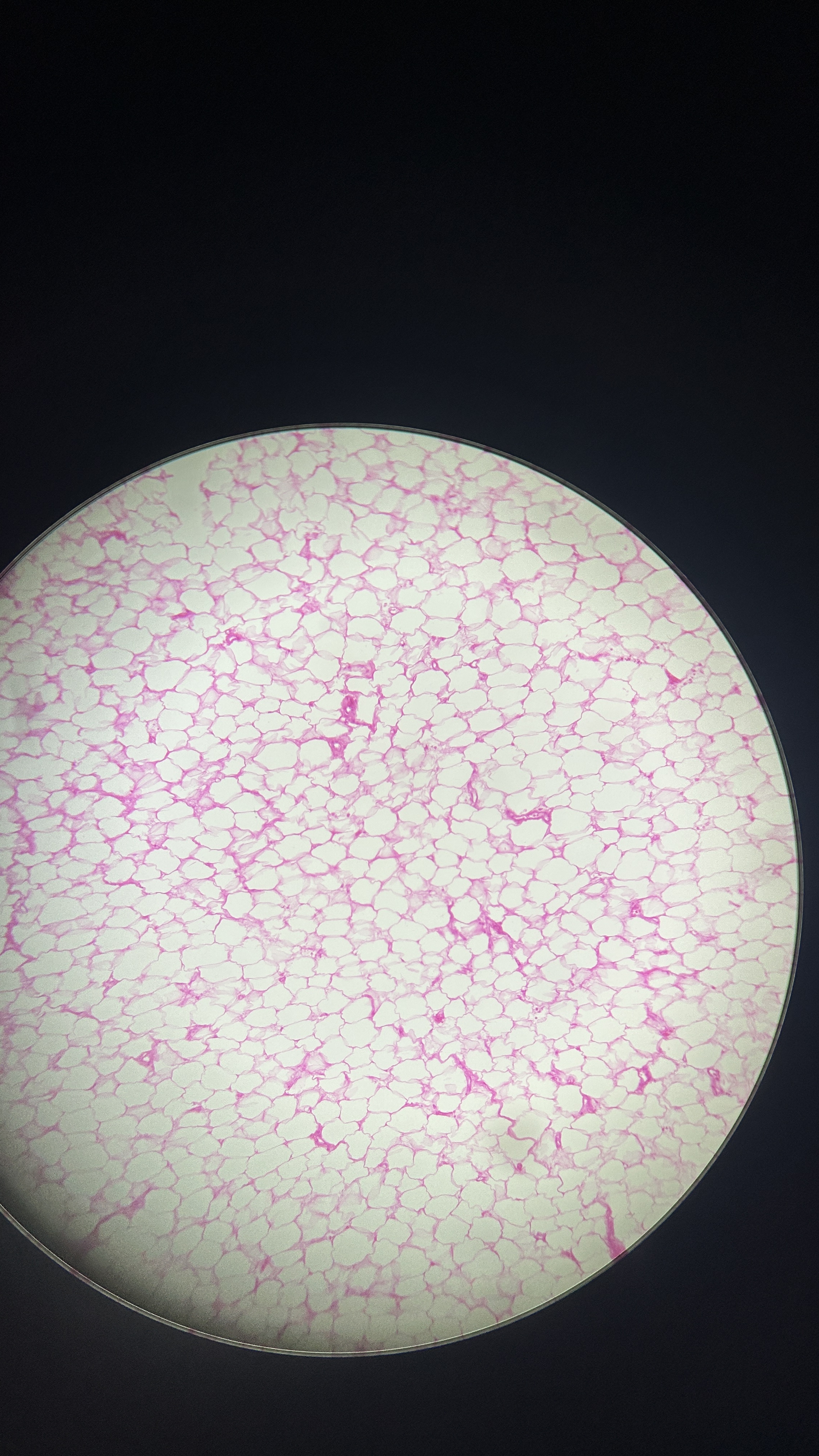
What is the magnification level of the Adipose Tissue?
10x
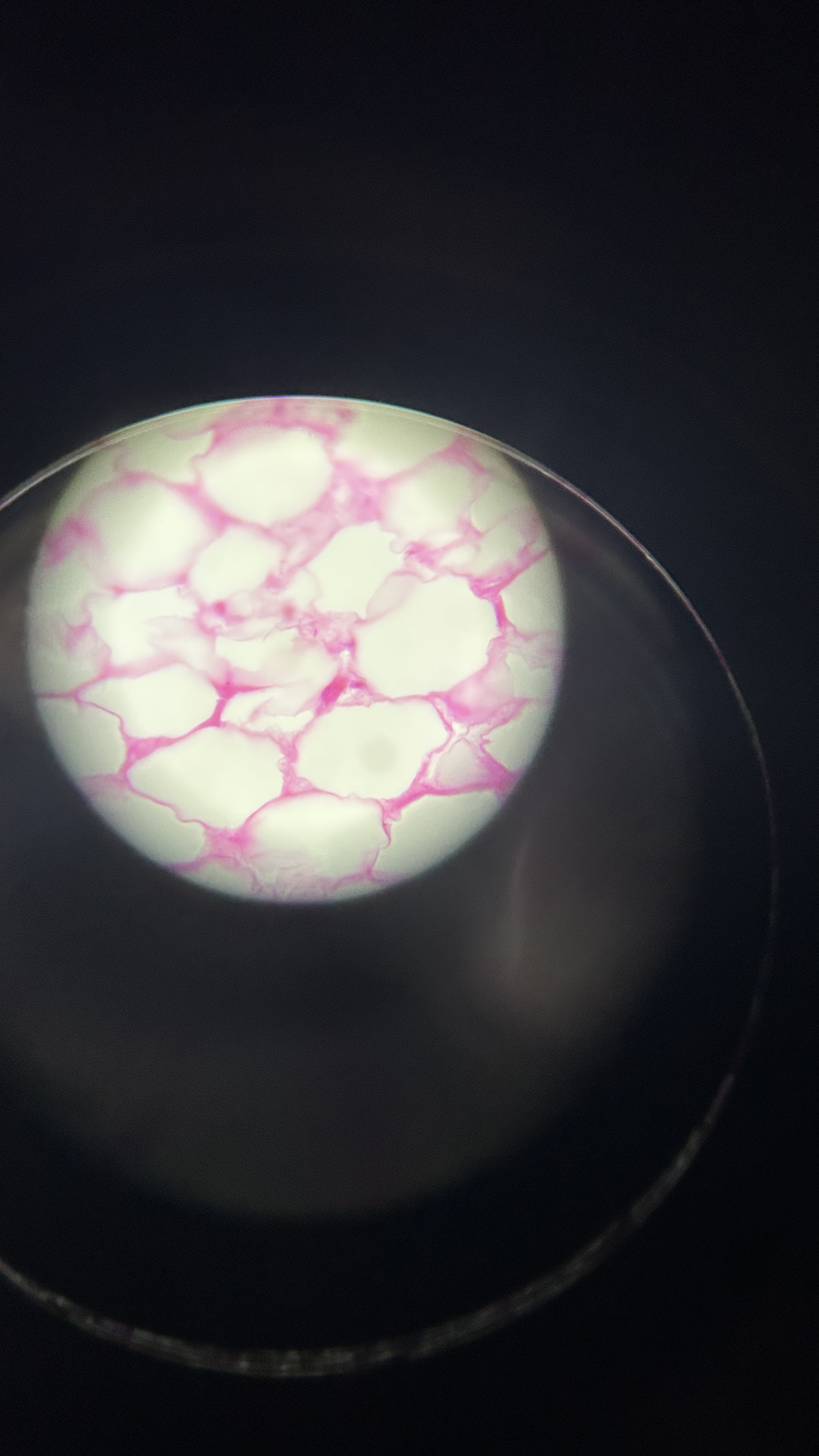
What is the magnification level of the Adipose Tissue?
40x
What is the magnification level of the Dense Regular CT?
4x
What is the magnification level of the Dense Regular CT?
10x
What is the magnification level of the Dense Regular CT?
40x
What is the magnification level of the Dense Irregular CT?
4x
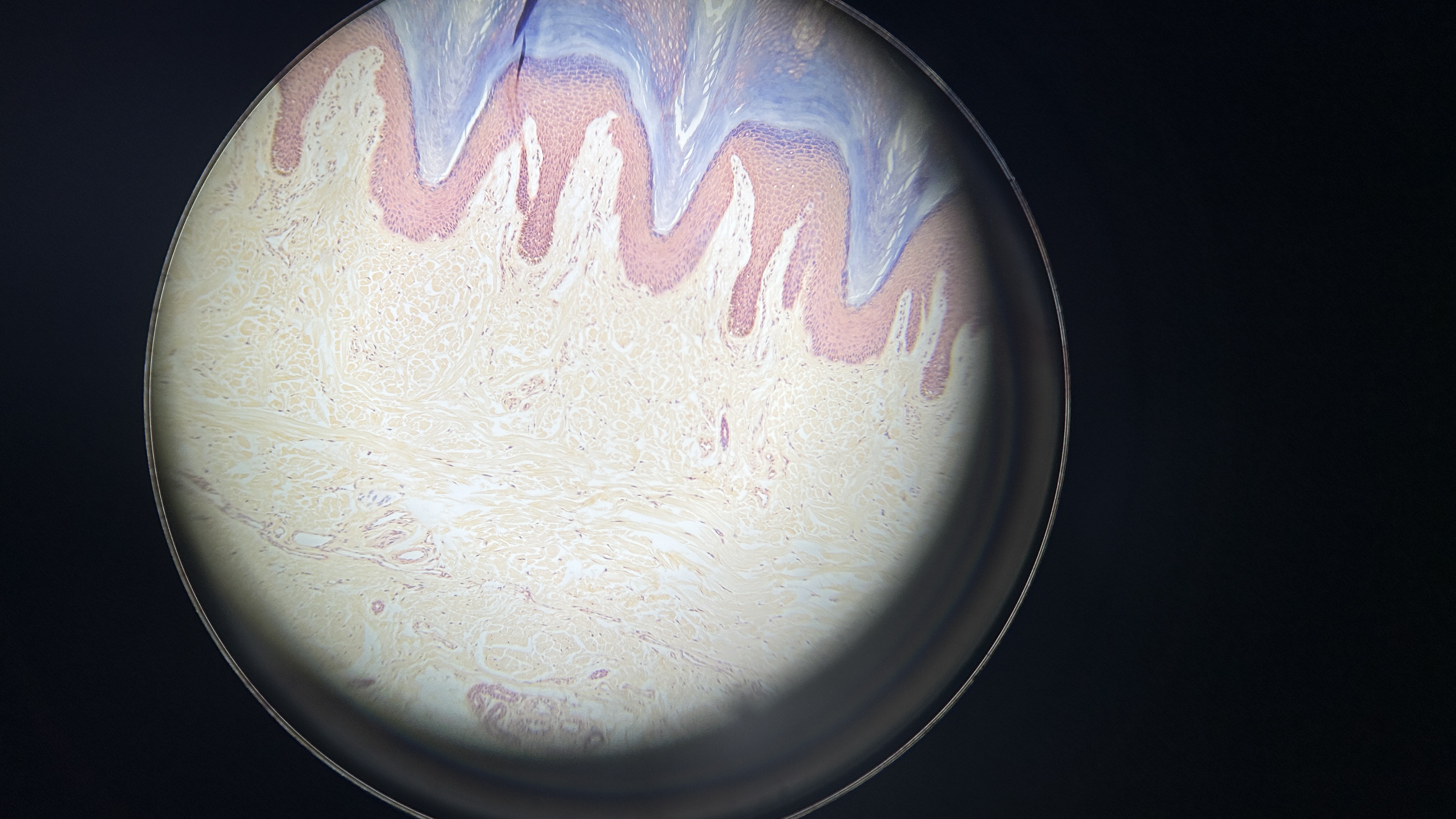
What is the magnification level of the Dense Irregular CT?
10x
What is the magnification level of the Dense Irregular CT?
40x
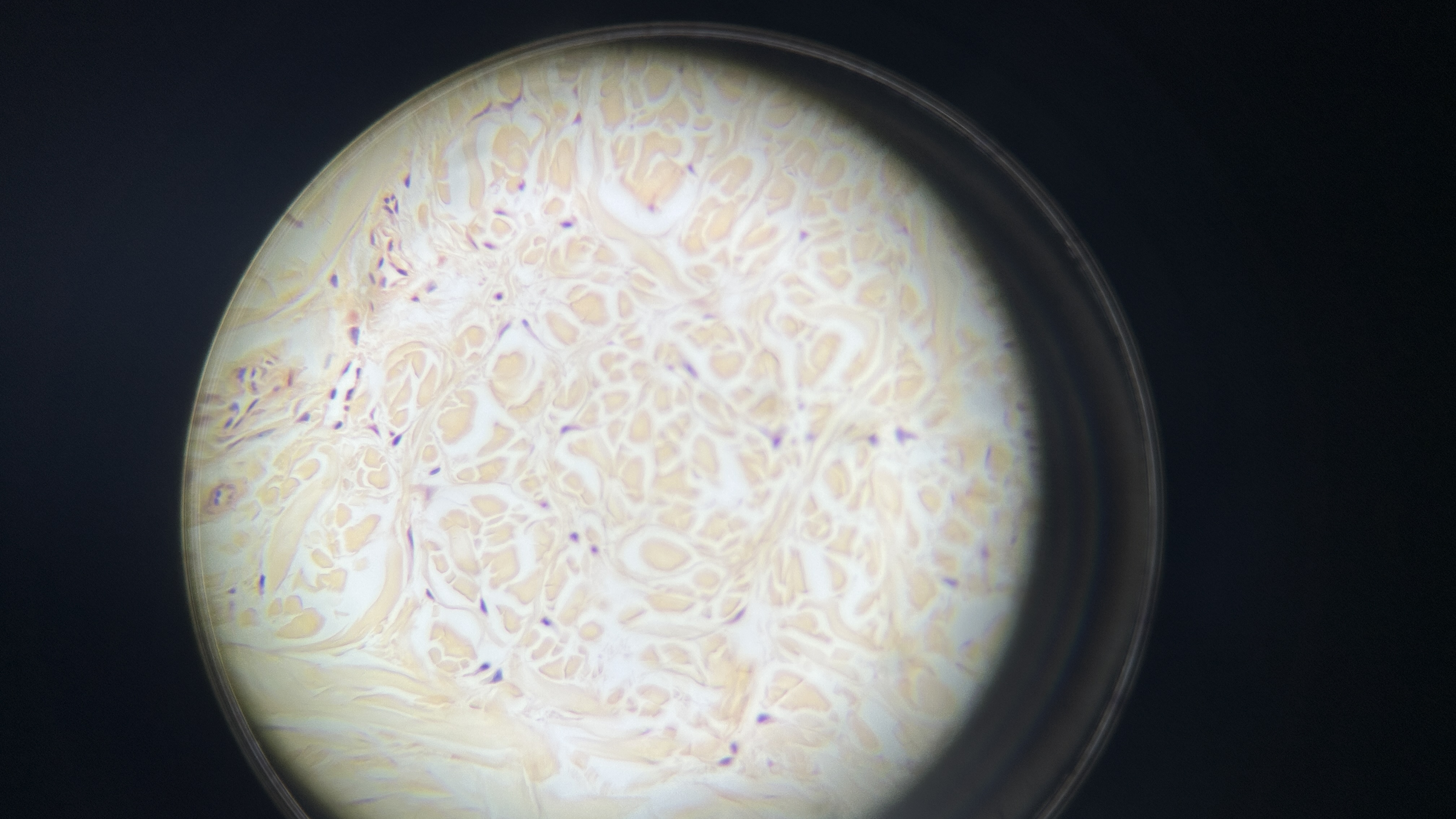
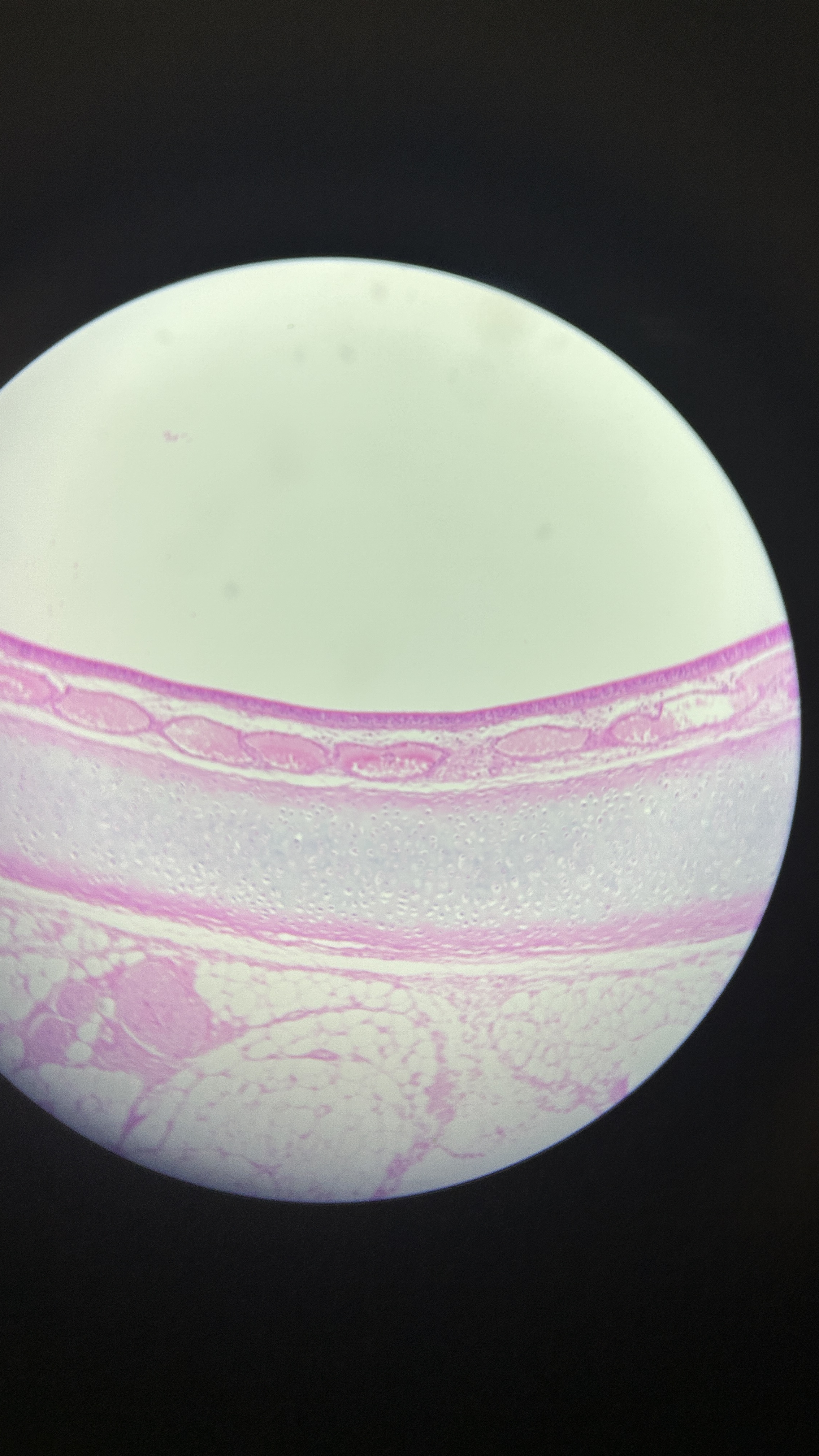
What is the magnification level of the Hydraline Cartilage?
4x
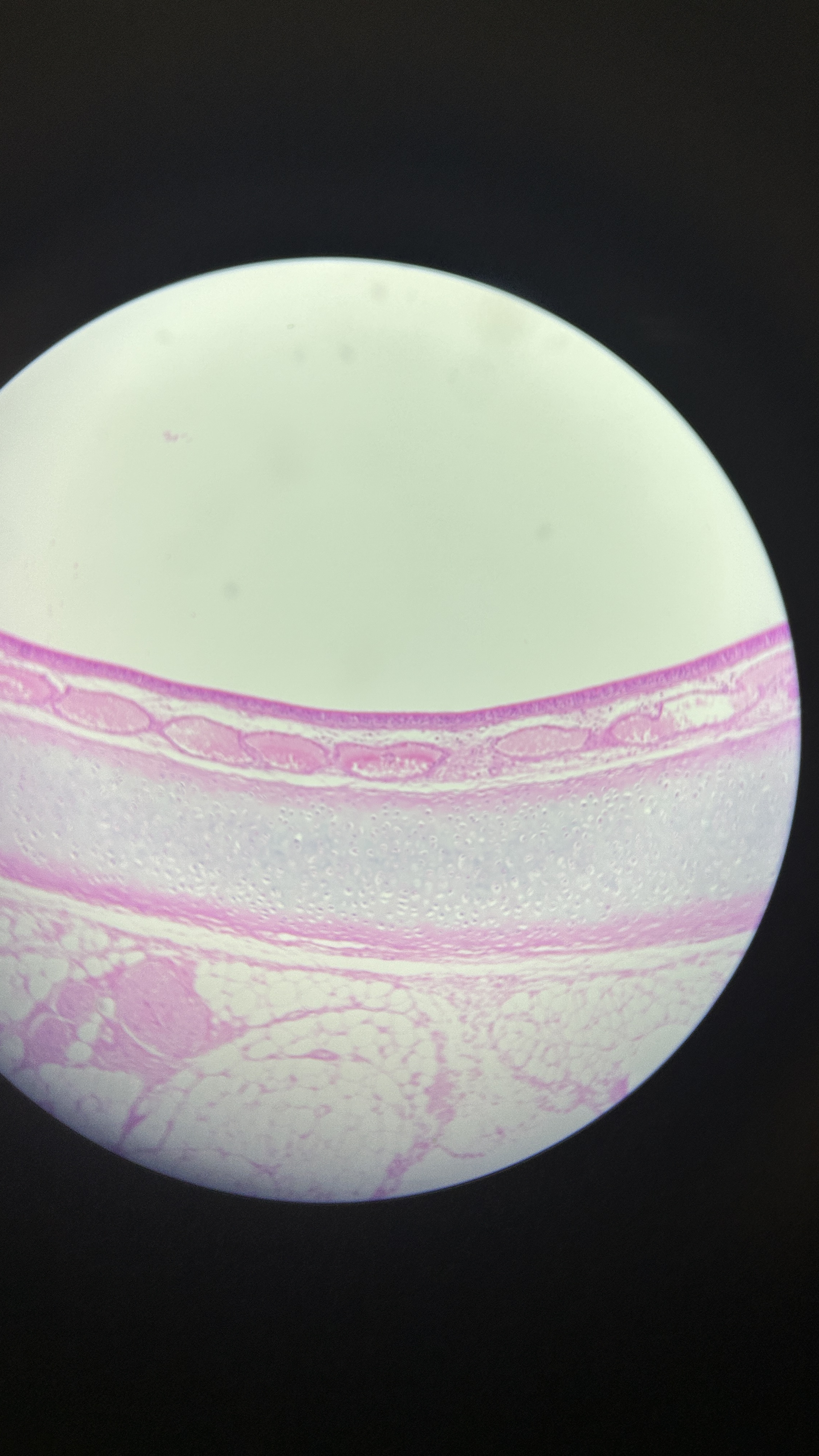
What is the magnification level of the Hydraline Cartilage?
10x
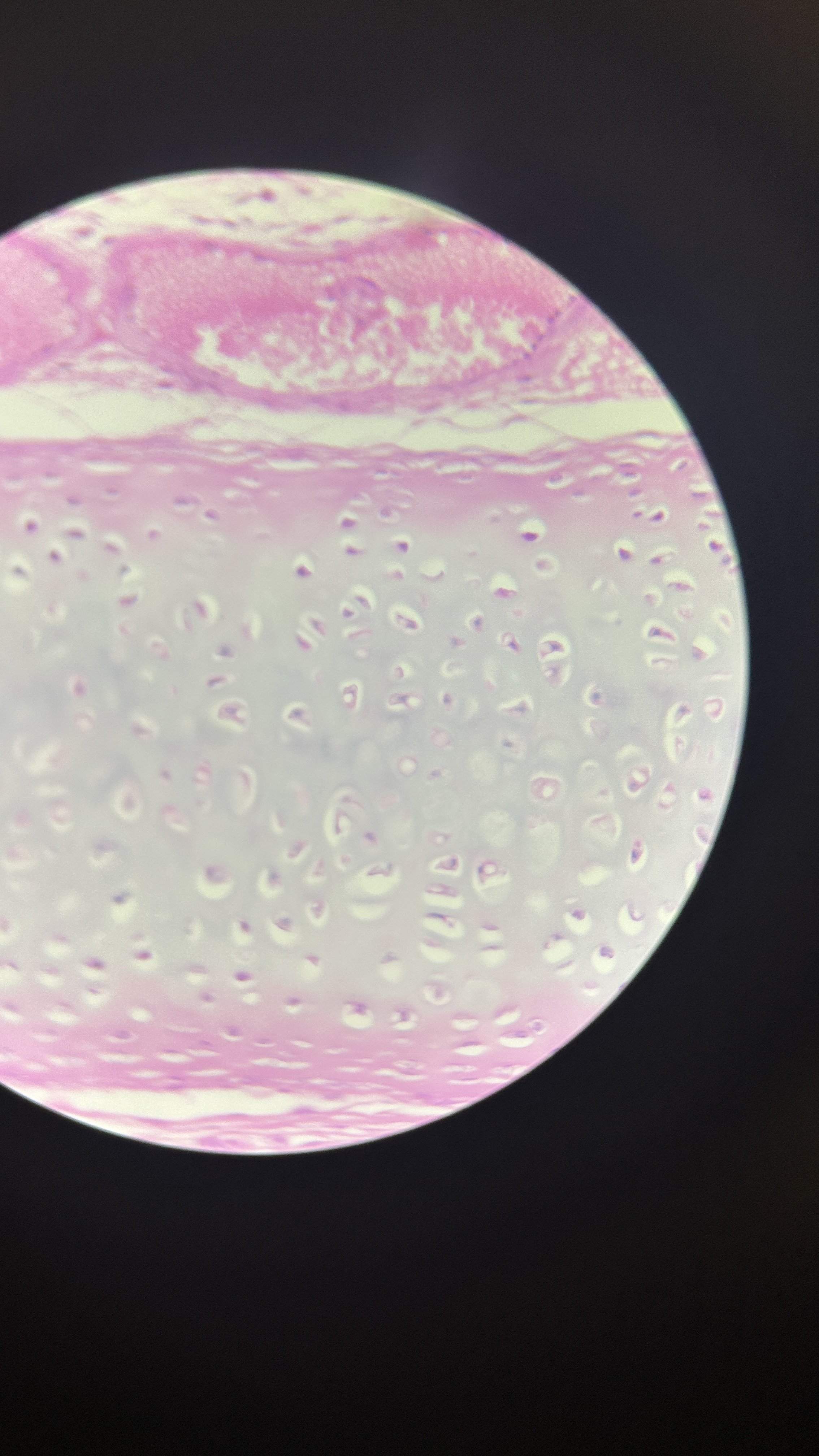
What is the magnification level of the Hydraline Cartilage?
40x
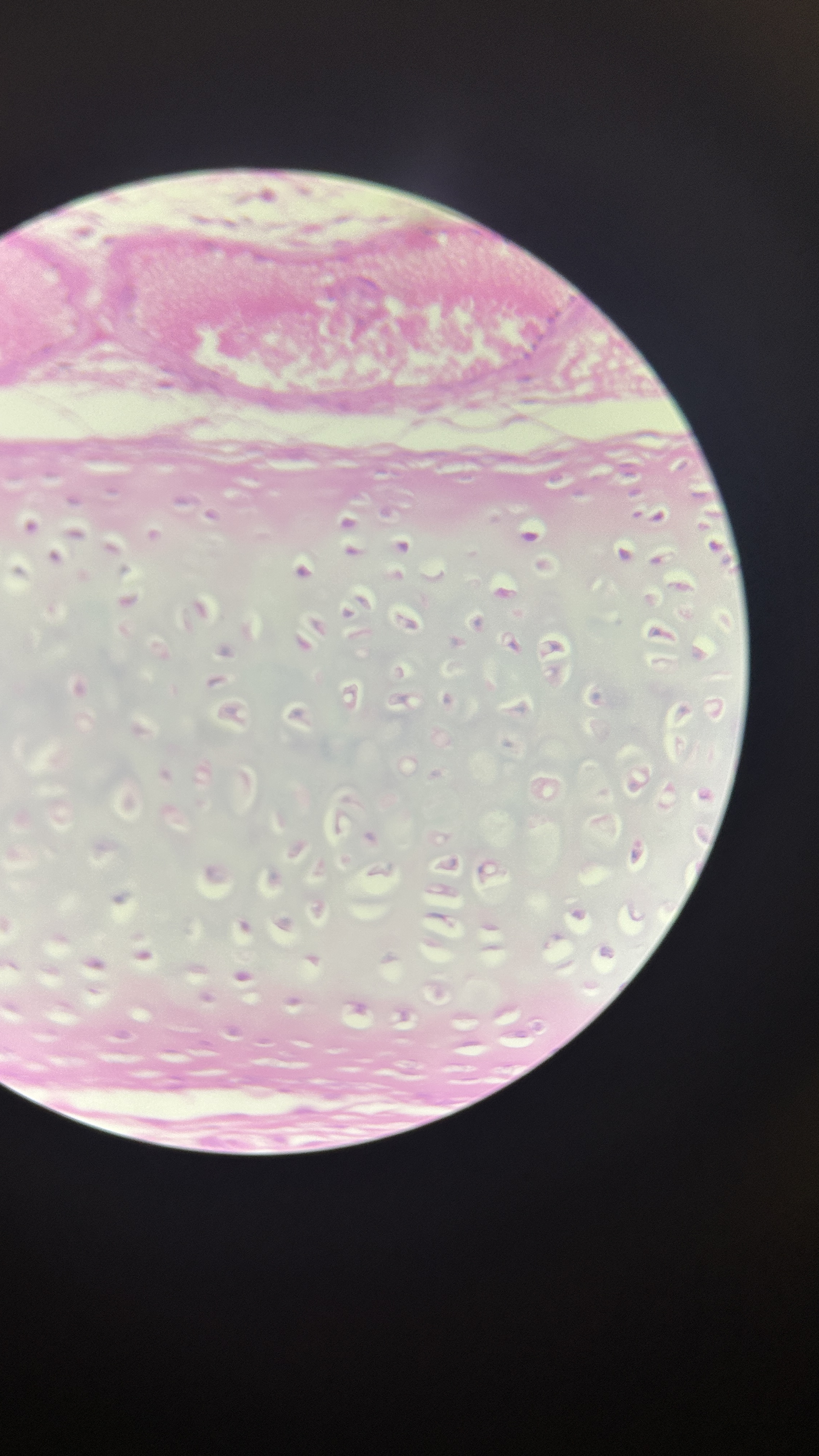
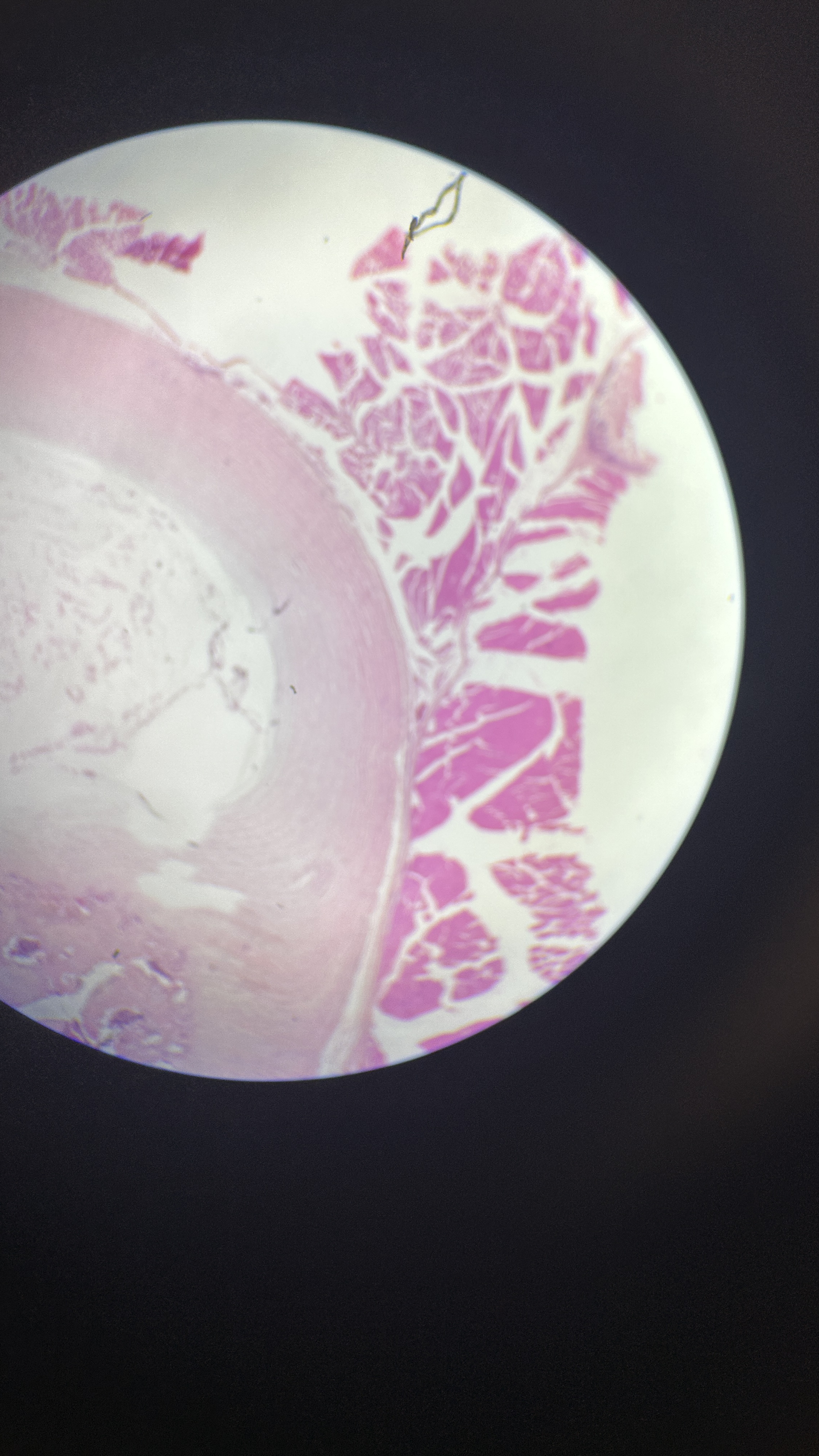
What is the magnification level of the Fibrocartilage?
4x
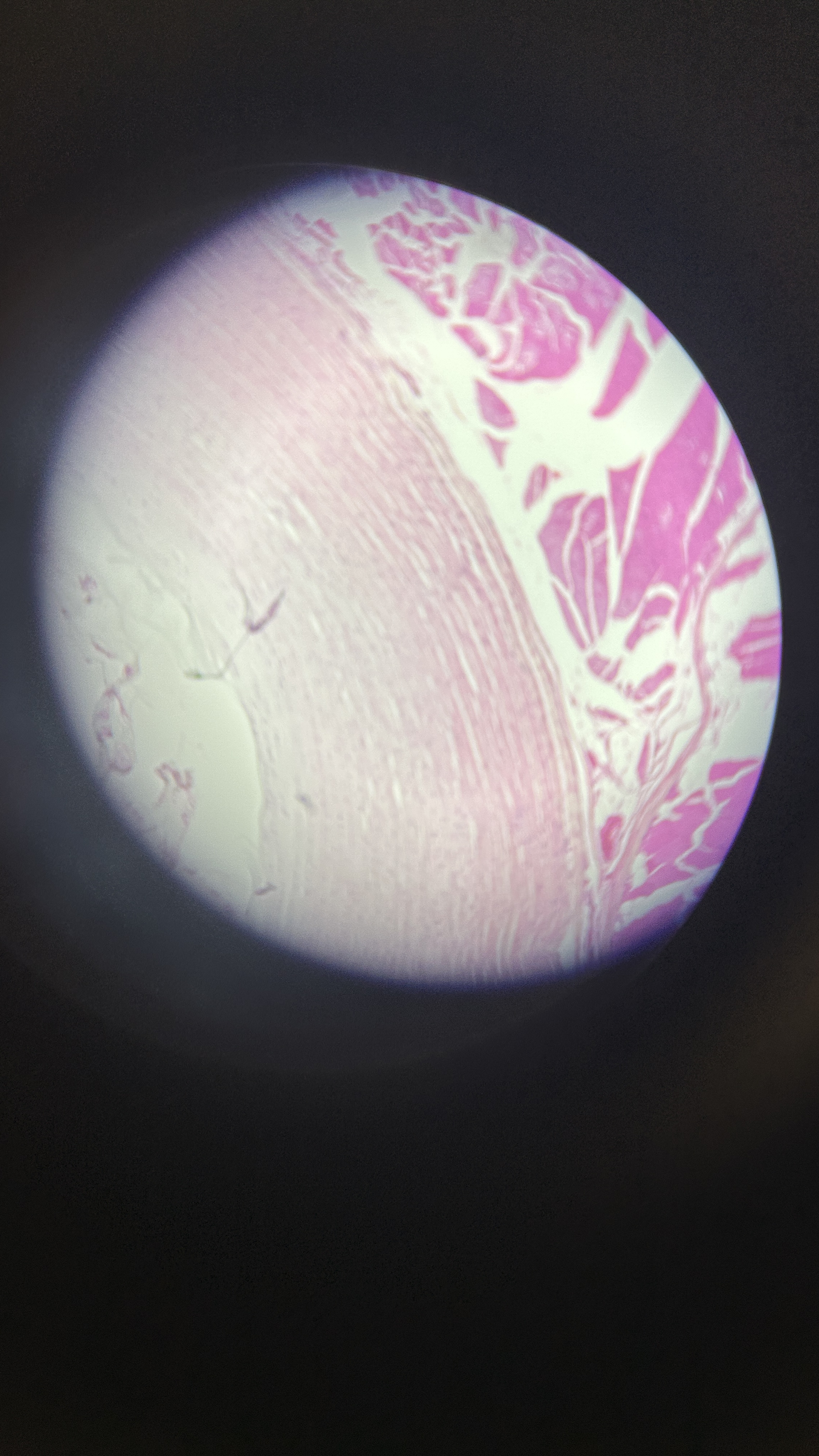
What is the magnification level of the Fibrocartilage?
10x
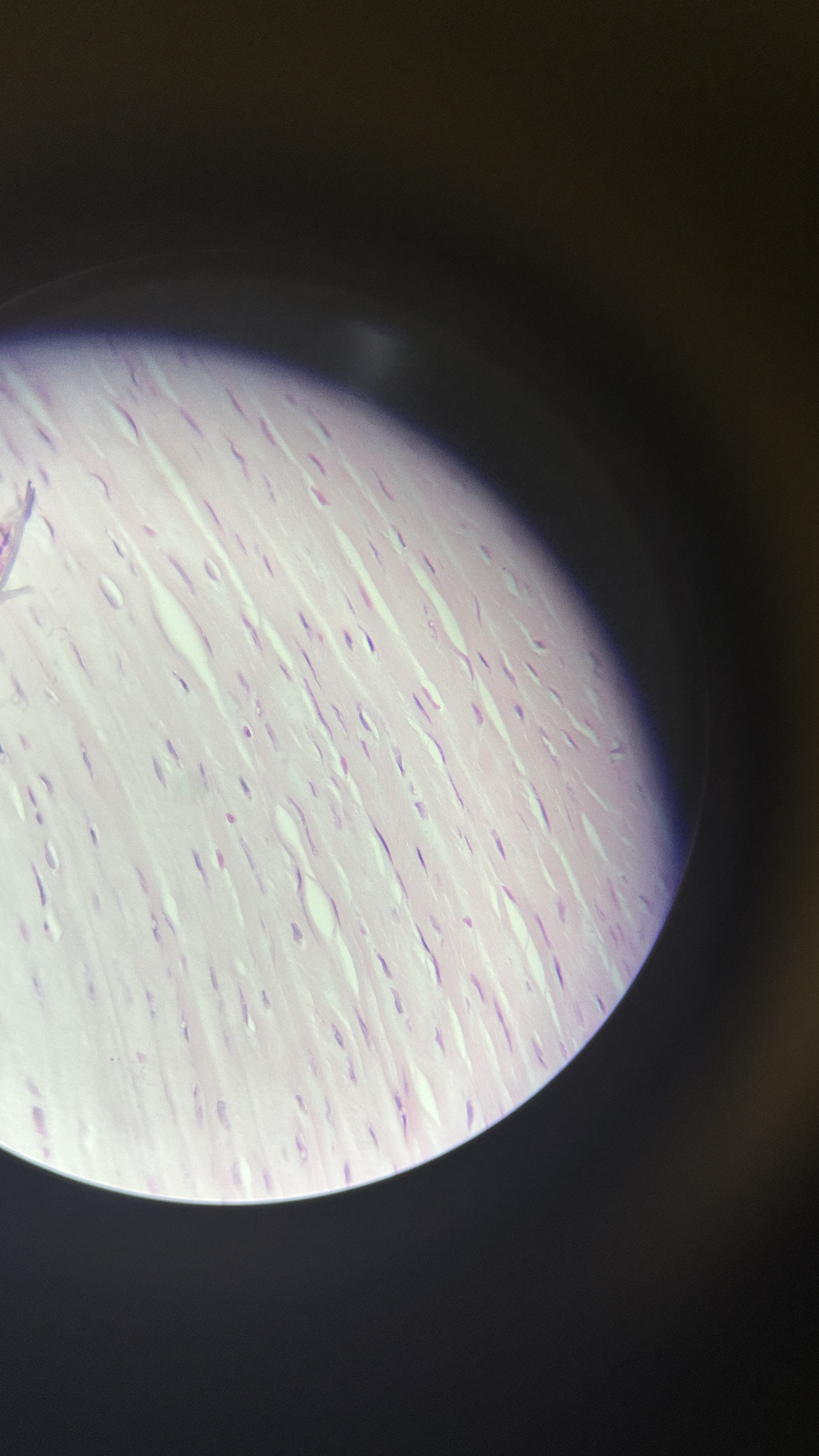
What is the magnification level of the Fibrocartilage?
40x
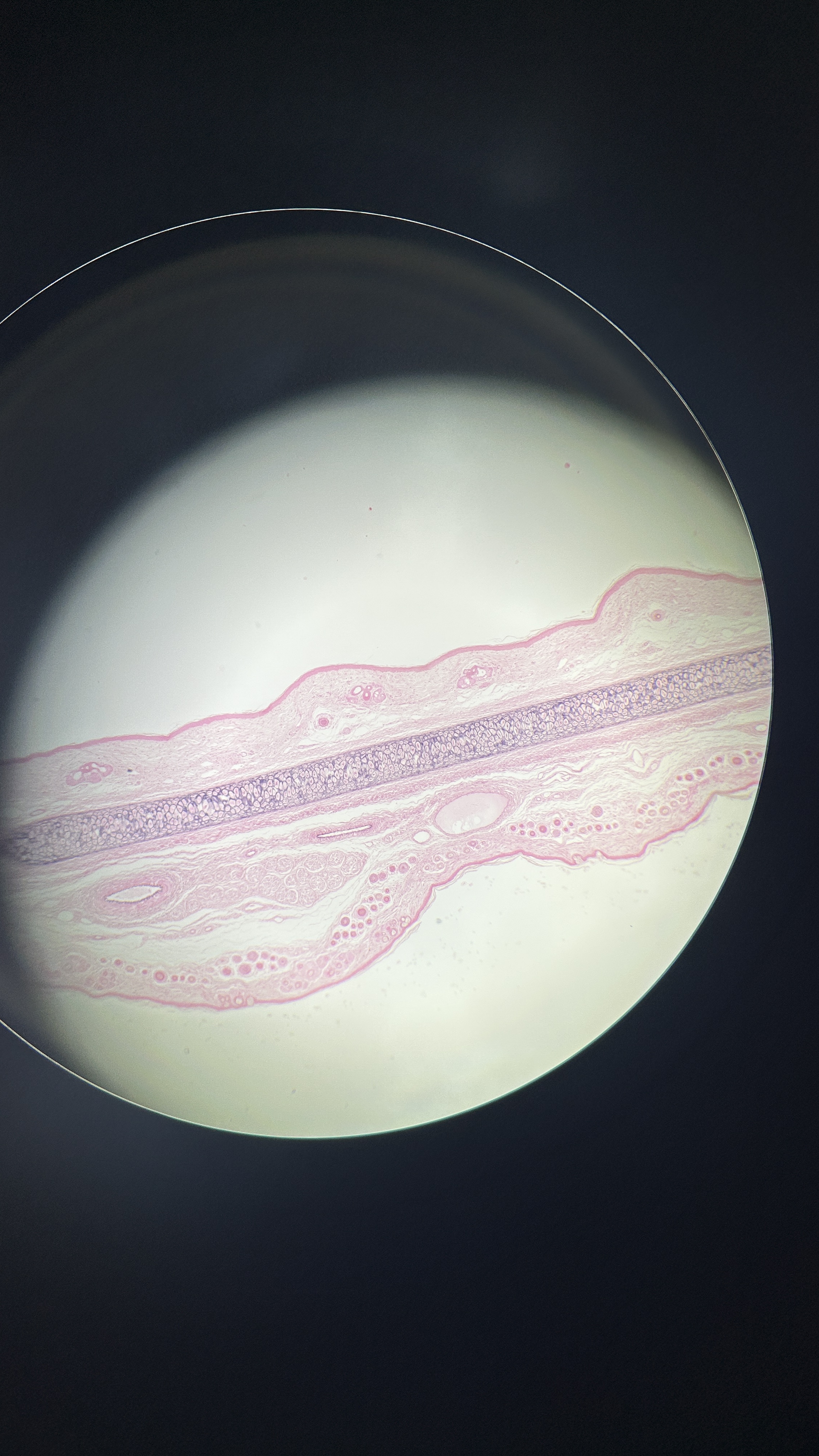
What is the magnification level of the Elastic Cartilage?
4x
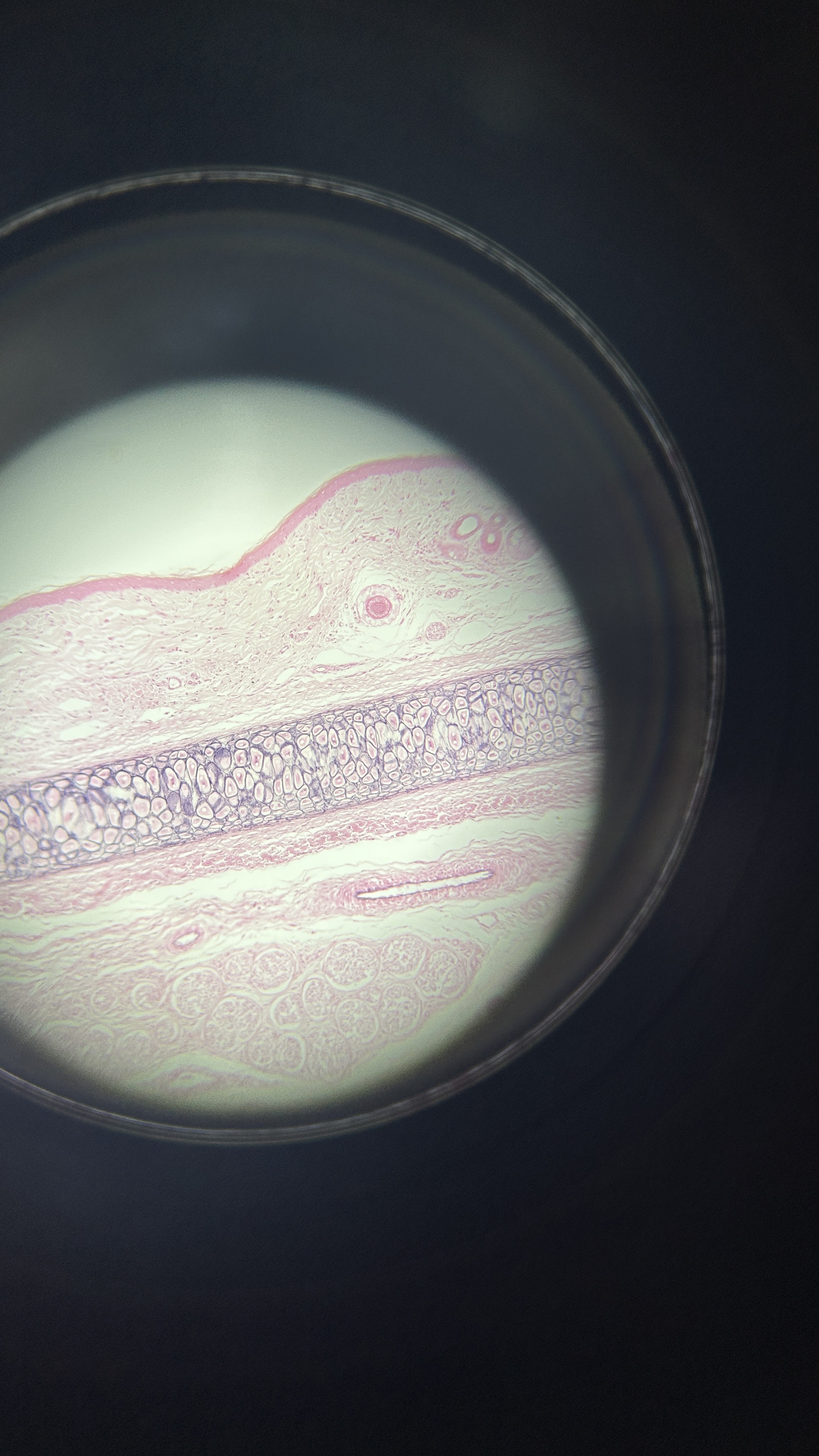
What is the magnification level of the Elastic Cartilage?
10x
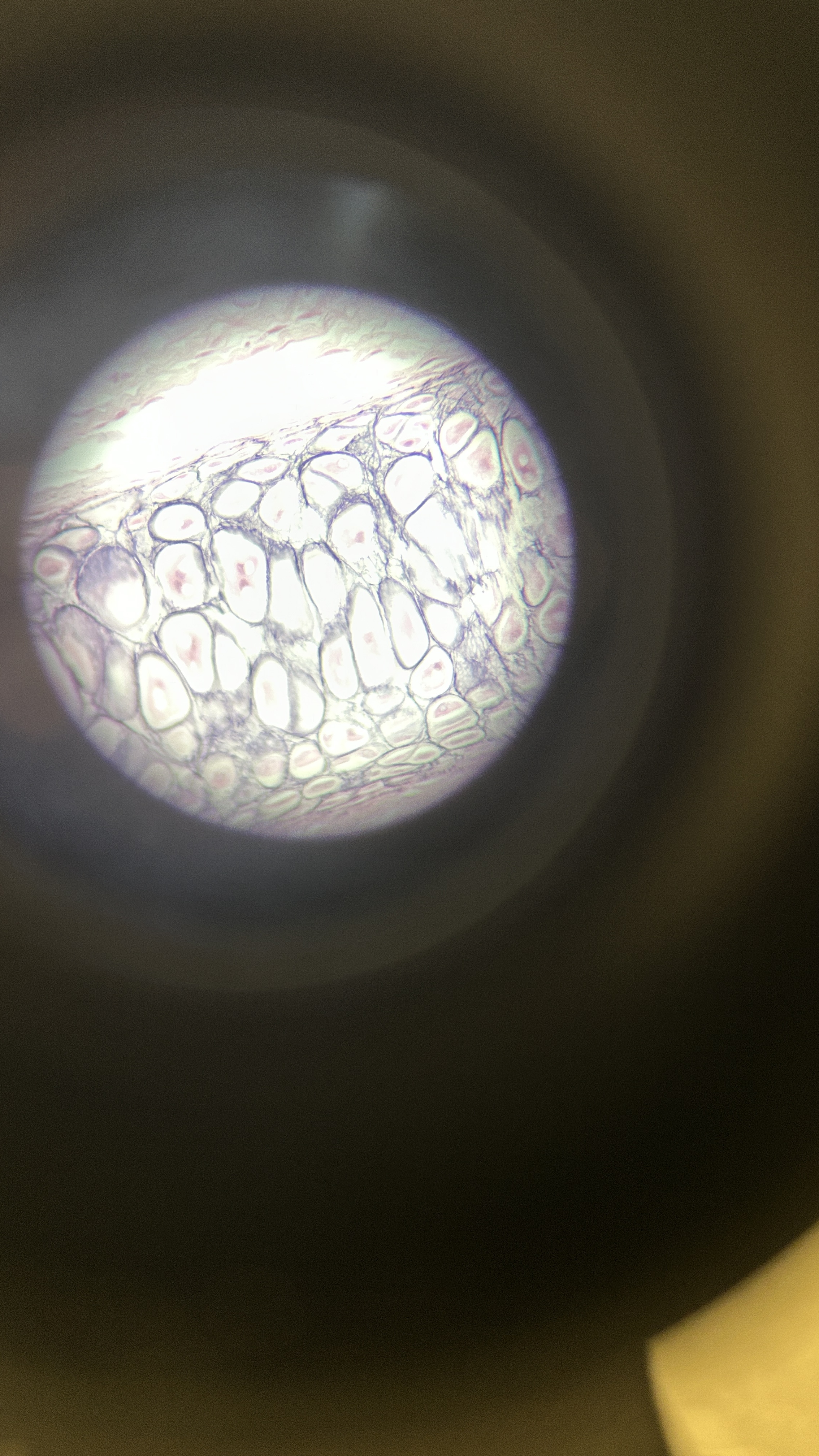
What is the magnification level of the Elastic Cartilage?
40x
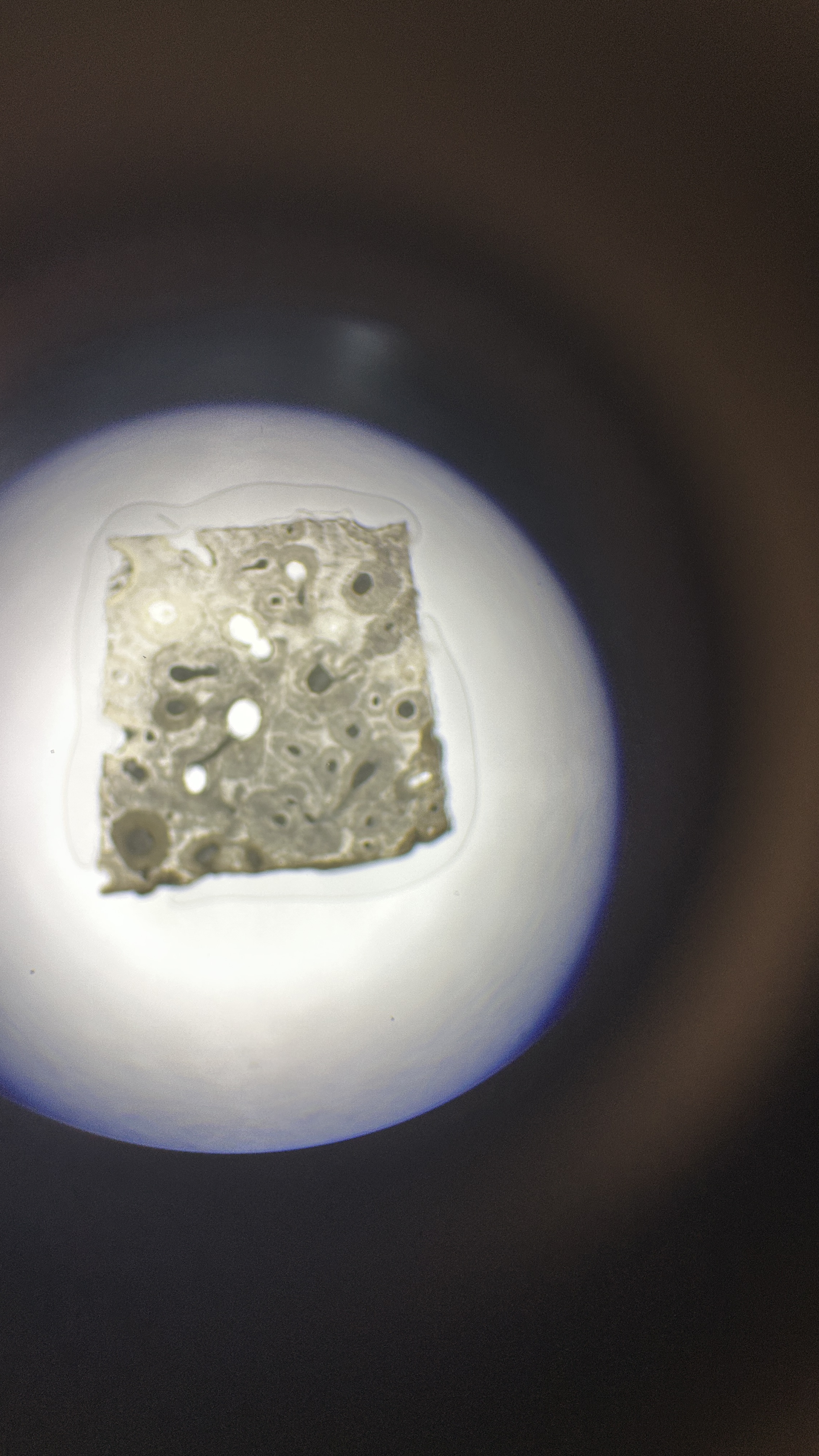

What is the magnification level of the Bone?
4x
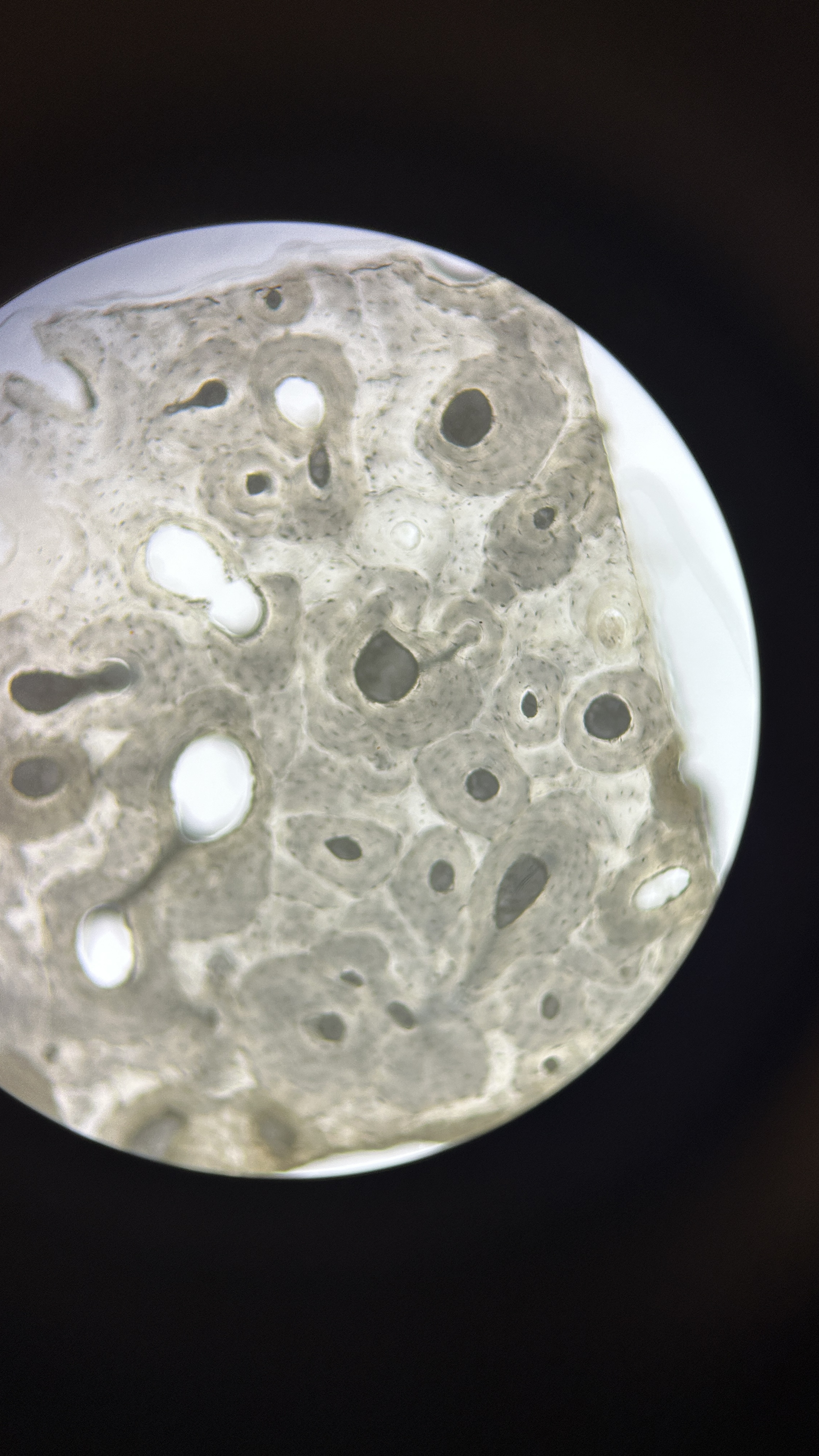
What is the magnification level of the Bone?
10x
What is the magnification level of the Bone?
40x
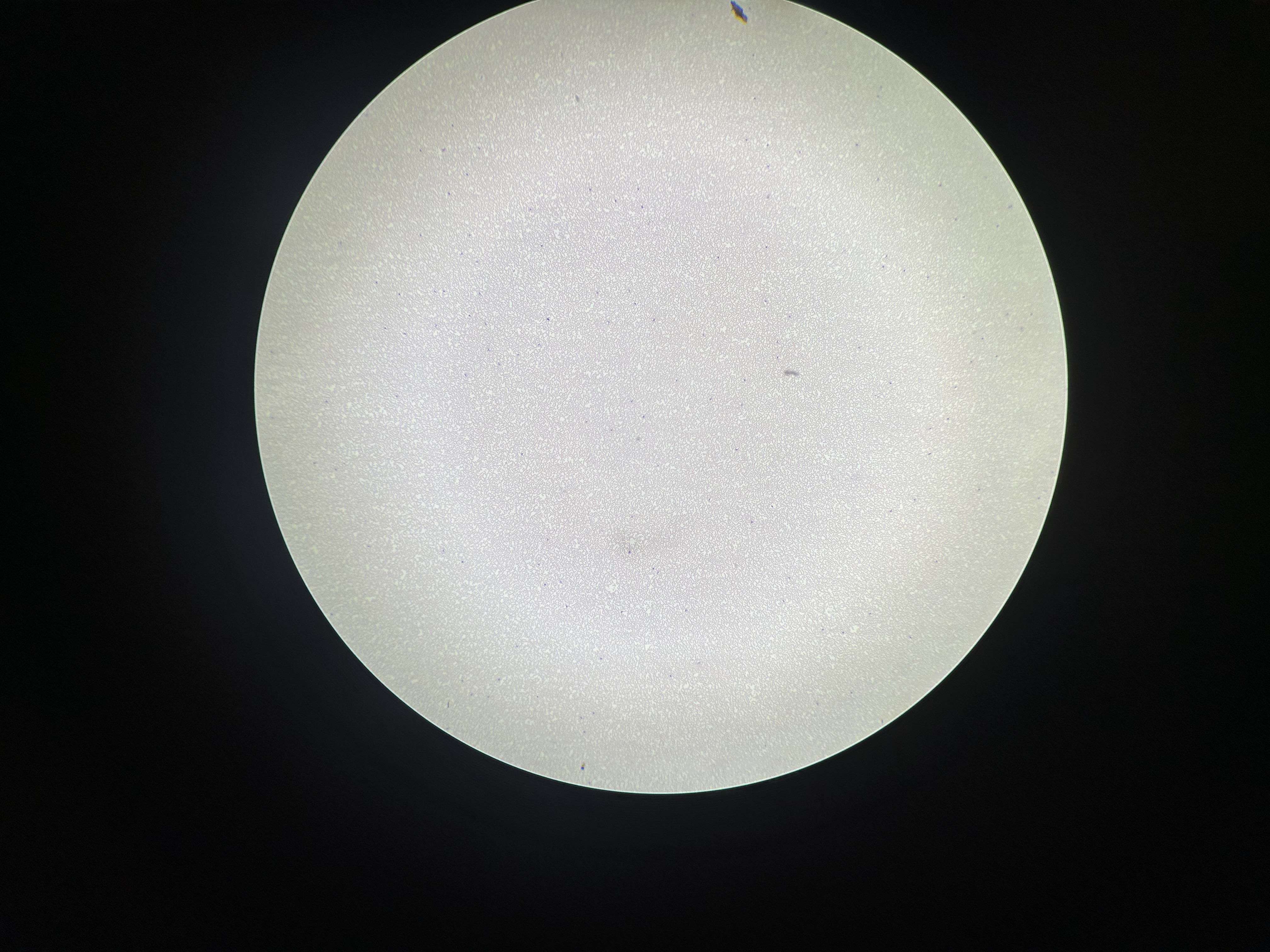

What is the magnification level of the Blood?
4x
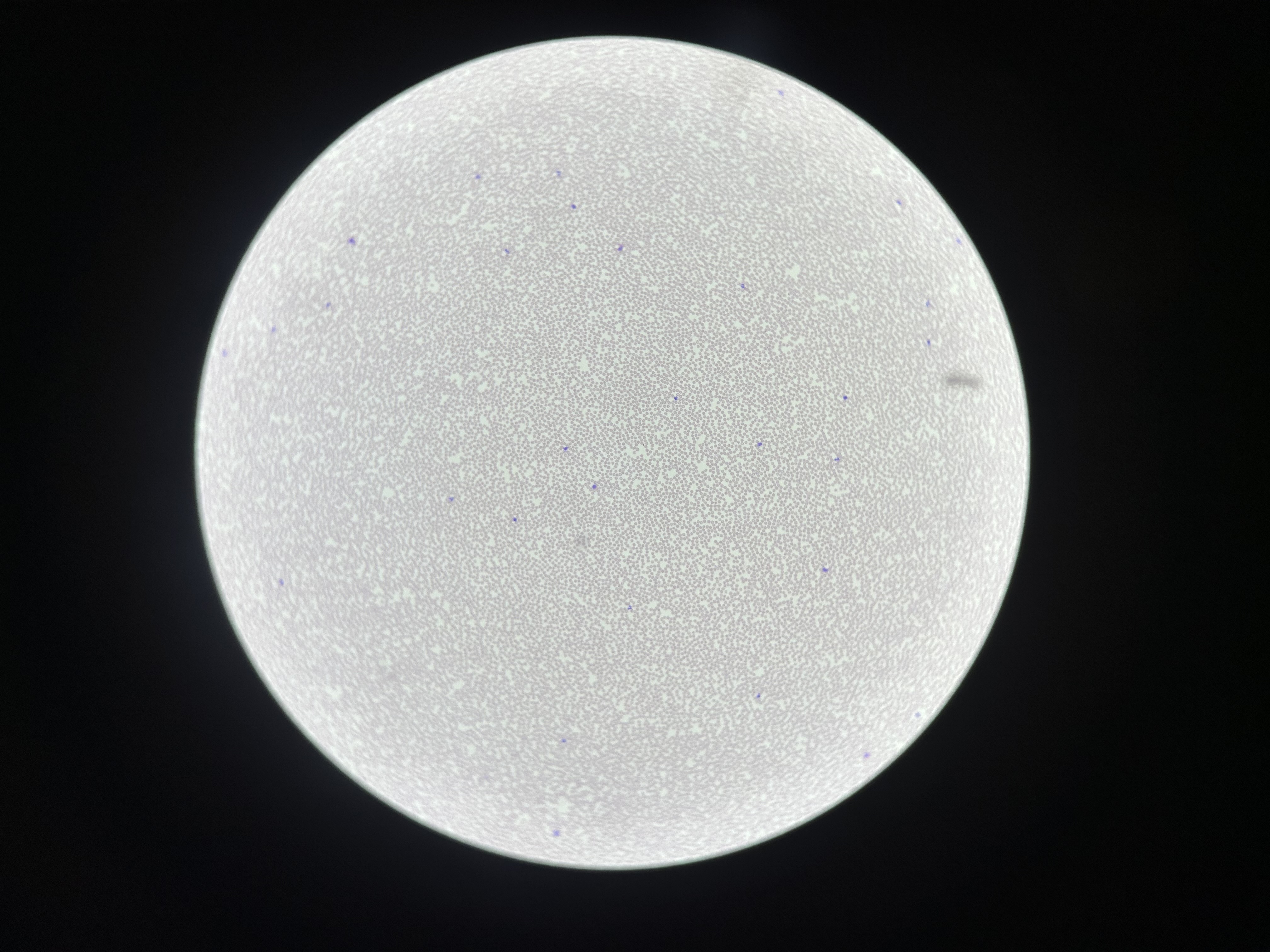

What is the magnification level of the Blood?
10x
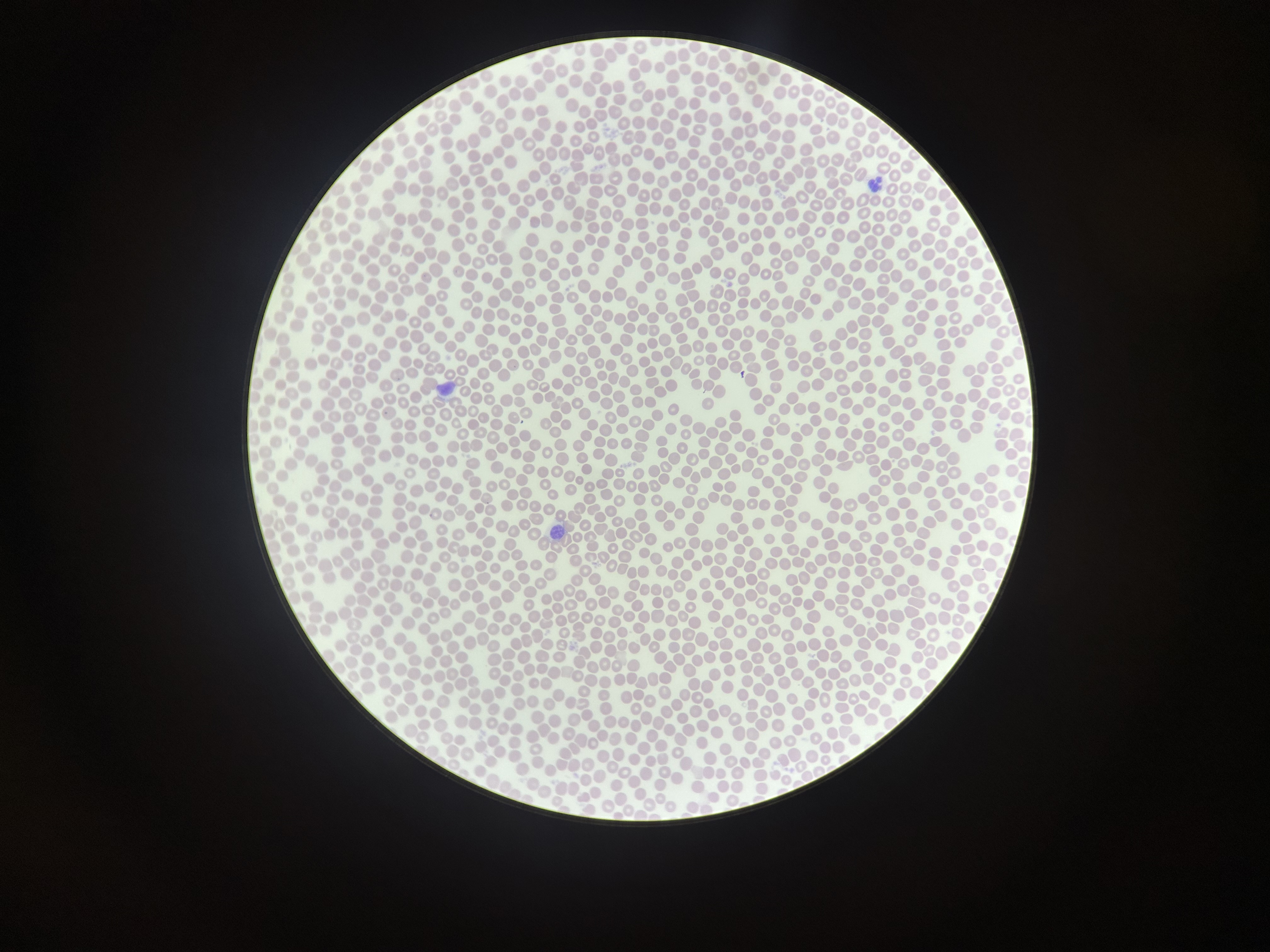
What is the magnification level of the Blood?
40x
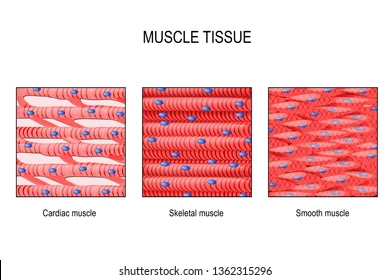
Muscle Tissue
located in skeletal muscles, in the walls of hollow organs, heart and iris of the eye. Consists of myocytes or muscle fibers and endomysium. Provides movement, pump blood, and produce a squeezing pressure in internal organs. Contractions are produced by the interaction of two
proteins: actin and myosin.
Myocytes
muscle cells/fibers are not shaped like epithelial cells or connective tissues because of the endomysium.
Endomysium
ECM in muscle tissue that is rich with collagen fibers that support the muscle fibers and blends with connective tissues.
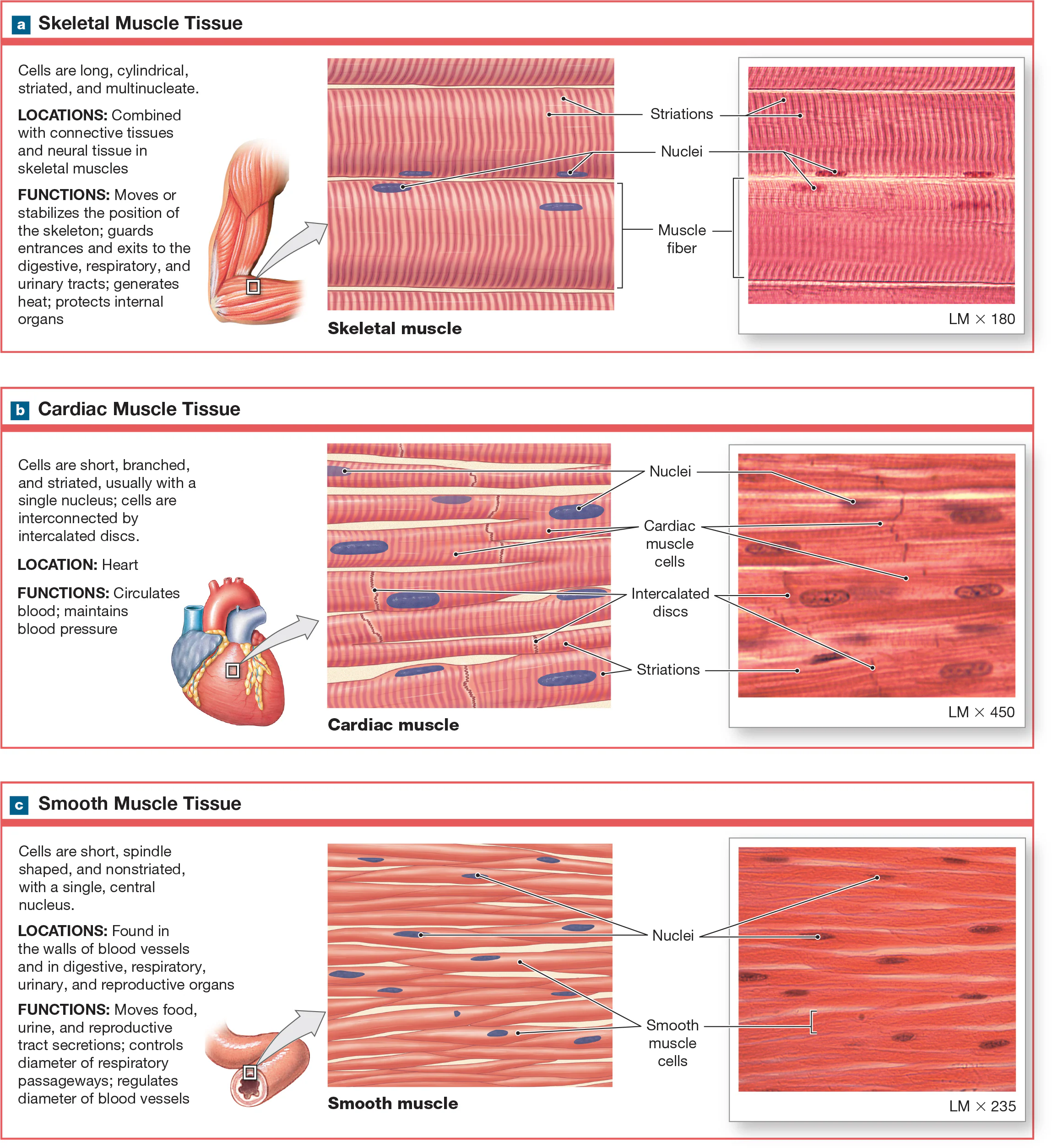
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
long, tubular, and striated. The striation results from myofilaments and myoblasts producing multiple nuclei. It is voluntary, causing it to have close relationships with the nervous system because skeletal muscle fibers must be stimulated by a nerve cell to contract. Cells don’t divide and new fibers are produced by divisions of myosatellite cells.
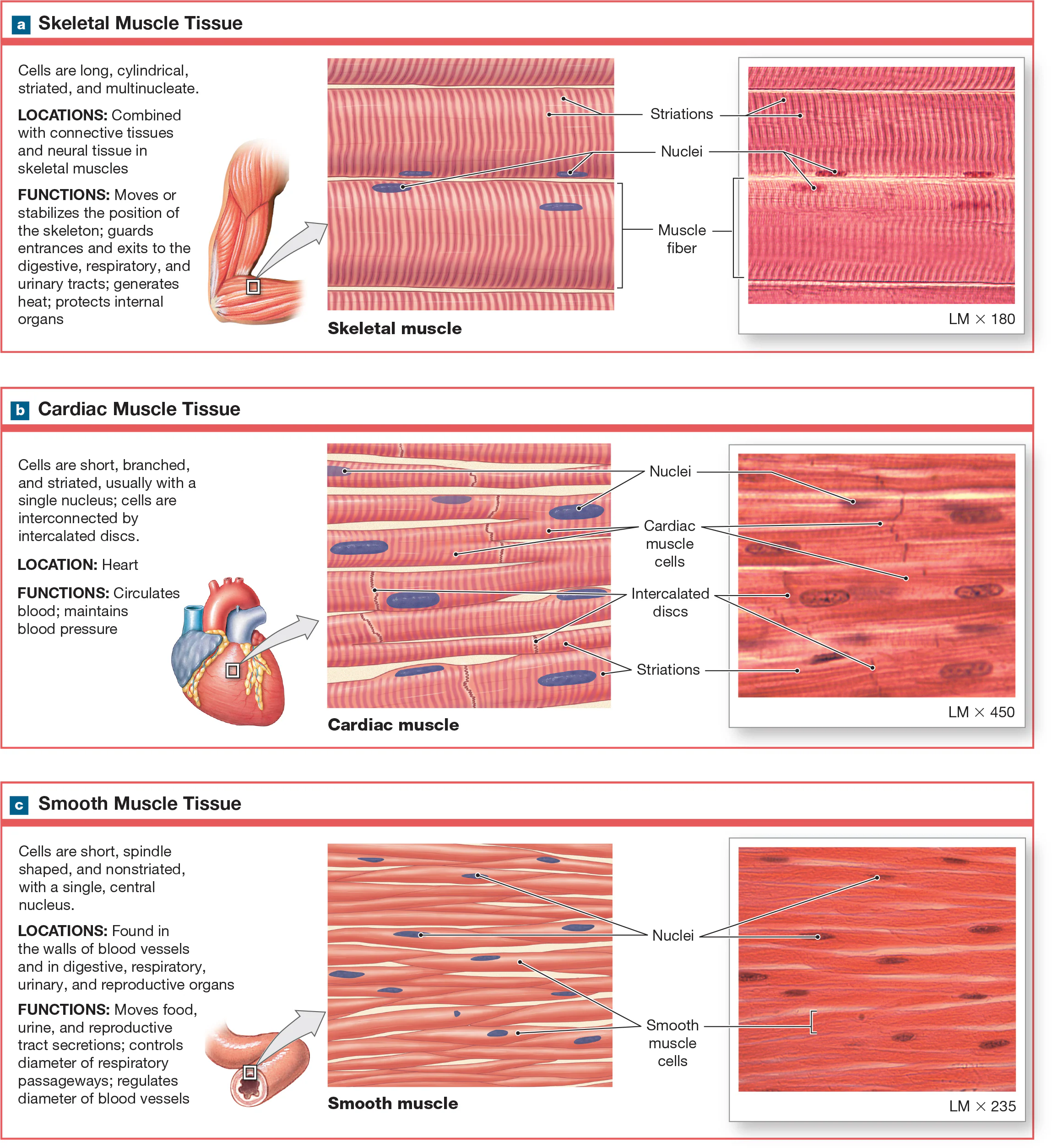
Stratied
striped appearance
Myofilaments
muscle fiber proteins
Myoblasts
skeletal muscle fibers cells
Voluntary
type of muscle tissue that is consciously controlled and can be contracted at will.
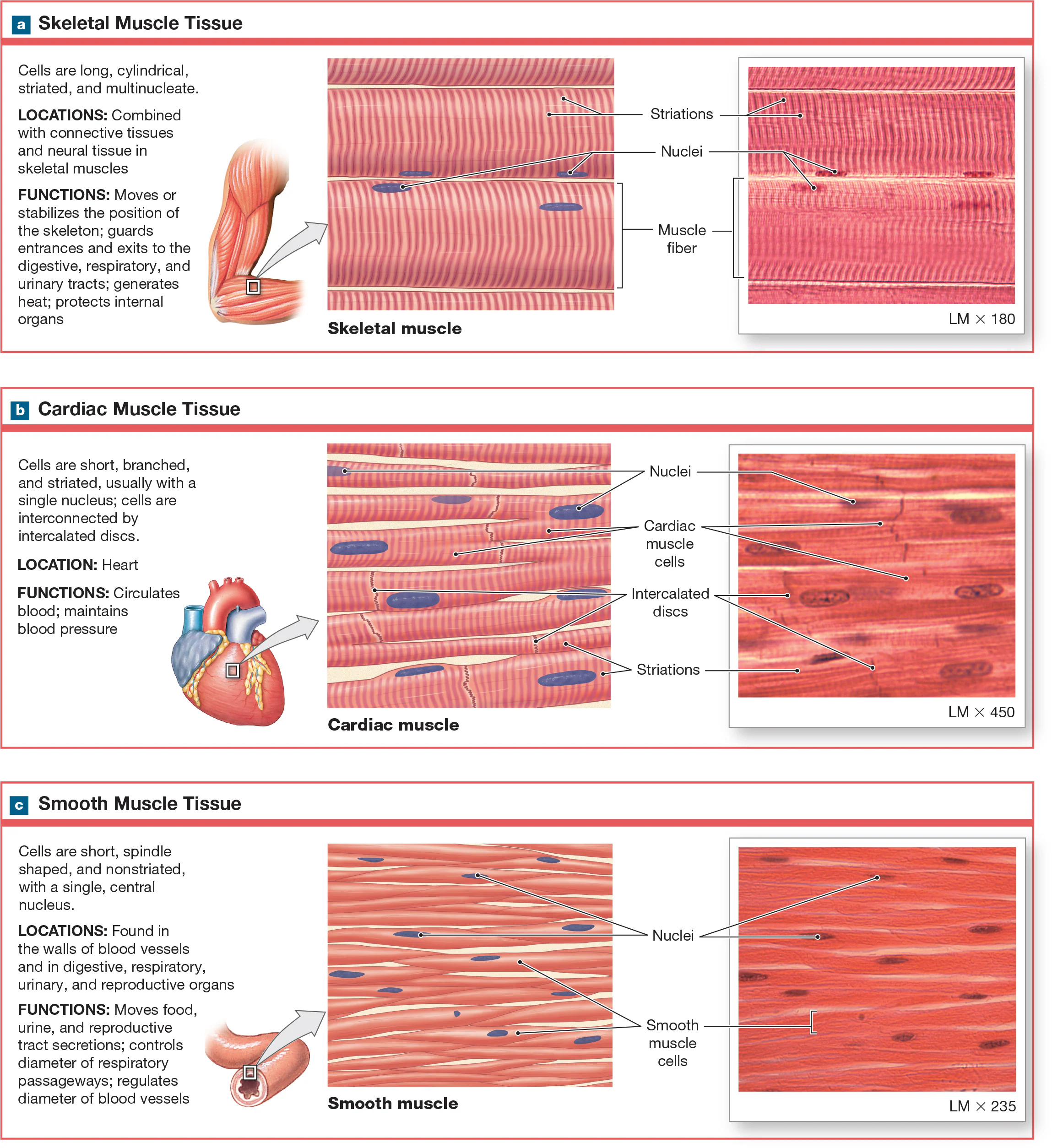
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Myocytes that are located in the heart are short, wide, striated, and tend to be branching. Have only one nucleus, sometimes more. Cells form branching networks connected at intercalated discs regulated by pacemaker cells. Involuntary
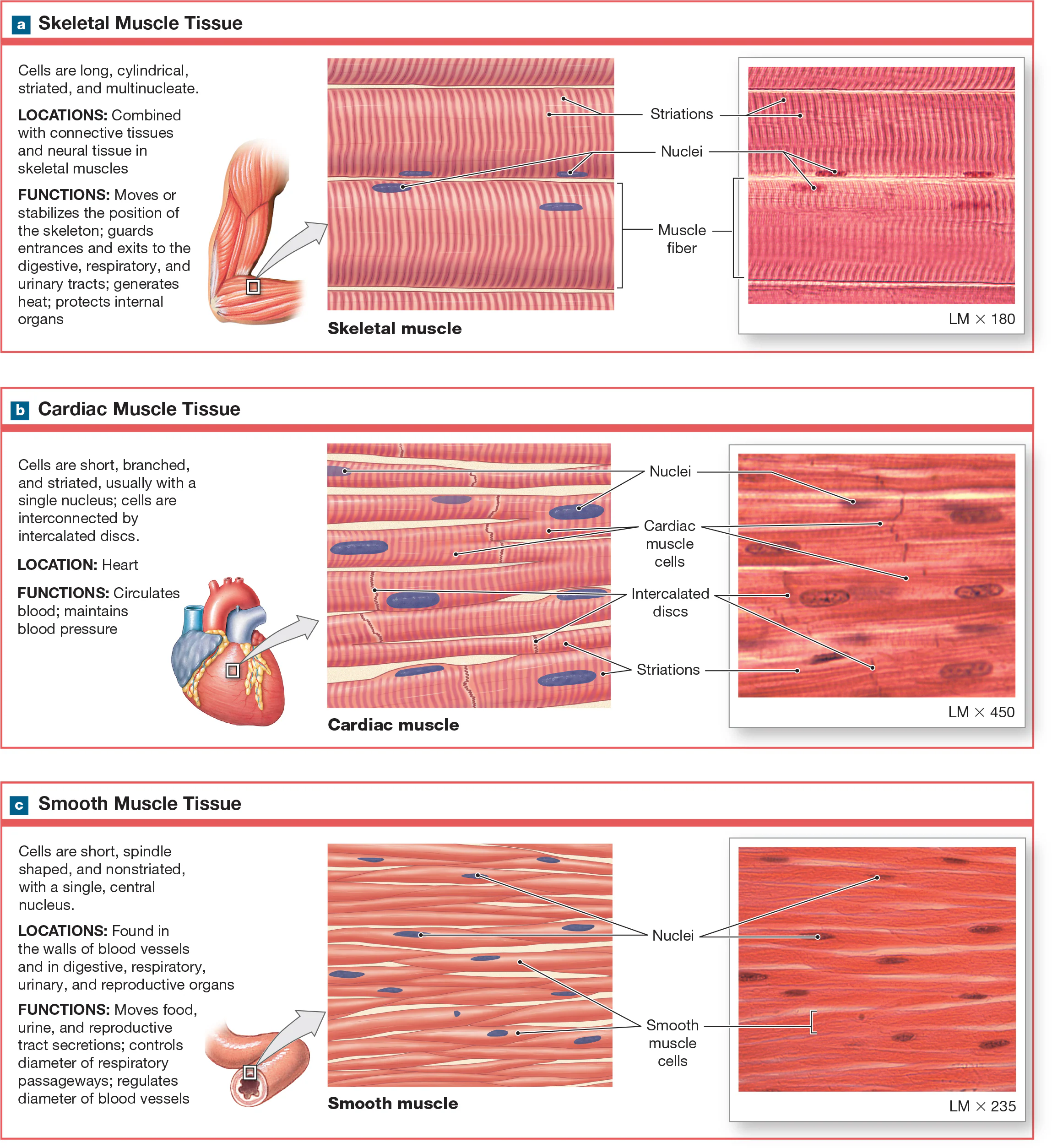
Intercalated Discs
adjacent cardiac myocytes that are linked physically and electrically by specialized junctions that contain desmosomes and gap junctions.
Involuntary/autorythmic
Requires no conscious control; they function automatically without voluntary input.
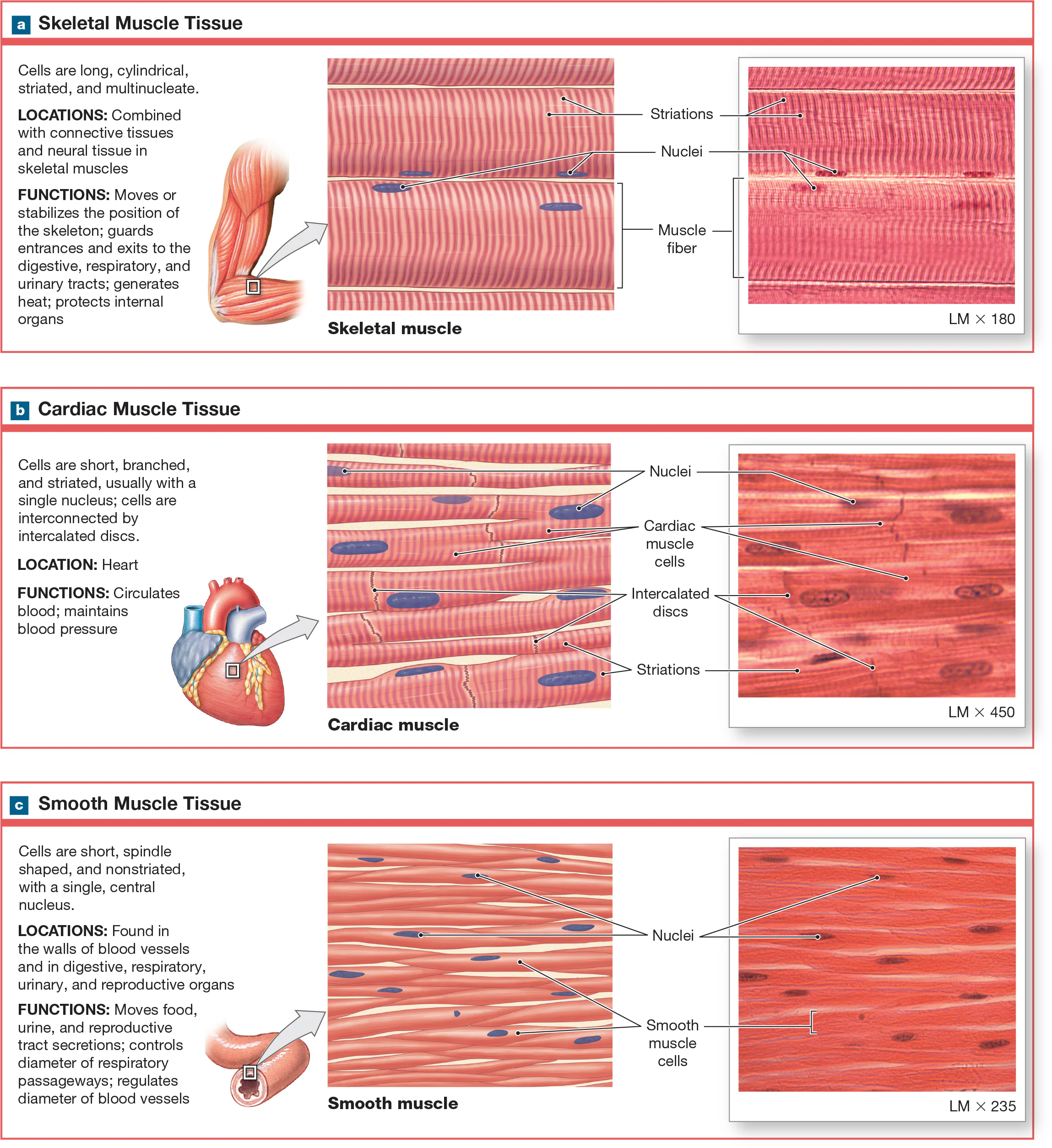
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Flat with a single nucleus in the center of the cell, and the arrangement of myofilaments differs from skeletal/cardiac muscle tissue, spindle-shaped, non-streaited, and they are involuntary, but some require stimulation. Found in the skin, eyes, and certain glands.
What is the magnification level of the Skeletal Muscle?
4x
What is the magnification level of the Skeletal Muscle?
10x
What is the magnification level of the Skeletal Muscle?
40x
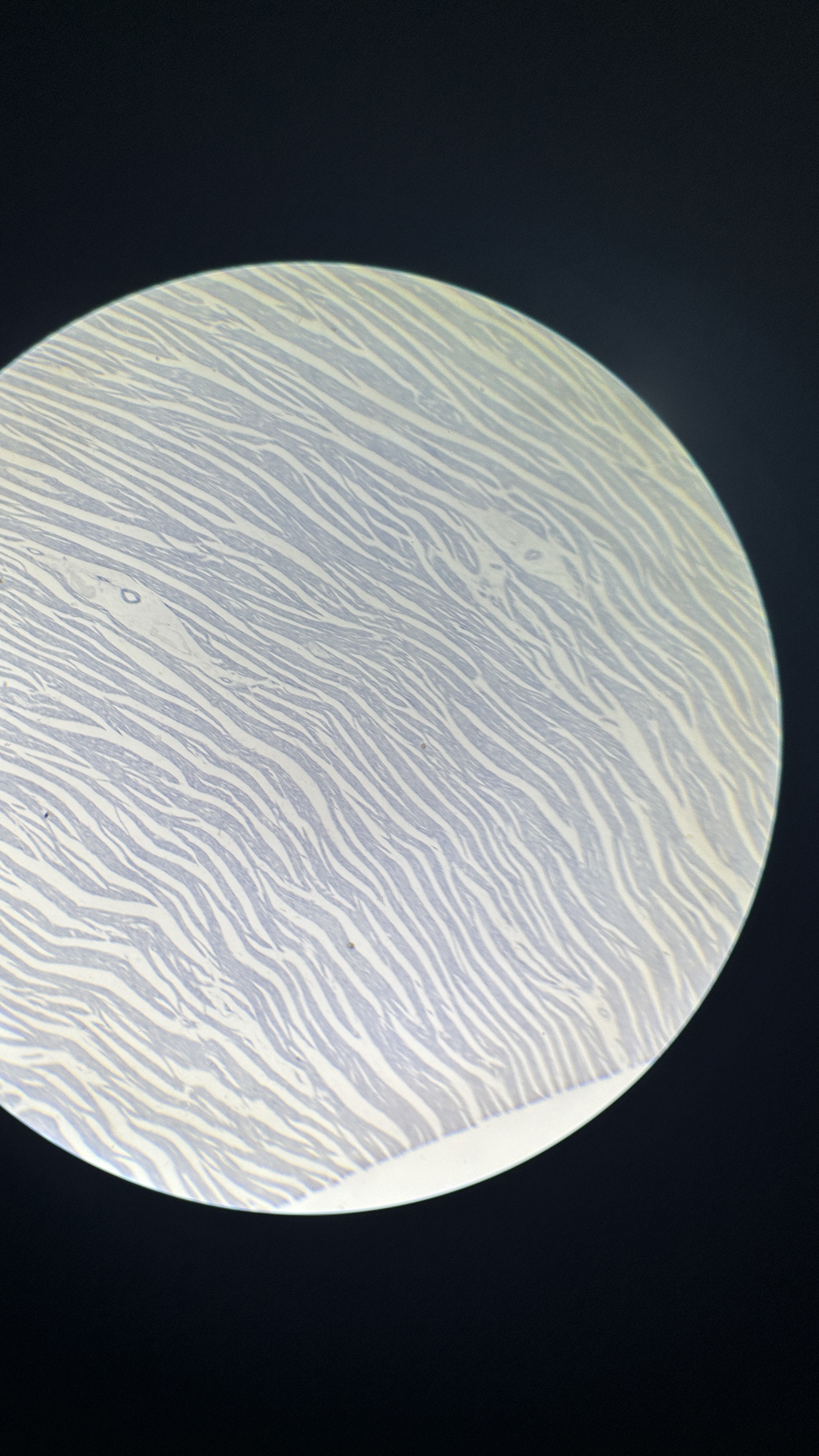
What is the magnification level of the Cardiac Muscle?
4x
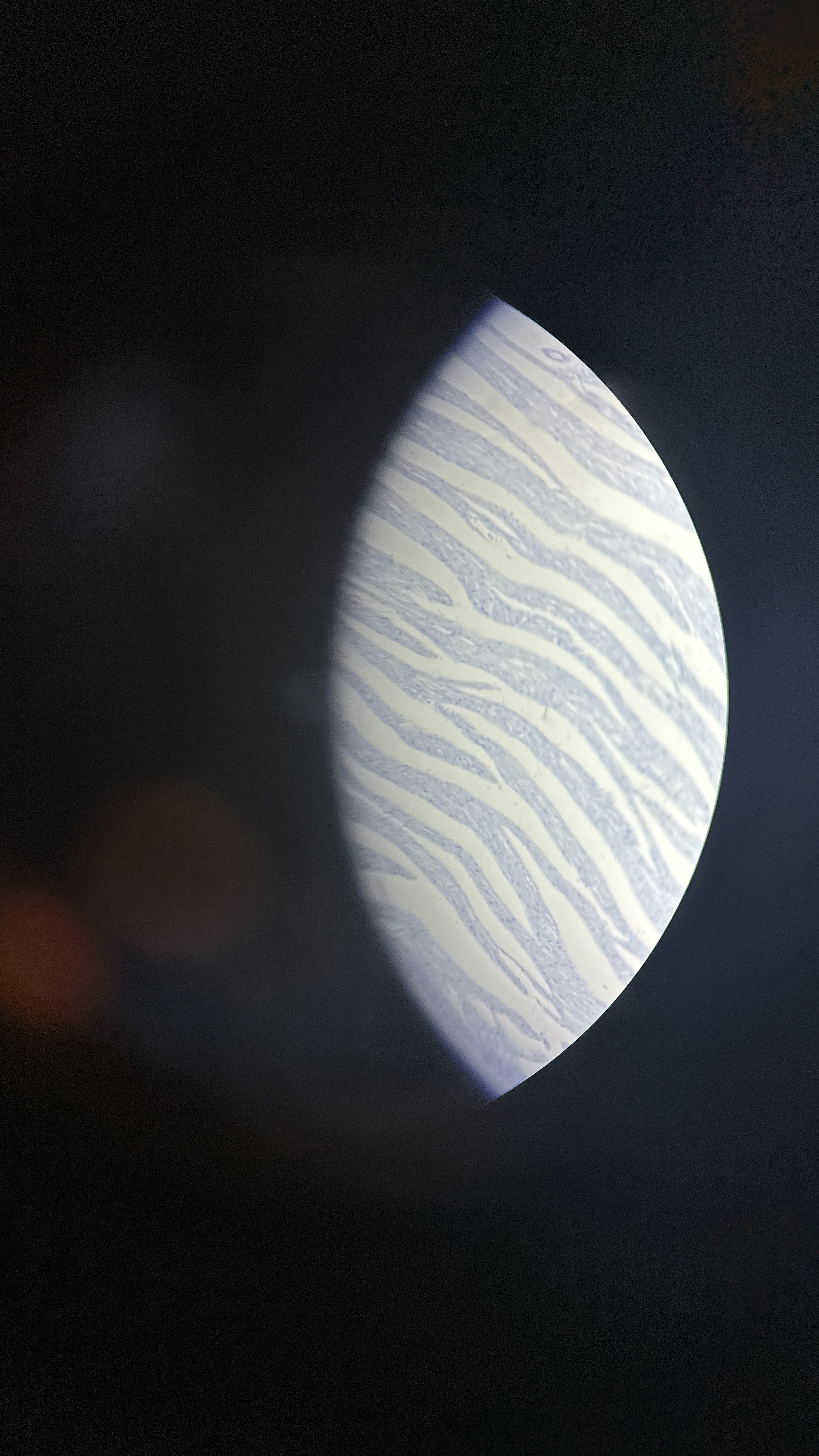
What is the magnification level of the Cardiac Muscle?
10x
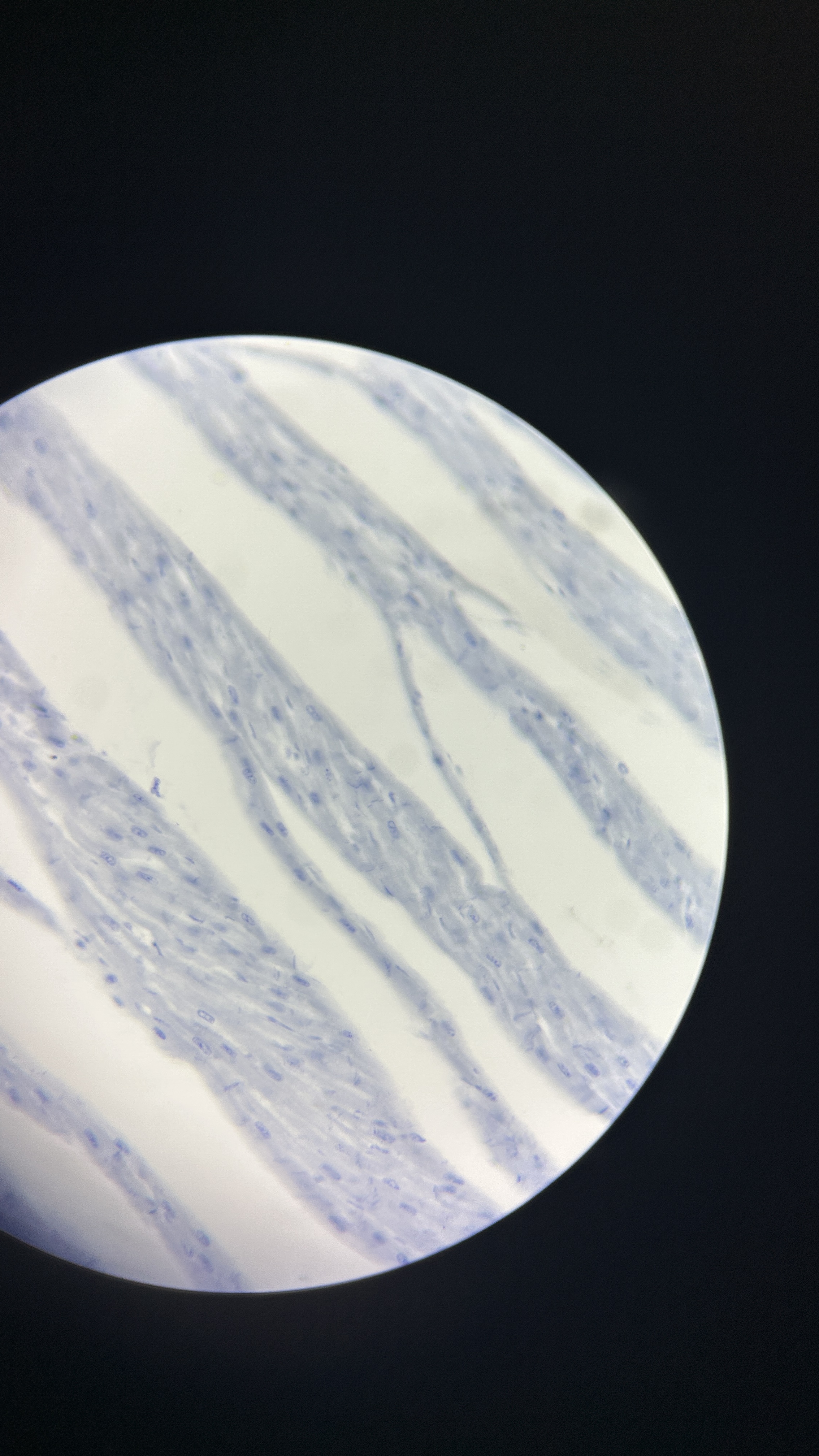
What is the magnification level of the Cardiac Muscle?
40x
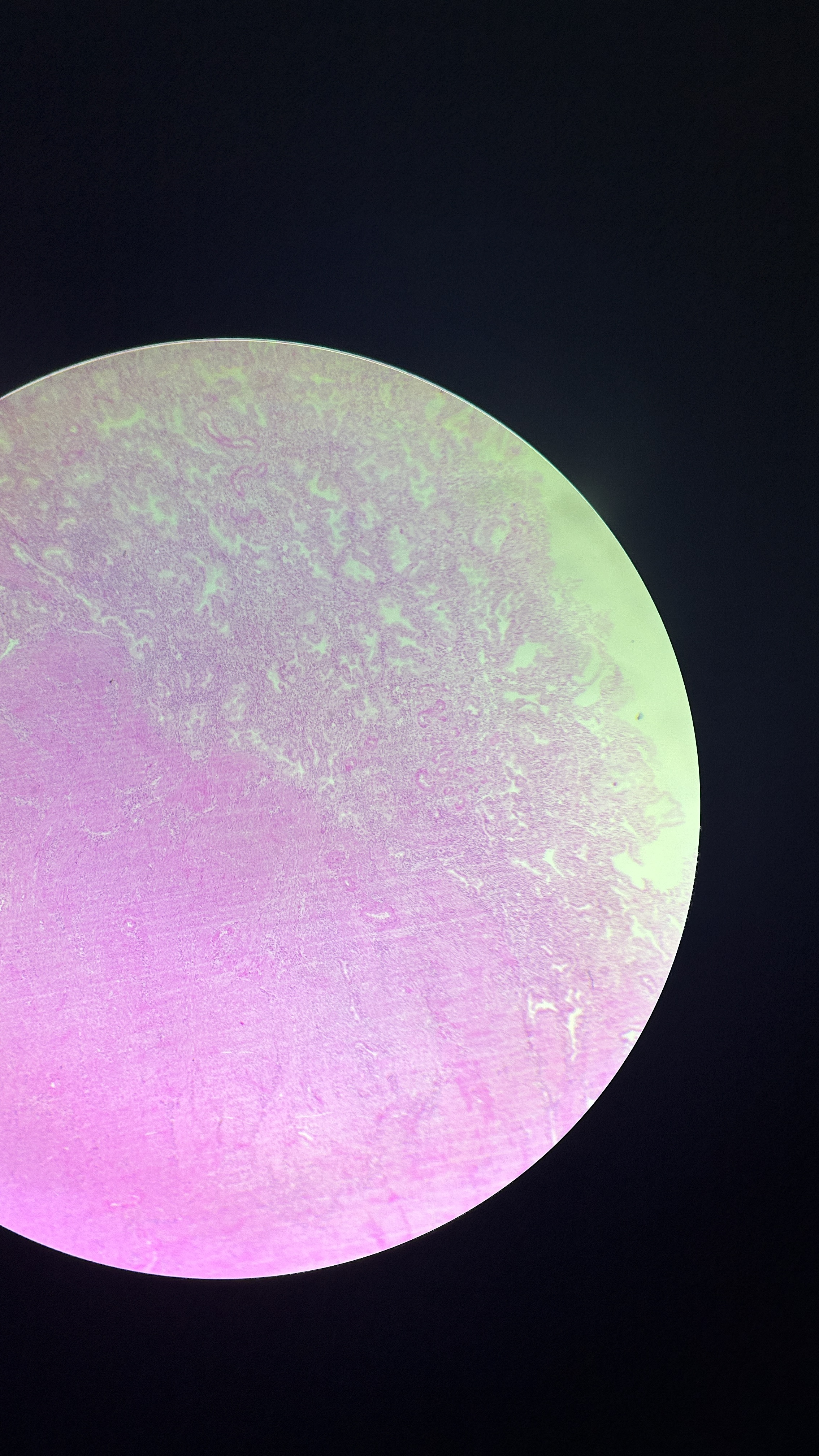
What is the magnification level of the Smooth Muscle?
4x
What is the magnification level of the Smooth Muscle?
10x
What is the magnification level of the Smooth Muscle?
40x
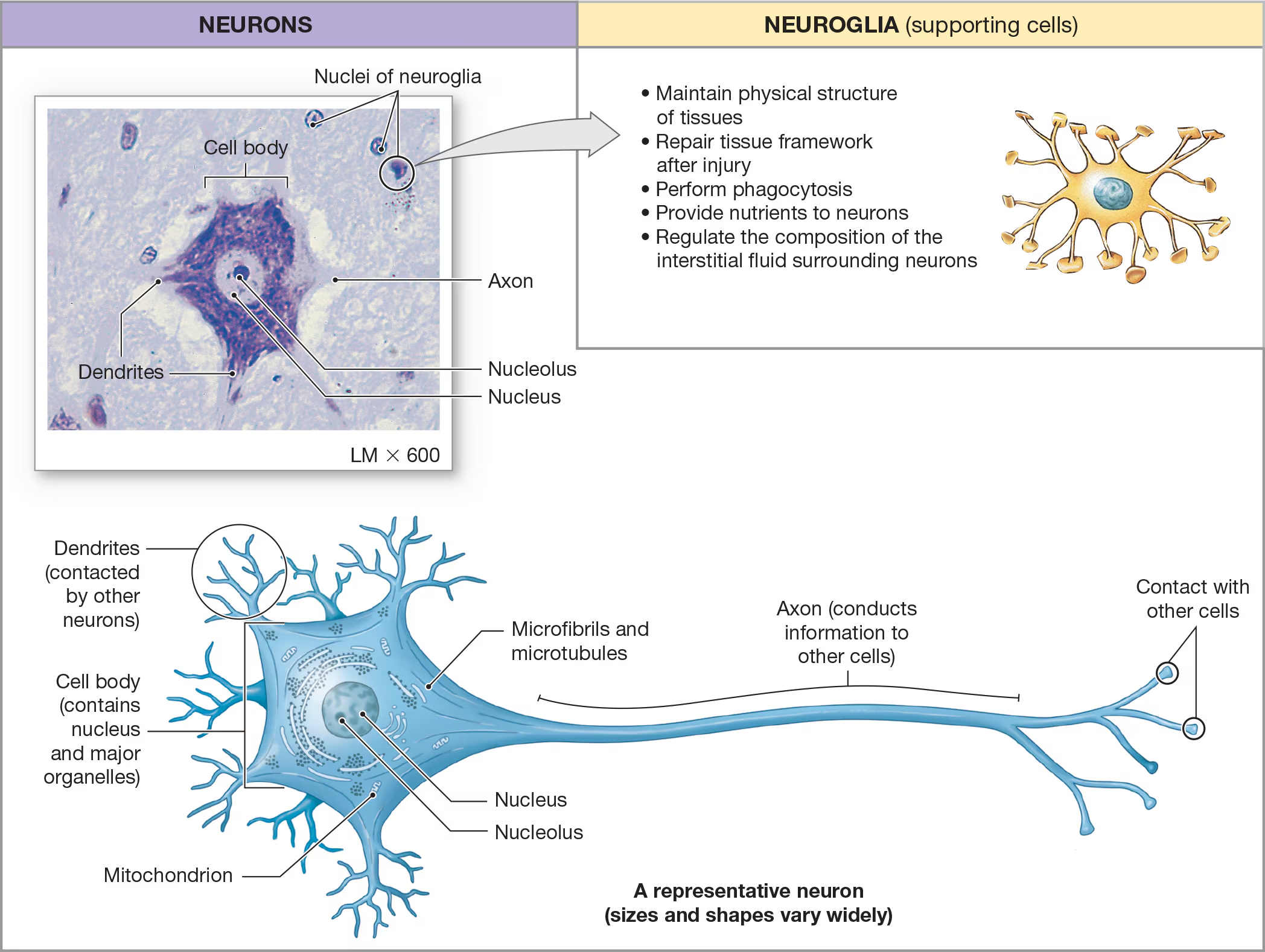
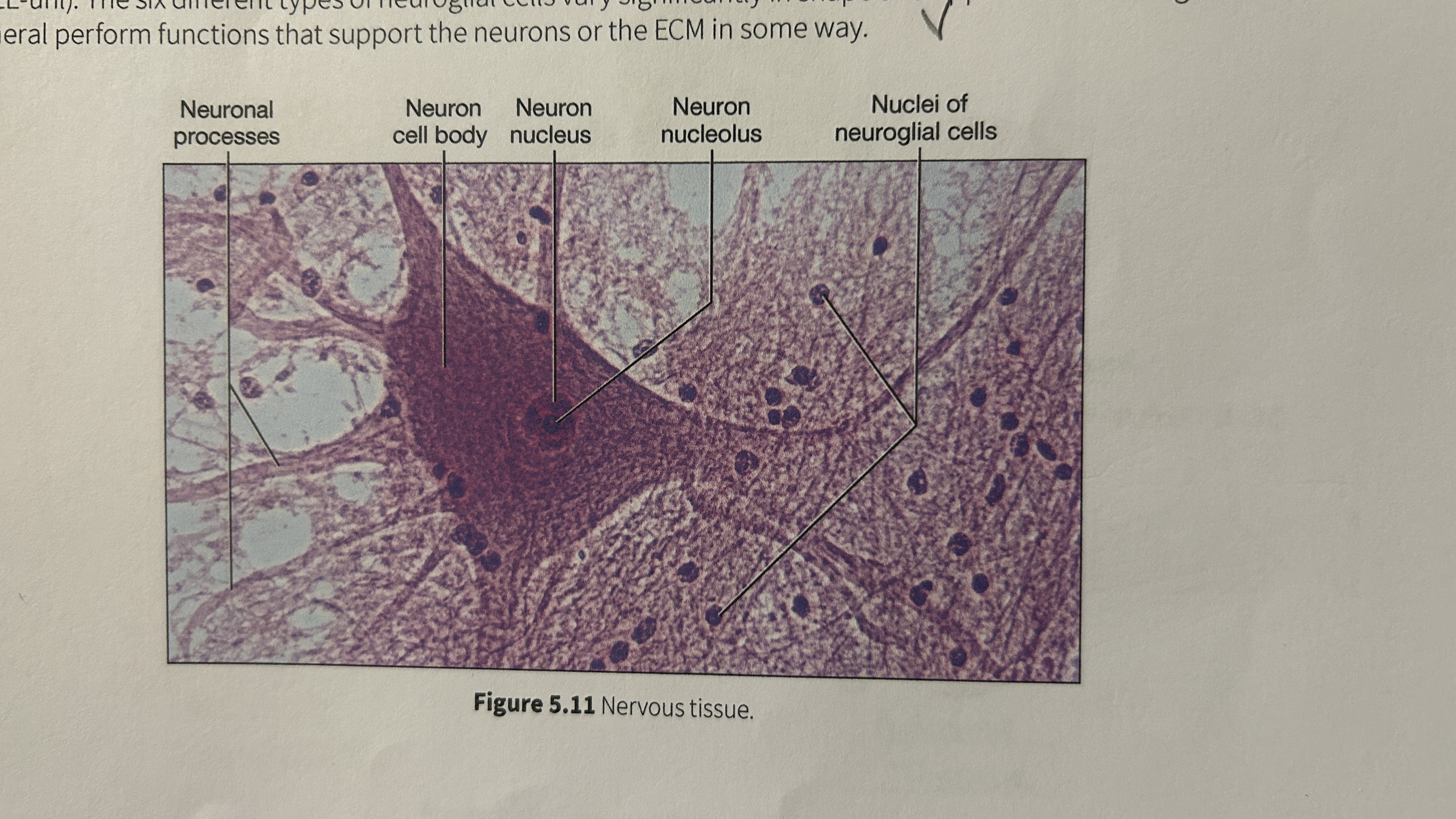
Neurons
responsible for sending and recieving messages within the nervous system.
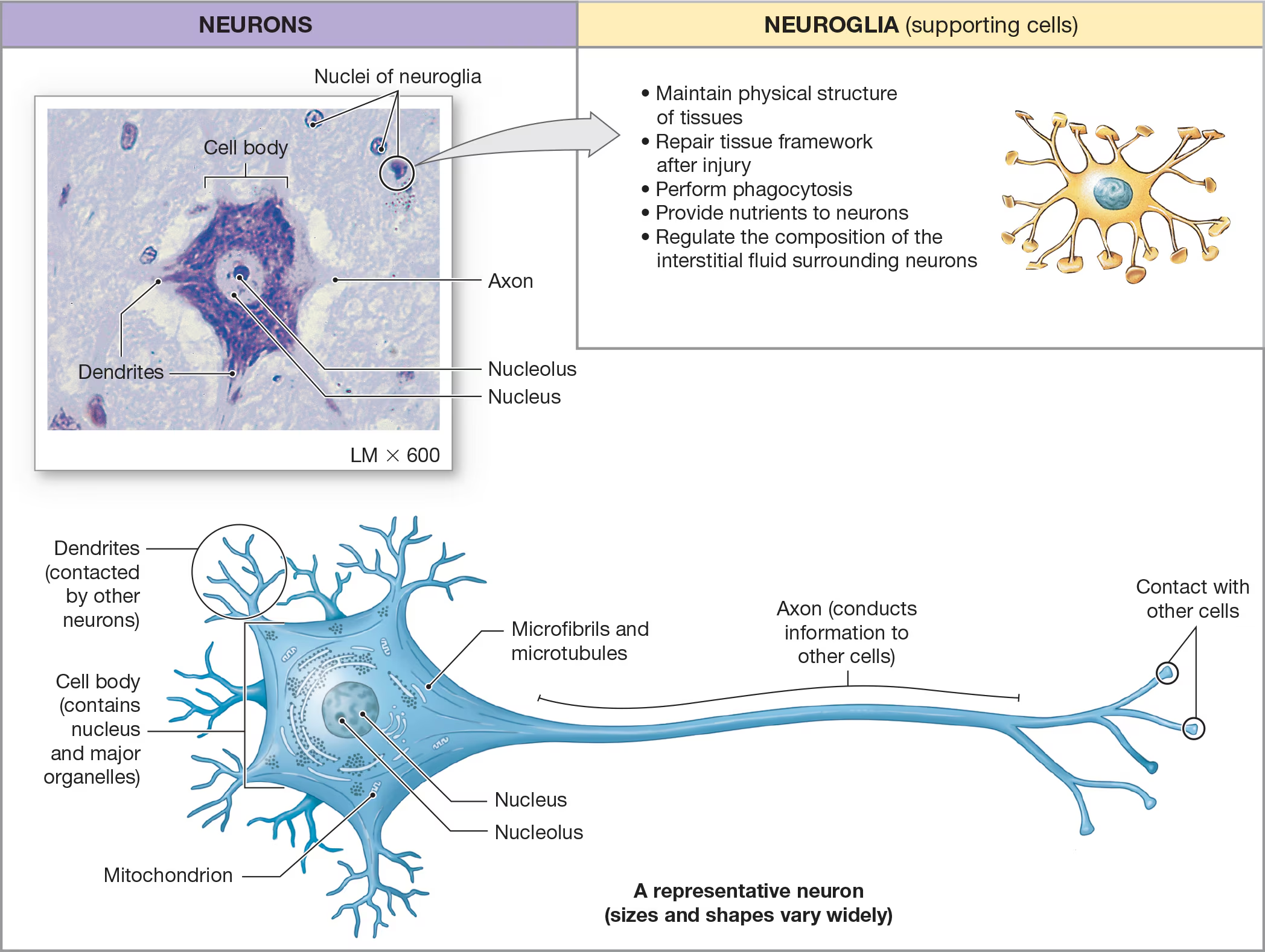
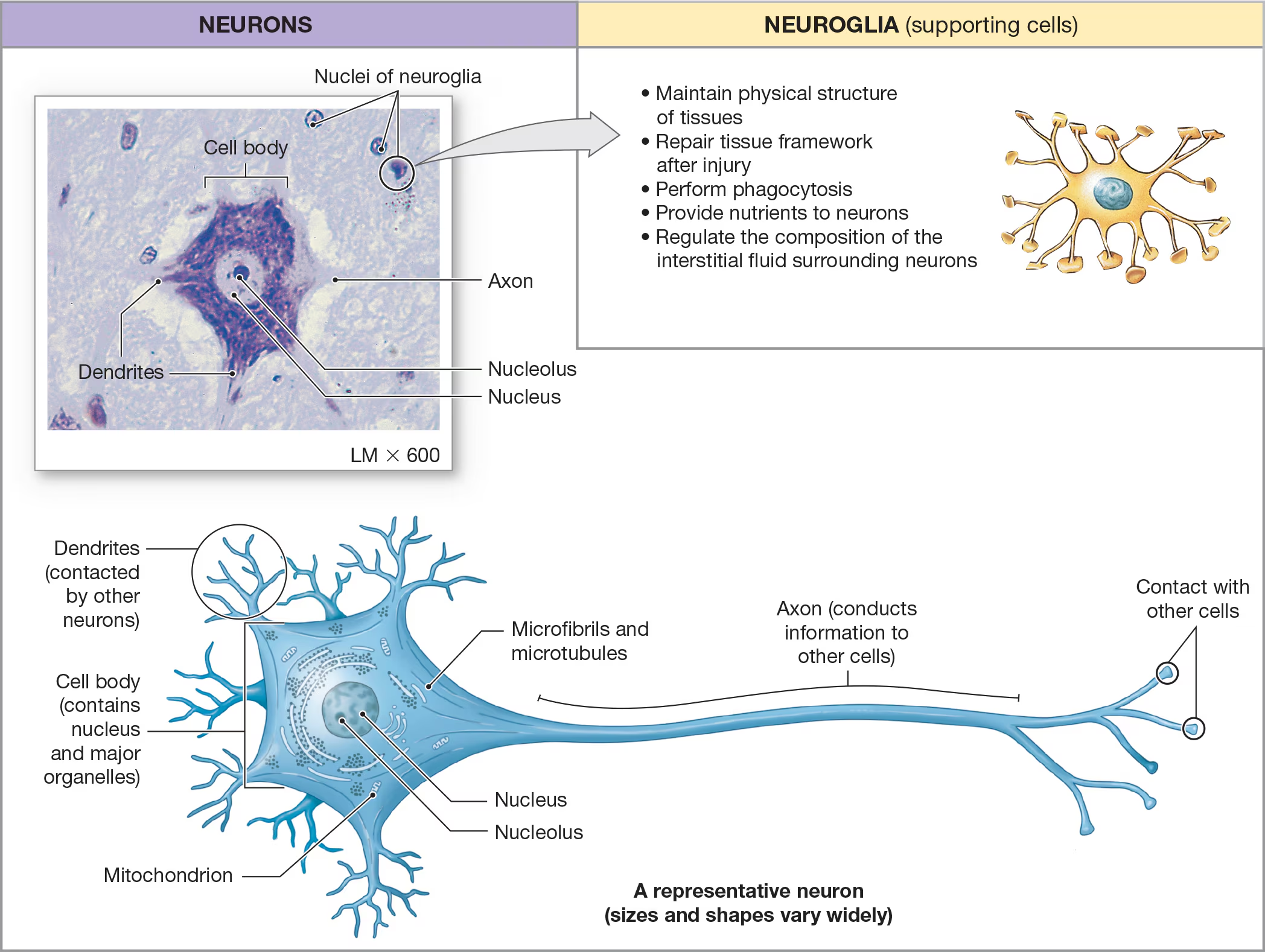
Cell body
The large, central portion of the neuron that contains the nucleus and nucleolus
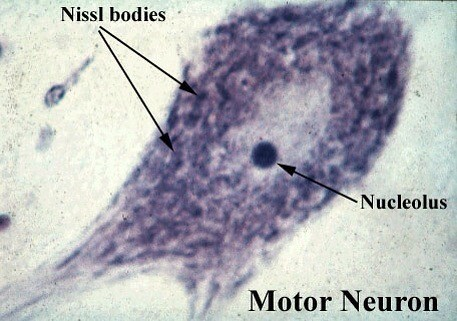
Nissl bodies
clusters of rough ER in the neuron’s organelles
What are the two types of arm-like processes extending from the cell body?
dendrites and axons
Dendrites
recieve messages from other neurons
Axons
sends messages to other neurons, muscle cells, or gland cells.
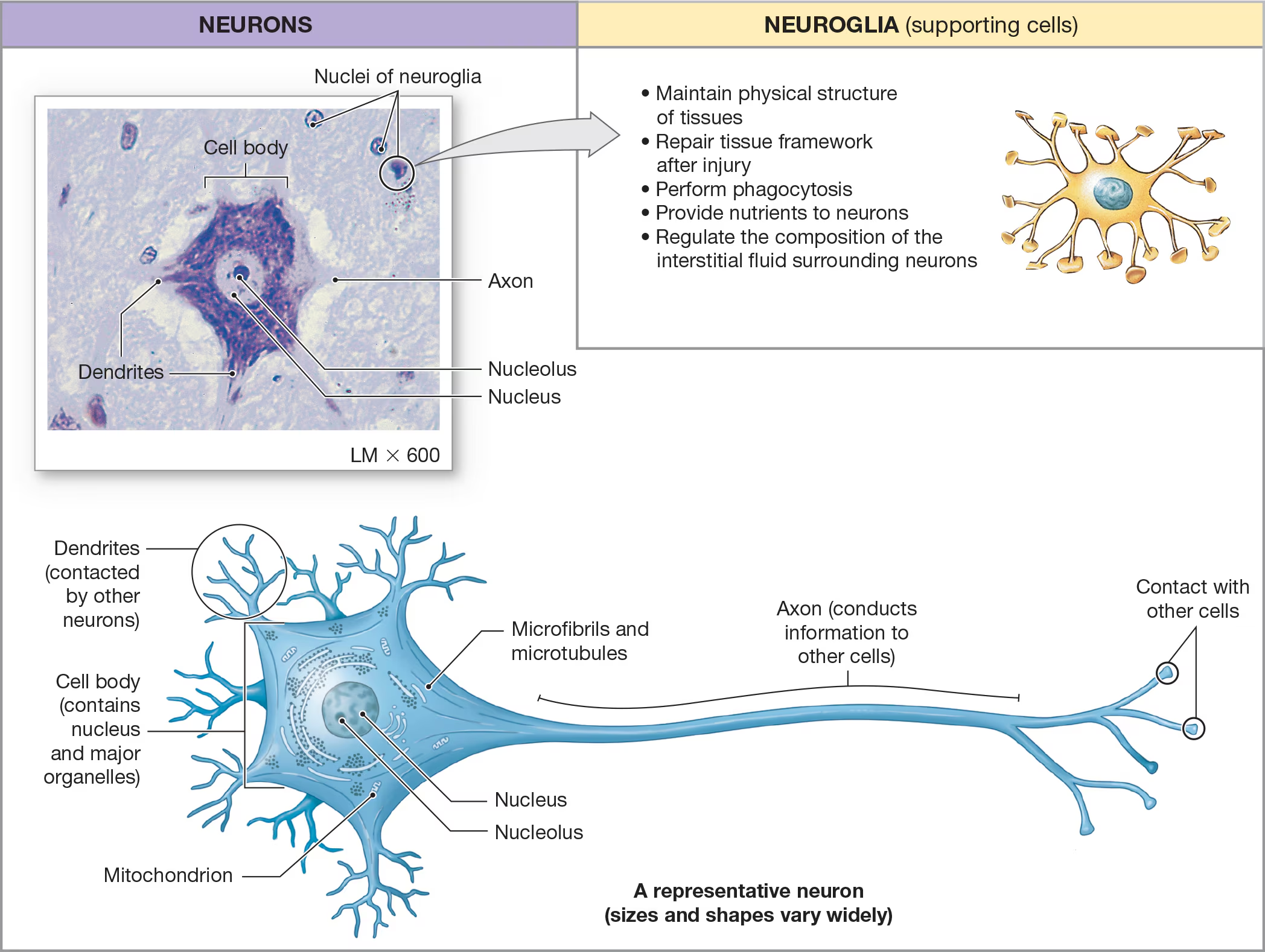
Neuroglial cells
The smaller and majority of cells around the neurons and contain6 different types of neuroglial cells that vary in shape/appearance and perform functions that support the neurons/ECM in some way.
Functions include:
• Maintain physical structure
of tissues
• Repair tissue framework
after injury
• Perform phagocytosis
• Provide nutrients to neurons
• Regulate the composition of the
interstitial fluid surrounding neurons
What is the magnification level of the Nervous Tissue?
4x
What is the magnification level of the Nervous Tissue?
10x
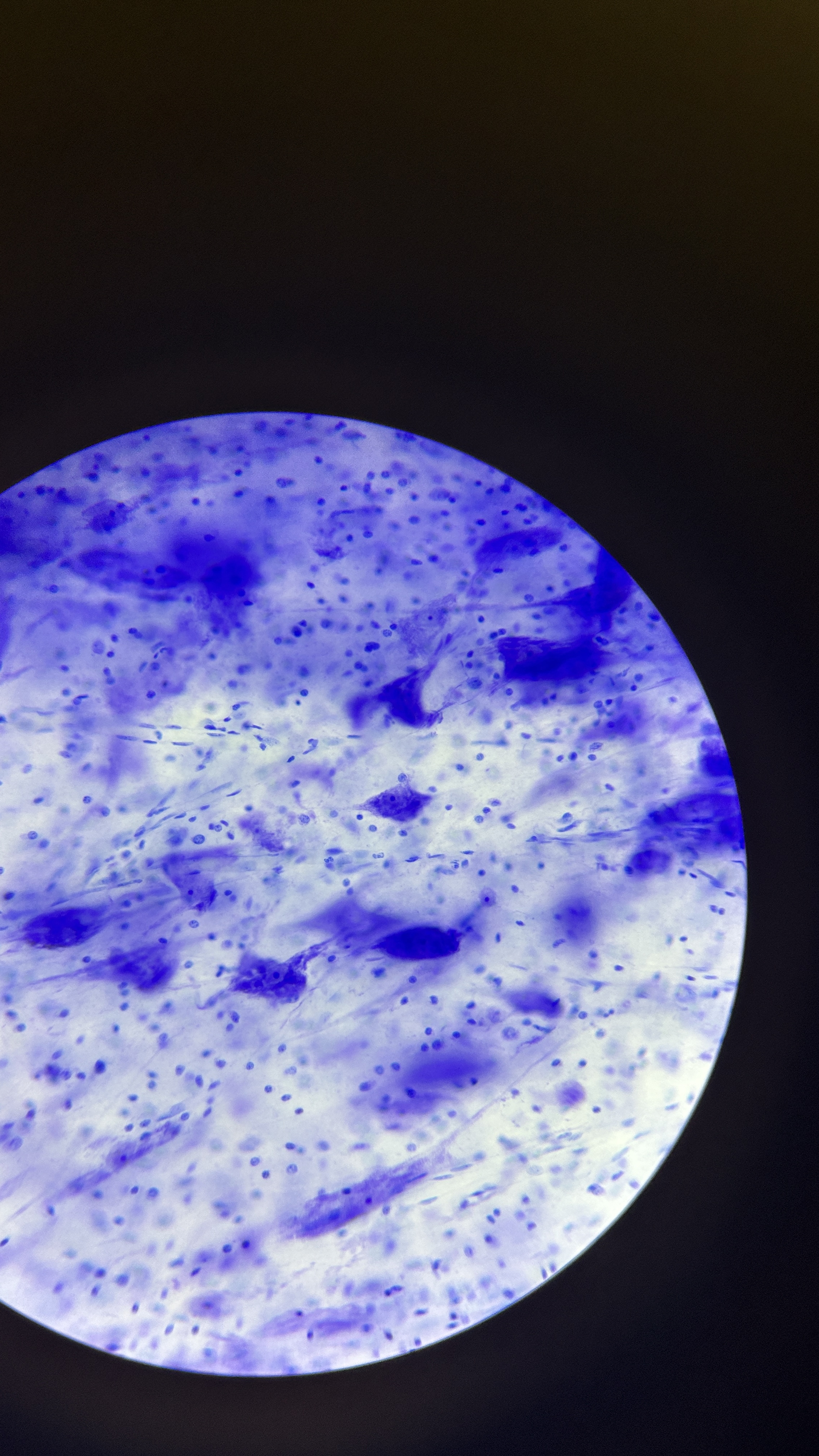
What is the magnification level of the Nervous Tissue?
40x
What 3 organs are found in the simple cuboidal epithelium?
Thyroid glands
kidneys
certain respiratory passageways
What 2 organs are found in the psuedostratified ciliated columnar epithelium?
Nasal Cavity
Larger respiratory passages
What organs are found in the Dense Elastic CT?
Large blood vessels
What organs are found in the stratified squamous keratinized epithelium?
Epidermis of the skin
What organs are found in the elastic cartilage?
Epiglottis and ear
What 4 organs are found in the smooth muscle tissue?
Skin
eyes
surrounding glands
lining of hollow organs
What 3 organs are found in the Dense irregular CT?
joints
organ capsules
the dermis of the skin
What organs are found in the fibrocartilage?
Articular discs and interverbral discs