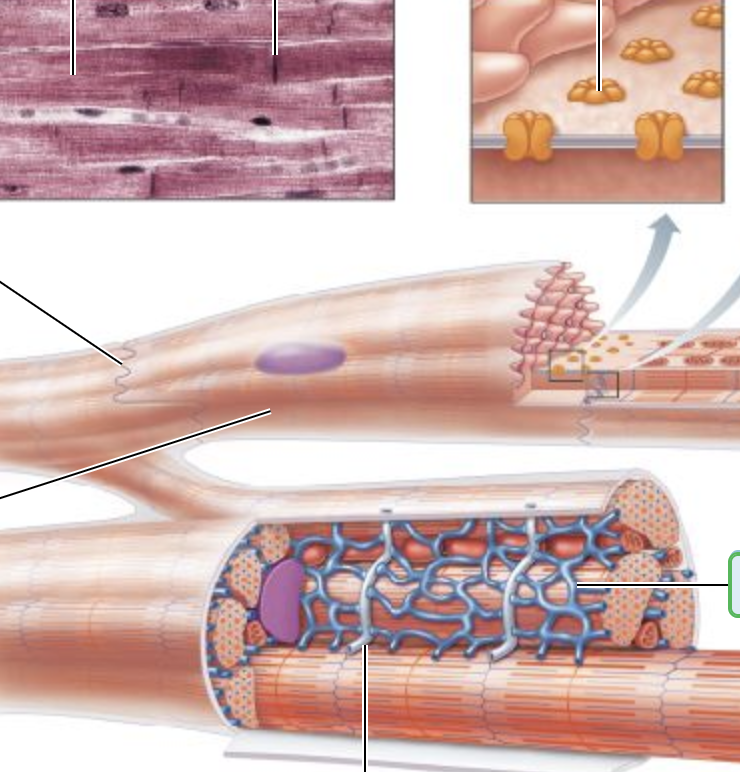
(18.4) Cardiac Muscle Fibers
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What cells are present in the cardiac muscle fibers?
Cardiac muscle cells
List two kinds of myocytes of the heart
Contractile cells → responsible for contraction
Pacemaker cells → non-contractile cells that spontaneously depolarize
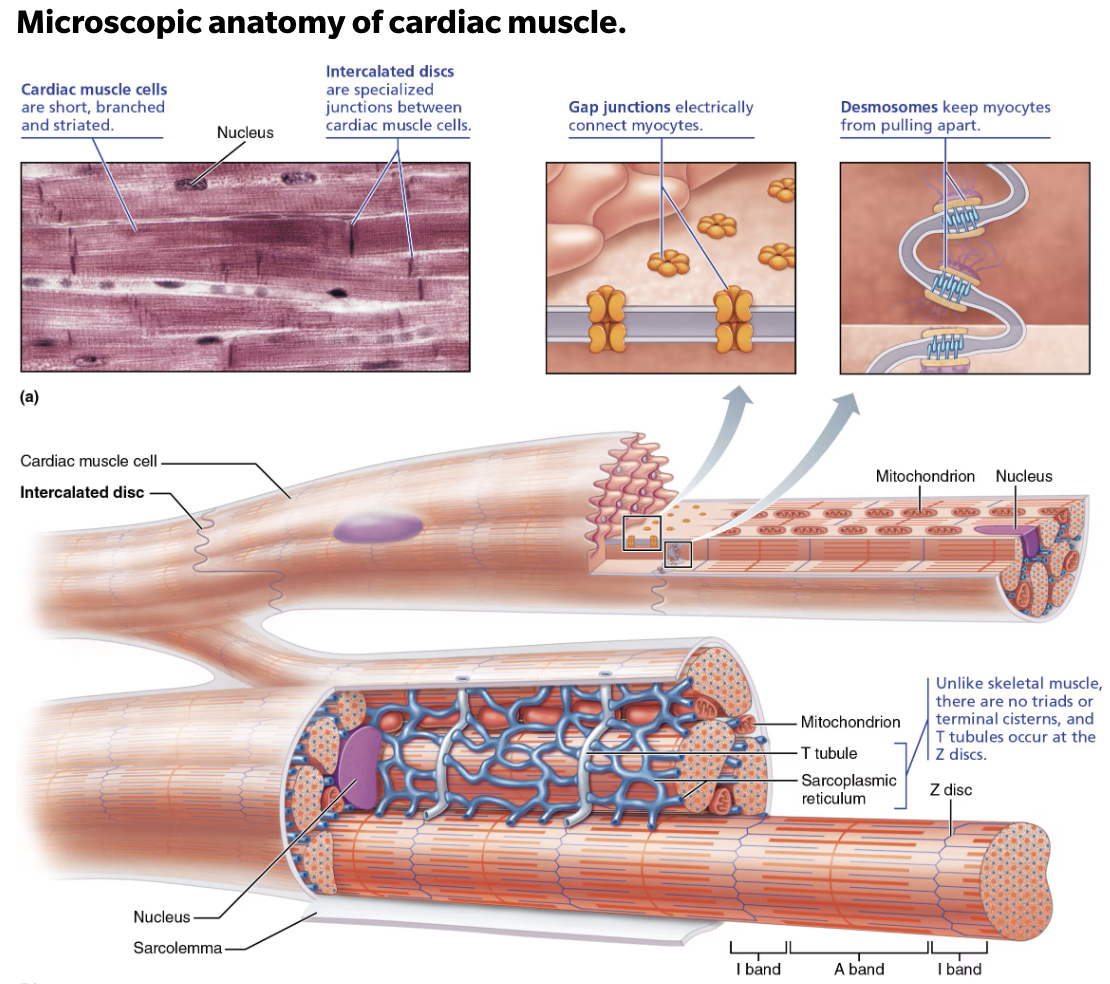
Explain Structure and Function of Cardiac Muscle Cells
Striated, Short, Branched, Fat, Interconnected
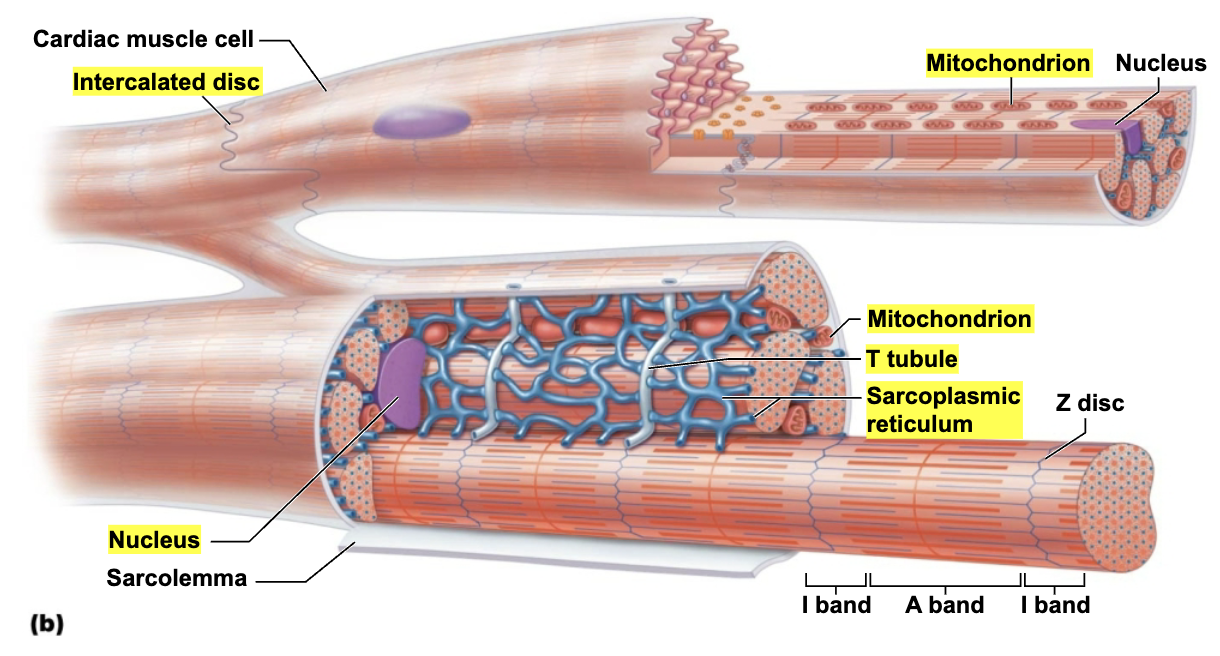
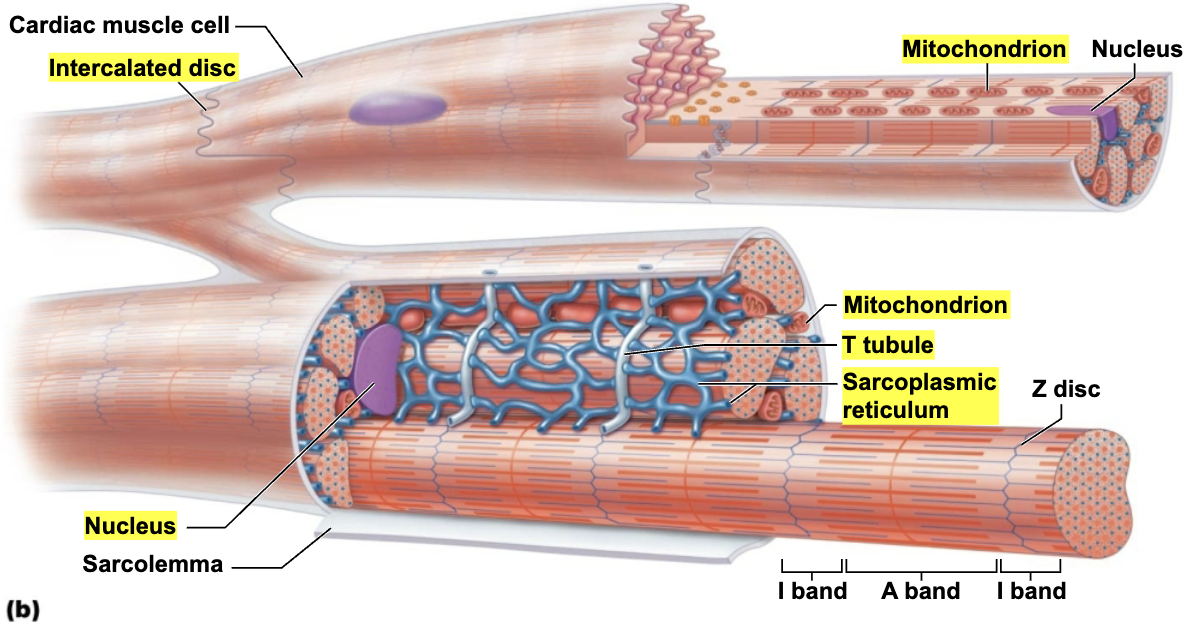
Contain numerous large mitochondria (25-35% of cell volume)
That afford resistance to fatigue
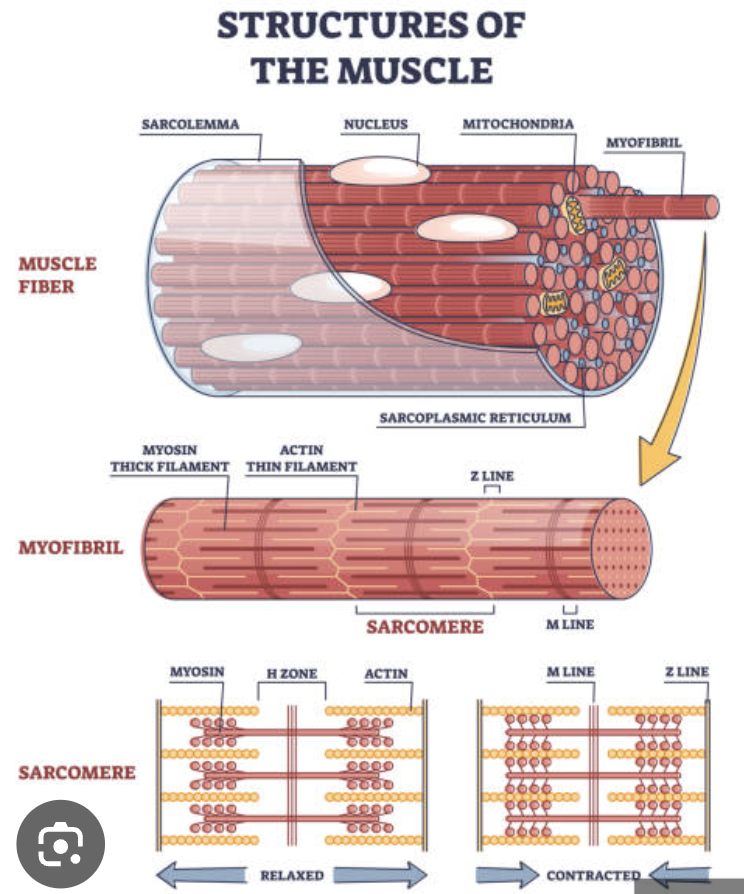
Rest of volume composed of sarcomeres
Z discs
A bands
I bands
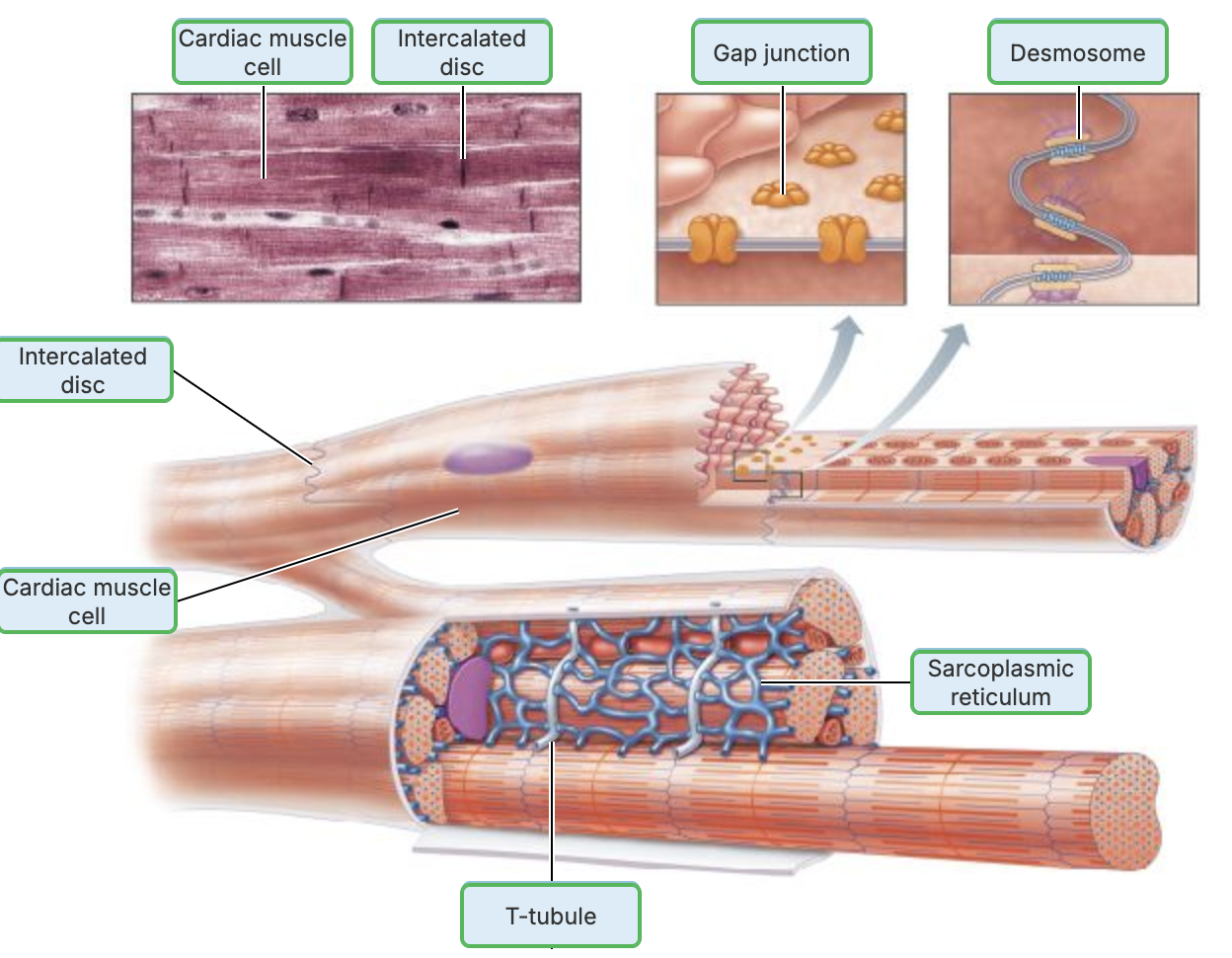
T tubules are wider, but less numerous
Enter cell only once at Z disc
SR simpler than in skeletal muscle → no triads
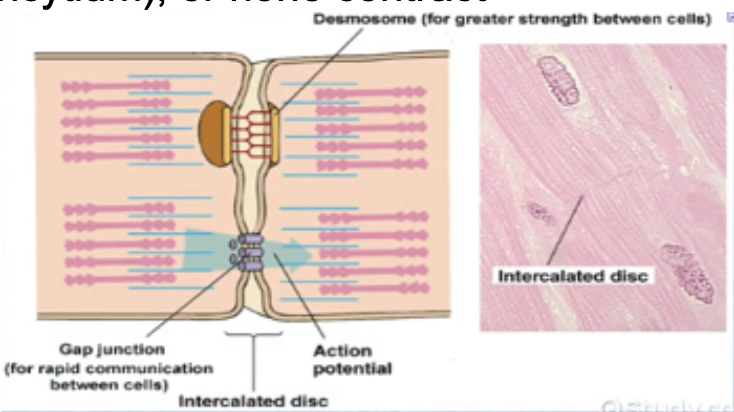
Intercalated discs are connecting junction between cardiac cells
Role of Intercalated Discs
Connecting junctions between cardiac cells that contain:
Gap junctions
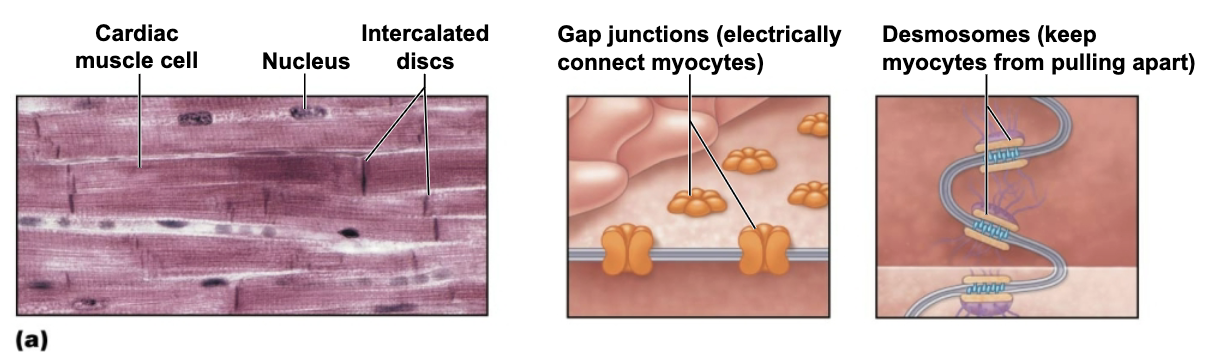
Role of Gap Junctions
Allows heart to be functional syncytium → a single coordinated unit
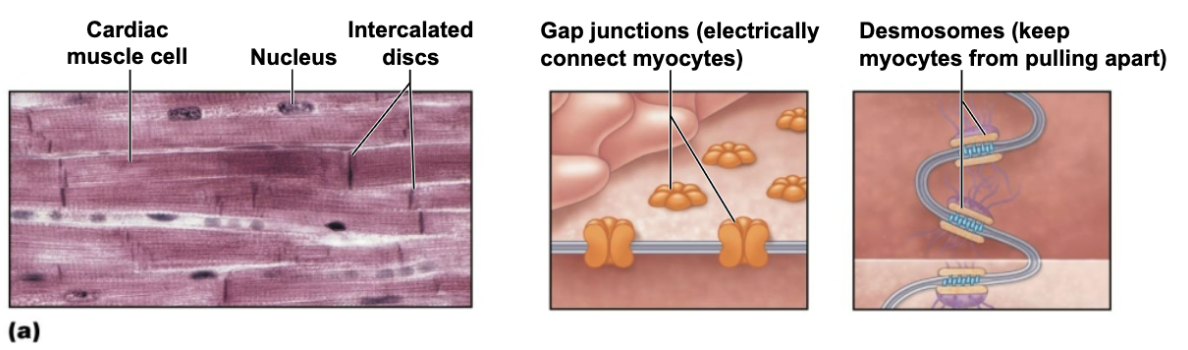
Explain Functional Syncytium
A group of cells that behaves as a single coordinated unit
EX: cardiac muscle cells that contract together because they are electrically coupled by gap junctions
Structure and Function of Endomysium
Intercellular space between cells has connective tissue matrix → Endomysium
STRUCTURE
Contains numerous capillaries
FUNCTION
Connects cardiac muscle to cardiac skeleton, giving cells something to pull against
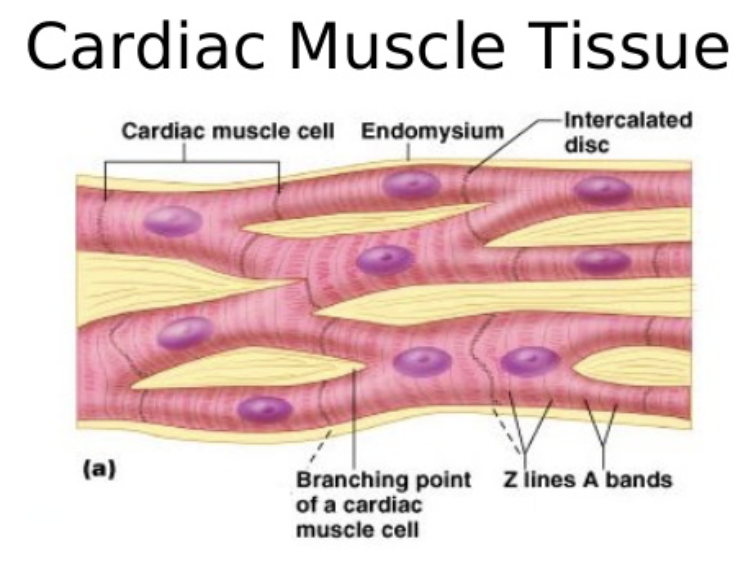
Describe cardiac tissue characteristics
Striated
Short
Branched
Fat
Interconnected
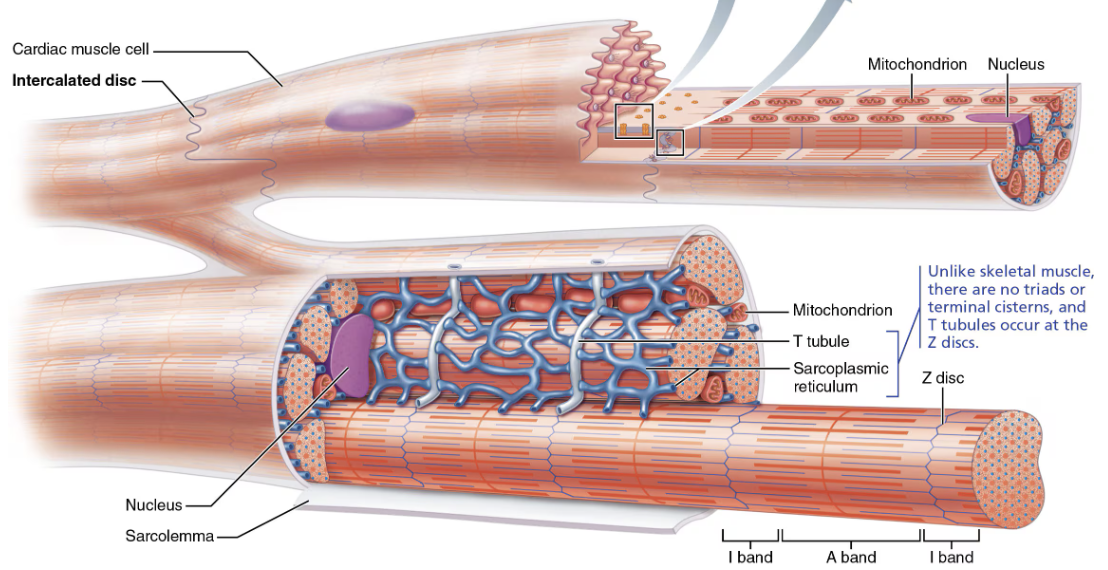
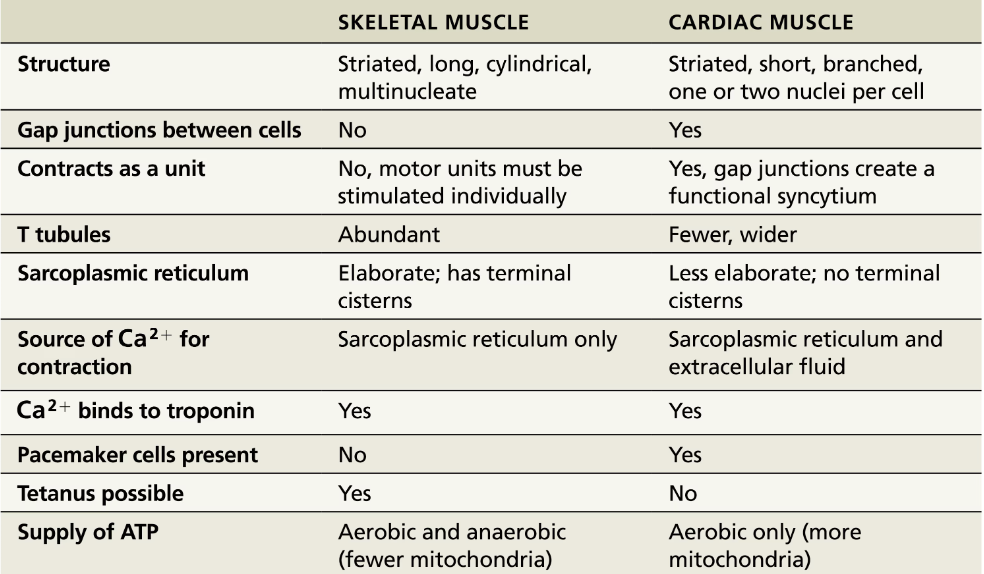
Similarity or Difference in Cardiac vs Skeletal Muscle: Structure ?
CARDIAC MUSCLE
Striated
Short
Branched
One or two nuceli per cell
SKELETAL MUSCLE
Striated
Long
Cylindrical
Multinucleate
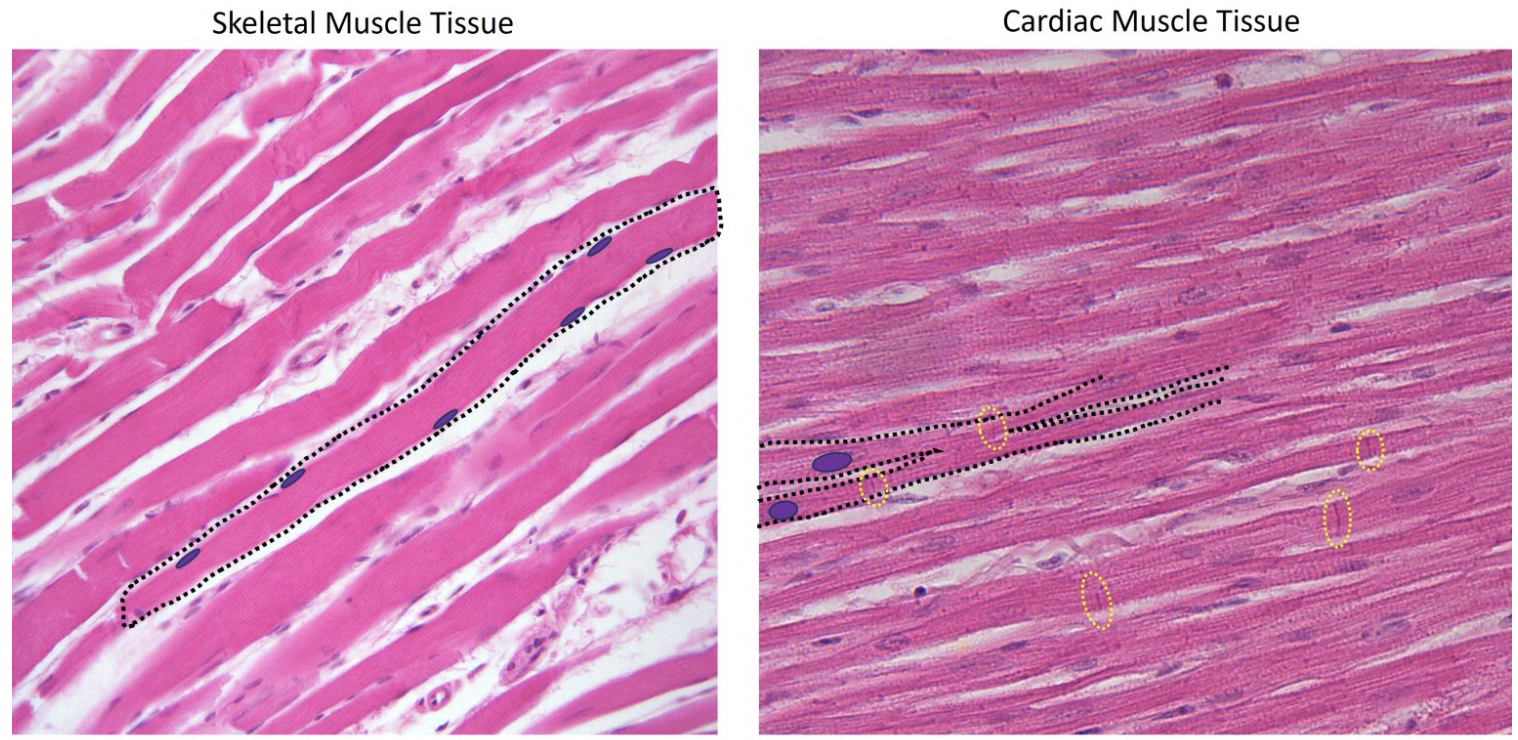
Similarity or Difference in Cardiac vs Skeletal Muscle: Are Contractile Tissues?
SIMILAR → BOTH SKELETAL & CARDIAC MSUCLE are contractle tissues
Muscle contraction is preceded by depolarizing action potential
Depolarization wave travels down T tubules → causes sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) to release Ca2+
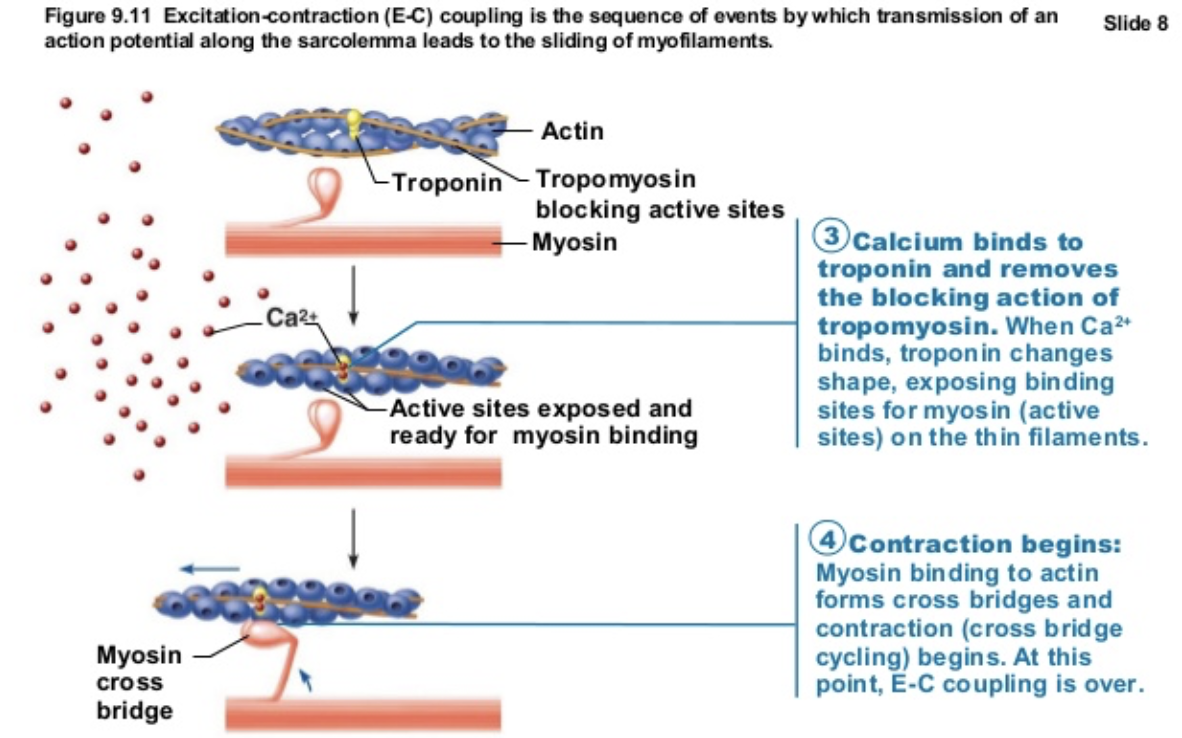
Excitation-coupling occurs → Ca2+ binds troponin causing myofilaments to slide in BOTH skeletal and cardiac muscle cells
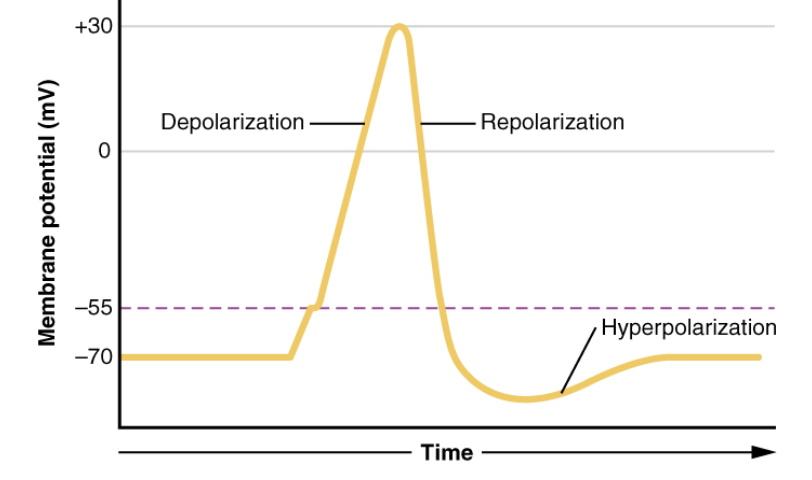
Similarity or Difference in Cardiac vs Skeletal Muscle: Ca2+ binds to troponin?
SIMILAR → Exication-contraction coupling occurs in BOTH SKELETAL & CARDIAC MUSCLE
Ca2+ binds troponin causing filaments to slide
Similarity or Difference in Cardiac vs Skeletal Muscle: Gap Junctions between cells ?
CARDIAC MUSCLE
Yes
SKELETAL MUSCLE
No
Similarity or Difference in Cardiac vs Skeletal Muscle: Contracts as a unit ?
CARDIAC MUSCLE
Yes
All cardiomyocytes contact as a unit (gap junctions create a functional syncytium) or none contract
SKELETAL MUSCLE
No
Motor units must be stimulated individually
Similarity or Difference in Cardiac vs Skeletal Muscle: T tubules?
CARDIAC MUSCLE
Fewer, wider
SKELETAL MUSCLE
Abundant
Similarity or Difference in Cardiac vs Skeletal Muscle: Sarcoplasmic reticulum?
CARDIAC MUSCLE
Less elaborate
No terminal cisterns (triads)
SKELETAL MUSCLE
Elaborate
Has terminal cisterns
Similarity or Difference in Cardiac vs Skeletal Muscle: Source of Ca2+ for contraction?
CARDIAC MUSCLE
Sarocplasmic reticulum AND extracellular fluid
Influx of Ca2+ from ECF triggers Ca2+ release from SR
Depolarization opens slow Ca2+ channels in sarcolemma, allowing Ca2+ to enter cell
Extracellular Ca2+ then causes SR to release its intracellular Ca2+
SKELETAL MUSCLE
Sacroplasmic reticulum ONLY
Similarity or Difference in Cardiac vs Skeletal Muscle: Contractile cells?
YES → Contractile cells: responsible for contraction
Muscle fibers → contains myofibrils composed of organized sarcomeres (thick myosin filaments & thin actin filaments)
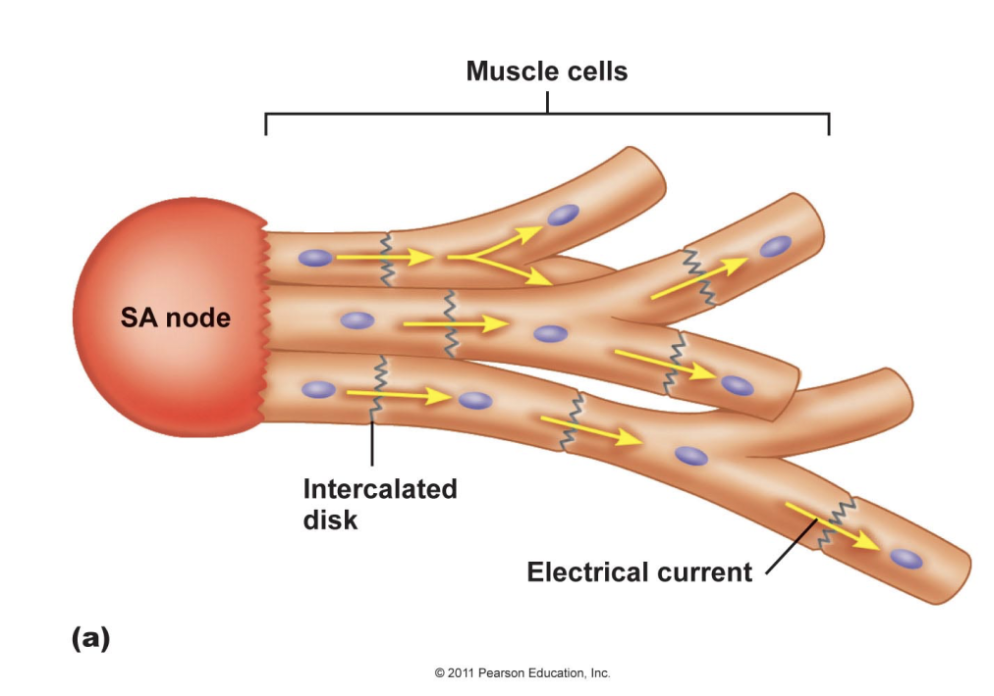
Similarity or Difference in Cardiac vs Skeletal Muscle: Pacemaker cells present?
CARDIAC MUSCLE
Yes → Pacemaker cells: non-contractile cells taht spontaneously depolarize
Initiate depolarization of entire heart
Do not need nervous system stimulate
SKELETAL MUSCLE
No → Needs the nervous system stimulation
Similarity or Difference in Cardiac vs Skeletal Muscle: Tetanus possible?
CARDIAC MUSCLE
No → Longer refractory period
Absolute refractory period is almost as long as contraction itself → prevents tetanic contractions
Allows heart to relax and fill as needed to be an efficient pump
SKELETAL MUSCLE
Yes
Similarity or Difference in Cardiac vs Skeletal Muscle: Supply of ATP?
CARDIAC MUSCLE
Aerobic ONLY → more mitochondria
Greater dependence on O2 → cannot function without O2
More adaptable to other fuels: lactic acid, but MUST have O2
SKELETAL MUSCLE
Aerobic AND Anaerobic → fewer mitochondria
Can go through fermentation when O2 not present
Key Differences between Skeletal and Cardiac Muscle
What makes the heart a functional unit
Gap junctions
Allows heart to be a functional syncytium
Endomysium
Connective tissue matrix that connects cardiac muscle to cardiac skeleton giving cells something to pull against
Pacemaker cells
Non-contracle cells that spontaneously depolarize; does not need nervous system stimulation
All cardiomyocytes contract as a unit
Ensures effective pumping action
Longer refractory period
Allows heart to relax and fill as needed