Topic 4 - DNA, chromosomes etc!
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What is a gene
A section of DNA that contains a code for making a polypeptide and functional RNA, the code is a specific sequence of bases.
what is a locus
the location of a particular gene on a chromosome
definition of an allele
An allele is one of a number of alternative forms of a gene. Most genes occur in two occasionally more different forms
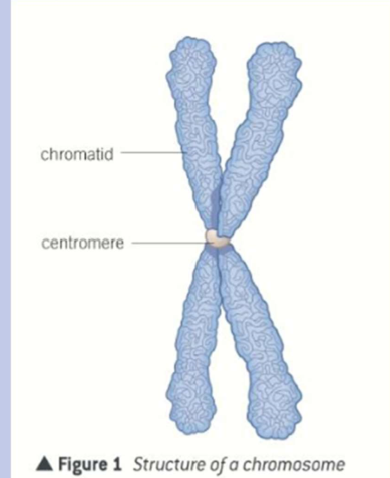
draw and label a chromosome
correctly labelled chromosome
What is a homologous pair
A homologous pair of chromosomes are exactly same size they have exactly same genes but might have different alleles
DNA storage in a eukaryote
DNA stored as chromosomes inside of the nucleus. Chromosomes in eukaryotic cells are linear in shape. To tightly coil the DNA to fit in the nucleus the DNA is tightly wound around proteins called histones.
This complex on DNA wrapped around a histone is called a nucleosome.
DNA in prokaryotic cells
Also carry DNA in chromosomes but DNA molecules are shorter and circular, not wound around histones.
Similarities between mitochondria, chloroplast and prokaryotic DNA
short and circular
There are 20 different amino acids the genetic code has to be able to code for. The genetic code is triplet (4³).
As 4³ = 64. 64 combinations is more than needed to code for 20 amino acids meaning each amino acid is coded for by more than one triplet of bases.
Why is the dna being degenerate an advantage
If a point mutation occurs even though the triplet of bases will be different it may still code for the same amino acid and therefore have no effect
How is genetic code universal
The same triplet of bases code for the same amino acid in all organisms
advantage of genetic code being universal
means genetic engineering is possible eg inserting human gene for insulin into bacteria
what does non overlapping mean for genetic code
Each base in a gene is only part of one triplet of bases that codes for one amino acid. Therefore each codon, or triplet of bases is read as a discrete unit
Eg
ACG GCT TCA ACT
Why is the genetic code being non overlapping an advantage
As if a mutation occurs it will only affect one codon and therefore one amino acid
What are introns
Introns are sections of DNA that do not code for amino acids and therefore dont code for polypeptide chains. Introns are found in eukaryotic DNA but not in prokaryotic DNA. They are in mrna but get spliced
What are exons
sections of dna that do code for amino acids
what is genome and proteome
The genome is an organisms complete set of DNA in one cell where as the proteome is the full range of proteins in one cell
what is in RNA nucleotide
ribose, nitrogenous base and phosphate
what are nitrogenous bases in RNA -
adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil
what is mrna and features
a copy of gene from dna. it is created in nucleus and leaves nucleus to carry the copy of the genetic code of one gene to a ribosome in the cytoplasm. mrna is shorter than dna so can leave the nucleus, but ie short lived as is only required temporarily.
mRNA is single stranded
trna facts and features
found only in the cytoplasm, single stranded but folded to create a cloverleaf like shape which is held in place by hydrogen bonds. contains anticodon which is complementary to codon on mrna
Compare RNA and DNA monomers
DNA contains bade thymine whereas rna contains uracil
DNA contains pentose sugar deoxyribose, whereas RNA contains pentose sugar ribose.
compare DNA and RNA polymers
DNA is much larger whereas rna is much shorter as its only the length of one gene
dna is double stranded whereas rna is single stranded
Describe process of transcription
the dna helix unwinds to expose the bases to act as a template, this is catalysed by dna helicase
only one chain of dna acts as a template
DNA helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between bases
free mrna nucleotides in the nucleus align opposite exposed complementary dna bases.
Joins adjacent nucleotides together
The enzyme rna polymerase bonds together the rna nucleotides to create a new rna polymer chain. one entire gene is copied.
premrna gets modified to become mrna by splicing. the introns are spliced out by a protein called splicesome. This leaves behind just the exons, coding regions.
describe translation
Once modified mrna has left the nucleus attaches to a ribosome in the cytoplasm
the ribosome attaches at the start codon
the trna molecule with the complementary anticodon to the start codon aligns opposite the mrna held in place by the ribosome.
The ribosome moved along the mrna molecule to enable another complementary trna to attach to the next codon on mrna
the two amino acids that have been delivered by trna molecule are joined by a peptide bond. this is catalysed by an enzyme and requires atp
This continued until ribosome reaches stop coronary at the end of mrna molecule. the stop codon does not code for an amino acids and therefore ribosome detaches and translation ends.
what is meiosis
type of cell division which produces daughter cells which are genetically different from each other.
meiosis involves two nuclear divisions and creates four haploid daughter cells from a single diploid ( two copies of homologous chromosomes ) parent cell.
what occurs in independent segregation / assortment
In meiosis 1, homologous pairs of chromosomes line up opposite eachother at the equator if cell. it is random placement of chromosomes along equator. these pairs are separated so one of each homologous pair ends up in the daughter cell. This creates a larger number of possible combinations in the daughter cells
what happens during crossing over
when homologous pairs line up opposite eachother other at the equator in meiosis 1, parts of the chromatids can become twisted around eachother (point of twist is called chiasmata) this puts tension on the chromatids causing parts of the chromatid to break. The broken parts of the chromatid recombine with another chromatid. resulting in new combinations of alleles
what is non disjunction
when chromosomes or chromatids do not split equally during anaphase
what is polploidy
changes in while sets of chromosomes occur when organisms have 3 or more sets of chromosomes rather than the usual two. normally occurs in plants
what js aneuploidy
individual homologous pairs of chromosomes fail to separate during meiosis. resulting in a gamete having one more or one fewer chromosome
what is genetic diversify
the number of different alleles of genes in a population
What is natural selection
Process which leads to evolution in populations, evolution is the change in allele frequency over many generations in a population. Natural selection results in species becoming better adapted to their encironment.
types of adaptations
anatomical - structural features eg shape of a beak of a bird
Physiological - chemical reactions within body eg quantities of chemicals or enzymes
behavioural - how the organism behaves eg penguins huddling together
Describe the Process of natural selection
1. new alleles for a gene created by random mutations
if the new alleles increase the chances of the individual to survive in that environment then they are more likely to survive and reproduce
this reproduction passes on the advantageous allele to the next generation
as a result over many generations the new allele increases in frequency in the population
what is directional selection
one of the extremes has the selective advantage
occurs when there is a change in the environment
the modal trait changes
eg antibiotic resistance in bacteria
what us stabilising selection
The modal traits has the selective advantag
occurs when there is no change in the environment
modal trait remains same
standard deviation decreases as individuals with the extreme trait decrease
eg baby birth weight
what is a species
a group if similar organisms that can breed to produce fertile offspring
what are courtship rituals
sequence of actions which are unique to each species this is how animals identify members of their own species to reproduce with.
what is the importance of courtship rituals
ensures successful reproduction
enabled them to recognise their own species and opposite sex
synchronises mating behaviour - indicates sexually mature and in season (releasing egg)
to ensure survival of offspring
form a pair bond
choose a strong and healthy mate
What is the binomial system
first name is genus second name is species
what is a hierarchy (in terms of classification)
smaller groups arranged within larger groups, there is no overlap between groups
modern and accurate classification methods
DNA sequence
mrna sequence
amino acids sequence
immunological - comparing similarities in self- antibody shape
What is phylogenetic classification
Arranging species into groups according to their evolutionary origins and relationships.
what is species diversity
The number of different species and individuals within each species in a community
Species richness definition
the number of different species in a particular area at the particular time
genetic diversity definition
the variety of genes amongst all the individuals in a population of one species
ecosystem diversity
range of different habitats
how does farming reduce biodiversity
destruction of hedgerows - as they provide habitats for insects etc
selective breeding - reduces gene pool
monocultures - only growing one plant species in the entire field
overgrazing reducing plants
filling in ponds and draining wetland to provide space
how to measure biodiversity
index of diversity - measure if species diversity. it is a calculation to measure relationship between the number of species in a community and the number of individuals in each species.
what is the cell cycle made out of?(in terms of stages )
Interphase (G1, S, G2)
G1- growth
S- DNA synthesis
G2- growth and preparation for mitosis
Interphase is the longest stage in the cell cycle. Interphase is when the organelles double, the cell grows and then DNA replicates.
Nuclear division -can be either mitosis, creating two identical diploid cells, or meiosis, creating four genetically different haploid cells. Mitosis creates cells with identical DNA for growth and repair, where as meiosis creates gametes.
Cytokinesis -the final stage. It is the division of the cytoplasm to create the new cells.
what occurs in prophase
chromosomes condense and become visible. In animal cells, the centrioles separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
metaphase
The chromosomes align along the equator of cell. The spindle fibres released from the poles now attach to the centromere and chromatid.
anaphase
The spindle fibres start to retract and pull the centromere and chromatids they are bound to towards the opposite poles. This causes the centromere to divide in two and the individual chromatids and pulled to each opposite pole. These separated chromatids and now referred to as chromosomes.
This stage requires energy in the form of ATP which is provided by respiration in the mitochondria.
telophase
The chromosomes are now at each pole of the cell and become longer and thinner again.
The spindle fibres disintegrate, and the nucleus starts to reform.
The final stage in the cell cycle is when the cytoplasm splits in two to create the two new genetically identical cells.