3-CGC1W1 Rock Types and The Rock Cycle
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Examples of Sedimentary rocks
Limestone
Chalk
Sandstone
Describe sandstone
An orangey-coloured rock which looks like lots of sand grains tuck together
Soft, breaks easily
Describe Limestone
A grey/white rock which is mostly made up of crushed sea shells (living organisms)
Contains fossils
Describe chalk
Fine grains
Contains fossils
What are the properties of sedimentary rocks?
Sedimentary rocks have layers showing the deposition of sediment at different time periods
Weak grains together
Fossils trapped within them
Sedimentary consist of layers of lots of small particles that are called..
Porous
Why are sedimentary rocks near the surface younger than sedimentary rocks deeper down?
The sediments deeper down are older because they’ve had more time to grow
The sediments near the surface are younger because they’ve had less time to grow than the ones deeper down
Stages of how sedimentary rocks get formed
Fast flowing water
Slow water
Pressure
Sedimentary rocks can also be formed when..
Minerals which are left behind when water evaporates
Examples of Metamorphic rock
Marble and slate
Properties of metamorphic rocks
Layer of structures of crystals caused by the effect of heat and pressure
Denser and harder than sedimentary rocks
Wavy and zig-zag arrangement because of no space particles, which are squares.
How metamorphic rocks are formed
Pressure from surface rocks together
Heat
Marble
A hard smooth rock made from sedimentary limestone or chalk in conditions of strong heat and low pressure
Slate
A grey rock with fine grains made from sedimentary shale in conditions of low temperature and low pressure
Thin sheets
Examples of igneous rocks
Granite
Pumice
Basalt
Granite
Hard grey rock with random arranged crystals
Pumice
Pale grey rock made up of very small crystals and porous, which is extremely light
Basalt
A dark glassy rock which has very fine crystals and often forms as columns of rock
Properties of igneous rocks
Interlocking crystals
Never contains fossils
How are igneous rocks formed?
Magma/lava cools and solidifies
Above - extrusive
Below - intrusive
Size of crystals
Above - small crystals are formed
Below - large crystals are formed
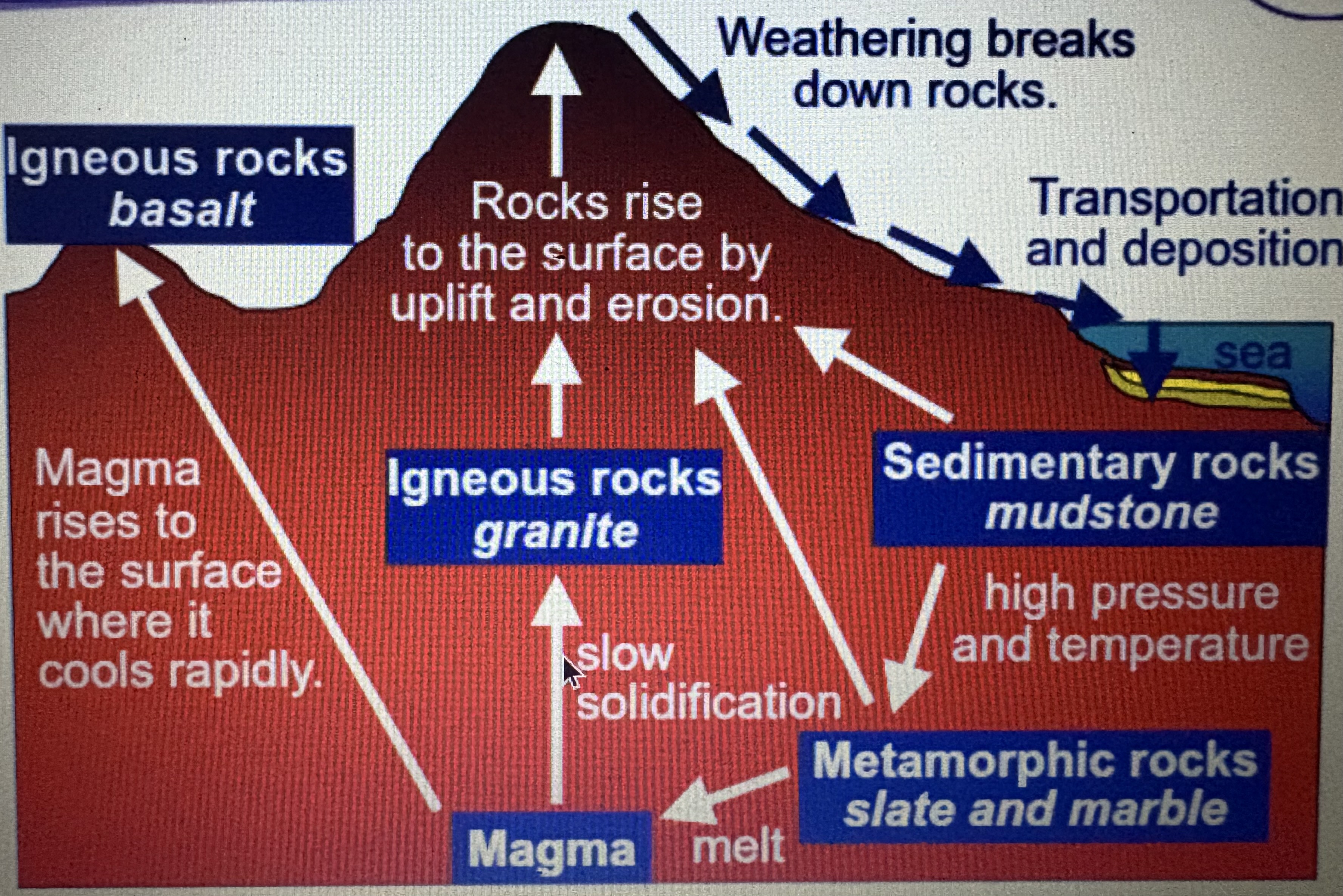
Rock cycle