Fundamentals of Computer Organisation and Architechture
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
What are the 5 main components of the CPU?
Arithmetic & Logical Unit (ALU)
Control Unit
Clock
General-Purpose Registers
Dedicated Registers
What does CU stand for?
Control Unit
What does ALU stand for?
Arithmetic & Logical Unit
What does CPU stand for?
Central Processing Unit
What are the key 5 dedicated registers?
Program Counter
CIR — Current Instruction Register
MAR — Memory Address Register
MDR or MBR — Memory Data or Buffer Register
Status Register
What does MDR stand for?
Memory Data Register
What does MAR stand for?
Memory Address Register
What does ISR stand for?
Interrupt Service Routine
What are the main 3 things which come together to make the CPU?
ALU — Arithmetic Logical Unit
CU — Control Unit
Registers (Like Cache)
What is the difference between General-Purpose and Special-Purpose registers?
General-Purpose can be used for any data simply requiring a register in order for the CPU to execute instructions while special purpose registers assign specific data for specific reasons.
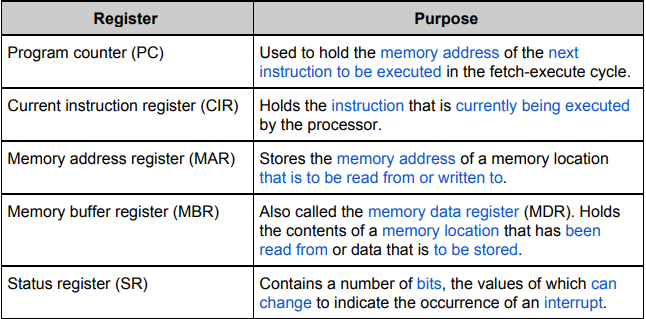
What is the purpose of the PC?
The PC — Program Counter is used to hold memory addresses of the next instruction thats to be executed
What is the purpose of the CIR?
The Current Instruction Register (Kind of gives it away) holds the instruction which is current being executed.
What is the purpose of MAR?
The Memory Address Register is what stores the actual address of the memory as in the locations.
What is the purpose of MDR?
The Memory Data Register is what holds the content of a memory location of what is going to be accessed or stored.
What is the SR?
The Status Register contains an amount of bits which is available to change corresponding to the occurrence of an interrupt.
What does the Computer Clock do?
The System clock is a device which ticks with a regular frequency and is used in order to synchronise communication.
What are the big 3 stages of the cycle used by the CPU in order to function?
Fetch
Decode
Execute
What is the entire Fetch-Decode-Execute cycle?
Fetch
Contents of PC → MAR
Contents of MAR → Main Memory via Address Bus
Contents of Main Memory → MDR via Data Bus
PC++ (Program Counter gets incremented)
Content of MBR → CIR
Decode
CIR gets Decoded via the CU
Decoded Piece gets split into
Opcode
Operand
Execute
Any required data not already in the registers gets fetched
Instruction gets carried out (Execution)
Results of possible calculations are stored within general-purpose registers or main memory.
Why aren’t Instruction sets universal?
Because a singular instruction set is made especially for that processor so it may not exactly be compatible with other processors.
What do Instructions look like?
Instructions commonly are stored in machine code as well as containing overall 3 main parts:
Opcode
Operand
Addressing Mode
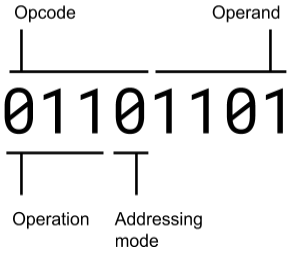
What does the Opcode do?
Opcode refers to the actual operation which is to be carried out.
What does the Operand do?
Operands are the bits of data which is used along with the Opcode fully completely all the parts required to accomplish the operation.
What are the 2 types of addressing?
Immediate
Direct
What is Immediate addressing?
Considering immediate addressing and building upon machine code. Immediate states that the operand is the actual value which the opcode and operand should be dealing with.
What is Direct Addressing?
Direct addressing linking to how machine code is laid out links directly to the operand and states that if it is direct addressing then the value which is stored within the operand isn’t the number but instead the memory address, location
What is logical shifting?
Logical Shifting corresponding to the direction which it is being done is when a binary number is being either halved or doubled.
Shifting all digits to the left once is = x2
Shifitng all digits to the right once is = /2
What is an interrupt?
An interrupt is like a message runner that will deliver its messages to the CPU from all types of different devices with the end goal of updating the user. For example if attempting to print but no paper then this corresponding interrupt will be sent telling such a message.
What does an increased address bus width mean?
it means that a greater range of addresses can be specified.
What does an increased Data bus width mean?
a large volume of data is able to be transferred elsewhere at a single time.
What are 6 pieces of internal hardware components?
Processor
Main Memory
Address Bus
Data Bus
Control Bus
I/O Controllers
What are 3 examples of Memory?
RAM — Random Access Memory
ROM — Read Only Memory
Cache
What are the main 3 buses?
Address Bus
Data Bus
Control Bus
What is a bus?
A bus is a parallel type connection of wires which bridge between internal components with different types of buses handling different jobs.
What does an Address Bus do?
An Address bus is responsible for transport of memory addresses for example where they’re being sent or retrieved.
What does a Data Bus do?
A Data Bus is responsible for sending data and relevant instructions to and from different components. (Wider this bus more the total that can be sent at once)
What does a Control Bus do?
A Control Bus is responsible for carrying Control signals that help regualtes the operations across the computer. (Also handles the clock signals)
What does I/O stand for?
Input/Output
What does the I/O Controller do?
The I/O Controller is responsible for pieces of hardware which control communication of data to the computer from peripherals.
What are 2 well-known architechtures?
von Neumann
Harvard
What is the difference between von Neumann and Harvard?
The Harvard Architecture makes use of two entirely separate main memory storages with one entirely regarding Data and the other entirely for instructions. While von Neumann uses one basis that controls both.
What does RFID stand for?
Radio Frequency IDentification.
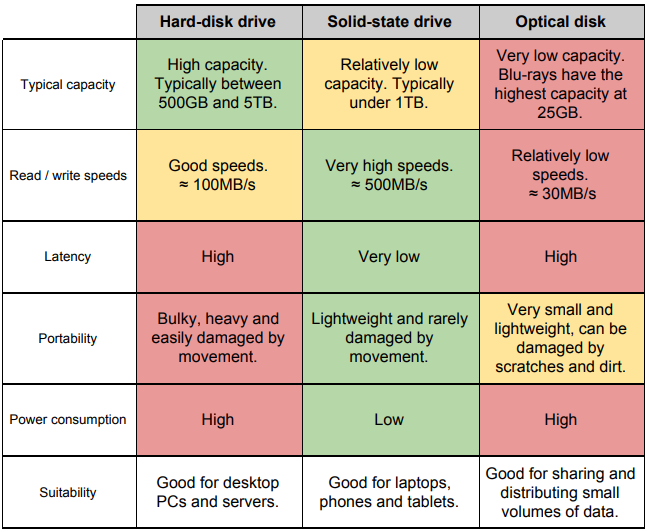
What does HDD stand for?
Hard Disk Drive
What does SSD stand for?
Solid State Drive
What are the 2 types of barcode?
Barcode — 1D
QR Code — 2D
What is the difference between 1D and 2D barcodes?
1D require the same amount of space as 2D however more processing power is needed in order to go through a 2D barcode.
How do barcodes work?
The black and white parts react differently to a barcodes readers eyes symbolise 1’s and 0’s like black and white.
They also make use of parity and check bits in order to verify proper data sending.
What are 2 ways used in order to keep Barcode transfer secure?
Parity Bits
Check Bits
What does CMOS stand for?
Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor
What does CCD stand for?
Charge Coupled Device
What is the Bayer filter?
A special filet used in digital cameras that has the correct ratio of blue red and green lights making it more similar to the human eye.
What are the 5 main parts of a printer?
Laser Light Source
Mirror
Drum
Toner Roller
Fuser
Why make use of a laser printer?
More expensive however the possibility of printing out high quality and entire pages at once becomes possible.
What is the process taken by a laser printer?
Firstly the drum is positively charged prior to any lasers being used.
Next main areas of the drum get discharged leaving behind the actual page being printed out or rather the template to follow.
The Toner dispenses negative charged toner onto the drum being attracted towards the positive parts.
Then the toner is added onto the paper and heated on with use of fusers.
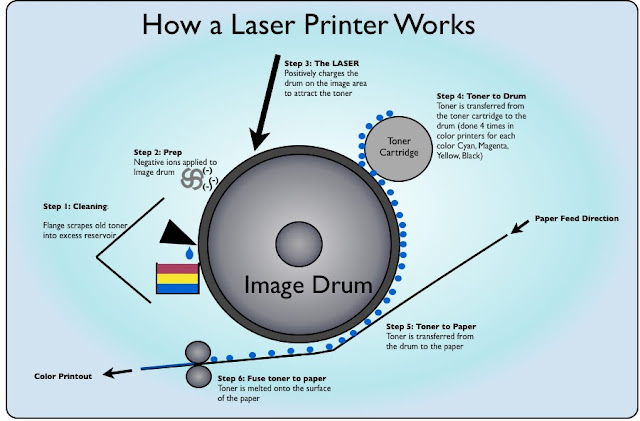
What colours are used for Laser Printing?
Cyan
Yellow
Magenta
Black
(Strangely somehow standing for CYMK don’t ask me :((( )
What are the two required pieces that end up allowing for proper RFID communication?
Radio Frequency IDentification needs both a tag and a reader in order to accomplish wireless accessing.
What is the difference between Passive and Active tags?
Majority of RFID are Passive meaning they simply release enough power wirelessly from the chip however active tags including a tiny power source allowing them to be used from further away.
What is the difference between Storage and Memory?
Storage is personal. Memory is for the system.
What are the disks of magnetic material called within a HDD?
Platters.
What allows the HDD to actually read the platters found on a HDD?
Actuation Arms — (Read/Write Head)
How is data actually read and written to platters on the magnetic platters?
Through use of magnetic polarity which writes into concentric tracks which are found on the platter and then further get organised into sectors.
Faster the platter rotates means faster the read and write speed.
How is more storage added to a Hard Disk Drive?
via addition of more platters and decreasing the width (to allow for more)
What makes up an SSD?
NAND Flash Memory Cells
Controllers
What is NAND Flash Memory?
A Non-Volatile Flash Memory that works through use of floating gate transistors which make it non-volatile because then instead of losing all the data like volatile storage instead it traps electric charge. Storing the data.
Which is safer: HDD or SSD?
HDD’s aren’t as safe compared to SSD’s because of the amount of moving parts feature in a HDD which can end up breaking thanks to wear and tear if poorly made or simply dropping it being tasks atleast harder for an SSD.
What are 3 types of optical disk?
CD
DVD
Blu-ray
How are optical disks read?
Optically with a laser looking for pits and lands
What are pits and lands?
Pits and lands refer to the engraving done onto a CD with use of a laser where a higher powered laser will create the Pits being simply just indentation while lands are the regular untouched material which gets read with use of a lower powered laser able to read the reflections resulting in 1’s and 0’s bits of data to be received by the PC.
How are CD’s and HDD’s different?
CD’s work like records where its a single spiralling channel going around the entire CD start-finish while HDD’s use tracks and sectors.
What are the 3 types of secondary storage?
HDD
SSD
Optical