Microbiology Exam 1, Dr. Collins
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
186 Terms
Microbiology
The study of organisms and agents too small to be seen clearly by the unaided eye
Organisms involved in the study of Microbiology
Prions, viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and algae
What are some chemical products that microbes produce?
Things like ethanol, acetone, and vitamins
The 3 domains in the Universal Phylogenetic Tree:
Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
Bacteria and Archaea are Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic?
Prokaryotic
Eukarya is Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic?
Eukaryotic
Eukaryotic
Have a nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, contains DNA, and has a larger genome
Prokaryotic
Do NOT have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles, contains DNA
Methanogens
Microorganisms that produce methane
Halophiles
Microorganisms that love salty conditions
Thermophiles
Microorganisms that love hot environments such as hot springs and underwater thermal vents.
Peanut plants have a symbiotic relationship with:
Rhizobium (nitrogen-fixing bacteria)
Arborvitae trees have a symbiotic relationship with:
mycorrhizal fungi
Coral have a symbiotic relationship with:
zooxanthellae (algae)
Squid have a symbiotic relationship with:
Vibrio fishcheri (bacteria). This bacteria give squid a bioluminescence that prevents predation.
Termites have a symbiotic relationship with:
Trichonympha (protozoans)
The rumen of cattle have a symbiotic relationship with:
methanogenic bacteria
Human intestines have a symbiotic relationship with:
E. coli (bacteria). E. Coli bacteria found in all human intestines are beneficial and produce Vitamin K.
Who was the first scientist to visualize and describe microorganisms under a microscope (50 to 300X)?
Antony van Leeuwenhoek (1623-1723)
What is spontaneous generation?
The evolutionary theory concerning the origin of life that says living organisms can develop from nonliving matter.
Who was Francesco Redi?
He was an Italian physician and one of the first scientists to DISPROVE spontaneous generation.
What years did Francesco Redi live in?
(1626-1697)
How did Francesco Redi disprove spontaneous generation?
He experimented with decaying meats and showed maggots wouldn't develop in the meat spontaneously if covered in gauze, but flies laid eggs on top of gauze which developed into maggots thus temporarily disproving spontaneous generation.
Did Redi work with prokaryotic or eukaryotic organisms?
Redi worked with eukaryotic organisms.
Why did the idea of Spontaneous Generation eventually resurface?
To try and explain where newly discovered microorganisms originated
Which two scientists performed experiments to prove microbes did not originate by spontaneous generation?
Schwann and Pasteur
What years did Schwann and Pasteur perform their experiments?
Between 1780 and 1870
With what experiment did Pasteur disprove spontaneous generation?
Pasteur disproves spontaneous generation by the famous swan necked flask experiment
Did Pasteur work with prokaryotic or eukaryotic organisms
Pasteur worked with prokaryotic organisms.
Pasteur’s experiments and observations were the basis for __________ techniques
aseptic
What did Pasteur’s experiment demonstrate
That microbes are present in nonliving matter and responsible for food spoilage
Abiogenesis
The idea that life grew from nonliving matter millions of year ago.
What was the purpose of the Miller-Urey experiment?
Attempted to replicate life on early Earth.
What was the Miller-Urey experiment able to produce?
Amino acids
What did the Miller-Urey experiment fail to do?
It failed to produce DNA, proteins, and cells. It does not explain how single-cell organisms evolve into multicellular organisms.
The Germ Theory
The idea that microorganisms or “germs” cause disease.
Who was the founder of the germ theory of disease
Luis Pasteur
Who were the other two scientists who played major roles in the germ theory?
Koch and Lister
What is Joseph Lister known for?
He developed the concept of antiseptic surgery in which the instruments are heat sterilized and phenol is used afterward to eliminate infection.
What year were Joseph Lister’s findings published
1867
What was Robert Koch known for?
He demonstrated the role of microbes in causing disease during his study of anthrax.
What years was Koch alive
(1843-1910)
What did Koch demonstrate in his studies?
Koch established the relationship between Bacillus anthracis and anthrax by isolating the organisms from infected animals and injecting them into mice.
Koch’s Postulates:
1. Microbe must be present in every case of the disease but not in healthy animal
2.Suspected microbe must be isolated and grown in pure culture
3.Same disease must result when pure culture is inoculated into healthy host
4. Same microbe isolated from infected host
Examples of exceptions to Koch’s postulates:
1.Some strains might be non-pathogenic.
2.There could be latent infections (when someone appears to be healthy but there is a lingering infection).
3.The healthy host could be asymptomatic but still spread disease. (example of this is typhoid Mary).
4.Some microbes are not able to be grown in culture not even pure culture (such as viruses or microbes with symbiotic relationships).
5.Organism can cause multiple diseases (example S. pyogenes can cause strep throat and scarlet fever).
6.Multiple organisms can cause the same disease (ex. Pneumonia).
7. It might be unethical to test certain theories about diseases.
Attenuated
No longer able to cause disease
What did Pasteur learn from his experiments with chicken cholera
If he incubated the cholera cultures for very long periods between transfers would become attenuated. He learned that the injection of attenuated form into healthy chicken made them resistant to infection
What other means did Pasteur develop to attenuate bacteria?
Via heat treatment or chemical treatment.
Vaccination
The idea of injecting attenuated strains to protect healthy animals or humans from microbial infection
Who developed the first vaccine, and against what?
Pasteur developed the first vaccine against anthrax and the viral disease rabies.
What is the acute contagious disease diphtheria caused by?
It is caused by the toxin produced by the bacteria Corynebacterium diphtheriae
The scientists _______________ and ____________ are responsible for identifying and creating a vaccine and antitoxin against diphtheria by injection of healthy animals with the inactivated toxin.
Von Behring, Kitasato
Edward Jenner created what?
A vaccine against smallpox and cowpox.
Most vaccines we have today are not made of attenuated bacteria, they’re made of ______________
the inactivated toxin
What was the first antibiotic
Penicillin
Penicillin was discovered in ________ by ____________
1929, Flemming
The two scientists ______________ and ______________ discovered restriction endonucleases in the 1960s
Werner Arber, Hamilton Smith
When did Rosalind Franklin discover DNA and Watson and Crick propose the model of DNA?
1962
When did scientists David Jackson, Robert Symons, and Paul Berg perform their experiments with recombinant DNA?
1972
When did Frederick Sanger perform his experiments with the sequencing of nucleotides in DNA?
1970s
What causes Anthrax
Bacillus anthracis
Endospores
A highly resistant morphology of bacteria. Found in the soil and can survive for decades.
Bacillus anthracis
- Gram-positive
- Endospore forming
- Causes animal disease anthrax
What causes endospores to form?
The microbe forms endospores to protect itself in an unhospitable environment, such as low nutrients, high heat, high UV, desiccation, etc.
3 forms of anthrax
Cutaneous, pulmonary, and gastrointestinal
What percent of anthrax is cutaneous?
95%
Who can be infected with anthrax?
Wild and domesticated herbivorous mammals, and humans
What makes Anthrax so bad is its toxin, which is carried on a ____________
plasmid
Cutaneous Anthrax
Most common
A black ulcer forms
The disease is caught by spore penetrating into a cut in the skin 2 to 5 days later
Rarely fatal
Pulmonary Anthrax
Begins with cold/flu-like symptoms
This type is a respiratory infection obtained by breathing in this type of Anthrax.
Symptoms are cough, chest discomfort, shortness of breath, tiredness and muscle aches
Most dangerous type
Another name for pulmonary Anthrax
Woolsorters' disease
Mortality rate for Pulmonary Anthrax
92% mortality, 45% mortality when treated early
Gastrointestinal Anthrax
- Infected by eating undercooked meat from infected animals.
- Symptoms are nausea, loss of appetite, bloody diarrhea, and fever, followed by bad stomach pain.
Is there a vaccine against Anthrax?
Vaccine is not yet available for the general public
Available for certain members of the U.S. armed forces, laboratory workers, and workers who may enter or re-enter contaminated areas
Treatment if you are exposed to anthrax, but is not yet sick
Use antibiotics combined with the anthrax vaccine
Treatment for anthrax after infection
Treatment is usually a 60-day course of antibiotics
Which plagues do some historians believe are evidence for Anthrax in biblical times?
The fifth (i.e. The Plague of Livestock)
The sixth (i.e. The Plague of Boils)
The tenth (i.e. The Plague of Firstborn)
When did Scandinavian rebels use anthrax with unknown results against the Imperial Russian Army in Finland?
1916
When was Anthrax tested by Unit 731 of the Japanese Kwantung Army in Manchuria?
1930s
In what year did the Royal Air Force contaminate Gruinard Island in Scotland with Anthrax?
1942
Where were the Anthrax-filled letters sent during the 2001 Anthrax attacks in the US?
The letters were sent to media offices, and Senators Tom Daschle and Patrick Leahy
Parameters used in the phenotypic identification of microbes:
Cell shape
Cell size
Colony morphology
Staining behavior
Physiological and biochemical characteristics
Vibrio
A bent rod shape, such as vibrio cholerae.
Spirilla
A squiggly line
Spirochete
A corkscrew shape
Pleomorphic
Bacterial cells that do not fall into any of the previous cell shape categories. Includes the Archaea shapes.
Flagella are made of:
a protein called flagellin
Three parts of a Flagella:
Basal body, Hook, Filament
Functions of Flagella:
Flagella are used for motility and in some cases it functions to attach cells to surfaces
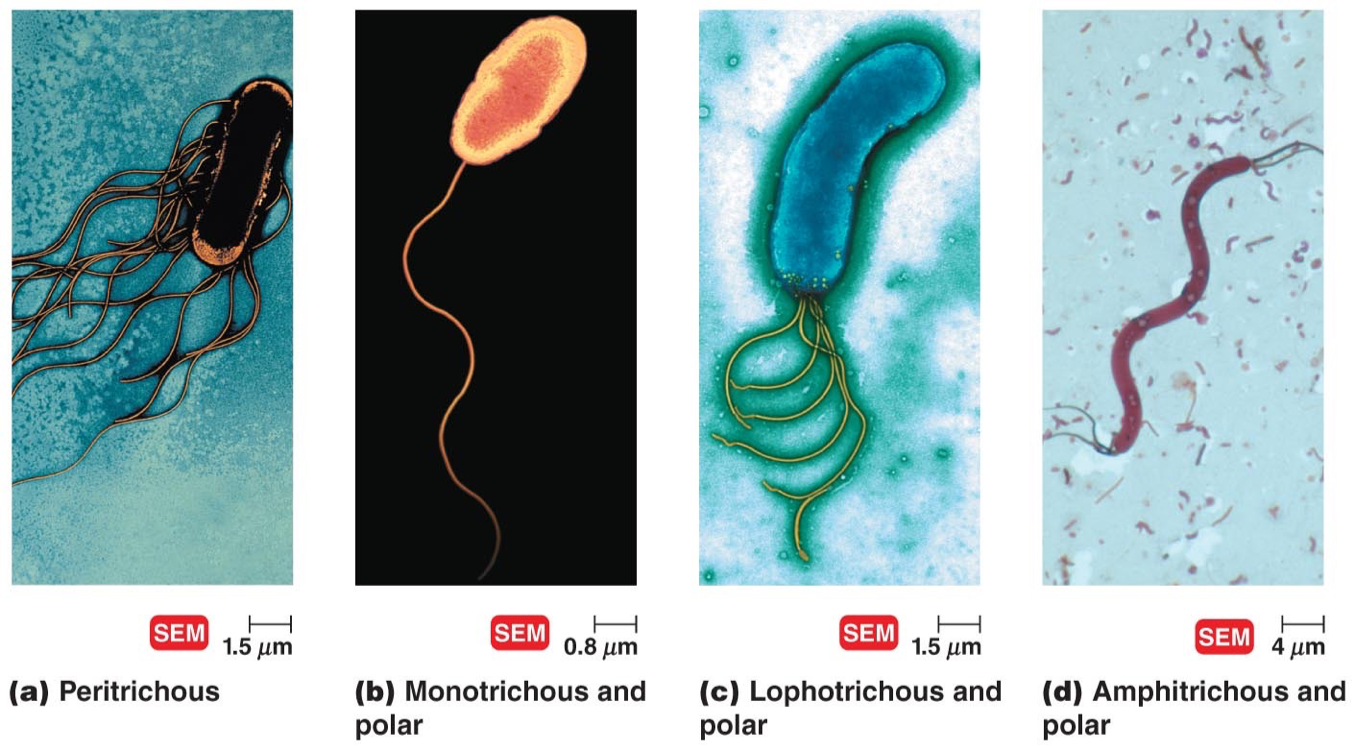
Monotrichous
One flagella located at a pole or end
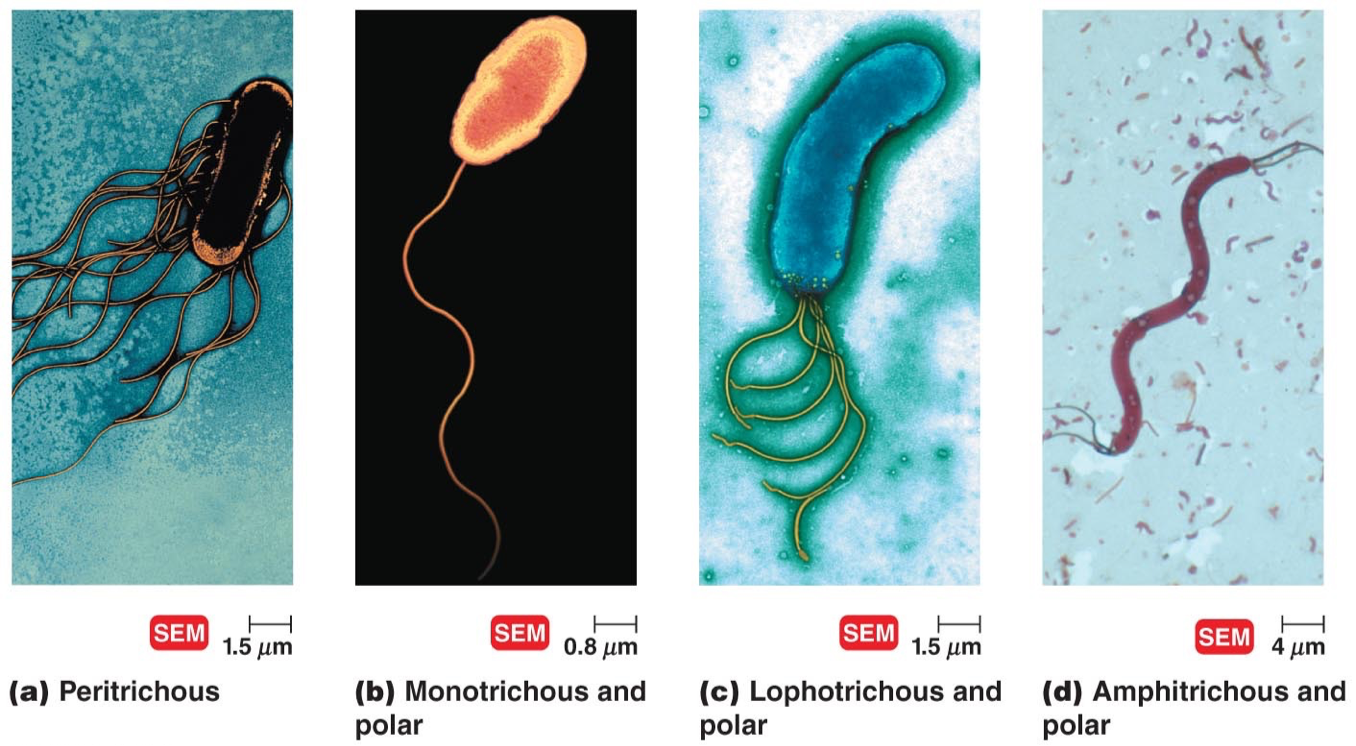
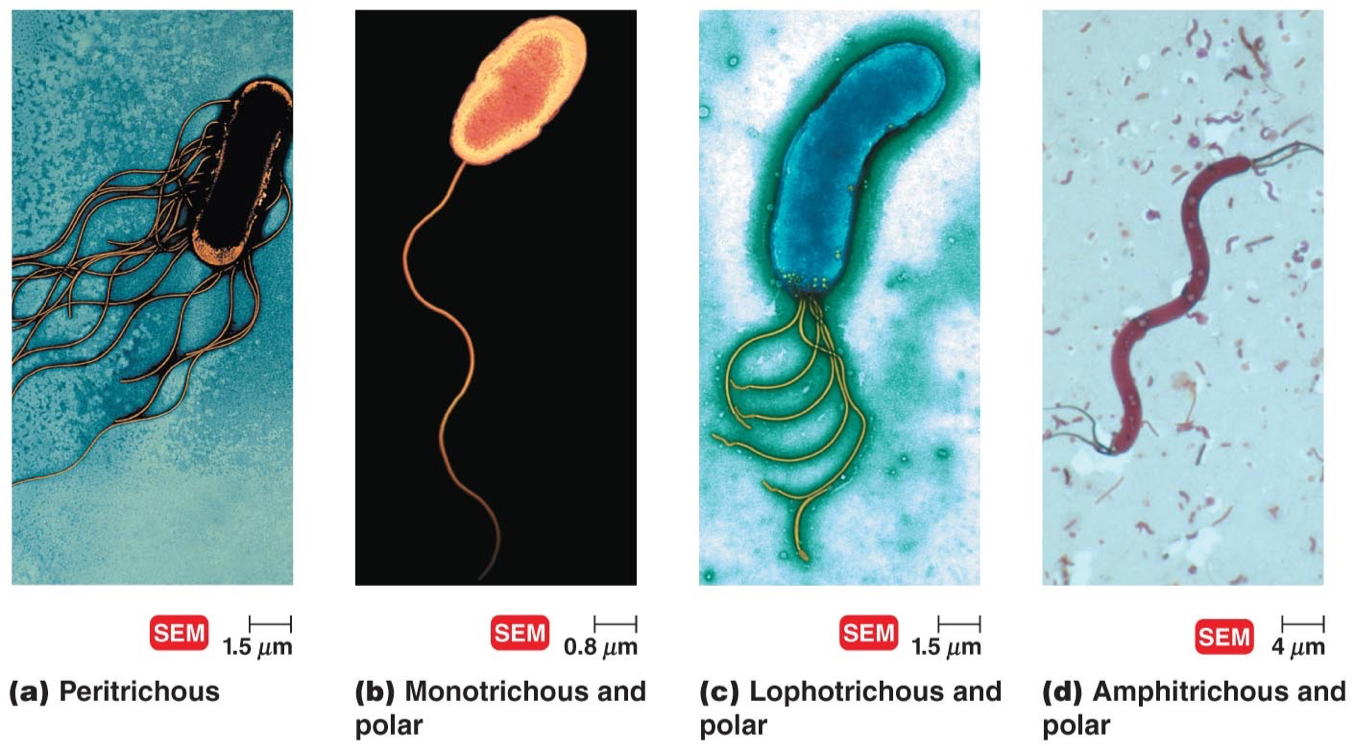
Amphitrichous
Single flagella at both ends
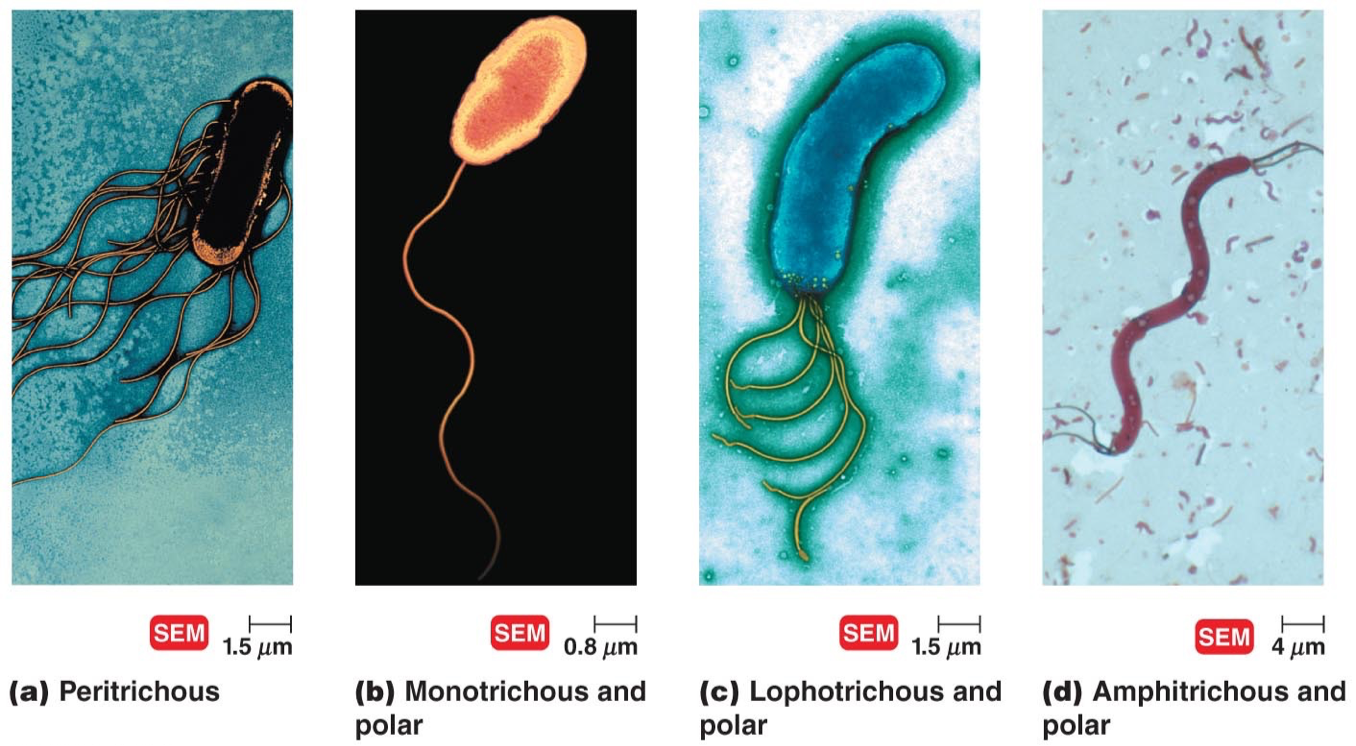
Lophotrichous
Tuft of flagella at one or both ends
Peritrichous
Flagella around entire surface of bacteria
What flagellar motion is required for a forward run?
Counterclockwise
What flagellar motion is required for a tumble?
Clockwise
Pili are made of ____________
the protein pilin
Pilli function:
Attachment to surfaces (biotic and abiotic)
Twitching motility
Transfer of genetic material
Sex pili
Function to transfer genetic material
What type of motion are flagella responsible for?
Swimming and swarming
What type of motion are pili responsible for
Twitching