Professor Messer 4.1 - 4.4 Study Sets
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
Secure Baselines
The security of an application environment should be well defined.
- Firewall settings, patch levels, OS file versions, etc
May require constant updates.
Integrity measurements check to see if baseline is met.
Establish Baselines
Security baselines are often available from manufacturer.
- Application developer.
- OS manufacturer.
- Appliance manufacturer.
Many operating systems have extensive options.
Deploy Baselines
Usually managed through a centrally administered console
May require multiple deployment mechanisms - Active Directory group policy, MDMs, etc.
Automation is the key
Maintain Security Baselines
Many are best practices - don't change often
Other baselines may require ongoing updates.
- A new vulnerability is discovered.
- An updated app has been deployed.
- A new OS is installed.
Some manuf baselines conflict with each other.
- Test before deployment.
- Audit after.
Hardening Guides
Guidelines on configs that keep everything on the device/system safe.
Are specific to platform or software.
Internet groups and manuf have details.
Mobile Device Hardening
Hardening checklist available from manufacturers.
Updates are critical
- to perform bug fixes and security patches.
Segmentation can protect data.
Work Station Hardening
Constant monitoring and updates.
- Oss, apps, firmware, etc.
Automate the monthly patches.
Connect to a policy management system
- Active Directory group policy.
Remove unnecessary software to limit the threats.
Network Infrastructure Device Hardening
Network Infrastructure Device Hardening
Switches, routers, etc. Purpose-built devices.
- Embedded OS, limited OS access.
Configure authentication - don't use the defaults.
Check with the manufacturer for security updates.
Cloud Infrastructure Hardening
To secure the cloud management workstation, use least privilege.
Configure Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
- monitor for potential attacks.
Always have backups.
Server Hardening
Many varied - windows, Linux, etc.
My have operating system updates/service packs, security patches
Has user accounts with minimum password lengths and complexity.
Limit which devices have access.
Monitor and secure with anti-malware and anti-virus.
SCADA/ICS Hardening
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition System.
- Large-scale, Industrial Control Systems (ICS).
PC manages equipment.
Distributed control systems
- real time info and system control.
Requires extensive segmentation.
- No access from the Outside.
Embedded Systems Hardening
Hardware and software designed for a specific function
- or to operate as part of a larger system.
Can be difficult to upgrade.
Correct vulnerabilities
- security patches.
Segment and firewall to prevent access from unauthorized users.
RTOS (Real-Time Operating System)
An operating system with a deterministic processing schedule. - No wait time for other processes.
- Used for industrial equipment, automobiles, military environments
Isolate the system from the rest of the network.
Run with minimum services
- prevent potential exploits.
Use secure communication to connect to a network
- firewall.
IoT Device Hardening
Deploy updates quickly.
Segment IoT devices onto their own network/VLAN
Site Surveys
Determine the wireless landscape
- Sample the existing wireless spectrum.
Identify existing access points.
- You may not control all of them.
Work around existing frequencies.
- Layout and plan for interference.
Plan for ongoing site surveys.
- Things will certainly change.
Heat maps
- Identify wireless signal strengths.
Wireless Survey Tools
Signal Coverage.
Potential Interference.
Built-in tools in OS. 3rd-party tools.
Spectrum analyzer.
Mobile Device Management (MDM)
Allows you to manage company-owned and user-owned mobile devices.
Centralized management of the mobile devices.
COPE (Corp Owned, Personally Enabled)
Company buys device
- used as corp and personal device.
Organization keeps full control of the device.
Information is protected using corporate policies.
Corporate data is partitioned off from personal data.
Some orgs allow you to CYOD - Choose Your Own Device.
-You can choose which device you'd like to receive.
Securing Cellular Networks
- Traffic monitoring.
- Location tracking.
-Worldwide access to a mobile device.
Securing Wifi Networks
- Data encryption.
- Monitor data (on-path) attack and Denial of service/frequency interferences.
Bluetooth (Security)
High speed communication over short distances.
- Personal Area Network/PAN.
Do not connect to unknown Bluetooth devices.
- That's why we pair first to prevent unauthorized connections.
Securing a Wireless Network
Authenticate the users before granting access
.- Username, passw, multi-factor authentication.
Ensure that all communication is confidential.
Verify the integrity of all communication.
- A message integrity check (MIC).
The WPA2 PSK Problem
WPA2 has a PSK brute-force problem.
- Listen to the four-way handshake.
- Capture the hash.
With the hash, attackers can brute force the pre-shared key (PSK).
- Has become easier as technology improves.
- A weak PSK is easier to brute force.
-GPU processing speeds.
- Cloud-based password cracking.
Once you have the PSK, you have everyone's wireless key.
- There's no forward secrecy.
WPA3 and GCMP
Wifi Protected Access 3
- introduced in 2018.
GCMP block cipher code (for brute force attacks).
- Galois/Counter Mode Protocol.
- A stronger encryption than WPA2.
GCMP security:
- Data encryption with AES protocol.
- Message Integrity Check (MIC).
SAE
Simultaneous Authentication of Equals.
Part of the WPA3 security standard.
- A Diffie-Hellman derived key exchange with an authentication component.
Creates a shared session key without sending it over the network.
- No 4 way handshake.
- No hashes.
- No brute force attks.
Everyone uses different session key, even with the same PSK. An IEEE standard - the dragonfly handshake.
Wireless Authentication Methods
Credentials provide wireless authentication.
- Shared password/pre-shared key (PSK).
- Centralized authentication (802.1X).
Wireless Security Modes
The different protocols/settings to protect a wifi-network. WEP, WPA, WPA2, and WPA3.
- Located in the configuration of the wifi settings on home router/wireless access point. An open system.
For personal use: WPA3-personal/ WPA3-PSK.
- WPA2 or WPA3 with a pre-shared key.
- Everyone uses the same 256-bit key.
Business: WPA3 enterprise/ /WPA3-802.1X.
- Authenticates users individuals with an authentication server (ie: Radius).
AAA Framework
Authentication
- Password and other factors.
Authorization
- What access do you have?
Accounting
- Resources used: Login time, data sent and received, logout time.
RADIUS
One of the more common aaa protocols. Known as Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service.
Centralized authentication server for users.
Supported on a wide variety of platforms and devices.
IEEE 802.1X
Port-based Access Control (NAC).
- No access to the network until you authenticate.
Used in conjunction with an access database.
- RADIUS, LDAP, TACACS+.
EAP
Extensible Authentication Protocol
- An authentication framework.
Manufacturers can build their own EAP methods.
EAP integrates with 802.1X.
IEEE 802.1X and EAP Services
Supplicant = Client.
Authenticator = device providing access.
Authentication server = validates the client credentials.
Input Validation (Secure Coding Concepts)
Any unexpected data that is input into the app will not be interpreted.
Document all input methods.
- Forms, field, type.
Check and correct all input.
- -A zip code should only be a certain amount of characters long. If anyone inputs something that doesn't match that, the application should prompt the user to correct the input.y
Fuzzers will find what you missed.
- Fuzzers put random data inputs in apps to see what it does.
Secure Cookies (Secure Coding Concepts)
Secure cookies have a secure attribute set and are only sent over HTTPS, or an encrypted connection.
Sensitive info should not be saved in a cookie.
Code Signing (Secure Coding Concepts)
Application code can be digitally signed by developer.
- Asymmetric encryption.
- A trusted CA signs the developer's public key.
- Developer signs code with their private key.
Sandboxing (Secure Coding Concepts)
When an application only has access to the data necessary for that application to run.
Commonly used during development.
Used in different ways/deployments:
- Virtual machines.
- Mobile devices.
- Browser inframes (Inline Frames).
- Windows User Account Control (UAC).
Application Security Monitoring (Secure Coding Concepts)
Monitoring information in real-time.
- App usage, access demographics.
Views blocked attacks.
Used to audit the logs
- Find the information gathering and hidden attacks.
Anomaly detection.
Acquisition/Procurement Process
Multi-step process for requesting and obtaining goods and services.
Start with a request from the user.
Negotiate with suppliers.
Purchase invoice, and payment.
Assignment/Accounting
A central asset tracking system.
- A way to manage all of the assets received by the company.
Ownership
- Associate a person with an asset.
- Useful for tracking a system.
Classification
- Type of asset.
- Hardware.
- Software.
Monitoring/Asset Tracking
Inventory of every asset.
Associate a support ticker with a device make and model.
Enumeration - list all parts of an asset.
Add an asset tag to the device.
- Barcode, RFID, tracking number.
Media Sanitation
System disposal or decommissioning.
- Completely removing data.
- No usable info remains.
Different ways to do it:
- Can delete certain files so another employee can use it.
- Wipe the whole hard drive to dispose.
- Etc.
Physical Destruction
Shredder/Pulverizer.
Complete destruction
- Drill/Hammer.
Electromagnetic/Degaussing.
Incineration.
Degaussing
Using a strong electromagnetic field to wipe all the data and makes the drive unusable.
Certificate of Destruction
Confirmation that your data is destroyed by a 3rd party.
Data Retention
Retaining data by backing up your data.
Regulatory compliance
- A certain amount of data backup may be required.
Used for operational needs
- Disaster recovery.
- Accidental deletion.
Different types of data may require different types of retention.
Vulnerability Scanning
Minimally invasive.
A port scan is a common type.
Identifies systems and devices.
Tests from the outside and inside.
Used to gather as much information as possible.
Static Code Analyzers
Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
- Helps to identify security flaws in source code of an app.
Many vulnerabilities can be found immediately
- buffer overflows, database injections, etc.
Doesn't find everything.
- Authentication security, insecure cryptography.
Verify each finding
- may be false positives.
Dynamic Analysis (Aka Fuzzing)
Sending random input into an application to see what happens.
Looking for something out of the ordinary
- Application crash, server error, exception, etc.
There are many different fuzzing options for different platforms and languages.
Very time and processor resource heavy.
Package Monitoring
Some apps are distributed in a package.
Confirm the package is legit.
- Trusted source.
- No added malware.
- No embedded vulnerabilities.
Confirm a package is safe before deployment.
Threat Intelligence
Research the threats and threat actors.
Data is everywhere.
Make decisions based on this intelligence and invest in the best prevention practices.
Used by researchers, security operations teams, and others.
OSINT (Open Source Intelligence)
Information/intelligence that is publicly available (open-sourced).
Internet, social media, gov data, etc.
Commercial data.
- Maps, financial reports, databases.
Propriety/Third-Party Intelligence
When someone has already compiled the threat information and you buy it.
Threat intelligence services:
- Threat analytics.
- Correlation across different data sources - can analyze threats over many diff orgs at the same time..
Offers constant threat monitoring.
- Identifies new threats.
- Creates automated prevention workflows.
Information-Sharing Organization
Some orgs will compile public threat intelligence and private threat intelligence.
Involves sharing critical security details.
Ex: Cyber Threat Alliance (CTA)
Dark Web Intelligence
Are overlay networks that use the internet
- requires specific software and configurations to access.
Contains hacking groups and services:
- Activities.
- Tools and techniques.
- Credit card sales.
- Accounts and passwords.
Monitor forums for activity - company names and executive names.
Penetration Testing
When you simulate an attack (on own system).
Similar to vulnerability scanning.
Often a compliance mandate
- Regular penetration testing by a 3rd party.
Rules of Engagement
An important document that defines purpose and scope.
- Makes everyone aware of the test parameters.
Provides type of testing and schedule. - Hours (after 6pm only), etc.
The rules:
- IP address ranges.
- Emergency contacts.
- How to handle sensitive Information.
- In-scope and out-of-scope devices or applications.
Exploiting Vulnerabilities
Trying to break into the system - be careful. Can cause a denial of service or loss of data.
You may need to try many diff vulnerability types.
- Password brute-force.
- Social engineering.
- Database injections.
- Buffer overflows.
You'll only be sure you're vulnerable if you can bypass security.
The Pentesting Process
Getting into the network.
Moving from system to system.
Persistence
- make sure there's a way back in.
Pivot and gain access to systems that would normally not be accessible.
- Use vulnerable systems as a proxy or relay.
Responsible Disclosure Program
Takes time to fix a vulnerability.
- Software changes, testing, deployment, etc.
Bug bounty programs
- A reward for discovering vulnerabilities.
(Occurs after vuln is discovered)
A controlled info release:
- A researcher reports the vulnerability.
- Manufacturer creates a fix.
- The vulnerability is then announced publicly.
False Positives
When a vulnerability is identified that doesn't really exist.
Update to latest signatures to prevent.
False Negatives
A vulnerability exists, but you didn't detect it.
Update to latest signatures to prevent.
Prioritizing Vulnerabilities
Not all vulnerabilities share the same priority.
- Some may not be significant, others may be critical.
May be difficult to determine.
Refer to public disclosures and vulnerability databases.
- Least critical - most critical.
CVSS
Common Vulnerability Scoring System.
- National Vulnerability Database list.
Scoring from 0-10 on severity.
Different scoring for CVSS 2.0 and CVSS 3.x
CVE
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures.
Vulnerabilities can be crossed-reference online.
- manuf databases.
Some vulnerabilities cannot be identified
- Generic, no CVE, etc.
- Scanner gives you a heads up.
Vulnerability Classification
The scanner looks for everything - the signatures are the key.
- use latest set of signatures.
Application scans
- Desktop, mobile apps.
Web application scans
- Software on a web server.
Network scans
- Misconfigured firewalls, open ports, vuln devices.
Exposure Factor
Loss of value or business activity if the vulnerability is exploited.
- Expressed as a %.
A small DDoS may limit access to a service.
- A buffer overflow may completely disable a service.
A consideration when prioritizing.
Environmental Variables
Environment associated with vuln.
- Internal server, public cloud, etc.
Every environment is diff.
- Internal/external.
- # and type of users.
- Revenue generating app.
- Potential for exploit.
Industry/Organizational Impact
Some exploits have significant consequences.
The type of organization is important consideration
Risk Tolerance
The amount of risk acceptable for an organization.
Patch testing takes time.
- You're vulnerable while testing.
There's middle ground.
- May change based on the severity.
Patching
Most common mitigation technique.
Can be scheduled monthly, quarterly, etc.
Can be unscheduled patches.
- Zero day, often urgent.
Insurance
Cybersecurity insurance coverage.
- Lost revenue.
- Data recovery costs.
- Money lost to phishing.
- Privacy lawsuit costs.
Doesn't cover everything.
- Intentional acts, fund transfers, etc.
Ransomware has increased the popularity of cybersecurity insurance.
Segmentation
Separate devices into their own networks/VLANs.
- Limit the scope of an exploit.
Use internal NGFWs.
- Block unnecessary traffic between VLANs.
Physical Segmentation

Logical Segmentation with VLANs
Cannot communicate between VLANs without a layer 3 device/router connecting the VLANs.
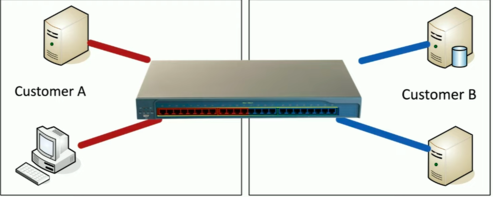
Compensating Controls
Optimal security methods may not be available.
- Can't patch, no firewalls.
Compensate in other ways:
- Disable the problematic service.
- Revoke access to the app.
- Limit external access.
- Modify internal security controls and software firewalls.
Exceptions and exemptions
Removing the vulnerability is optimal.
- Not everything can be patched.
Maintain uptime by providing but service, but also protect the data and systems.
Not all vulnerabilities share the same severity.
An exception may be an option
- usually a formal process to approve.
- Not made by one individual, usually made by a group.
Validation of Remediation
Okay you patched - did it really stop the exploit?
Rescan to confirm.
Audit to make sure the patch was successfully deployed.
Verification
- manually confirm the security of the system.Okay you patched - did it really stop the exploit?
Rescan to confirm.
Audit to make sure the patch was successfully deployed.
Verification
- manually confirm the security of the system.
Reporting
Ongoing checks for vulnerabilities and patches.
Difficult or impossible to manage without automation.
Since there are many different types of apps, vulnerabilities, and patches, you'll need continuous reporting on:
- # of identified vulnerabilities.
- Systems patched vs unpatched.
- New threat notifications.
- Errors, exceptions, and exemptions.
4.4
4.4
Security Monitoring
Needed 24/7 365 days per year.
Monitor all entry points.
React to security events.
Status dashboards.
- Get the status of all systems at a glance.
Monitoring Computer Resources
Systems:
- Authentication - logins from strange places.
- Server monitoring (backups, software versions).
Apps:
- Availability - uptime/response times.
- Data transfers - increases or decreases in rates.
- Security notifications from developer/manuf.
Infrastructure:
- Remote access systems.
- Firewall and IPS reports.
- if there's an increase in a type of attack.
SIEM/SEM Tools
Allows you to consolidate many different logs to a central database and have centralized reporting.
- Allows you to grab files from servers, firewalls, VPN concentrators, SANs, cloud services and bring that back to the central database.
Because logs go into the database, you can then correlate data between diverse systems.
- View authentication and access.
- Track app access.
- Measure and report on data transfers.
Scanning
A constantly changing threat landscape.
- New vulnerabilities discovered daily.
Actively check systems and devices.
- OS types and versions.
- Device driver versions.
- installed apps.
- Potential anomalies.
Reporting
Analyzing and collecting data
- creating "actionable" reports.
Status information:
- Number of devices up to date/in compliance.
- Devices running older operating systems.
Determine best next steps.
Ad hoc information summaries.
- Hypothetical scenarios.
- Prepare for the unknown.
Archiving
Access to data is critical.
- Archive over an extended period.
May be mandated by state or federal law
- or organizational requirements.
Alerting
Real-time notification of security events.
Notification methods:
- SMS/text.
- Email.
- Security console/SOC.
Alert Response and Remediation
Quarantine the system.
- Prevent further access.
Alert tuning - Prevent false positives and negatives.
SCAP (Security Content Automation Protocol)
Managed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST framework).
Allows tools to identify and act on the same criteria. - Scans, patch installs, etc.
Using SCAP
SCAP content can be shared between tools to help with automation and detect applications with known vulnerabilities.
Ex: Scanner sends system info to management system, management system patches it automatically.
Especially useful within large environments with lots of devices and you need to patch a lot of different vulnerabilities across multiple operating systems.
Enables automation.
Automation types:
- Ongoing monitoring.
- Notification and alerting.
- Remediation of noncompliant systems.
Benchmarks
Apply security best-practices to everything.
Agents/Agentless
Check to see if the device is in compliance.
agent = install a software on the device.
- agentless = run on demand checks.
Agents:
- Usually provide more detail.
- Always monitoring.
- Must be maintained and updated.
Agentless:
- Runs without a formal install.
- Performs the check, then disappears.
- Does not require updates.
- Will not inform if not running.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
A system that can identify critical data, monitor how it is being accessed, and protect it from unauthorized users.
Stop the data before the attacker gets it.
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol.
A database of data - a management information base.
Poll devices over udp/161
- at fixed intervals.
Request statistics from a device like a router, switch, etc.
- device responds.
SNMP Traps
Communicates over udp/162.
Sets threshold for alerts by acting as alert messages sent from a remote SNMP enabled device to a central collector.
- Monitoring station can react immediately.
NetFlow
Gathers traffic statistics from all traffic flows.
Standard collection method
- many products and options.
- Can be built into software of network devices or sep device.
- Can connect to the network via monitoring port or tap.
A probe and collector.
- Probe watches network communication, summary records are sent to NetFlow collector.
Vulnerability Scanners
Minimally Invasive.
Can port scan.
Identify systems.
Will test from the outside and inside.
Gathers as much info as possible.