C4 - Chemical Changes
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Reactivity series
Potassium
Sodium
Lithium
Calcium
Magnesium
Aluminium
Carbon
Zinc
Iron
Tin
Lead
Hydrogen
Copper
Silver
Gold
Platinum
*carbon and hydrogen are not metals but are a useful comparison
Displacement Reaction
Occurs when a more reactive metal displaces (kicks out) a less reactive metal from a compound
Most metals react with acids to produce what?
A salt and hydrogen
Metal carbonates react with acids to produce what?
A salt, carbon dioxide and water
Group 1 metals are more reactive than hydrogen, so they displace it to form what?
Hydrogen gas and a metal hydroxide
What can we use displacement reactions for?
Extracting metals from their ores by displacing with a more reactive, less valuable metal
Oxidation
Loss of electrons
Reduction
Gain of electrons
acid + alkali →
salt + water
Using sulphuric acid results in what type of salt?
Metal sulphate salt
Using nitric acid results in what type of salt?
Metal nitrate salt
When an acid and an alkali are reacted together the salt produced is left in solution, which means that we have a mixture of dissociated ions. How can we obtain crystals of salt?
By gently heating and evaporating the water, leaving behind the salt crystals
Why does an acid have a pH < 7?
Due to its H+ ions
Why does an alkali have a pH > 7?
Due to its OH- ions
A neutral substance has what?
An equal number oh H+ and OH- ions
A change in 1 pH is equal to what?
A 10x change in concentration of H+ or OH- ions
A strong acid dissociates more completely. If at the same concentration, it will have a lower/higher? pH than a weak acid
lower
Examples of strong acids
Hydrochloric
Sulphuric
Nitric
Examples of weak acids
Ethanoic
Citric
Carbonic
Electrolysis
Involves passing an electrical current through a substance to cause oxidation and reduction at the anode and cathode
Electrolysis can only happen when ions are …
Free to move
In ionic compounds in what state must it be in for electrolysis
Molten or in solution
What can electrolysis be used for?
To obtain pure metals from a compund/ore
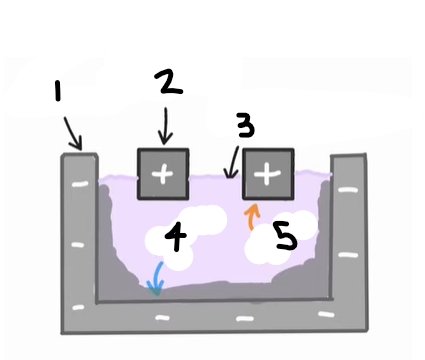
1?
Anode (graphite)
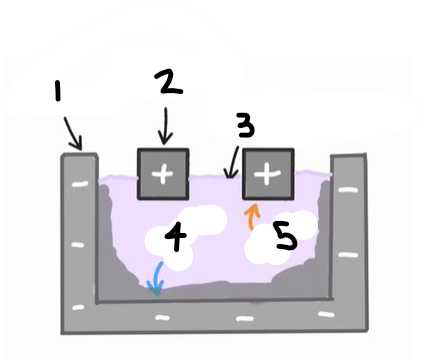
2?
Cathode
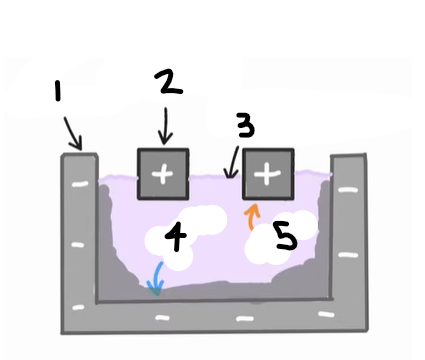
3?
Cryolite and aluminium oxide
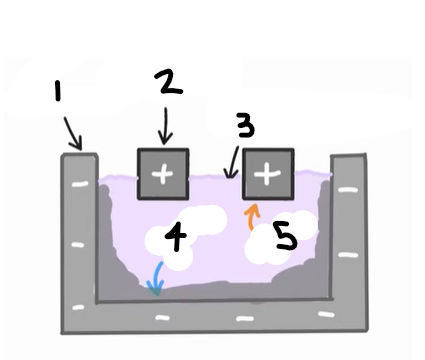
4?
The positive ions e.g. Al3+ are attracted to the cathode, where they are reduced
Al3+ (l) + 3e- → Al (l)
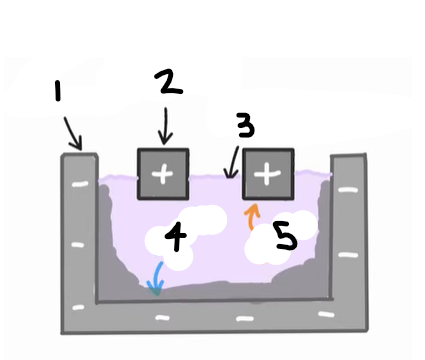
5?
The negative ions e.g. O2- are attracted to the anode, where they are oxidised
2O2- (l) → O2 (g) + 4e-
Oxygen reacts with carbon in the anodes to produce CO2 , this means what?
They need to be replaced periodically
Why is cryolite added to electrolysis with molten compounds?
Lowers the melting point of the aluminium oxide - cheaper
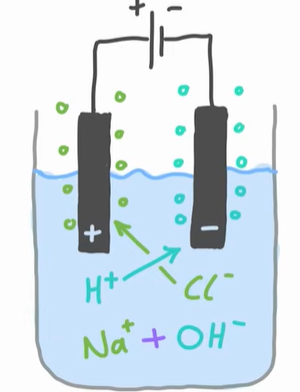
What is happening with the H+ ions?
H+ ions are less reactive than Na+ ions, so they move to the cathode to be reduced
2H+ (aq) + 2e- → H2 (g)
The more reactive cation (positive ion) remains in solution while the less reactive one is reduced at the cathode
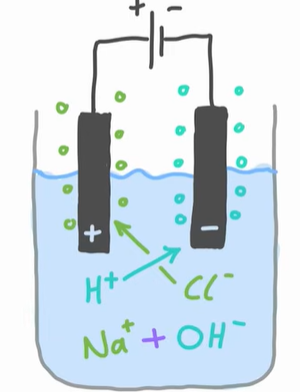
What happens to halide ions (F-, Cl-, Br-)
They are always oxidised at the anode. If the anion (negative ion) isn’t a halide, the oxygen is oxidised instead and oxygen gas is produced
2Cl(aq) → Cl2 (g) + 2e-