CDC Draccunculiasis
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Guinea worm disease
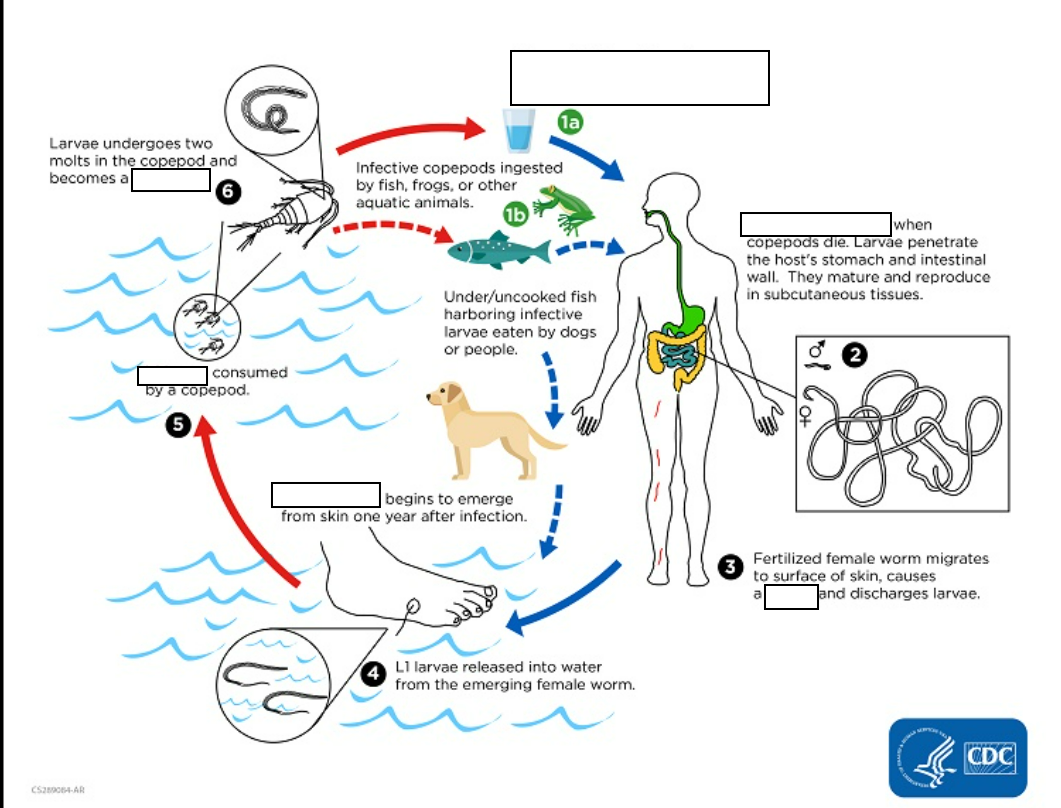
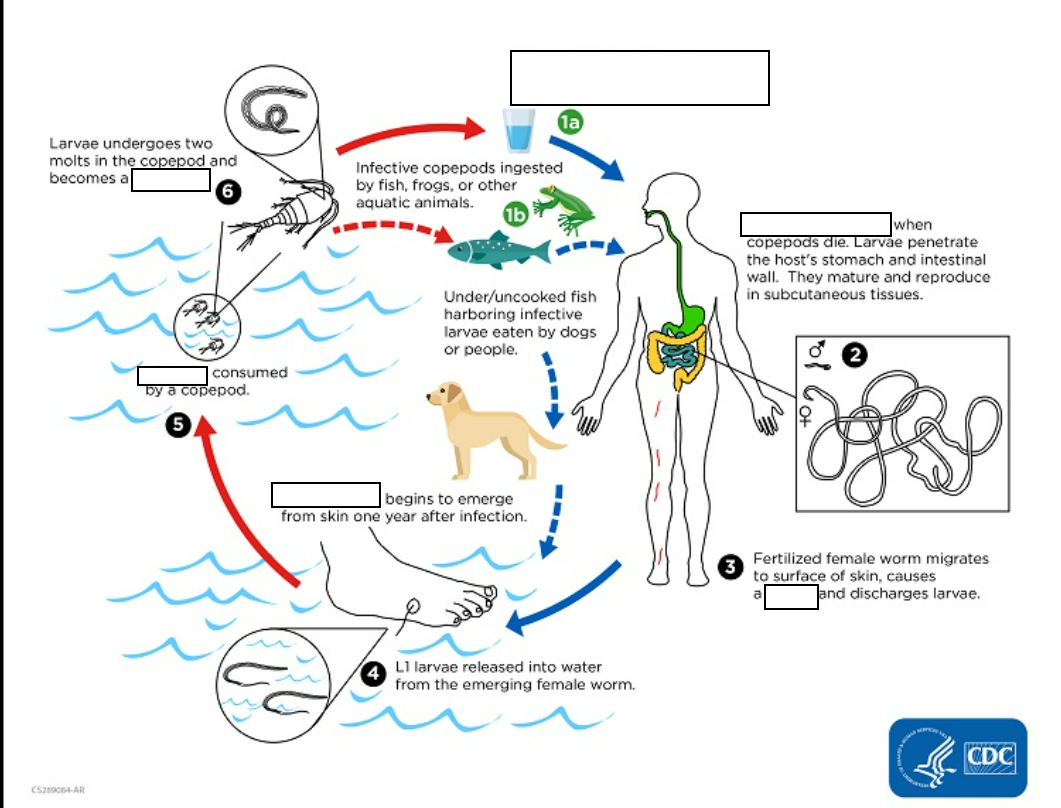
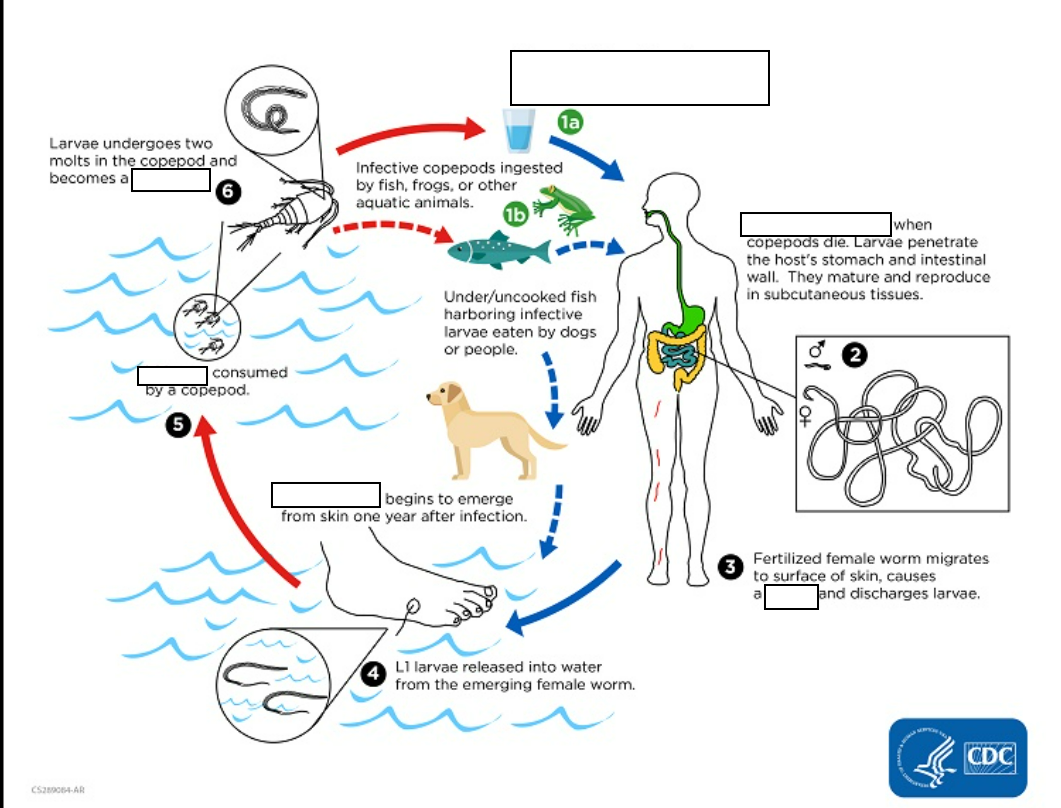
Dracunculiasis (_____________)is caused by the nematode (roundworm) Dracunculus medinensis.

unfiltered water containing copepods
Humans become infected by drinking (small crustaceans) which are infected with larvae of D.
medinensis
die
(1) Following ingestion, the copepods ________and release the larvae, which penetrate the host stomach and intestinal wall and enter the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space
subcutaneous tissues
(2) After maturation into adults and copulation, the male worms die and the females (length: 70 to 120 cm) migrate in the _____________ towards the skin surface
blister on the skin
(3) Approximately one year after infection, the female worm induces a _________, generally on the distal lower extremity, which ruptures.
emerges and releases larvae
When this lesion comes into contact with water, a contact that the patient seeks to relieve the local discomfort, the female worm _______________.
two weeks
(4) The larvae are ingested by a copepod and after_ (and two molts) have developed into infective larvae Ingestion of the copepods closes the cycle
African countries
An ongoing eradication campaign has dramatically reduced the incidence of dracunculiasis, which is now restricted to rural, isolated areas in a narrow belt of ___________________.
whitish filament
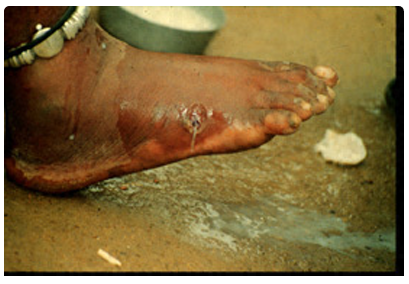
The clinical manifestations are localized but incapacitating. The worm emerges as a ________(duration of emergence: 1 to 3 weeks) in the center of a painful ulcer, accompanied by inflammation and frequently by secondary bacterial infection.
serologic test
The clinical presentation of dracunculiasis is so typical, and well known to the local population, that it does not need laboratory confirmation. In addition, the disease occurs in areas where such confirmation is unlikely to be available. Examination of the fluid discharged by the worm can show rhabditiform larvae. No _________ is available
L3 Larvae
(6)
L1 Larvae
(5) (4)
Human drinks unfiItered water containing copepods with L3 larvae.
1a
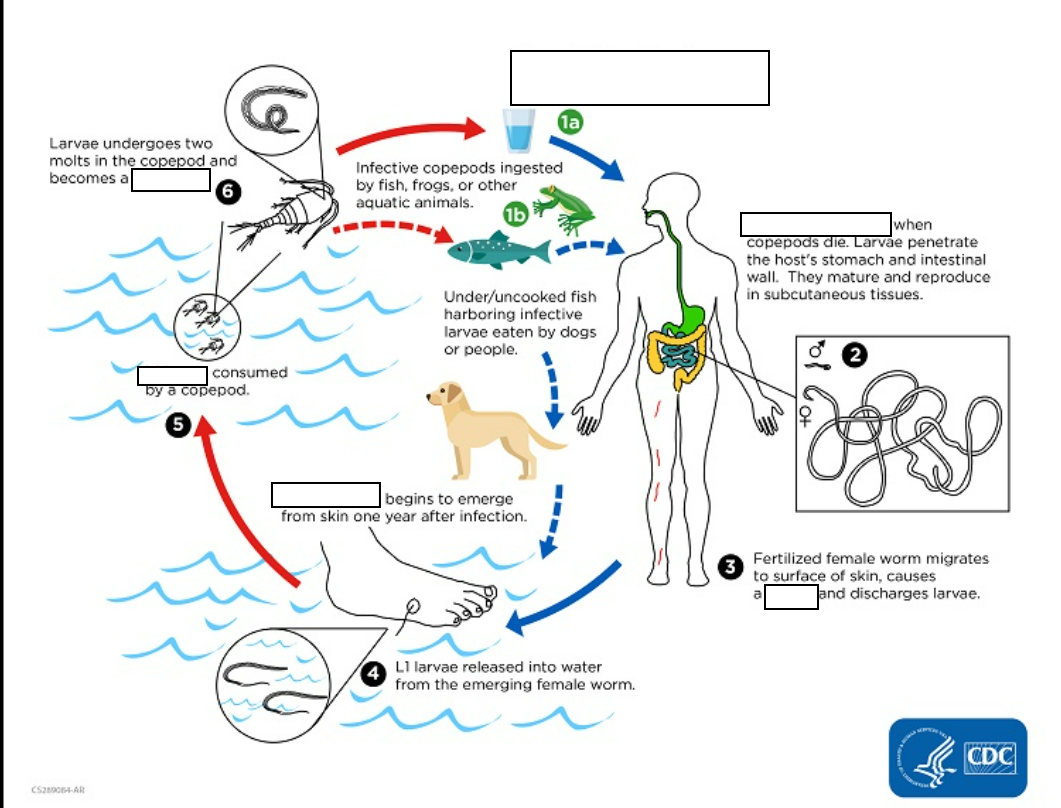
larvae are released
when copepod die