Earth in Space Slide 8
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Troposphere
Lowest Layer. Where most weather occurs.
Stratosphere
Layer above the troposphere, contains the ozone layer and is where jets typically fly.
Mesosphere
Layer above the stratosphere. Coldest layer with temperatures dropping to -90C
Thermosphere
Layer above the mesosphere, characterized by high temperatures and the presence of ionized gases.
Exosphere
The outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere, extending into space, where atmospheric particles are very sparse and satellites orbit.
Air Pressure
The force exerted by the weight of air molecules above a given point, decreasing with altitude.
Heat
Energy that causes an increase in temperature, transferring from warmer to cooler objects.
Temperature
A measure of the average kinetic energy of particles in a substance, indicating how hot or cold it is.
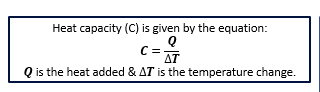
Heat Capacity Equation
Q is the heat added and T is the change in temperature.
Conduction
The process by which heat energy is transferred through direct contact between materials, allowing thermal energy to flow from hotter to cooler areas.
Convection
The transfer of heat through the movement of fluids (liquids or gases) caused by differences in temperature and density.
Radiation
The transfer of heat energy through electromagnetic waves, allowing energy to move through a vacuum or across space without the need for a medium.