CompTIA A+ Part 2 CORE 1 (Information)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Network Interface Card (NIC)
Adapter card that provides one or more Ethernet ports for connecting hosts to a network so that they can exchange data over a link.
Serial Attached SCSI Small Computer System Interface (SAS)
Another interface used for high-performance storage devices, often in enterprise environments. The drives offer faster data transfer rates and better reliability compared to SATA drives. It connects multiple devices to a single controller using a point-to-point serial protocol, enabling high-speed data access and robust performance. They are commonly used in servers and workstations.
CD Capacity
Up to 700 MB
DVD Capacity
4.7 GB (single-layer, single-sided) to about 17 GB (dual-layer, double-sided)
Blu-ray
25 GB per layer
Data Pathway
Determines the amount of information transferred per clock cycle. In a single channel memory controller, this bus is typically 64 bits wide.
Address Pathway
Determines the number of memory locations the CPU can track, thus limiting the maximum physical and virtual memory.
A 32-bit CPU with a 32-bit address bus can access up to ___________.
_______________________ 4 GB of memory.
A 64-bit CPU could theoretically use a 64-bit address space (16 exabytes), but most use a 48-bit address bus, allowing up to ___________.
_______________________ 256 terabytes of memory.
Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
Stores data bits as electrical charges in bit cells made of capacitors, that hold a charge, and transistors, that read the capacitor's contents. A charged capacitor represents 1, non-charged represents 0.
Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM)
Synchronized to the system clock, ensuring that memory operations are timed with the CPU's instructions.
Single-channel
Features one 64-bit data bus between the CPU, memory controller, and RAM, which can limit data transfer rates.
Dual-channel
Utilizes two 64-bit pathways, allowing 128 bits of data per transfer, effectively doubling the data bandwidth. This requires support from the CPU, memory controller, and motherboard, but not from the RAM modules themselves. Ordinary RAM modules are used; there are no specific "_______" DDR memory modules.
Flex Mode
The system might enable dual-channel mode but disable the spare module, effectively ignoring the additional memory.
Triple-Channel Memory and Quadruple-Channel Memory
A memory architecture that utilizes memory channels to increase data transfer rates between the CPU and RAM. This configuration allows for simultaneous data access across the channels, effectively doubling the bandwidth compared to single-channel memory. The amount of memory channels is mentioned in the names.
DDR5 introduces a _____________.
_____________ new data bus architecture.
Error correction code (ECC)
It can detect and correct single-bit memory errors, preventing data corruption and system crashes. It can also detect (but not correct) multi-bit errors, generating an error message and halting the system if such an error occurs.
X86 CPU Architecture
Supports both 32-bit (IA-32) and 64-bit instruction sets
X64 CPU Architecture
The 64-bit extension of the x86 architecture. This extension allows CPUs to handle 64-bit instructions, data paths, and memory addressing, enabling access to more than 4 GB of RAM. 64-bit CPUs can run both 32-bit and 64-bit software, whereas 32-bit CPUs cannot run 64-bit software.
ARM (Advanced RISC Machines)
Provide CPU designs that are customized and manufactured by companies like Qualcomm, Nvidia, Apple, and Samsung. A typical ____ design implements a system-on-chip (SoC), integrating components like video, sound, networking, and storage controllers into the CPU, making ____ ideal for mobile and fan-less devices due to its power efficiency and compact size.
ARM's architecture is based on ______________.
______________ Reduced Instruction Set Computing (RISC), which uses simpler, more efficient instructions compared to the Complex Instruction Set Computing (CISC) architecture used in x86/x64 CPUs from Intel and AMD.
While RISC may require more instructions to perform certain tasks, _____________________.
_____________________, each instruction typically completes in a single clock cycle, allowing for better performance-per-watt and increased battery life.
Simultaneous multithreading (SMT)
Allows multiple instruction streams (threads) from software applications to be processed concurrently, reducing CPU idle time and enhancing performance in multithreaded applications.
Land Grid Array (LGA) Sockets
The pins are located on the motherboard socket, and the CPU has contact pads.
LGA 1200
Used for the 10th and 11th generation Core processors, offering compatibility with Intel's Comet Lake and Rocket Lake CPUs.
LGA 1700
Designed for the 12th generation Alder Lake CPUs, supporting Intel's latest architecture improvements.
LGA 3647
For older Xeon Scalable models
Trusted-Platform-Module (TPM)
Hardware that securely stores digital certificates, cryptographic keys, and hashed passwords.
Power-On Self-Test (POST)
A diagnostic program implemented in the system firmware that checks the hardware components required to boot the computer.
Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology(S.M.A.R.T.)
Can alert the operating system if a failure is detected.
Real-Time Clock (RTC)
Powered by a coin-cell lithium battery (usually CR2032) when the computer is off.
CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor) RAM
The battery mainly supports the RTC in older systems stored settings.
NVRAM (non-volatile random-access memory)
Or flash memory for configuration data, so the battery mainly supports the RTC. Used in Modern systems.
100BASE-T
Refers to Fast Ethernet over copper twisted pair cabling. Fast Ethernet works at 100 Mbps.
1000BASE-T
Refers to Gigabit Ethernet over copper twisted pair cabling. Gigabit Ethernet works at 1000 Mbps (or 1 Gbps). It is the mainstream choice of standard for most LANs.
10GBASE-T
Refers to a copper cabling standard working at 10 Gbps.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
Spans multiple geographic locations. One example of a _____ is the Internet, a global network of networks.
Wireless-Local-Area-Network (WLAN)
Uses radios and antennas for data transmission and reception. Most ______ are based on the IEEE 802.11 series of standards. IEEE 802.11 is better known by its brand name, Wi-Fi.
Metropolitan-Area-Network (MAN)
Can be used to mean a specific network type covering an area equivalent to a city or other municipality. It could mean a company with multiple connected networks within the same metropolitan area.
Local-Area-Network (LAN)
A group of computers connected by cabling and one or more network switches that are all installed at a single geographical location. A _____ might span a single floor in a building, a whole building, or multiple nearby buildings (a campus). Any network where the nodes are within about 1 or 2 km (or about 1 mile) of one another can be thought of as "local."
Personal-Area-Network (PAN)
Refers to using wireless connectivity to connect to devices at a range of a few meters. A _____ can be used to share data between a PC and mobile devices and wearable technology devices, such as smartwatches.
Storage Area Network (SAN)
Refers to a specialized network that is dedicated to storage devices. Servers can connect to the storage devices as if they are directly attached.
Key characteristics of a SAN include:
________
________
________
________
Key characteristics of a _____ include:
Dedicated Network
Block-Level Access
Consolidated Storage
High Speed
Small-Office-Home-Office (SOHO) LAN
A small network possibly using a centralized server, in addition to client devices and printers, but often using a single networking appliance to provide LAN and Internet connectivity.
Power-over-Ethernet (PoE)
A means of supplying electrical power from a switch port over ordinary data cabling to a powered device (PD), such as a voice over IP (VoIP) handset, camera, or wireless access point.
802.3af (Type 1 PoE or 2-pair PoE)
Allows powered devices to draw up to about 13 W. Power is supplied as 350mA@48V and limited to 15.4 W, but the voltage drop over the maximum 100m (328 feet) of cable results in usable power of around 13 W.
802.3at (PoE+ or Type 2 PoE)
llows powered devices to draw up to about 25 W, with a maximum current of 600 mA.
802.3bt (PoE++, Type 3 and Type 4 PoE, 4PPoE)
Supplies up to about 51 W (Type 3) or 73 W (Type 4) usable power.
Unshielded-Twisted-Pair(UTP)
A _____ cable consists of four copper conductor wire pairs. Each pair of insulated conductors is twisted at a different rate from the other pairs, which reduces interference. The electrical signals sent over each pair are balanced. This means that each wire carries an equal but opposite signal to its pair. Strong at standing out in the midst of interference but suffers from attenuation over long ranges.
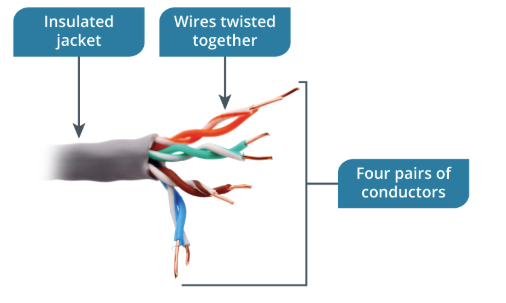
Shielded-Twisted-Pair (STP)
Provides extra protection against interference. _____ cables are typically a requirement in environments with high levels of external interference, such as cable that must be run in proximity to fluorescent lighting, power lines, motors, and generators.