Microbiology Exam 2
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
chapter 6,7,&8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
All cells need to accomplish two fundamental tasks?
synthesize components for growth
produce/convert energy for biochemical reactions
metabolism
sum total of all chemical reactions in a cell
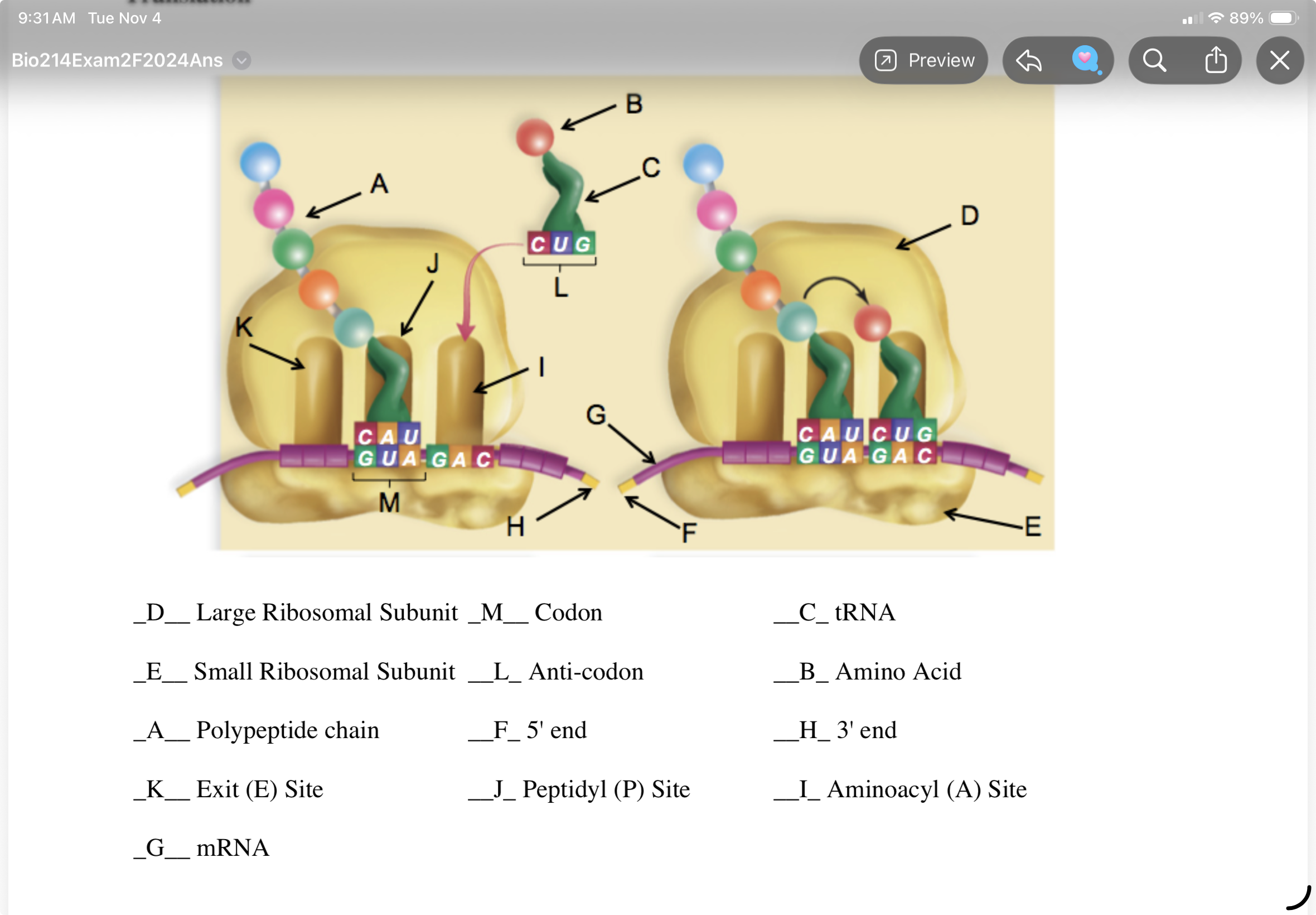
what is the product of translation?
protein
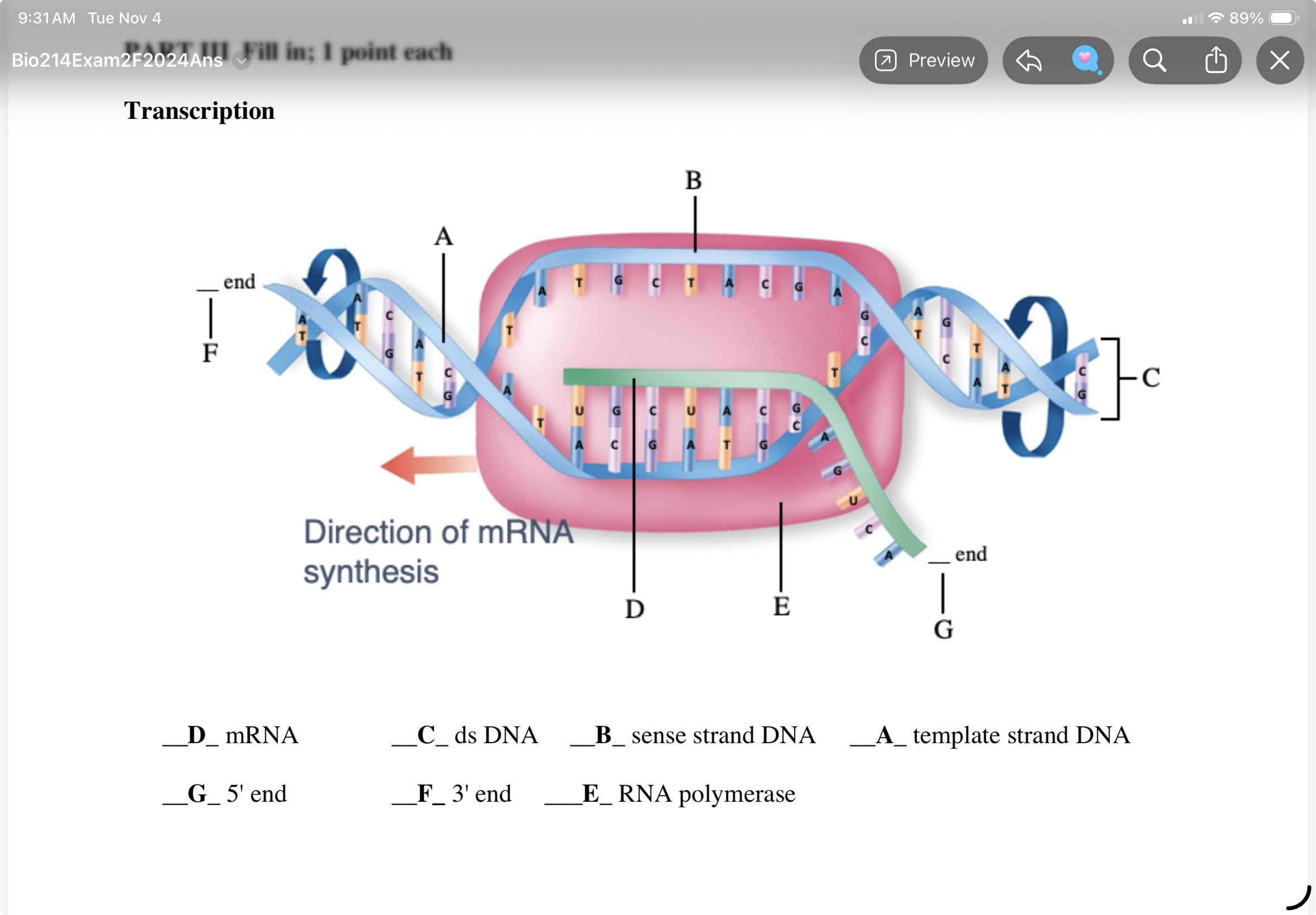
what is the product of transcription?
RNA
If an mRNA codon reads 5' UAC 3', its complementary anticodon will be (read 5' to 3')
GUA
The building blocks of DNA are callled?
Nucleotides
For the mRNA shown, at which codon will translation likely begin?
5′ GCCGGAAUGCUGCUGGC 3'
AUG
To turn genes off, a regulatory protein called a(n) __________ is bound to the operator site so that
RNA polymerase is blocked from transcribing further
Repressor
RNA Polymerase transcribes which strand of DNA?
1.Template strand
Antisense strand
The 3' end of DNA?
1.refers to the end that has a hydroxyl group attached to the number 3 carbon of deoxyribose.
2. attaches to the 5' phosphate group of the incoming nucleotide.
If 18% of nucleotides in an organism's DNA are guanine (G). What is the percent represented by
thymine (T)?
32%
The scientist(s) that located the gene on the chromosome was?
Thomas Hunt Morgan
The lac operon is NOT transcribed in the presence of glucose because?
The CAP protein does not bind to the CAP DNA binding site.
The lac repressor is a(n)?
protein molecule
The term antiparallel
refers to the opposite orientation of the two strands in DNA.
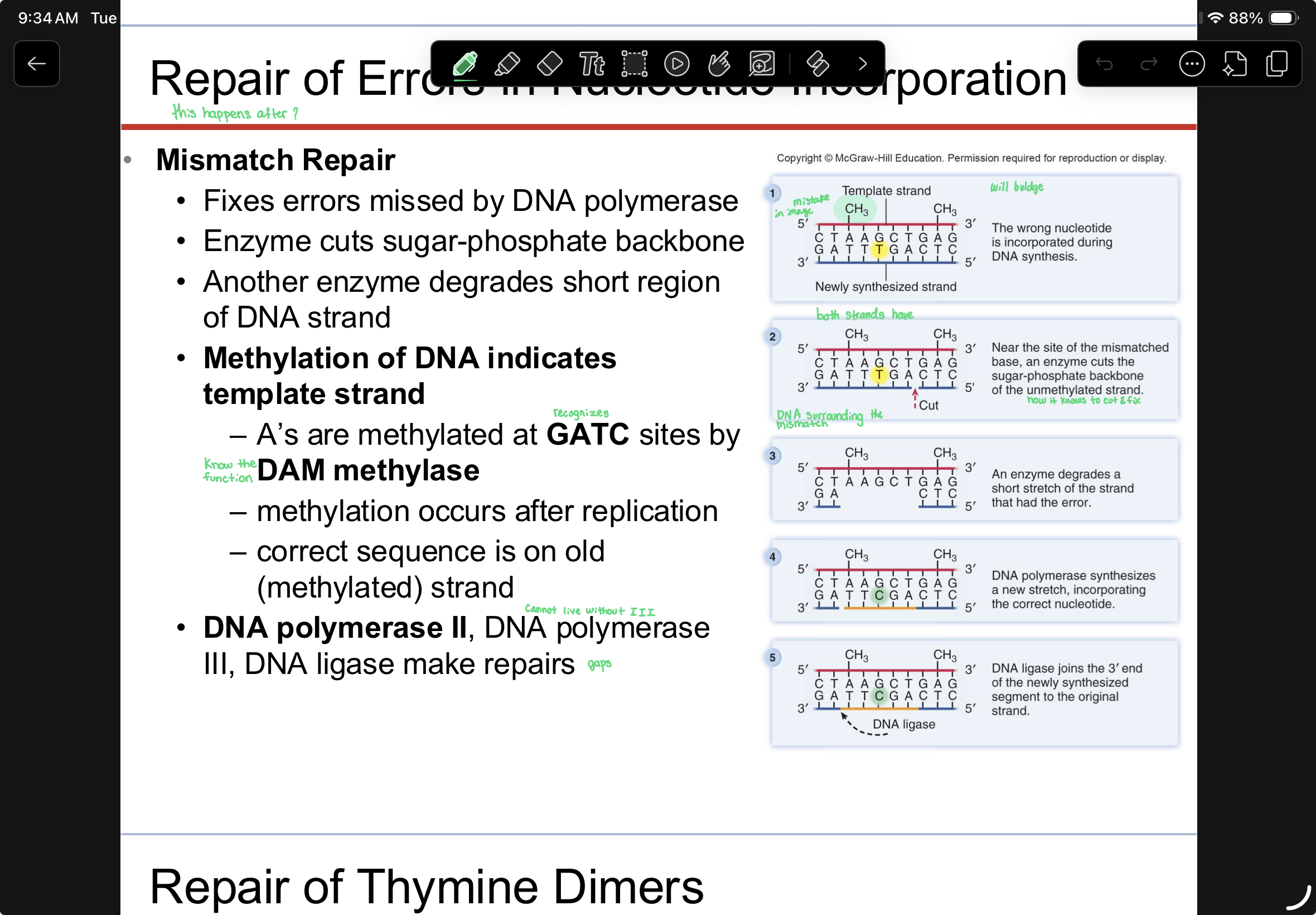
Repair mechanism that occurs during DNA synthesis is?
proofreading by DNA Polymerase.
An F pilus is essential for?
plasmid transfer by conjugation.
A culture of E. coli is irradiated with ultraviolet (UV) light. The UV light specifically
forms covalent bonds between thymine nucleotides (thymine dimers) on the same strand of
DNA
Segments of DNA capable of moving from one area of the DNA molecule to another are called?
transposons
A silent DNA mutation?
has no effect on the activity of the coded protein
X-rays
cause single and double strand breaks in DNA molecules.
Repair mechanism that occurs after DNA replication is?
1.mismatch repair
light repair
SOS repair
Antibiotic resistance genes are commonly found on?
Plasmids
The genetic makeup that controls specific characteristics of an organism is its?
Genotype
What enzyme is responsible for adding methyl (CH3) groups to newly synthesized strands of DNA?
DAM methylase
Intercalating agents like Ethidium Bromide mutate DNA by?
inserting in between base pairs of a strand of DNA.
All proteins are coded for by genes but not all genes code for proteins.
True
In eukaryotes transcription and translation are occurring simultaneously.
False
Transposons were first discovered by Barbara McClintock through her work with corn.
True
Each strand of the DNA double helix is identical to the other.
False
In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, the ribosome is composed of a small and a large subunit.
True
Galactose binds the lac repressor and inhibits transcription of the lac operon.
False
Organisms termed his- are considered prototrophic for histidine.
False
During E. coli conjugation the F plasmid moves from the F+ bacteria to the F- bacteria without
replication.
False
A deletion of one nucleotide within a gene, results in a frame shift mutation.
True
Environment causes and selects mutants that grow under its conditions.
False
After two weeks of taking fecal samples of 50 piglets, what did the piglets do as soon as Pete
entered their pen?
The piglets defecated.
Describe mismatch repair in E. coli. How does the system recognize the correct base. What enzymes are
involved.
A gene has the following DNA sequence (coding strand is shown):
5' 3'
GGGCTATATGTCTGACGAGCTTCTATATGGGAGAAAGCCAGTATTCTCGCTTATCGTGTAATCCTC
What is the sequence of the mRNA?
5' GGGCUAUAUG UCU GAC GAG CUU CUA UAU GGG AGA AAG CCA GUA UUC
UCG CUU AUC GUG UAAUCCUC 3'
What is the amino acid sequence of the protein (use the codon table below)?
met ser asp glu leu leu tyr gly arg lys pro val phe ser leu ile val
Assuming that each amino acid has a molecular weight (MW) of 120, what is the MW of the
protein.
120 x 17 = 2040 MW
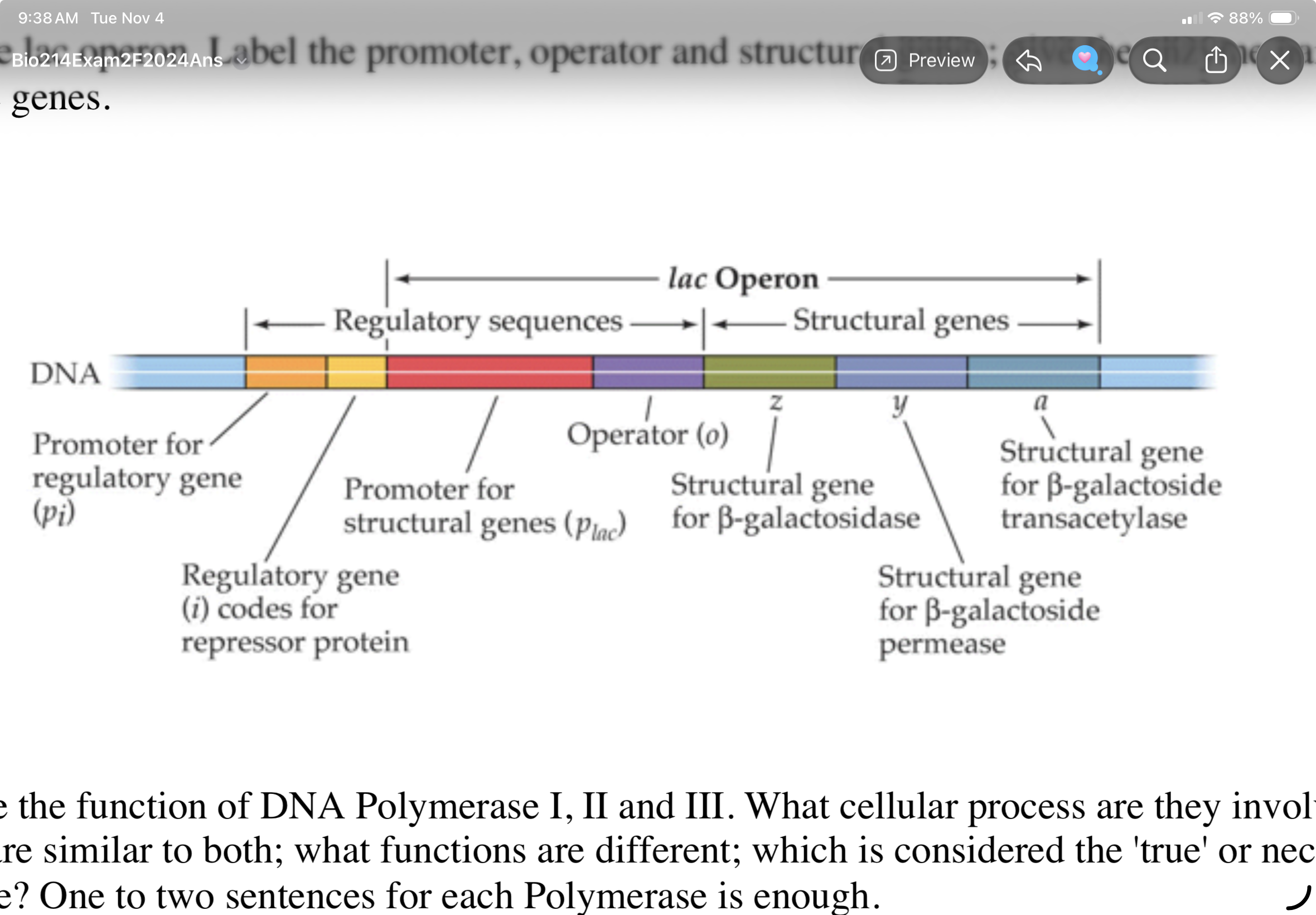
Draw the lac operon. Label the promoter, operator and structural genes; give the enzyme name for
each of the genes.
Describe the function of DNA Polymerase I, II and III. What cellular process are they involved in; what
functions are similar to both; what functions are different; which is considered the 'true' or necessary DNA
Polymerase? One to two sentences for each Polymerase is enough.
DNA Polymerase I - adds complementary nucleotides to the growing DNA strand during DNA
replication primarily on the lagging strand. It removes the RNA primer and replaces it with DNA. It
has proofreading activity.
DNA Polymerase II - It's primary functions is to fill in the gap created by enzymes during
Mismatch Repair.
DNA Polymerase III - adds complementary nucleotides to the growing DNA strand in the 5' to 3'
direction during DNA replication. It cannot start DNA synthesis de novo and cannot remove the
RNA primer. It has proofreading activity. This is the main and necessary ('true') DNA Polymerase.
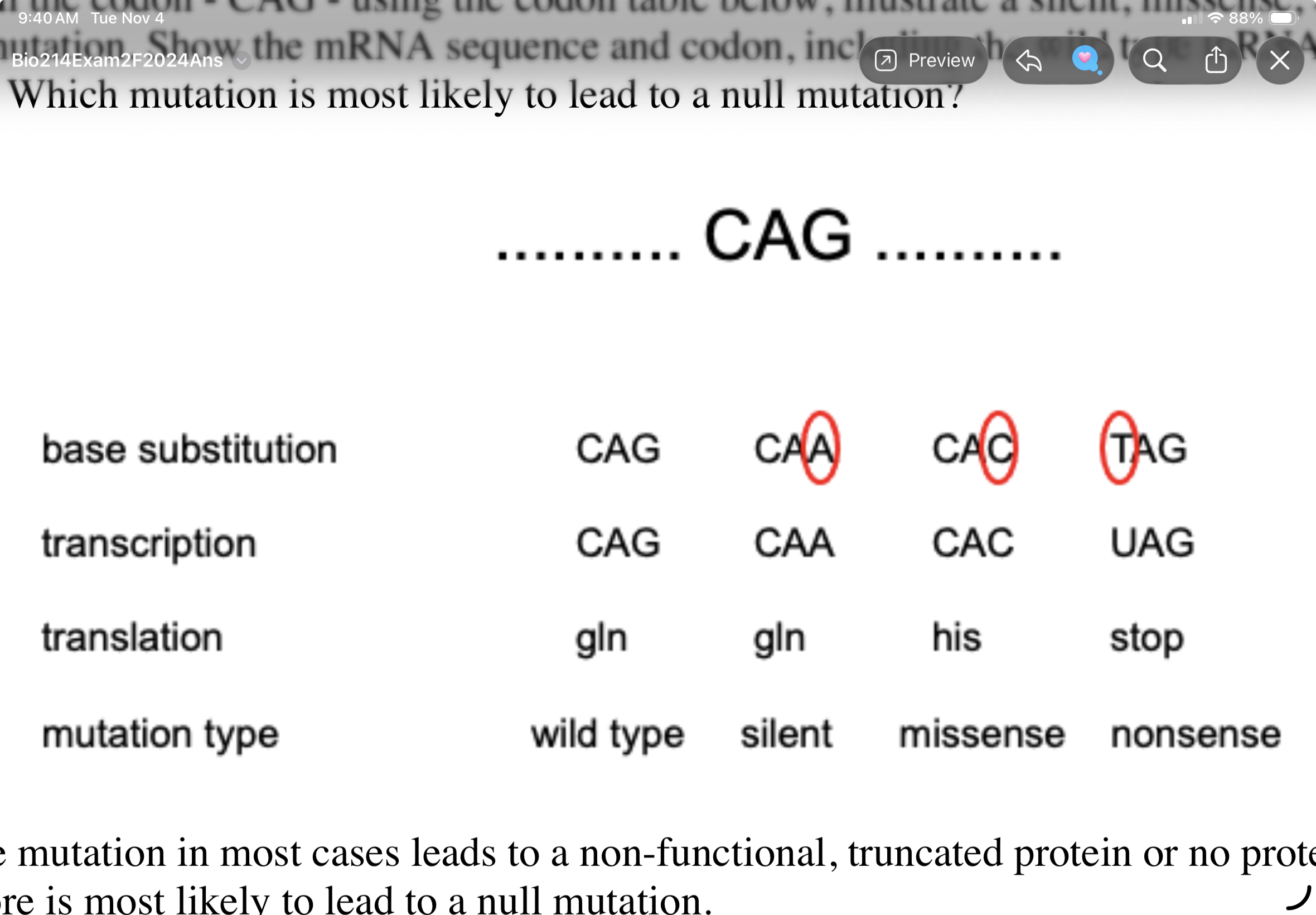
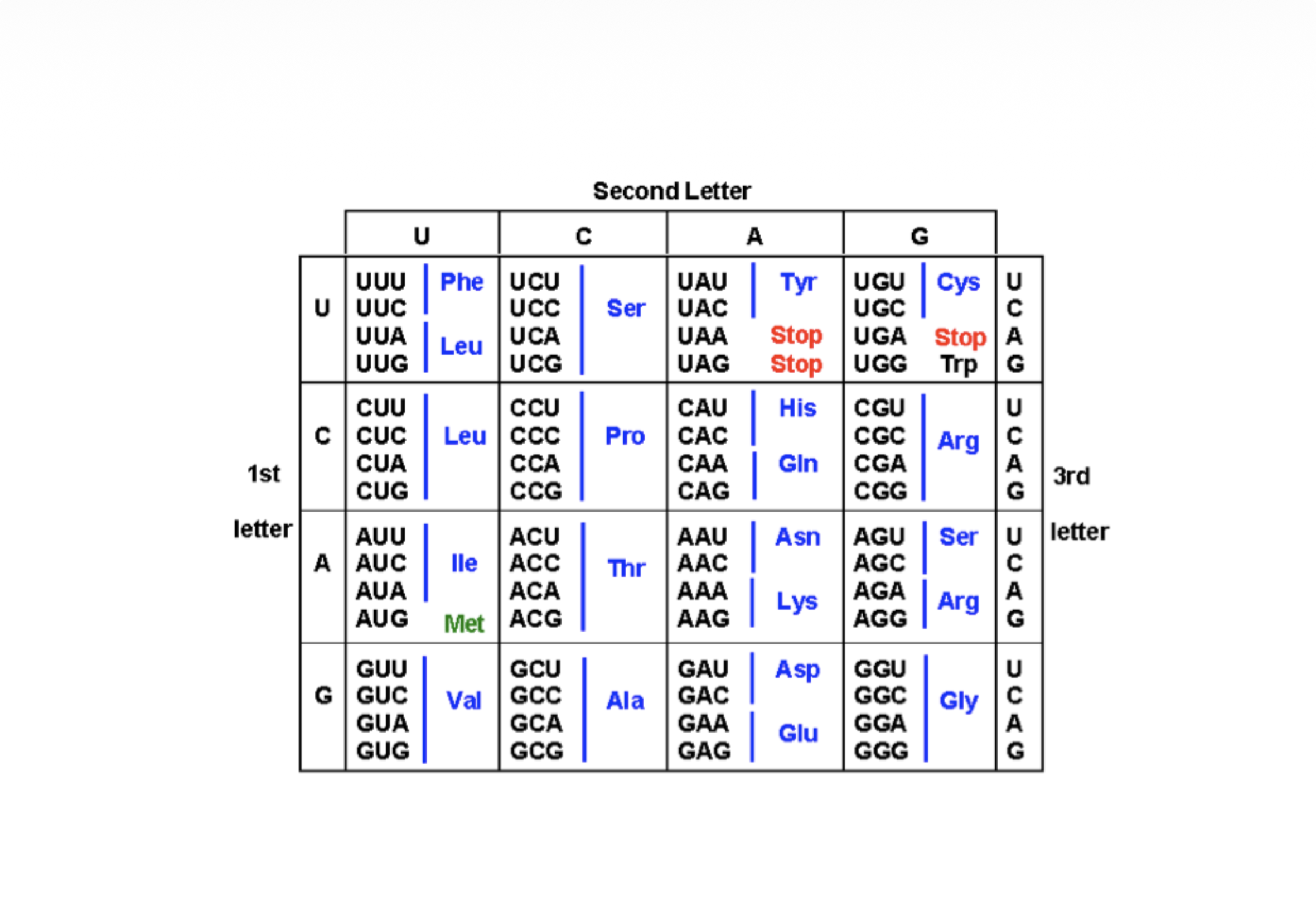
Start with the codon - CAG - using the codon table below, illustrate a silent, missense, and
nonsense mutation. Show the mRNA sequence and codon, including the wild type mRNA sequence
and codon. Which mutation is most likely to lead to a null mutation?
A nonsense mutation in most cases leads to a non-functional, truncated protein or no protein at all
and therefore is most likely to lead to a null mutation.
What is the function of the bacterial sigma factor. Give one example of how either E. coli or B.
subtilis uses sigma.
The sigma factor is a protein that loosely binds to the RNA Polymerase and allows RNA
Polymerase to recognize specific classes of promoters, thereby controlling a set of specific genes. E.
coli will use σ70 for normal/healthy growth conditions and will switch to σ32 under heat shock
conditions. B. subtilis with use σA for normal/healthy growth conditions and then will switch to σE
and σK under stress conditions to transcribe genes needed for sporulation
catabolism
breaks down of compounds to release energy- large molecules are broken down into smaller molecules for energy to be released
cells capture energy to synthesize ATP
energy source is glucose
creates waste products ex. acids&carbon dioxide
Energy is released when breakdown occurs of compounds and ATP & uses it to make ATP
anabolism
biosynthetic process- small molecules are assembled into bigger ones, but energy is requires for this process
assemble subunits to make macromolecules
uses ATP to drive reactions, processes intimately linked
creates nutrients ex. sulfur&source of nitrogen
The processes use the ATP & precursor metabolites-glucose produced in catabolism
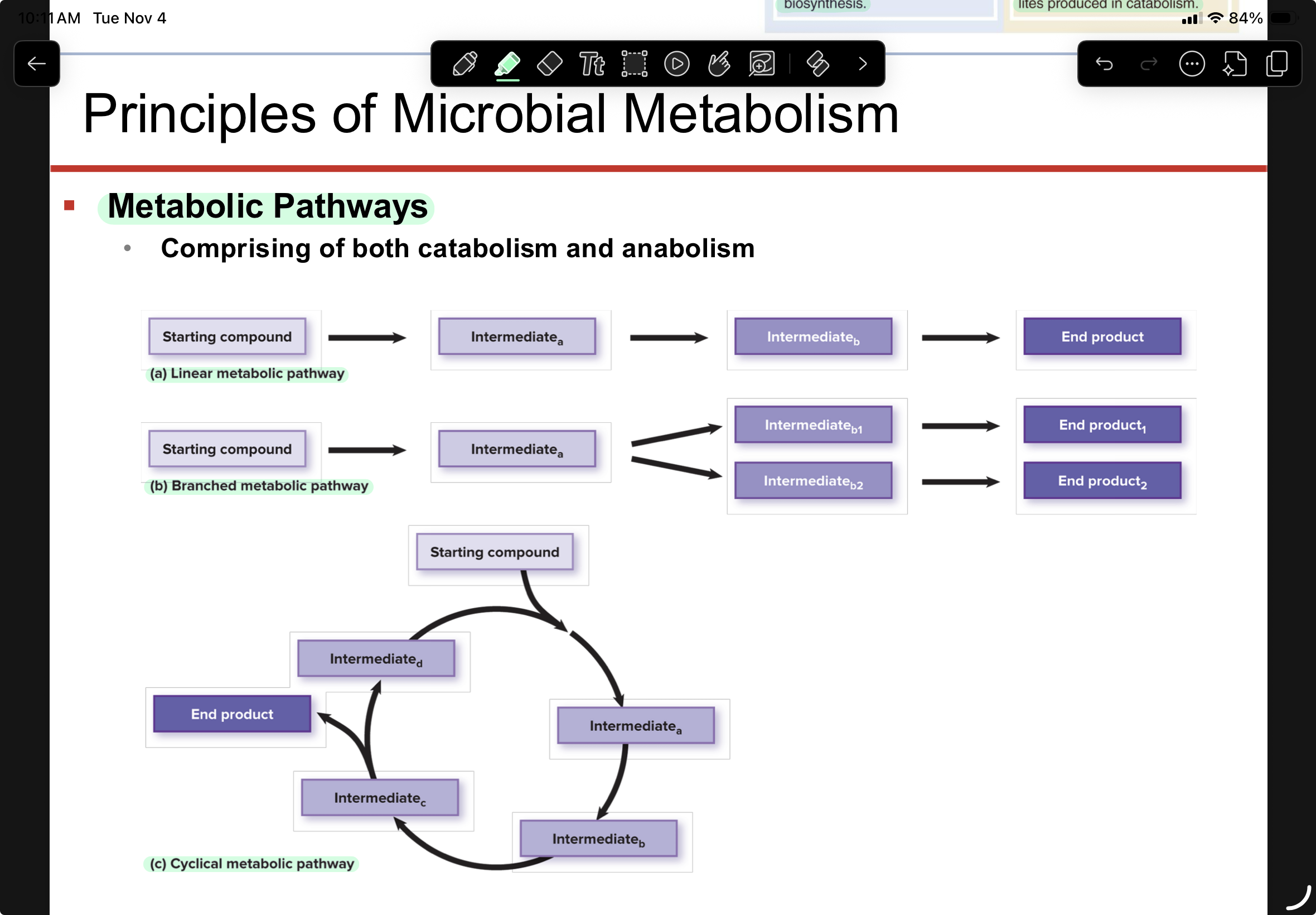
Metabolic Pathways
Energy
Defined as the capacity to do work.
potential:stored energy (ex. chemical bonds, rock on hill, water behind dam)
kinetic: energy of movement (ex. moving water, vibration of molecules)
first law of thermodynamics
the total amount of energy in the universe remains constant
energy can change from one state to another but it can never be created or destroyed
second law of thermodynamics
the amount of disorder, or entropy-(is a measure of the disorder in a system), in the universe is increasing “entropy increases”
the increasing disorder means that energy is transforming from potential to heat (kinetic) energy
disorder is closed systems is continuously increasing ex. a clean to messy room
free energy
is energy available to do work.
energy is released when a chemical bond is broken
Exergonic- exothermic
Reactants have more free energy (triangle G)than products, energy exits the system, energy is released during the reaction
endergonic- endothermic
reactants have less free energy than products. reaction requires input energy to proceed.
couple reactions
within a cell - energy released from exergonic reactions power endergonic reactions
chemical reactions
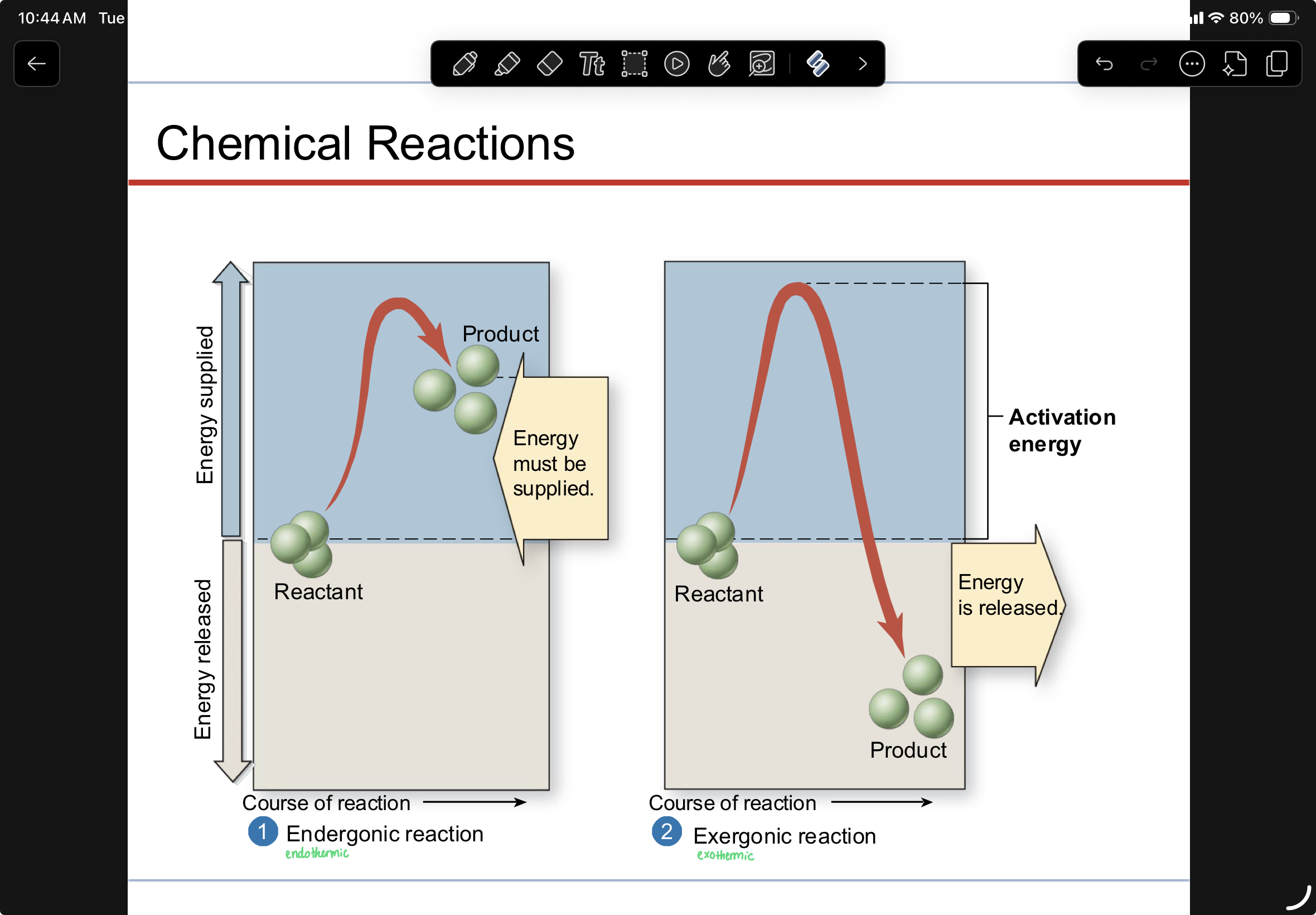
spontaneous chemical reaction
very little activation energy is needed ex. sodium in air & sodium in water
chemical reaction
food breaking down
lighting up wood
fire releasing heat and light
products have less energy than the starting materials
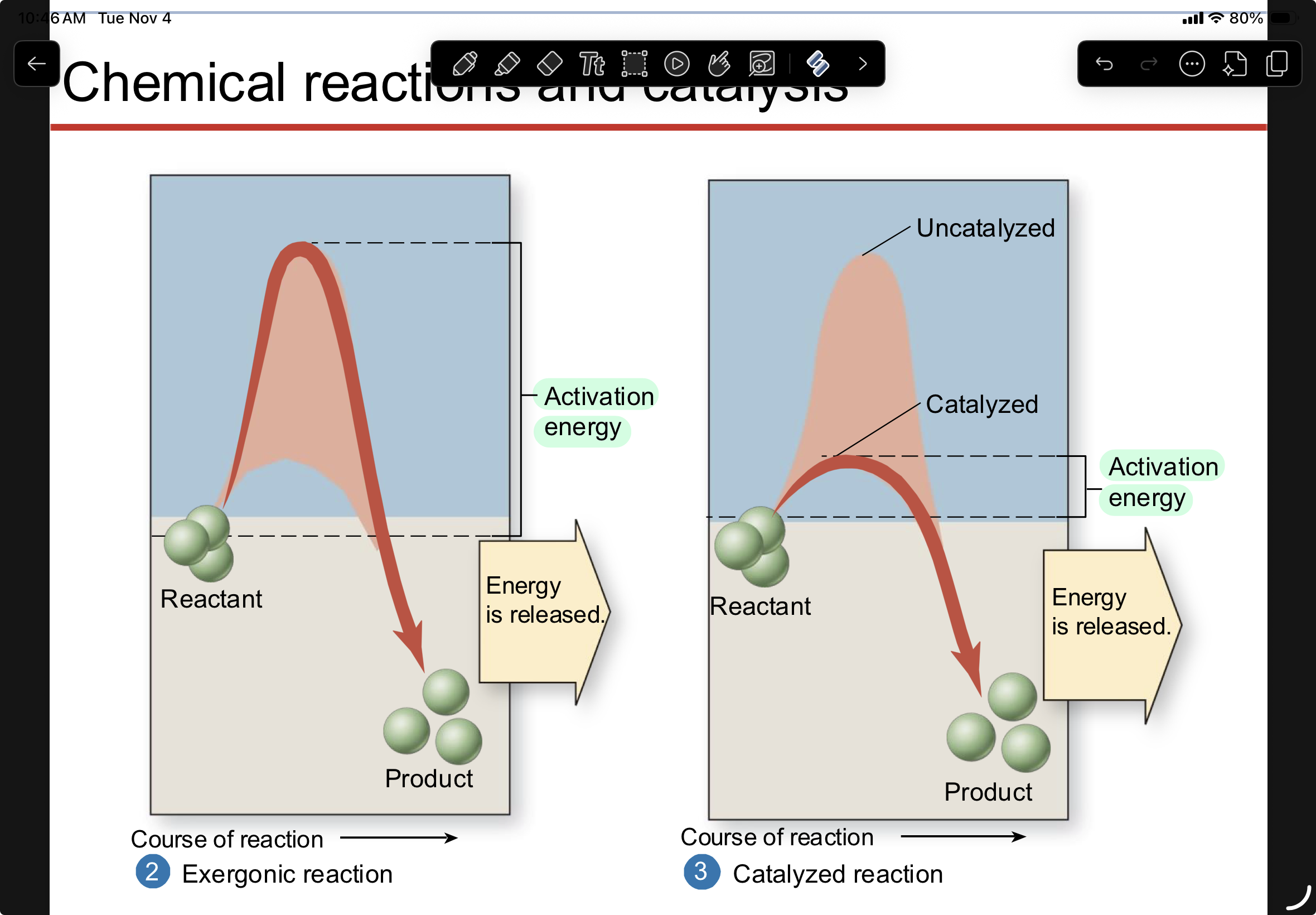
catalysis
the process of lowering the activation energy- reaction occurs after
catalyzed reactions proceed much faster than non catalyzed reactions
a substance that lowers the activation energy is called a catalyst
catalysts do not take a part in the reaction- they are not used up or changed
the lower the activation energy, the easier it is for a chemical reaction to initiate
chemical reactions and catalysis
enzymes
all enzymes are proteins, but not all proteins are enzymes
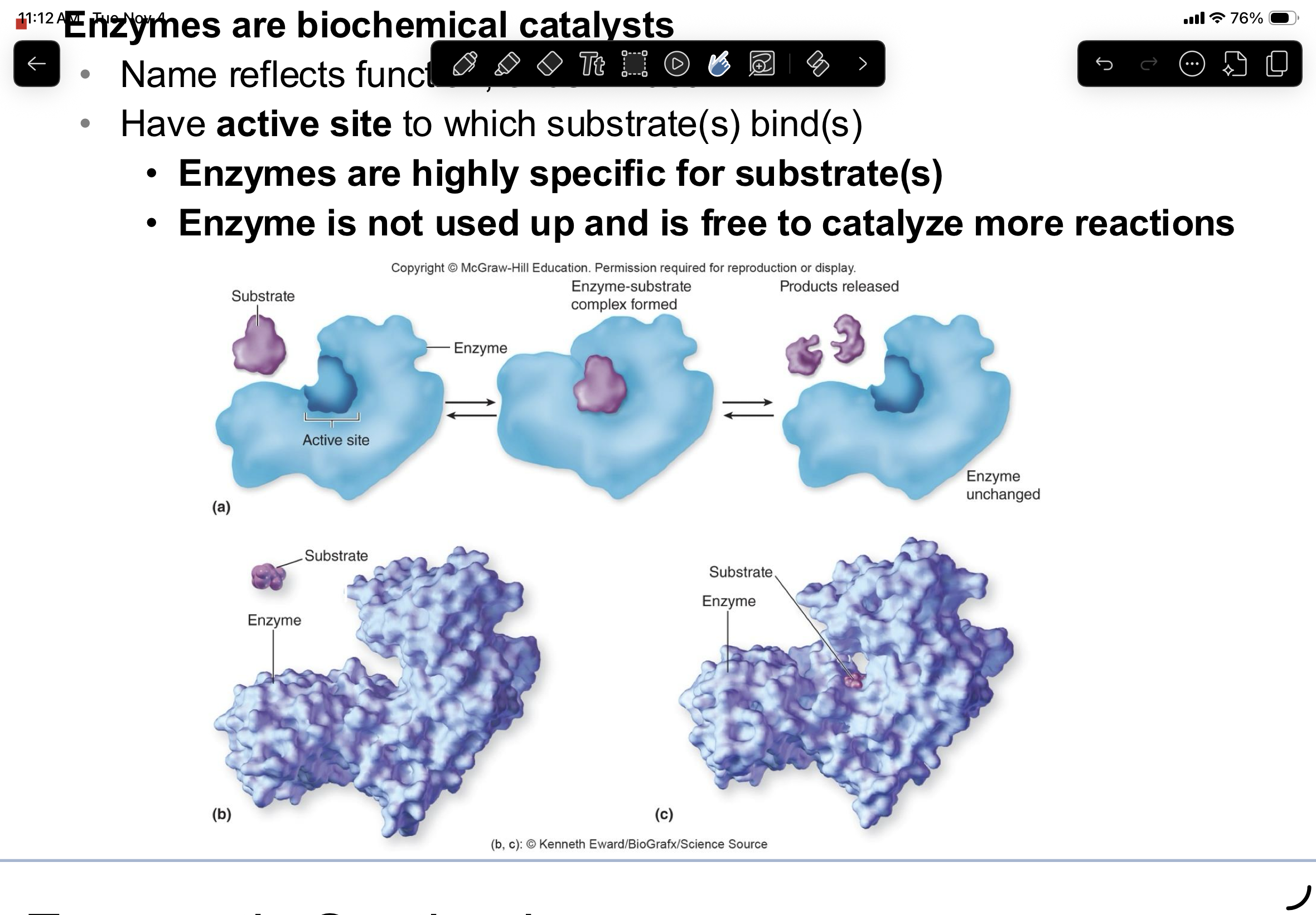
are biochemical catalysts
name ends in -ase
have active sites to which substrates bind
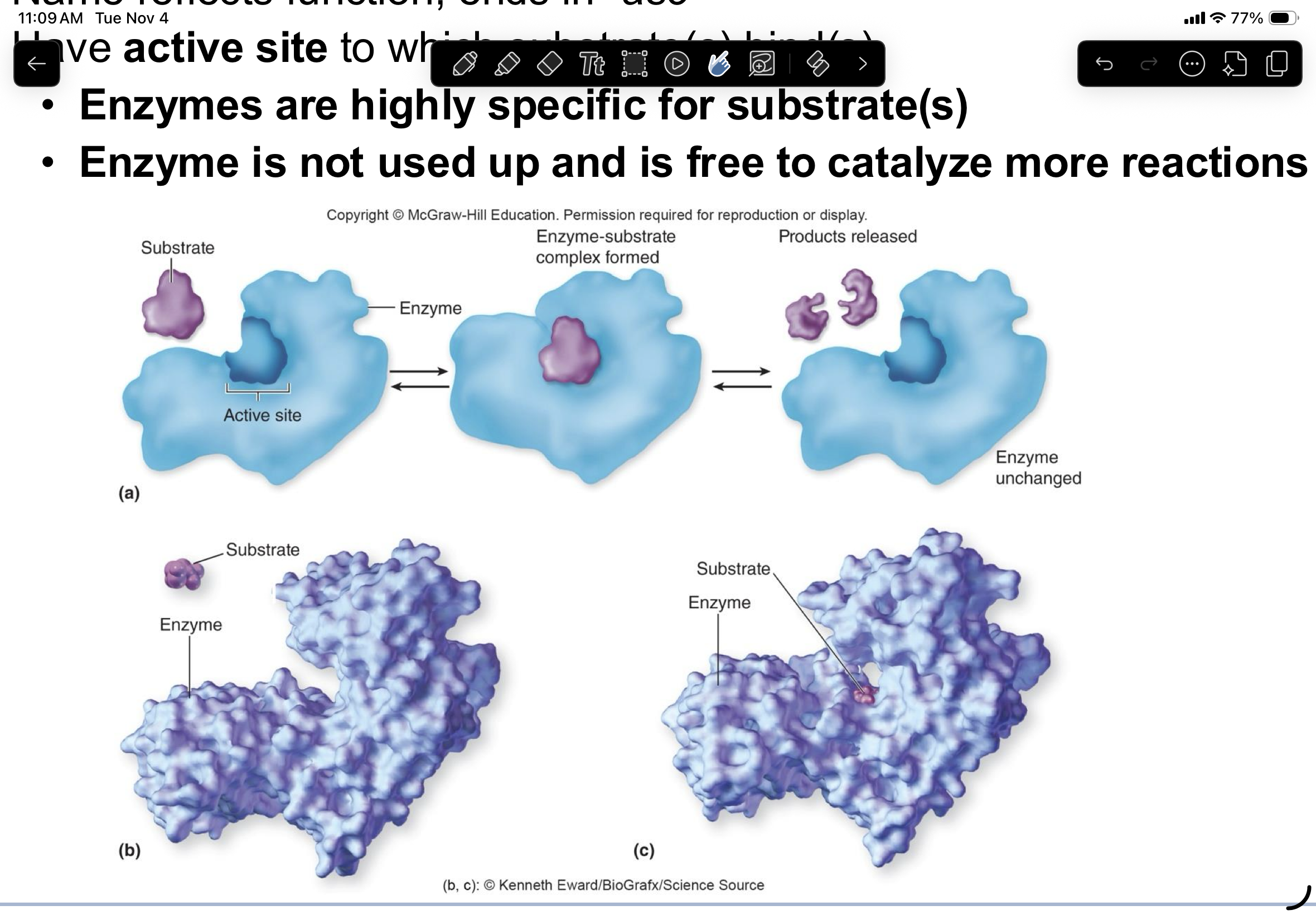
biochemical catalysts
speed up conversion of substrate into product by lowering activation energy
highly specific for their reactants
do not take part in the reaction
reactions will occur without enzymes, but very slowly