Endocrine System Anatomy and Physiology II
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
What does the endocrine system do?
it regulates the functions of the body to maintain homeostasis. (coordinates communication)
In the endocrine system, are organs connected?
No
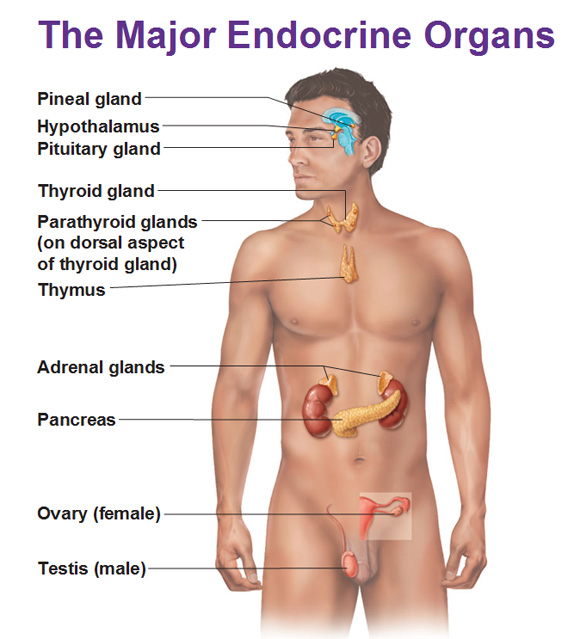
What are the major endocrine glands?
Pituitary gland
Thyroid gland
Parathyroid gland
Adrenal gland
Pancreas
Pineal gland
Thymus
Ovaries and Testes (reproductive glands)
What all makes up the endocrine system?
cells, tissues, and organs
What are some characteristics of the endocrine system?
its ductless, which means it secretes hormones directly into the blood system
What does endocrine mean?
Internal secretion
Can hormones act on any kind of cell? Why?
No, because that target cell has to have a receptor for that specific hormone
Where does the exocrine gland secrete hormones?
into tubes that leads to the body surface
Where exactly does the exocrine glands secrete things?
directly to a specific site that leads to the bodies surface
what does paracrine substances do?
they affect nearby cells and organs
what does autocrine substances do?
affects only the cell that is secreting the substance.
What kind of chemical signals do the nervous system send and where?
they send neurotransmitters to the synaptic cleft.
What kind of chemical signals do the endocrine system send and where?
they send hormones through the bloodstream
What kind of cells are in the nervous system?
neurons
What kind of cells are in the endocrine system?
Glandular epithelium
How long does it take for neurotransmitters to start (onset)? What is the duration of that?
seconds. very brief
How long does it take for hormones to start (onset)? What is the duration of that?
seconds to hours. can be brief or can last for days
What are some general functions of hormones?
regulate metabolic process
control the rates of certain chemical reactions
aid in transporting substances through membranes
help regulate water balance, electrolyte balance, and blood pressure
they also help with reproduction, development, and growth.
What are the two major types of hormones?
steroid and non-steroid
What are steroids synthesized from?
cholesterol
What are non-steroids synthesized from?
amino acids, amines, peptides, proteins, and glycoproteins
What is the distinction of a steroid hormone?
there’s complex rings of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
What are some steroid hormones?
sex hormones (testosterone, estrogens)
adrenal cortex secretions (aldosterone, cortisol)
Non-steroid Hormones that are amines are derived from what? What are some examples of amines?
derived from amino acids. Norepinephrine and epinephrine are derived from tyrosine(an amino acid). Thyroid hormone (synthesized in the thyroid gland) is composed of tyrosine. Melatonin is also from the amino acid tryptophan.
Where is norepinephrine and epinephrine synthesized?
the adrenal medulla (the inner portion of the adrenal gland)
What are protein hormones composed of?
long chains of amino acids that are linked and folded.
What are some protein hormones?
parathyroid hormone- secreted by the parathyroid gland
growth hormone and prolactin- secreted by the anterior pituitary gland
What are peptide hormones composed of?
they are a short chain of amino acids.
What are some peptide hormones?
antidiuretic and oxytocin- posterior pituitary gland
thyrotropin-releasing hormone- produced in the hypothalamus
What are prostaglandins?
are lipid-based signaling molecules that regulate inflammation, pain, fever, blood clotting, and smooth muscle contraction
Are prostaglandins paracrine or autocrine? What does that mean?
paracrine- they act on neighboring cells
Where are prostaglandins produced?
in cells of the liver, kidneys, heart, lungs, thymus, pancreas, brain, and reproductive organs.
What are prostaglandins synthesized from?
The lipid (fatty acid) arachidonic acid
If a cell has lots of receptors for a hormone, what happens?
it gives the cell a better binding response for that hormone.
What is upregulation?
the increase of receptors on a target cell. this happens when there is a decrease of a hormone
What is downregulation?
This is a decrease in receptors on a target cell due to having too much of a hormone
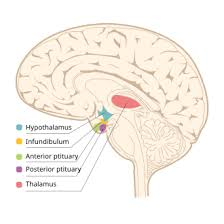
What are some hormones produced by the hypothalamus?
corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
Gonadotropin-Releasing hormone (GnRH)
Somatostatin (SS)
Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH)
Prolactin-inhibiting hormone (PIH)
Prolactin-releasing factor (PRF)
Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH)
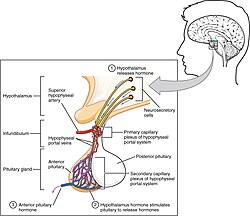
What are some hormones produced by the Anterior Pituitary Gland?
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Follicle- Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Growth Hormone (GH)
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Prolactin (PRL)
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
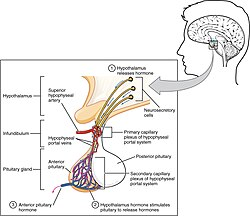
What are some hormones produced by the Posterior Pituitary gland?
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Oxytocin (OT)
What are some hormones produced by the Thyroid gland?
calcitonin
thyroxine (T4)
Triiodothyronine (T3)
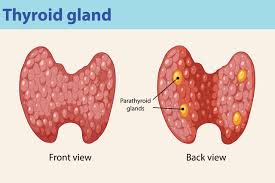
What hormone is produced by the Parathyroid gland?
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
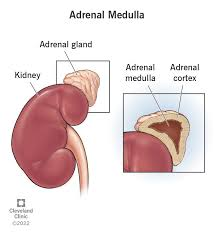
What are some hormones produced by the Adrenal medulla?
epinephrine (EPI)
noreoinephrine (NE)
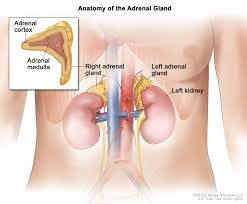
What are some hormones produced by the Adrenal cortex?
Aldosterone
Cortisol
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA)
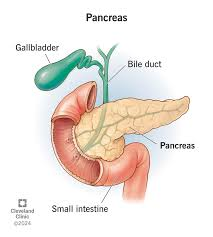
What are some hormones produced by the Pancreas?
Glucagon
Insulin
Somatostatin (SS)
What are glycoproteins formed out of?
Protein and carbohydrate
Are steroid hormones soluble in water? So what then happens?
No. They have to be carried by hydrophilic plasma proteins through the bloodstream
What is a benefit of being protein bound?
they are protected from enzyme degradation and being filtered and excreted by the kidneys- they get to circulate in the bloodstream longer.
When a steroid hormone and a thyroid hormone enters a target cell, what then happens?
They combine in the nucleus with specific protein receptors.
The hormone receptor complex binds to what? then what happens?
to particular DNA sequences and either activate or repress specific genes. Once activated, the genes are transcribed into Messenger RNA.
Where does the mRNA’s go? What do they do?
the cytoplasm. they direct the synthesis of specific proteins.
What is an example of a steroid hormone? Where is it secreted? Why?
aldosterone- adrenal glands. When blood pressure drops, it stimulates the kidneys to retain sodium and excrete potassium.
What are some nonsteroid hormones?
amines (derived from tyrosine: epinephrine and norepinephrine), proteins (made of long chains of amino acids: growth hormone), peptides (short chains of amino acids: ADH and oxytocin), and Glycoproteins (carbohydrates joined in proteins: TSH)
What are amines, peptides, and proteins all formed from?
amino acids
Can nonsteroid hormones enter the cell membrane easily?
No, it has to combine with a specific receptor molecule on the target cell membrane.
What is considered a first messenger?
hormones
What are second messengers?
chemicals that induce changes leading to the hormones effect.
What is the entire process of chemical communication from outside to the inside of a cell called?
signal transduction
What does many hormones use as second messengers?
cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)
When using the cAMP mechanism, what is happening?
the hormone binds to the receptor site of its target cells, which then activates G protein. Adenylate cyclase molecules are then activated in the target cells membrane and converts ATP into cyclic AMP. The cAMP then activates protein kinase, which then activate protein substrates in the cell, which changes metabolic processes.
Which hormones use cAMP?
nonsteroid hormones
What is G protein?
it is a enzyme complex that is joined to the intracellular side of the hormone receptor and is the link between the first and second messenger.
What is adenylate cyclase?
it is an enzyme that is an integral membrane protein with its active site facing the inside of the cell.
What adenylate cyclase is activated, what happens?
it removes two phosphates from ATP and reconnects the exposed oxygen, forming cyclic AMP.
What are protein kinases?
a set of enzymes that transfer phosphate groups from ATP molecules to protein substrate molecules.
What is phosphorylation?
is the addition of a phosphate group to a molecule (like a protein or sugar), acting as a molecular "on/off" switch to activate or deactivate it.
What are some cellular responses to to second messenger activation?
altering membrane permeability
activating enzymes
promoting synthesis of certain proteins
stimulating or inhibiting specific metabolic pathways
promoting cellular movements
initiating secretion of hormones and other substances
What is an example of cellular response in relation to second messenger activation?
epinephrine being the second messenger to cAMP to increase the activity of the enzyme that breaks down liver glycogen. (This increases the number of glucose molecules)
What does phosphodiesterase do?
quickly and continuously inactivate cAMP so its actions are short lived.
What hormones require cAMP?
in the anterior pituitary gland:
thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
luteinizing hormone (LH)
in the posterior pituitary gland:
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
and more- the parathyroid hormone (PTH) from the parathyroid glands, norepinephrine and epinephrine from the adrenal glands, calcitonin from the thyroid glands, and glucagon from the pancreas
What is an example of an abnormality in cAMP mediated signaling?
McCune- Albright syndrome- a defect in the G protein activates the adenylate cyclase to convert ATP into cAMP even without stimulation. - this leaves certain cells to secrete hormone excessively. Symptoms: infant girls menstruate, boys producing mature sperm at around six years old.
Can other nonsteroid cells use second messengers other than cAMP?
Yes, they can.
What happens when calcium ions are stimulated?
they diffuse from the extracellular fluid and into the cytosol of smooth muscle cells, bind to calmodulin, and activate contractions.
What is cGMP?
cyclic guanosine monophosphate. it is a nucleotide derivative that functions like a second messenger.
What are prostaglandins?
paracrine substances that are secreted into the extracellular fluid and acts locally.
In terms of abusing hormones , what are some side effects of steroid hormones?
a decrease in natural testosterone production
stunting growth
breast development in males
male sexual characteristics in females
damage to kidneys, liver or heart
psychiatric problems
In terms of abuse, why are growth hormones used?
to enlarge muscles, this is used instead of or along with steroids
In terms of abuse, why is erythropoietin used?
to increase the number of red blood cells and oxygen delivery to muscles
it can also be used to treat certain forms of anemia
this can lead to heart attack and death
What is used in small amounts, yet are very potent?
prostaglandins
Are prostaglandins stored in cells? How does that work?
No, they’re synthesized just before they are released- they’re rapidly inactivated after they are used.
What can activate or inhibit adenylate cyclase? What does this do?
Prostaglandins- controls cAMP production and changes cells responses to hormone.