Bio 11- Adaptations and Evolution & Evidence for evolution
1/45
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Adaptation
A characteristic that helps an organism survive and reproduce in its environment
Includes structures and behaviours for finding food, a mate, for protection, and for moving from place to place
(ex. bears hibernating)
Adaptations for a snake
Can unhinge jaw
Can smell with tongue
Adaptations for a kangaroo
Large ears to hear predators
Powerful back legs to hop long distances
Adaptations for a spider
Can easily sense vibrations on the ground
Special hairs to tickle predators
Adaptations for a monkey
Apposable thumbs
Teeth for omnivorous diet
Adaptations for a cheetah
Camouflage from spots
Adaptations for an Elephant
Trunk used to bathe, drink, and wash themselves
Large tusks for defence
Natural Selection
Process where organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring, leading to evolutionary change.
These are organisms that have traits that highly benefit them to have a greater likelihood of survival and higher rate of reproduction success
4 Key Conditions for Natural Selection to occur
struggle for survival
inheritable variation within a population
variation of fitness amongst members of the same population
lots of time
Origin of Species Hypothesis I
Aristole believed that all plants and animals had been placed on Earth from the start and never changed
This is incorrect
Origin of Species Hypothesis II
Life has changed over time
This branches out into Lamark’s theory and Darwin’s theory
Lamark’s theory of Evolution
i) “Law of Use and Disuse”
ii) “Inheritance of Acquired Characterstics”
Law of Use and Disuse
The more a body part is used, the more developed it will be
(ex. an ancestral giraffes stretches its neck a lot, so the neck will become longer over time)
(ex. penguins never used wings, so wings became smaller over time)
Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics
The more developed traits are passed down to its offspring
(ex. never used thumbs, their offspring would have weak thumbs)
Disproving Lamark’s Theory
August Weissman cut the tails off 20 generations of parent mice
If Lamark was correct, the tails of the 20th generation should be underdeveloped because tails were not used
Result of August Weissman Experiment
No change in tail length or size, therefore disproving Lamark
Darwin’s Theory of Evolution
His theory is that evolution happens by natural selection
He proposes that organisms with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on those traits to their offspring.
Struggle for survival
Competition between organisms to survive in the same environment
Occurs when there are more animals born than the environment can handle because there isn’t enough food and resources
Result of Struggle for Survival
Not all animals survive
Inheritable Variation within a population
Within a population, organisms have differences like longer giraffe necks due to variations in the gene responsible for neck length
Inheritable Trait
A trait that can be passed down to offspring
Traits caused by variations in the genes (DNA) can be passed down onto the offspring
Variation of fitness amongst members of the same population
An organism must stay alive to reproduce
When they reproduce, they will get good genes that result in a useful trait
(ex. having a longer neck only matters if it helps the organism survive long enough to reproduce and pass on those genes)
Fitness
Determined by the organism’s ability to produce offspring
More offspring = higher
Lots of Time
Natural selection causes a gradual change that happens over many generations, this is a must for the result of all the organisms acquiring the advantageous traits
(ex. long neck in all giraffes)
Evolution
A process of gradual change that takes place over many generations
During which organisms slowly change some of their physical and behavioural characteristics
Speciation
The product of evolution
Formation of new, distinct (different) species due to evolution
Distinct species
Two organisms when they produce infertile offspring
Two organisms produce a hybrid animal offspring
Fertile Offspring
The offspring of two organisms of the same species
3 type of evolution
convergent
divergent
coevolution
Define Convergent Evolution
Two or more species share similar traits that did not come from a common ancestor
Convergent evolution, why?
Happens because when different species that live in similar environments, they will develop similar characteristics that allow better survival in the given environment
(ex. to survive better in the water, sharks, and dolphins developed fins)
Analogous Structures
Shared structures between organisms that have the same function, but come from a different origin
(ex. wings of bats, birds, and insects)
Define Divergent Evolution
Two or more species diverge from a common ancestor
The species will look very different from each other despite sharing the same ancestors
Divergent evolution, why?
Happens when part of a population becomes isolated due to migration or geographical barriers
Organisms of the divided population, will become adapted to different environmental changes, making them different
(ex. humans, bats, frogs, porpoises, and horses have the same limbs as us humans as we inherited from a common ancestor)
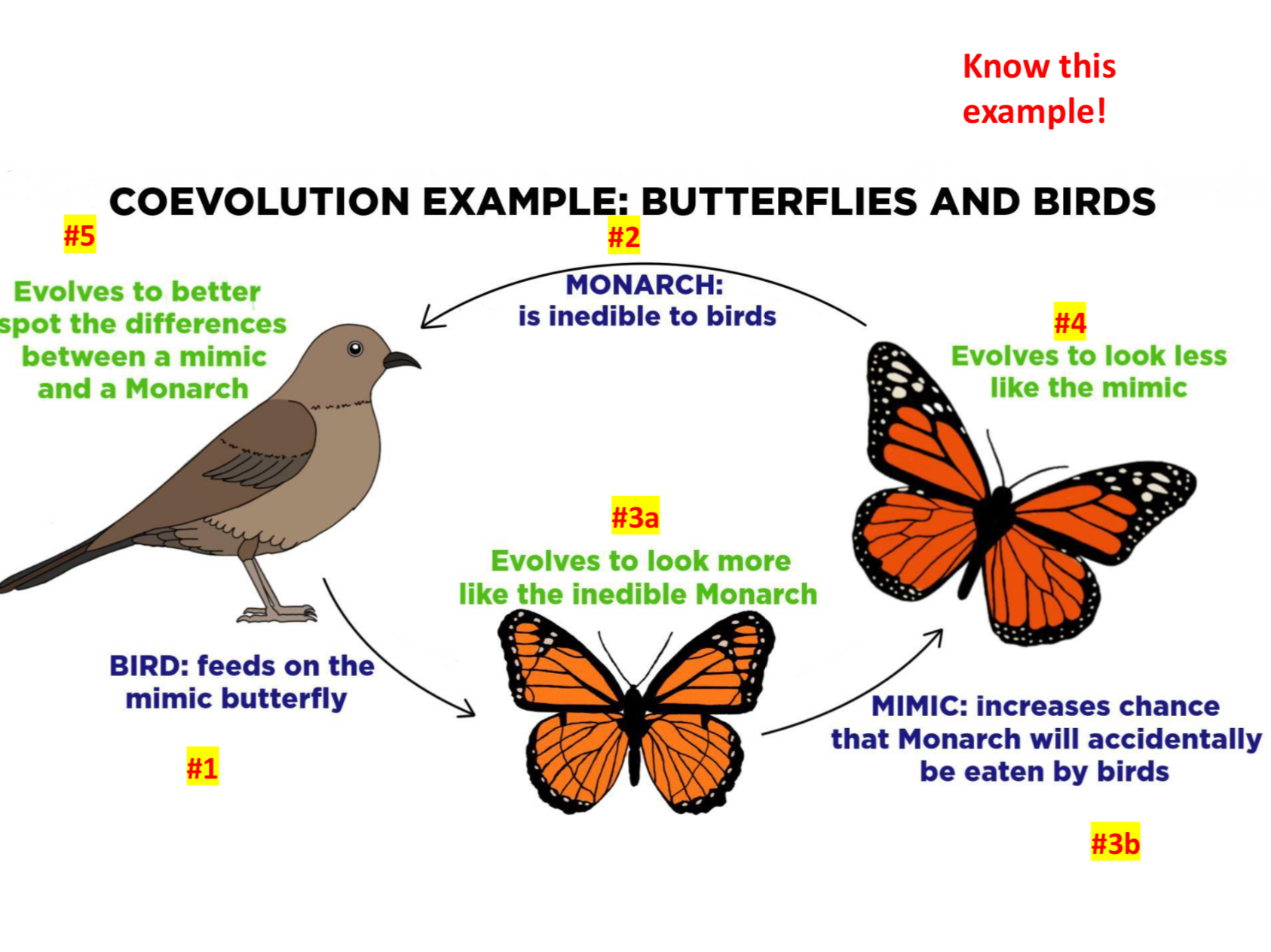
Define Coevolution
Happens when two or more species influence each other’s evolution because of their interactions
Coevolution, why? (ex.1)
In order for it to happen, the species must have dependence on each other, and reciprocal influence
Example: Butterflies and Birds
1) The bird wants to eat the mimics because the monarchs are inedible, so it evolves to be able to differentiate them better
2) The mimic itself evolves more to look like the inedible monarch
3) The monarch evolves to look less like the mimic
Artificial selection
Also called, selective breeding
Happens when humans, rather than the environment, decide which traits are useful
(Ex. Cauliflower, broccoli)
Advantages of selective breeding
It tries to establish certain traits that animals will pass to the next generation
Examples of desirable traits in selective breeding
Disease resistance, calmness, more lean meat, endurance
Disadvantages of selective breeding
Results in decreased genetic diversity found in the population
Undesirable traits from both parents may appear in the offspring
(Ex. Diseases and health problems that accumulate in the population)
Homologous structures
Parts of the body that are similar in structure (same origin but have different functions)
This occurs because of Divergent evolution
(Ex. The relationship between human, cat, and whale)
Vestigial structures
A structure that has been reduced in size and function but may once have been complete and functional
(Ex. Whale’s leg bones)
The more recent two species are separated = more
More closely related they are
Gradualism
Means that changes happen slowly and gradually over a long period of time rather than suddenly or in large leaps
Punctuated equilibrium
Punctuated equilibrium suggests that species often experience long period of little or no significant change, stopped by short periods of rapid and substantial change
Factors that cause punctuated equilibrium
Mass extinction events
Migration into new environments
Isolation of small populations