OCM Ch.3 - Small Scale Industry and Business
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Traditional meaning of Small Scale Industries
Industries in India which are organized on a Small Scale and produce goods with help of machines, labour and power are considered as Small Scale Industries.
Meaning of Small Scale Industries as per MSMED (2006)
An industrial unit can be categorized as small business if it fulfills the capital investment limit fixed by Government of India.
What are the 2 Sectors of Business?
1) Manufacturing sector
2) Services Sector
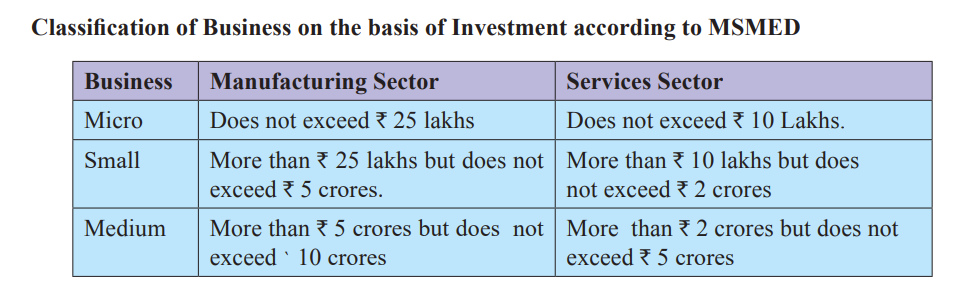
Classification of Business on the basis of Investment according to MSMED
Definition of Small Scale Industries
‘‘Investment in fixed assets like plant and equipment either held on ownership terms or on lease or hire purchase should not be more than one crore. However, the unit in no way can be owned or controlled or auxiliary for any other industrial unit.’’
Importance of Small Scale Industries (5m)
1) SSI is second largest industry which creates huge employment opportunities. Because it can be operated with minimum amount of capital, basic and potential skills. This is a boost for a labour surplus country like India.
2) Regional Balance : In India, all regions are not developed due to lack of industrialization SSI can be setup with minimum amount of capital. Small industries manufactures products using simple technologies, local available resources, material and labour. Thus, they contribute significantly to the balanced development of the country.
3) Increase Competitive Strength : Small scale industries enjoy the advantages of low cost of product. These industries use locally available resources which are less expensive. Establishment and running costs of small industries are comparatively less. Low cost of production, low overheads, ultimately result in low price of goods. Increased turnover increases competitive strength.
4) Maximum Use of Natural Resources : Small scale industries are labour intensive. They utilize available natural resources and raw materials from local areas. Such use of local natural resources minimizes the cost of production which result into reasonable price of the goods.
5) Reduces Migrations : Small Scale industries can create a large number of employment in rural area. small scale industry is also a best example of self employment. Therefore, migration of people from rural area to urban area can be reduced or minimized.
6) Support to Large Scale Industries : Maximum large scale industries depend upon small scale industries. Many Small Scale industries provide raw material, semi finished goods to large scale industries. For e.g. spare parts.
7) Developing New Entrepreneurs : Small enterprises have the potential to attract the young aspirants to entrepreneurship. Small Scale Industry can accommodate the technical and non-technical young first generation entrepreneurs. India is the country of villagers. Therefore government has to pay attention to the development of small and cottage industries in order to create a balanced economy.
Classification of Small Scale Industries
Traditional Small Scale Industries - Handloom, handicraft, coir, etc.
Modern Small Scale Industries - Bicycle parts, Sewing Machines, Razors
Advantages of Small Scale Industries
1) Large Employment : India is labour abundant country. Small Scale Industries have potential to create employment opportunities on a mass scale. They are labour intensive They use more labour than other factors of production. Their gestation period is low and can provide employment opportunities to large number of people.
2) Less Capital Requirement : SSIrequiresless capital as compared to large scale industries. SSI can be started and run by small entrepreneurs with limited capital resources. 49
3) Utilization of Domestic Resources : SSI make use of local resources which are available in a greater extent. Small amount of savings which normally remains idle are now channelized. This will increase capital formation and investment in the economy.
4) Increases Industrial Output : SSI produce consumer goods as well as industrial components. The goods are cheaper and satisfy the needs of poor sections of the society. Products produced by SSI form a significant portion of industrial output of a country.
5) Contribution to Export : Nearly 40% of the industrial exports are contributed by SSI. Product such as hosiery, knitwear, gems and jewellery, handicrafts, coir products, woolen garments, processed food, chemical and allied products and a large number of engineering goods contribute substantially in India’s exports. Also products produced by SSI are used in the manufacturing of products by large scale industries which are exported. It contribute directly and indirectly to exports and earn valuable foreign exchange.
6) Equitable Distribution : Large scale industries lead to inequalities in income distribution and concentration of economic power. But small scale industries distribute resources and wealth more equitably. This is because income is distributed among more number of workers as it is labour intensive. This results in both economic and social welfare.
7) Earning Foreign Exchange : Small scale industries earn valuable foreign exchange for the country by exporting products to different countries of the world. At the same time, their imports are very little. e.g. The Small Scale industries in Tiruppur contribute to a substantial portion of India’s textile export and earn valuable foreign exchange for the country.
8) Opportunities for Entrepreneurship : Small scale industries provide opportunities for entrepreneurs with limited capital. SSI requires less capital and lower investment in technology and machines as compared to large scale enterprises. Therefore small entrepreneurs can start small scale industries easily. SSI in Japan, which was devastated by the second world war became a major economic power because of many small entrepreneurs who contributed greatly to the nations development.
9) Cost Efficiency : Small Scale units can adopt micro production method which offer better quality and more variety at a lower cost. They are most cost effective as compared to large scale, because their expenses are lower.
10) Reduces Migration : Migration happens when people living in rural areas are not able to find employment and therefore, they migrate to urban areas seeking employment. Large scale migration puts tremendous pressure on land, water and other resources in urban areas. The skills and talents of rural craftsmen, artisans etc. leads to gainful employment to those with inheritant skills resulting in their economic upliftment. Thus Small Scale industries help in reducing migration.
11) Flexibility in Operation : Small scale industries are more flexible. They can adopt themselves to changing market requirement very fast.
Challenges before Small Scale Industries
1) Old Methods of Production : Generally Small scale industries use outdated technology and old methods of production. The use of low grade technical know-how and skills is resulting in low productivity in many industries.
2) Inadequate Finance : Non availability of adequate finance is a serious problem faced by Small scale industries. Generally, SSI begins with a small capital base. Many of the units in the small sector raise funds from capital market. These units frequently suffer from lack of adequate working capital.
3) Problem of Raw Material :Another major problem of Smallscale industriesisinadequate supply of raw materials. Due to that SSI have to compromise on the quantity and quality of raw material, or pay more price to good quality of raw material.
4) Labour Problem : Most of the small industries recruit unskilled and semi skilled workers on daily wages. This creates the problem of low labour productivity, higher absenteeism and poor job commitment. The wages are low due to financial limitations which turn into labour dissatisfaction and increases labour turnover. Improper shifts and lack of job security makes employment in small industries unattractive and the talented work force does not opt for such job.
5) Marketing Problem : Marketing is one of the most important activity as it generates revenue. Effective marketing of goods requires a thorough understanding of the customers needs and requirements. In most cases, marketing is a weaker area of small industries. These SSI have to depend excessively on middlemen who at times exploit them by paying low prices and delayed payments. Further, direct marketing may not be feasible for small business firms as they lack the necessary infrastructure.
6) Problem of Transport : It is necessary for SSI to spend on transporation of raw material and finished goods. Due to lack of transport facility, it is difficult to transfer raw material from market to factory and finished product from factories to consumers.
7) Sickness : Prevailence of sickness in small industries has become a point of worry to both the policy makers and the entrepreneurs. The causes of sickness are both internal and external. Internal problems includes lack of skilled and trained labour, lack of managerial and marketing skills etc. External problems includes delayed payment, shortage of working capital, inadequate loans and lack of demand for their products.
8) Power Shortage and Irregular Supply : Higher cost of power acquisition, load shedding, frequent power cuts, irregular supply of power, voltage fluctuation and rising power charges badly affect the productivity.
9) Global Competition : Apart from the problems stated above, small businesses are facing problems on the context of Liberalization, Privatization and Globalization (LPG) policies being followed by several countries across the world.
Steps in Setting Up a Small Scalae Business
1) Decision of Business Area : One need to prepare the description for the Small scale business one wants to setup. It is necessary to decide whether one wishes to set up a corporation, proprietorship or partnership. The potential entrepreneur has to analyze his strength, weakness while deciding for entrepreneurship career. This analysis helps in knowing what type and size of business would be the most suitable.
2) Study of Business Environment : Before setting up an industry, it is always essential to study and understand the prevailing business environment in which they operate particularly the industrial policy, economic policy, licensing policy, legal environment, and technological environment. The environment impacts a lot in setting up a proper industry.
3) Selection of Product : One needs to decide the product to manufacture or the service to offer. While choosing the product or service which one wants to offer, one must conduct a good market research and learn about the prevailing competition in the market.
4) Selection of Place : One needs to choose a location to set up small scale business. While choosing the location, factors such as nearness to market, sources of availability of raw materials, labour, transportation services, modern infrastructural facilities and other things are considered. Location determines the success or failure of the industries.
5) Selection of Technology : To manufacture any item technology is used. Entrepreneur should posses information of all available technologies and its suitability. It will be also useful to determine the need of money, material and equipment to be installed.
6) Business Proposal : Project appraisal means the assessment of a project. It is a technique for analysis of a scheme or project while preparing to set up an enterprise.The entrepreneur has to appraise the project carefully from the economic, financial, technical, market, social and managerial point of view.
7) Finance : Finance is the lifeblood of the enterprise. So, the next big step is to arrange for finance. No business can be created, with zero capital. If one dosen’t have enough finance then the best way is to borrow from outside.
8) Registration : It is always worthwhile to get the unit registered with the government. The entrepreneur has to obtain the prescribed application form from District Industries Centre (DIC). After having duly filled in the application form, he has to submit the application with all relevant documents in the local DIC.
9) Actual Arrangements of Resources : The required resources are arranged.
a) Physical Resources : This includes allocating space for different operations and choosing production methods. One is required to purchase machinery and hire employees and workers for different departments.
b) Arrangement of Power and Water Supply : The sites where the enterprise will be located should either have adequate power connections, or it should be arranged. The entrepreneur can calculate the total power requirement and determine the nearest pole from which power will be available for a business, as it can materially affect the installation cost.
c) Staffing : Once machines are installed, the need for manpower arises to run them. So the quantum and type of manpower are to be decided. The sources of getting desired labour is also important. This follows the recruitment, training and placement.
10) Production and Marketing of Product : Production is the next step. Once Small scale business is started. Marketing is the most important activity as far as the entrepreneurial development is concerned. Marketing and business advertising form next step of setting up Small Scale business. Online business directories and various traditional forms of advertising can gain exposure for business.
11) Review or feedback for Future Changes : Periodical monitoring and evaluation not only of markets but also production quality and profitability help in knowing where the firm stands in comparison to the performance envisaged in the business plan. It also identifies the direction of future growth. It can be concluded that setting up Small scale business is not a difficult task. The steps to set up Small scale business are simple and easy than the large scale business. So if one wants to set up business, one can surely go for it. It is profitable, easier and helps in the growth of the economy of the country