hormones of posterior pituitary gland
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
what 2 hormones dies posterior pituitary gland secrete
vasopressin (ADH or AVP)
oxytocin
where are posterior pituitary hormones synthesised
in hypothalamus - supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei
how do posterior pituitary hormones reach the bloodstream
they are transported down unmyelinated nerve fibres and released directly into circulation
role of vasopressin
encourages reabsorption of water from distal convoluted tubules and collecting ducts of kidney so conserving body fluid
what effect does vasopressin have on blood pressure
at high concentrations, it causes vasoconstriction and increases systemic blood pressure
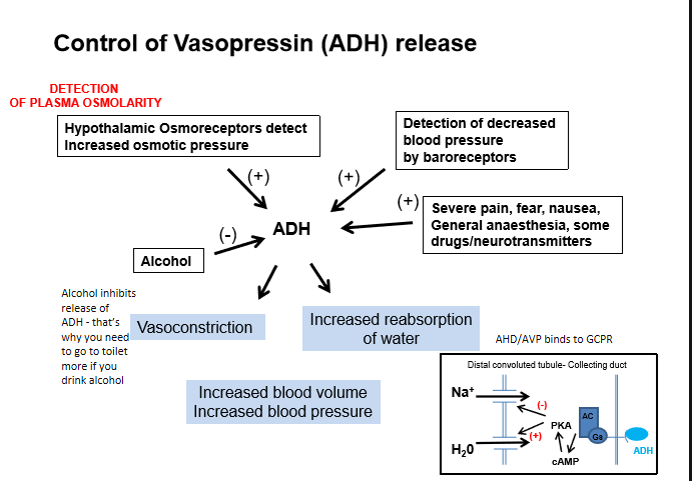
what is the most important stimulus for vasopressin release
increased plasma osmolarity detected by hypothalamic osmoreceptors
how does blood volume or pressure affect vasopressin release
low blood volume or pressure increases vasopressin release due to reduced baroreceptor stimulation
which factors increase vasopressin release
severe pain
fear
nausea
general anaesthesia
nicotine
noradrenaline
which substance inhibits vasopressin release
alcohol
summary of control of vasopressin (ADH) release
what condition results from vasopressin hyposecretion
diabetes insipidus
what are the features of diabetes insipidus
excessive production of large volumes of dilute urine
how is diabetes insipidus treated
synthetic vasopressin (argipressin) or desmopressin (intranasal)
what condition results from vasopressin hypersecretion
Schwartz–Bartter syndrome (SIADH) - caused by small cell lung carcinoma
what are the key features of Schwartz–Bartter syndrome
excessive water retention
low serum osmolarity
hyponatraemia
concentrated urine
how is vasopressin hypersecretion treated
tumour removal if possible
tumours are those that produce ADH inappropriately leading to hypersecretion
ectopic tumours so located outside pituitary
use of AVP anatagonist demeclocycline
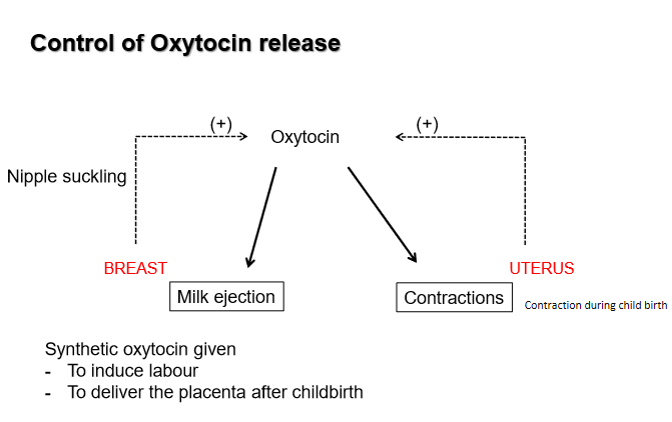
what is the primary role of oxytocin in childbirth
stimulates rhythmic contractions of uterine smooth muscles
what is oxytocins role in lactation
stimulates milk ejection in response to suckling
is oxytocin essential for initiation of labour
no, it contributes but not essential
how is oxytocin release regulated
by neurogenic positive feedback from sensory stimulation of the nipple (suckling) and uterus (labour)
true or false: disorders of oxytocin secretion are common
false - rare
what are the clinical uses of synthetic oxytocin
induction of labour and stimulation of uterine contractions after childbirth for placental delivery