Animal Nutrition Final (ALL)
1/559
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
560 Terms
Roles of digestive tract
Acquisition of food
Absorption of nutrients
Protection from foreign invaders
breakdown of feeds into absorbable nutrients
elimination of waste
mastication
chewing
goal: to reduce particle size of feed
prehension
taking food/water into mouth
major roles of saliva
Moistens feed
Provide ions & water
Lubricate to aid in swallowing
Produces salivary amylase
Aids in starch digestion
Not secreted in ruminant saliva
Specialized functions
Draculin in vampire bats
Prevents blood from clotting
3 major salivary glands present in the mouth of an animal
Parotid
Type: serous (watery)
Main components: water, enzymes, ions
lubrication
Sublingual
Type: mucosal
Main component: mucus
Protection of irritation of skin linings
Submaxillary
Type: mixed
Main components: mucus, ions, enzymes, water
deglutition
Swallowing
Reflex initiated by presence of food in the pharynx
Propulsion of food to stomach by esophageal peristalsis
peristalsis
Process animal uses to move through the digestive tract
Sequential muscle contractions that push food through digestive tract
major roles of the stomach
Storage of food
Control release of digest into small intestine
Control passage rate throughout digestive tract
Initial breakdown of food
Mechanical
Acid
Enzymatic
Regulates hunger
What hormone(s) are secreted by the stomach?
Pepsin (proteolytic hormone)
Responsible for breaking down protein
Grehlin
growling/responsible for immediate drive for hunger
Short term regulation of hunger
3 regions of the stomach
cardiac
fundic
pyloric
cardiac region
produces mucus for lubrication and protection
fundic
Produces hydrochloric acid and enzymes
Parietal cells
Chief cells
pyloric
End of digestion tract
Secretes hormones and mucus
which cells secrete hydrochloric acid
parietal cells
which cells secrete pepsinogen
chief cells
zymogen
non-activated hormone that must be activated by something
major roles of small intestine
Produces enzymes
Produces bile acids
Responsible for fat absorption
Produces hormones
What is the role of the gall bladder, what is stored there, and what do those stored molecules do within the digestive process?
Role: to store bile so that it can be released later
Stored: bile
What they do: breaks down fats into smaller particles
3 sections of the small intestine
(first) duodenum
jejunum
(last) ileum
duodenum
Enzyme secretion
Bile secretion
Absorption
jejunum
absorption
Ileum
Transition from small to large intestine
Less absorption
Immune cells
Which section of the small intestine is densely populated by immune cells?
Ileum
What structures in the small intestine exist to increase the surface area for absorption
villi
Define emulsification in the context of lipid digestion
Process of taking big fat particles & adding amphipilic molecules and then breaking up the big fat particles into smaller fat particles
which secretions from the liver/gall bladder play a role in emulsification
Pancreas secretes digestive enzymes to break down feeds
Metabolic hormones (insulin)
Bicarbonate salts to buffer small intestine
Glucagon
Bile is produced in liver and stored in gallbladder, released into duodenum
major roles of large intestine
Resorbs water from GIT
Microbial fermentation
What is secreted into the large intestine to aid in digestion?
mucus
What is secreted into the small intestine to aid in digestion?
bile
What is secreted into the stomach to aid in digestion?
hydrochloric acid, pepsin
3 sections of large intestine
cecum, colon, rectum
cecum
First section
Microbial fermentation/creates stable fermentation area, slow rate
Most active part
Most absorption occurs
colon
Second section
Some absorption of short chain fatty acids
rectum
Last section
Regulates excretion of feces
Which molecules are starch broken down into
maltose, glucose
enzyme that breaks down protein
pepsin
enzyme that breaks down fat
lipase
enzyme that breaks down starch
amylase
Which glucose transporter brings glucose into an enterocyte
SLGT1
Which glucose transporter brings fructose into an enterocyte
GLUT5
Which glucose transporter moves glucose from the enterocyte to circulation
GLUT2
role of gastrin in digestive tract
stimulates HC: and pepsin production
secreted by stomach
role of ghrelin in digestive tract
increases hunger signaling
secreted by stomach
major short term hunger signal
CCK & feed intake
decreases food intake
causes the release of digestive enzymes and bile into small intestine
secreted by duodenum
PYY & feed intake
decreases food intake
increases retention in the intestine
increases water & electrolyte absorption
secreted from duodenum & jejunum
role of incretins in nutrient metabolism
to sense nutrients to prime insulin signaling
incretin examples
GLP-1: increases insulin signaling & retention in intestine, decreases food intake
GLP-2: increases intestinal growth
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic hormone: stimulates insulin secretion & inhibits GI motility
How does the saliva of dairy cows differ from pigs
Cows: continuous saliva production-25 to 40 gallons per day
Pigs: saliva is lower in volume, functions more as a lubricant
Sheep: produces 2 gallons of saliva per day
rumination
regurgitation and rechewing of a bolus of food (called cud) to further mechanically break down fibrous feeds & increase surface area for microbial digestion
stimulates additional buffering through saliva production
why do ruminants perform rumination
to help rechew their food, stimulates saliva production, undergo fermentation
4 compartments of a ruminant stomach
rumen, reticulum, abomasum, omasum
rumen
undergo lots of fermentation
reticulum
trap larger feed particles & regulate the flow of nutrients down to the lower digestive tract
abomasum
secretes HCL & pepsin and begins the degradation of protein
omasum
absorbs residual water and VFAs
3 major volatile fatty acids produced in the rumen
butyrate, propionate, acetate
how are VFA used by the animal
used as primary energy source
What structures in the rumen exist to increase surface area for absorption
papillae
4 major microbial groups in the rumen of ruminants
Bacteria: 90% of rumen microbial genetic diversity, 7000 species
Archaea: methanogens, 1500 species
Protozoa: 50% total mass of rumen microorganisms
Fungi: 6 genera, 18 species
which microbial group has the most genetic diversity
bacteria
why can’t horses vomit
Because their esophagus only allows one-way peristaltic movements
Horses are missing an organ that releases stuff into the small intestine. What is the organ they are missing, what stuff does it release, and how does the lack of this organ affect horse digestion?
Missing organ: gallbladder
Release: bile
Affect digestion: less bile secreted, less lipid digestion
How does hindgut acidosis lead to inflammation and potentially laminitis in horses?
if too much starch is fed
which organ is enlarged in horses that helps it digest fiber?
cecum
What is the function of the crop in the chicken digestive tract
Allows breakdown by salivary amylase
Moistens digesta
Regulatres flow of food to lower GIT
function of the proventriculus in the chicken digestive tract
true stomach, production of HCL & pepsin
function of the gizzard in the chicken digestive tract
Pepsin and HCL from proventriculus secretion will be mixed with feed in gizzard and aid in digestion
What are the differences in the way chickens excrete nitrogen compared to mammals?
chickens: excrete uric acid
mammals: excrete urea
What is the difference in the large intestine between avian species and mammals?
Avian: 2 cica
Mammals: 1 cica
7 physiological roles of lipids
Provide long-term energy storage,
Cell signaling,
Formation of steroid hormones (Cortisol, Testosterone, Estrogen, Progesterone),
Formation of vitamin D,
Bile acid,
Inflammatory signals (eicosanoids/oxylipins),
Provide cellular structure,
Provides insulation for nerve cells
general structure of a triglyceride
glycerol back bone and 3 fatty acid tails
general structure of a diglyceride
glycerol backbone and two fatty acids
monoglyceride
glycerol backbone and 1 fatty acid tail
difference between a “free fatty acid” and an “esterified fatty acid”
free fatty acid: chain of carbon molecules with methyl and carboxyl end
esterified fatty acid: formed an ester bond with a glycerol molecule
which type of fatty acids are pro-inflammatory
omega-6
which type of fatty acids are anti-inflammatory
omega-3
which end of a fatty acid do you begin counting from using the delta counting scheme?
count from carboxyl end
which end of a fatty acid do you begin counting from using the omega counting scheme?
count from methyl end
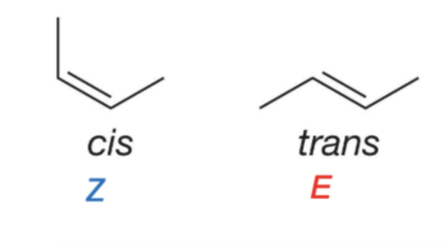
cis double bond and a trans double bond
cis is more of a hexagonal shape
trans is like a squiggle
C16:0
palmitic acid
C18:0
stearic acid
C18:1
oleic acid
C18:2
linoleic acid
C18:3
linolenic acid (essential, omega-3)
C20:4
arachidonic acid (conditionally essential, omega-6)
C20:5
EPA (conditionally essential, fish oil, omega-3)
C22:6
DHA (conditionally essential, fish oil, omega-3)
antidioxants prevent which type of rancidity of fats
oxidative rancidity
rank the following animal species by their fat requirement: cats, pigs, horses, ruminants
highest: cats, pigs, horses, ruminants : lowest
saturated fats
no double bonds between carbon atoms in fatty acid chains
saturated with hydrogen atoms
unsaturated fats
1 or more double bonds (kinks) between carbon atoms
have fewer hydrogen atoms than saturated fats
symptoms of a dietary fat deficiency
reduced growth & feed deficiency
poor reproductive performance
skin lesions, hair loss, poor feathering
subcutaneous hemorrhage
what are the 3 essential fatty acids in all animals
linoleic, linolenic, arachidonic
orexigenic
signals that stimulate food intake
induces animals to eat more
anoerexigenic
tells the animal to stop eating, shuts down feed intak
hunger
feeling of discomfort or weakness caused by a lack of food with the desire to eat
satiety
satisfied feeling of being full after eating
satiation
completely satisfied to the point where a need or desire is no longer felt, often to the point of feeling weary or overindulged
From an animal standpoint, what is generally the major factor driving feed intake
All senses: sight, smell, taste, texture, temperature, sound
Food characteristics / palatability
Other animals, “feeding time”
Social pressure
Environmental discomfort
which region of the brain integrates feed intake signals to regulate hunger and satiety
hypothalamus