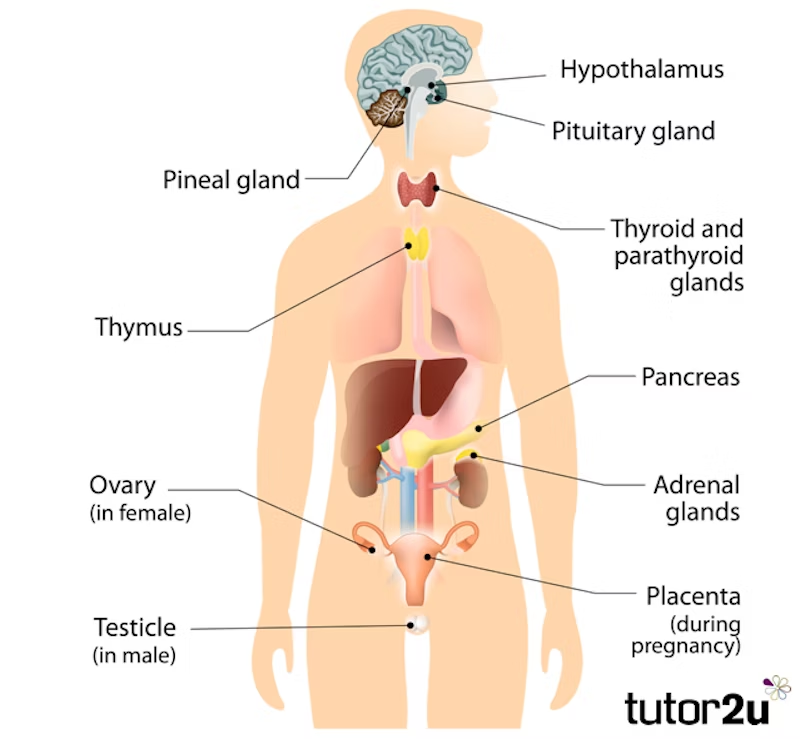
What is psychology?
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is psychology?
Psychology is the scientific study of the mind and behaviour
What is the mind?
The mind is defined as the part of us that reasons, thinks, feels, perceives, and judges
What is behaviour?
The response of living organisms to stimulus, both internal and external
Nature vs. Nurture
Nature is the natural/genetic behaviours of a person, while Nurture is the environmental factors of how a person was rasied
Why is Psychology still not considered a science in some places?
Due to methodological challenges, historical baggage, and misconceptions
Cognitive process
explains how the mind works. These include memory, perception, attention, deicision-making, and thinking/reasoning
What makes a good theory? (TEACUP)
T - Testiable (Flaseafilable)
E - Experiment
A - Application (Can be applied to real world situations)
C - Concepts
U - Unbiased
P - Perdictable
What psychological factors can affect our behaviour and cognition?
Neurotransmitters/Brain structure
Hormones
Genes
Interactionist approach
Lots of things are responsible for psychological effects
Reductionist approach
One thing is responsible for psychological effects
What is the difference between MRI, FMRI, and PET scans?
MRI - 3D picture of the brain structure
FMRI - Scan of brain activity
PET - invasive brain scan
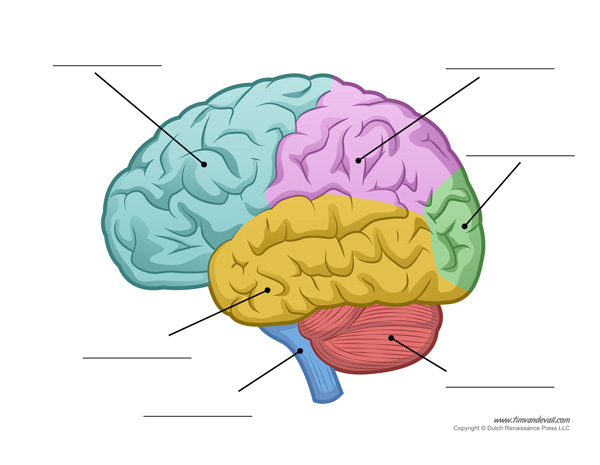
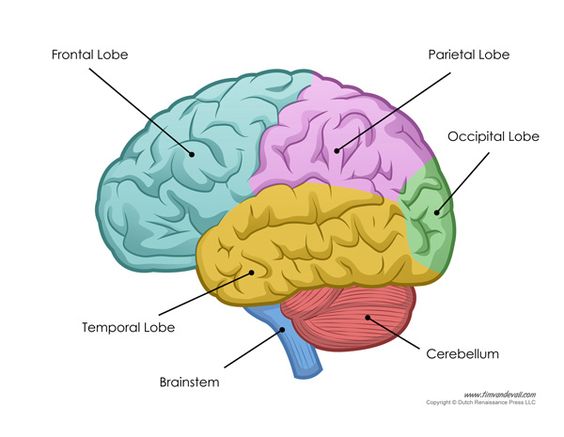
Label the brain
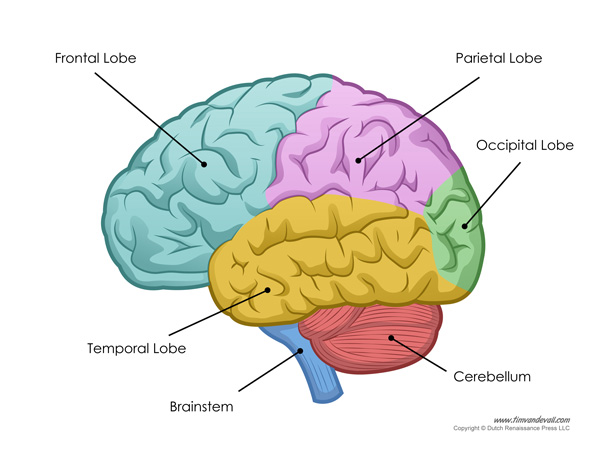
What is Neuroplasticity?
The brain’s ability to change it’s structure in response to stimuli
LTP
Long term potentiation - The process of strengthening the connection between neurons
Synaptic Pruning
The breaking of neural connections
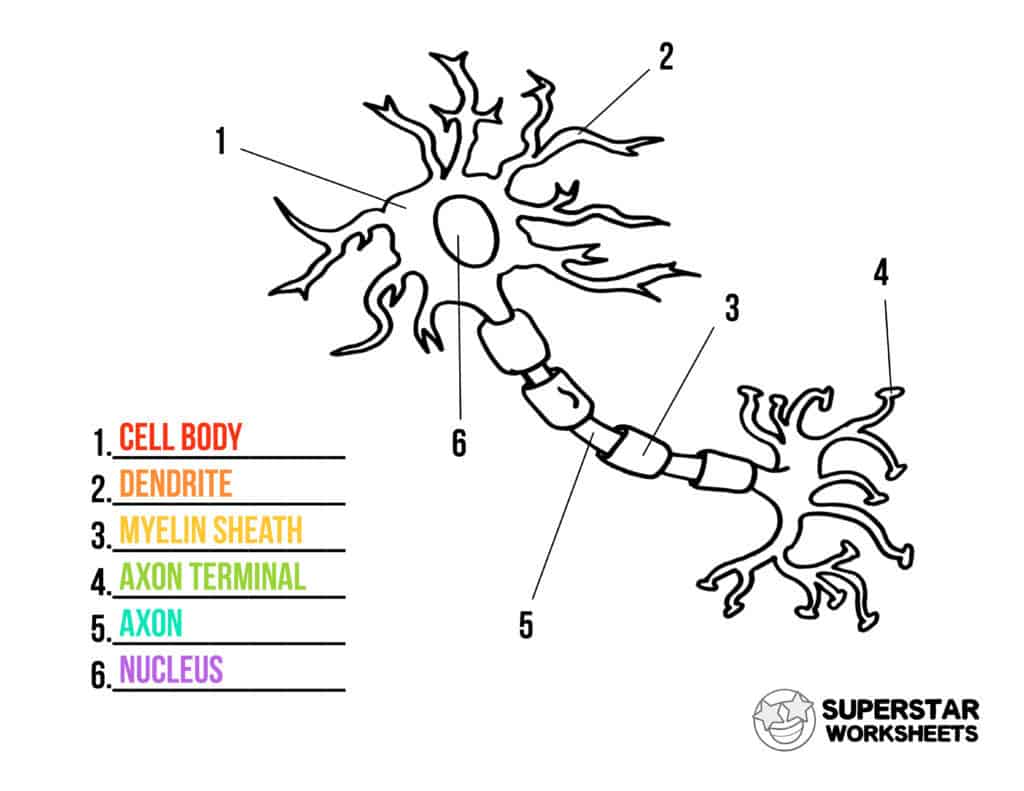
What is a synapse?
A signal sent to the detrite, passes through the body of the neuron, then through the axon terminal to another neuron
What are the two types of synapses?
Electrical - Less complex signals and allows ions to pass through
chemical - Slower than electrical signals but more complex
What are neurotransmitters?
electro-chemical signals
What happens if neurotransmitters aren’t taken by the post-synaptic neuron?
They are either diffused by enzymes or taken back by the pre-synaptic cell via a process called “re-uptake”
What are hormones?
Hormones are similar to neurotransmitters but are secreted by glands in the body and travels through the blood
What are beta-blockers and what are they used for?
blocks/stops development of emotional memories and are used to prevent PTSD
Excitatory
Higher likelihood of a neuron firing to another neuron by depolarizing the neuron
Inhibitory
Lowers likelihood of a neuron firing to another neuron by hyper-polarizing the neuron
Diathesis Stress Model
Behaviour is determined by both a person’s genetic vulnerability and environmental factors
Genetic predisposition
Your likelihood of developing a certain trait based on your genetics (inheritance)
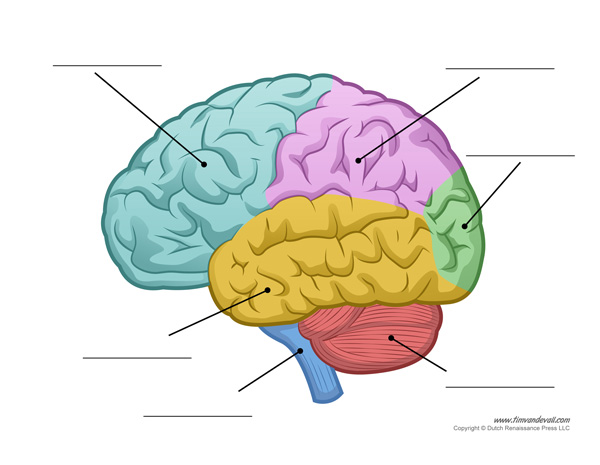
Label
.
Label
.
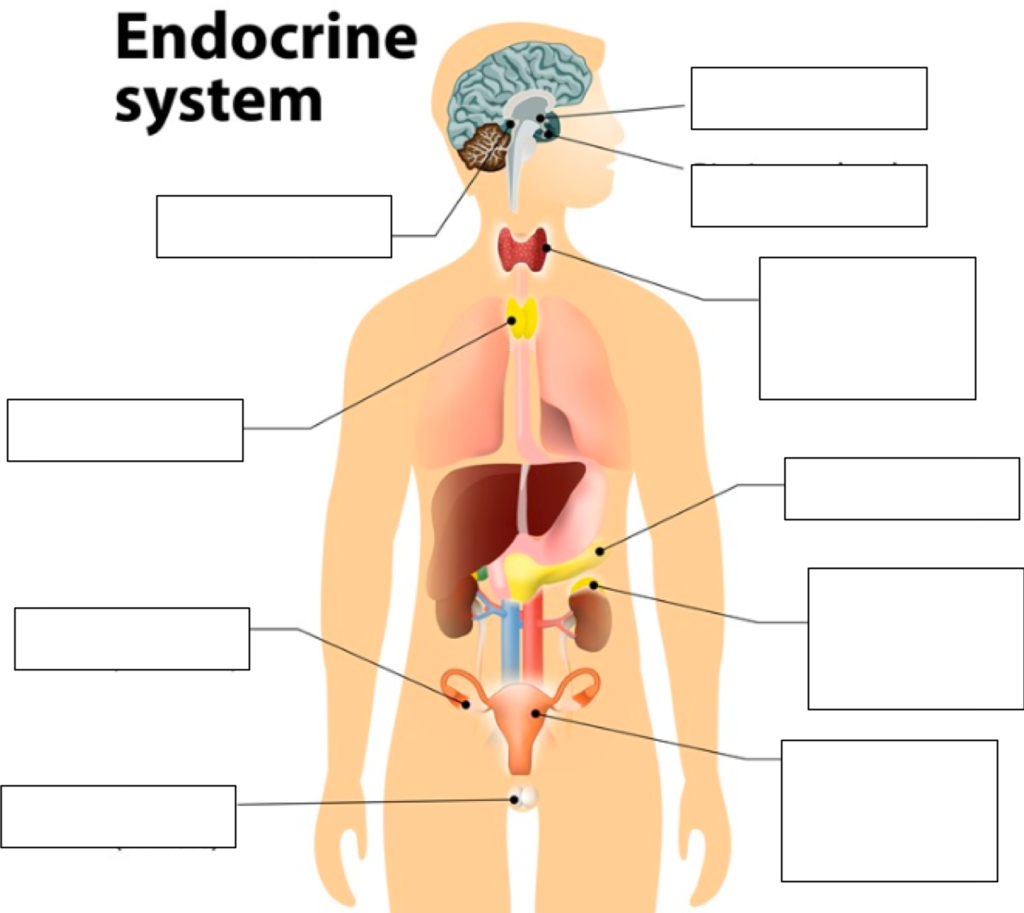
Label
.