1.2 Photosynthesis 🌱
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GCSE CCEA Specification GCSE Biology Double Award Science, Triple Award Science Unit 1: Cells, Living Processes & Biodiversity
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Photosynthesis
endothermic process by plants to create glucose, oxygen and remove carbon dioxide
Uses of glucose from photosynthesis
Respiration- used to provide energy
Storage- converted into starch and oils
Useful substances- creates cellulose for cell walls, protein for growth and chlorophyll
Chlorophyll
green pigment that absorbs light energy to carry out photosynthesis made from magnesium ions
Photosynthetic rate
speed which plants carry out photsynthesis
Testing leaves for starch
adding iodine solution after leaf has been heated and submerged in ethanol
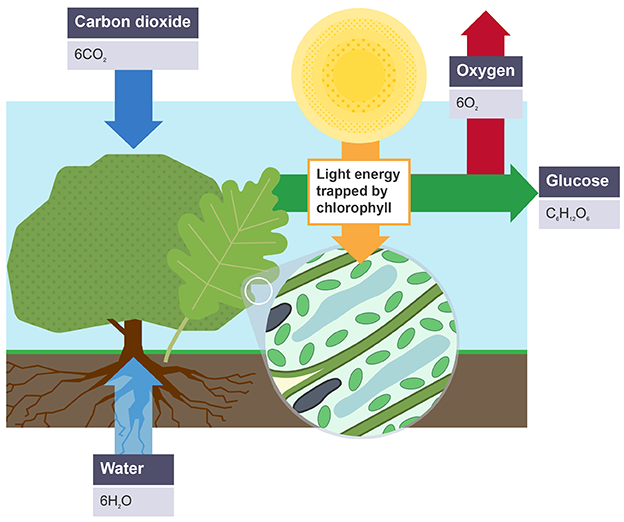
Photosynthesis word equation
Carbon Dioxide + Water (Light/Chlorophyll) → Glucose + Oxygen
Balanced equation for photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Endothermic reaction
energy is taken in from surrounding environment
Temperature effect on photosynthesis
rate increases to an optimum before decreasing due to denaturing enzymes
Cellulose
Carbohydrate component of cell walls made from glucose
Amino acids
Building blocks of protein made from photosynthesis
Enzymes
should be maintained in optimal conditions for efficient rates of photosynthesis
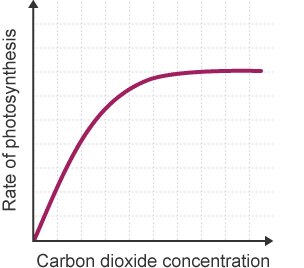
Limiting factors
as factor increases, so does rate of photosynthesis until a certain point where it plateaus (another factor must be limiting)
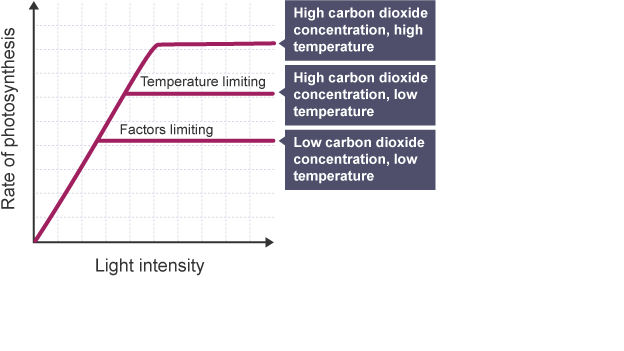
Maximum rate of photosynthesis
all limiting factors must be at optimum level, else rate will be determined by factor in shortest supply
Three main limiting factors
Temperature, light intensity and carbon dioxide concentration
Plateau
graph levels off and no longer increases past a certain point
Purpose of photosynthesis
products used for respiration and to make new molecules
When photosynthesis occurs
light conditions during the day
When respiration occurs
all the time in animals and plants, but plant respiration is more observable at night
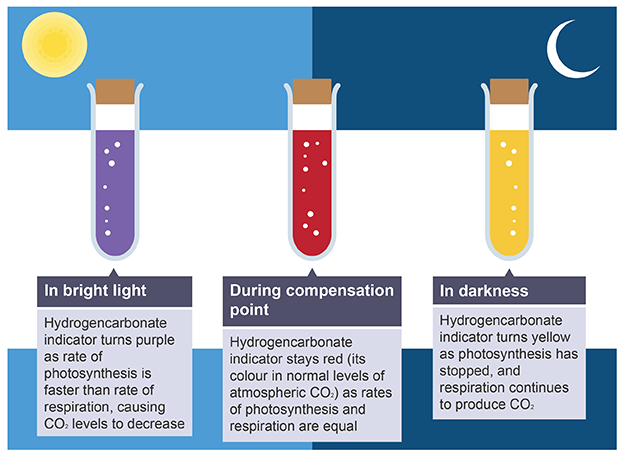
Hydrogencarbonate indicator
detect increases and decreases of carbon dioxide concentration
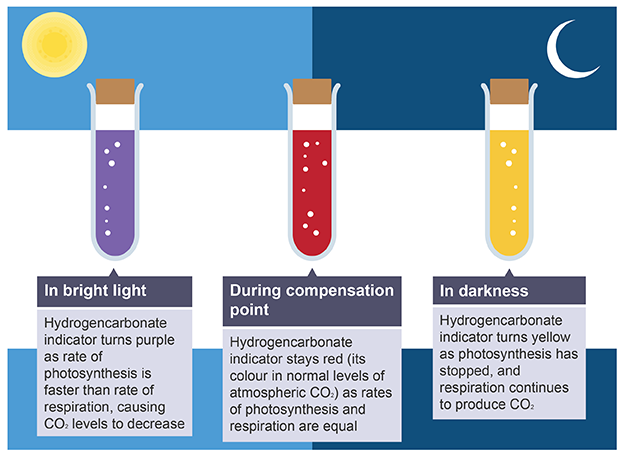
Hydrogencarbonate indicator low concentrations (midday)
purple
rate of photosynthesis is faster than respiration
CO2 produced from respiration is used, then plateaus as no longer limiting factor
Decreases net levels of CO2

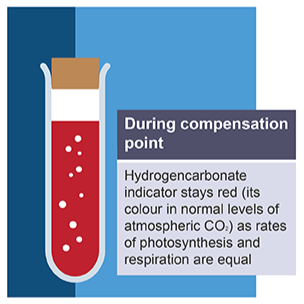
Hydrogencarbonate indicator normal concentrations (dusk/ dawn)
red
rates of photosynthesis and respiration are equal
volume of CO2 produced is the same as the volume used by photosynthesis
known as compensation point
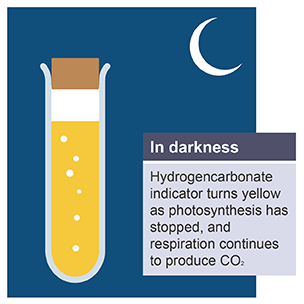
Hydrogencarbonate indicator high concentrations (midnight)
yellow
photosynthesis has stopped due to no light being available
respiration still occurs, producing CO2
Increases net levels of CO2
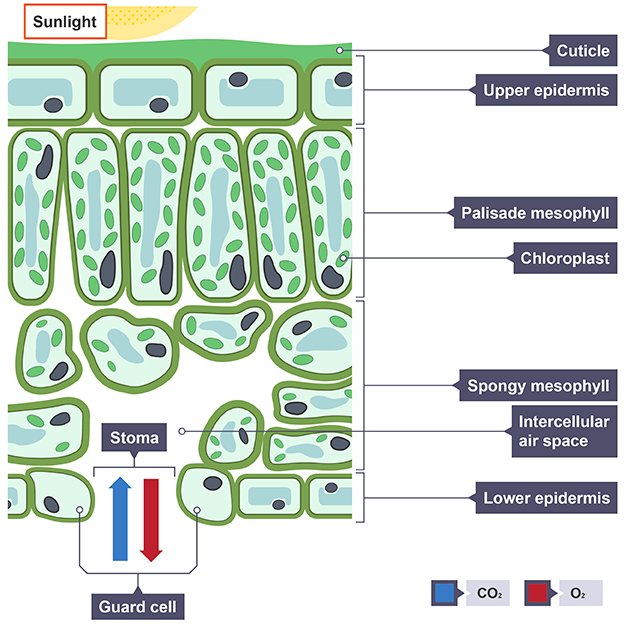
Structure of leaf
Cuticle
Upper epidermis
Palisade mesophyll
Chloroplast
Spongy mesophyll
Intercellular air space
Lower epidermis
Stomata
Guard cell
Mesophytic leaf
adapted to general conditions, not too dry or too humid
Adaptations of the leaf for light absorption
Each leaf is not in the shade of another
Thin to ensure all cells receive light
Large surface area
Transparent waxy cuticle
Epidermis transparent
Palisade mesophyll layer
Waxy cuticle
protective layer that is transparent to allow light to pass through and waterproof to reduce loss by evaporation
Epidermis
physical defence layer containing no chloroplasts so it is transparent and allows light into leaf
Palisade mesophyll
regularly shaped, so can pack closely together at top of the leaf, and contains many chloroplasts to trap as much light as possible
Adaptations of the leaf for gas exchange
Spongy mesophyll
Intercellular air spaces
Stomata
Spongy mesophyll
have very few chloroplasts and packed loosely for efficient gas exchange with increased surface areas
Intercellular space
space between to provide room for an increased rate of diffusion
Stomata
Small pores on underside of leaf to allow gases to pass through
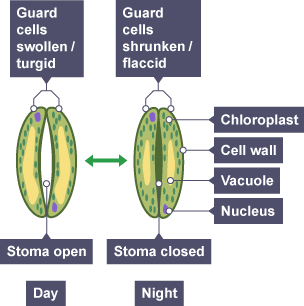
Guard cells
pairs of cells that surround stomata and control opening to optimise gas exchange and reduce water loss
Activity of guard cells
usually open during the day and closed at night