L3 connective tissues
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
How is connective tissue distributed in the body?
Abundant and widely distributed
Where is connective tissue found?
Makes up part of every organ in the body
How are connective tissue cells arranged?
Cells are separated from each other by extracellular matrix (ECM)
What are the three main classes of connective tissue?
Connective tissue proper
Supporting connective tissues
Fluid connective tissue
What functions does connective tissue perform?
Connection (tendons, ligaments)
Support (bones, cartilage)
Enclosing/protection (capsules, bones)
Separation (sheaths)
Cushioning/insulation (adipose tissue)
Storage (adipose tissue)
Transportation (blood)
What is the germ layer origin of connective tissue?
Embryonic mesoderm
What are connective tissues composed of?
Cells
Extracellular matrix (ECM)
How does this differ from other primary tissues?
Other primary tissues are composed mainly of cells
What types of resident cells are found in connective tissue?
Blasts – create the ECM
Cytes – maintain the ECM
Clasts – break down the ECM
Give examples of bone and cartilage cells.
Osteoblasts / Chondroblasts – create
Osteocytes / Chondrocytes – maintain
Osteoclasts / Chondroclasts – break down
What other cell types are found in connective tissue?
Adipose cells (adipocytes)
Mast cells (mastocytes)
Macrophages (phagocytes)
White blood cells (leukocytes)
Lymphocytes
Undifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells
What is the ECM composed of?
Ground substance
Extracellular protein fibres
What do the properties of the ECM allow connective tissue to do?
Bear weight and withstand tension and trauma
What remains after a heart is de-cellularised?
Only the ECM scaffold
Why is an ECM scaffold useful?
Useful in artificial tissue and organ regeneration
Why is recellularising with a patient’s own cells beneficial?
Eliminates adverse immune responses and is better than a donor heart
What is ground substance?
: A gel-like fluid that fills the space between cells
What does ground substance contain?
Water
Two main groups of soluble proteins
What are the two main groups of soluble proteins in ground substance?
Cell adhesion proteins
Proteoglycans
What are cell adhesion proteins?
Connective tissue glue
Give examples of cell adhesion proteins.
Fibronectin
Osteonectin
Chondronectin
What are proteoglycans?
Macromolecules with a protein core to which glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are attached
What is attached to the protein core of a proteoglycan?
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
What properties does this proteoglycan arrangement confer?
High viscosity
Low compressibility
Why is low compressibility useful?
Good for joints
How does GAG content affect ground substance
The higher the GAG content, the more viscous the fluid
List the important glycosaminoglycans (GAGs).
Hyaluronic acid
Chondroitin sulfate
Heparan sulfate
Dermatan sulfate
Keratan sulfate
What is the function of connective tissue fibres?
Provide support
What are the three types of fibres?
Collagen
Elastic
Reticular
What are key features of collagen fibres?
Most abundant (6% body weight)
Created by fibroblasts
Rope-like structure requiring vitamin C
What are the main collagen types listed? and how many types are there?
Type I – most abundant (tendons, ligaments)
Type II – cartilage
Type III – reticular fibres
25 types
What are the characteristics of elastic fibres?
Long and thin
Contain elastin
Secreted by fibroblasts
Form branching networks
Where are elastic fibres found?
Lungs and blood vessel walls
What are reticular fibres?
Short, fine fibres
Type III collagen
Form branching networks
Where are reticular fibres abundant?
Liver, spleen, lymph nodes
What components make up connective tissue?
connective tissue proper, supporting connective tissue and fluid connective tissue
what are the parts of connective tissue and what makes them up?
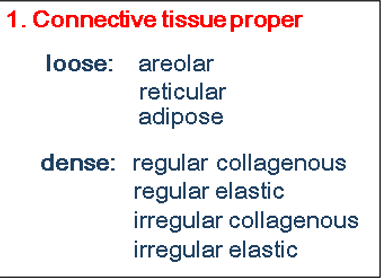
what are the parts of supporting connective tissue and what makes them up?

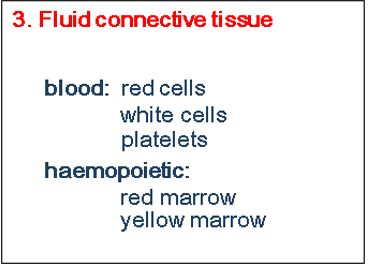
what are the parts of fluid connectuve tissue and what makes them up?
what are some examples of loose connective tissue proper?
areolar. adipose and reticular
what are some examples of dense connective tissue proper?
regular collagenous and regular elastic, irregular collagenous and irregular elastic
What components make up connective tissue?
Cells
Extracellular matrix (ground substance + fibres)
What is connective tissue classification based on?
Physical properties
What are the three main classes?
Proper, supporting, fluid
What causes scurvy?
Vitamin C deficiency leading to defective collagen fibres
What causes Marfan’s syndrome?
Defective elastic fibres due to abnormal fibrillin-1
What causes pulmonary emphysema?
Destruction of elastic tissue from increased elastase activity
What is fibrosis?
formation of excess fibrous connective tissue
What is confluent fibrosis?
Scarring that obliterates normal tissue architecture
Where is bone marrow found?
Central cavity of large bones and spaces of spongy bone
What does bone marrow produce?
Red blood cells
White blood cells
Platelets
Lymphocytes
as you become a adult what areas no longer produce blood in the bone marrow?
arms apart from elbow and shoudlder and hand. and legs apart from hip, knee and feet.
What is leukaemia?
High numbers of immature or abnormal white blood cells
What treatments are listed for leukemia?
Radiotherapy
Chemotherapy
Bone marrow transplant