week 4- CII composites
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
when should you decide the shade of composite
before you place the rubber dam, bc the teeth can desiccate teeth
what type of questions should be answered before placing restorative material
is all the infected dentin removed
is the DEJ caries-free
it there poorly supported enamel
any pulp cap needed
how to maximize bonding
how to minimize stress; shrinking factors
other considerations like biomechanics, durability, esthetics, bevels, etc
what is a matrix
a device that sequesters, supports, controls, and forms the restorative material in its unset form to facilitate placement of a clinically appropriate restoration
goals of matrices
provide good proximal contact
create good interproximal contours
provide good gingival margin seal
help for, accurate occlusal table
minimize finishing time
how to get a good proximal contact
the matrix must be in contact w the adjacent tooth
how to get a good interproximal contour
B, L, G, O embrasures are formed by the matrix → the better the matrix → the less finishing is needed

first arrow on the top
head

2nd arrow on the top
locking vise

3rd arrow on top
large knurled nut

first bottom arrow
pointed spindle

2nd bottom arrow
small knurrled nut
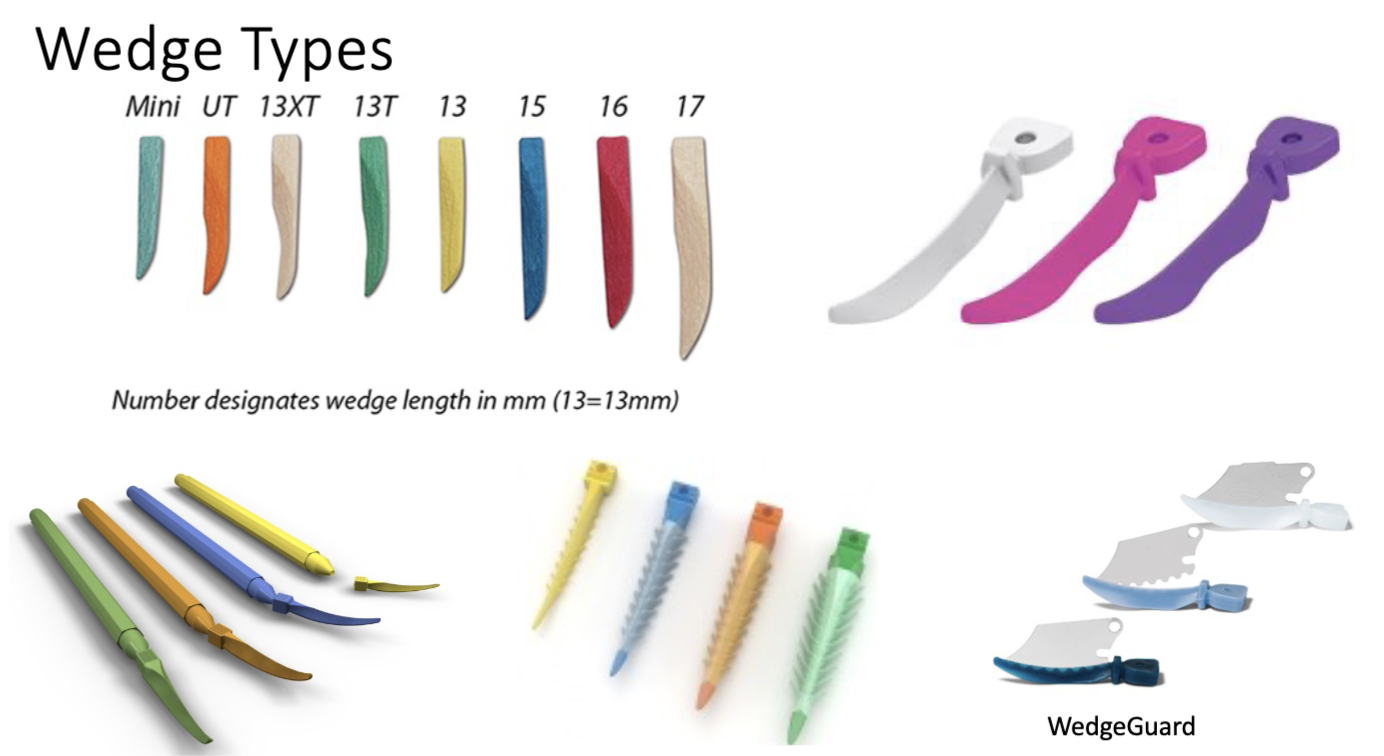
what is a wedge
a device employed to stabilize the matrix, seperate the teeth, and shape the gingival embrasure, and secure the gingival prep margin
wedging separates the teeth by stretching the…
periodontal ligament
wedging is nearly always mandatory for what types of restorations
C II and III
what do the numbers represent in wedges
length in mm

wedging goals
separate the teeth
stabilize the matrix
close the gingival margin
prevent an overhang of the restoration
shape the gingival margin embrasure
steps to prepping and restoring a CII
evaluate tooth size and position
pre-wedge
cut prep, remove pre-wedge
place the wedge
place the ring
wedge check
burnish the proximal contact
evaluation → if not okay → DO OVER
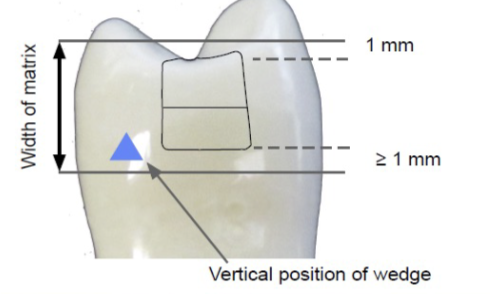
matrix dimensions to provide adequate coverage
must be at least 1 mm gingivally from gingival margin, 1 mm above the adjacent marginal ridge
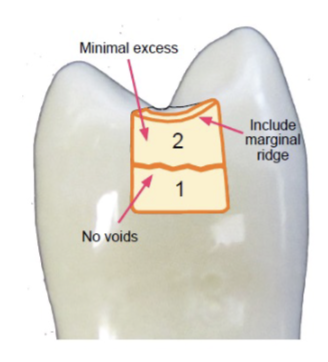
composite addition to CII
add composite to proximal contact area
start to form interproximal anatomy
photocure
don’t contaminate the polymerized surface
bulk-filling options
flowable bulk-fill + capping layer
high viscosity single increment bulk-flling
injection over molding w heated composites
composite layering techniques
horizontal layering
vertical layering
oblique layering
anatomical layering
increment placement handeling techniques
direct
pre-shaped increment
resin coating
snowplowing
what is the direct technique
the hybrid composite is directly extruded from the nozzle into the preparation and manipulation by an instrument
what is the pre-shaped increment
balls or sausage of hybrid composite are formed on the instrument and then placed into the prep
what is the resin-coating technique
a thin (.5) coat of flowable is placed over the preparation as a first increment sealing the gingival margin and/or the entire dentin
what is the slow plowing technique
a small amount of uncured flowable is placed followed by direct or pre-shaped increments of hybrid composite
how to remove the matrix
remove the ring
remove the wedge
remove the sectional matrix
final photo-polymerization from B and L
steps to finishing
course contour
final contour
final polish
what areas should be addresses first in finishing
interproximal area: gingival margin, embrasures, marginal ridge
what you can use to coarse contour the gingival margin
#12 scalpel
#7901 bur
strips
then chekc w an explorer or floss → should not shred
what can you use to coarse contour the interproximal contour
use strips or sof-lex discs
what are interproximal strip saws
interproximal reduction system that makes interproximal enamel stripping safe and accurate without creating sharp corners or subgingival ledges. are flexible, diamond strips curve and conform along the natural contours of the teeth to maximize pt comfort and safety
what to check after the rubber dam removal
occlusion
proximal contact
gingival debris
shade → note ti will not be apparent until ~24 hours
any final re-polishing
what can polishing pastes made of
aluminum oxide
polymer, pumice
or other abrasive FINE particles
when are polishing pastes recommended
anterior and esthetic cases
how to use polishing pastes
apply w rubber cup or rotary brush on slow sleep w water use