Adaptive Metallurgy Midterm Exam
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Casting
Mechanical Working
Fabrication by Joining
Machining
Powder Metallurgy
5 Principal Methods in Shaping Metals
Casting
the production of shaped articles by pourung molten metal into moulds
Mechanical Working
the shaping of metals in the solid state by plastic deformation above or below the recrystallization temperature.
Fabrication by Joining
the production of structural units by the joining of smaller components manufactured in other ways
Machining
the production of shaped articles by cutting from plain or roughly shaped forms using machine tools
Powder Metallurgy
The production of shaped parts by the die pressing and sintering of metal powders
No restriction on the type of metal or alloy
No restriction on the size of the component
Intricate external and internal shapes
A wide range of properties
Economically suitable
Cheapest available technique
6 Advantages of casting
High energy consuming process
Highly labour intensive
The quantum of raw materials required is quite high
The time required is quite long
Quite bad working condition in foundries at different stages
5 Disadvantages of Casting
According to the type of metal or alloy cast in the unit
Nature of their production
Basis of the casting process
3 Classification of Foundries
Jobbing
Production
Semi-production
Captive
Independent
5 Types of Foundries according to the Nature of their Production
Jobbing
one having a physical plant such that it usually contracts to produce a casting or a small number of castings of a given kind
Production
a highly mechanized shop which requires that large numbers of a given kind of casting be made in order to produce them at low cost
Semi production
are those in which a portion of the work is a jobbing nature while the balance is production casting.
Captive
one which is an integral part of some manufacturing company and whose castings are consumed mainly in the products of the parent organization
Independent
usually a separate company that produces castings for any number of customers
2 Types of Foundries on the Basis of the casting Process
Expendable mold processes
Permanent mold processes
Expendable mold processes
uses an expendable mold which must be destroyed to remove casting
Permanent mold processes
uses a permanent mold which can be used over and over to produce many castings
ARCO METAL PRODUCTS COMPANY, INC.
CEBU IRON FOUNDRY CORP. (CIFCO)
FONDERIE OUELLET ASIA, INC.
MAKATI FOUNDRY, INC.
QAMTIS PHILIPPINES, INC.
SUPERCAST FOUNDRY AND MACHINERY CORP.
SAN GABRIEL METAL CONCEPTS, INC.
TIGER MACHINERY AND INDUSTRIAL CORP.
8 Factories that produce metal castings
Lack of quality of raw material
Shortage of electric power in many regions
Shortage of capital/finance (use of obsolete equipment causing low productivity)
Lack of trained manpower
Metal casting is generally a low profit-making, low productive industry with larger risks from capital, employees, power and materials.
Environmental Pollution
6 Challenges for Filipino Foundry Industry
Mining and mineral processing
Core sector
Chemicals, machine tools, transport, textiles etc.
3 Important Industrial Sectors using castings
liquid or is in a highly plastic condition
Solidification Processes
We consider starting work material is either and a part is created through solidification of the material
Metals Ceramics, specifically glasses
Polymers
polymer matrix composites (PMCs)
Solidification processes can be classified according to engineering material processed:
Casting
Process in which molten metal flows by gravity or other force into a mold where it solidifies in the shape of the mold cavity The term casting also applies to the part made in the process
Melt the metal
Pour it into a mold
Let it freeze
Steps in casting seem simple:
Big parts
Small parts
2 Parts Made by Casting
Big parts
Engine blocks and heads for automotive vehicles, wood burning stoves, machine frames, railway wheels, pipes, bells, pump housings
Small parts
Dental crowns, jewelry, small statues, frying pans
ferrous and nonferrous
All varieties of metals can be cast
foundry
Casting is usually performed in a
making molds
melting and handling molten metal
performing the casting process
cleaning the finished casting
Foundry = factory equipped for
Mold
is a container with cavity whose geometry determines part shape
shrinkage
Actual size and shape of cavity must be slightly oversized to allow for of metal during solidification and cooling
sand
plaster
ceramic
metalTwo forms of mold:
Molds are made of a variety of materials, including
open mold
closed mold
Two forms of mold:
open mold
simply a container in the shape of the desired part
closed mold
in which the mold geometry is more complex and requires a gating system (passageway) leading into the cavity.
Expendable mold processes
Permanent mold processes
Two Categories of Casting Processes
Expendable mold processes
uses an expendable mold which must be destroyed to remove casting Mold materials: sand, plaster, and similar materials, plus binders
Permanent mold processes
uses a permanent mold which can be used over and over to produce many castings Made of metal (or, less commonly, a ceramic refractory material)
Sand casting
cast part produced by forming a mold from a sand mixture and then pouring molten liquid metal into the cavity in the mold. The mold is then cooled until the metal has solidified
Pour the molten metal into sand mold CAVITY
Allow time for metal to solidify
Break up the mold to remove casting
Clean and inspect casting
Separate gating and riser system
Heat treatment of casting is sometimes required to improve metallurgical properties
5 Steps in Sand Casting
5 General Steps in Casting terms
Pattern-making
Core-making
Molding
Melting and pouring
Cleaning
Pattern-making
design to be replicated
Core-making
internal cavity surface
Molding
preparation for the receiving of molten metal
Cleaning
removal of mold, core, scales, or excess metal
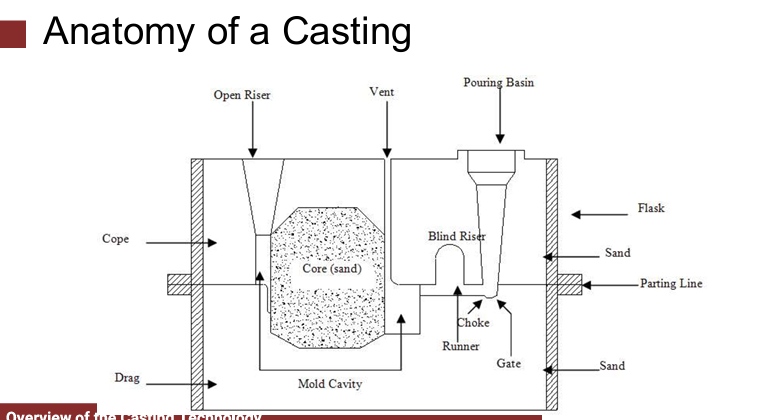
Cope
Drag
Mold consists of two halves
Cope
upper half of mold
Drag
bottom half
flask
Mold halves are contained in a box, called a
parting line
The two halves separate at the
The cavity in the sand mold is formed by packing sand around a pattern, then separating the mold into two halves and removing the pattern
The mold must also contain gating and riser system If casting is to have internal surfaces, a core must be included in mold
A new sand mold must be made for each part produced
Making the Sand Mold
Cavity
inverse of final shape with shrinkage allowance
Pattern
model of final shape with shrinkage allowance
Wet sand
made by adding binder in the sand
Cavity is inverse of final shape with shrinkage allowance
Pattern is model of final shape with shrinkage allowance
Wet sand is made by adding binder in the sand
Mold cavity is formed by packing sand around a pattern When the pattern is removed, the remaining cavity of the packed sand has desired shape of cast part The pattern is usually oversized to allow for shrinkage of metal during solidification and cooling
Forming the Mold Cavity
Cavity
provides the external features of the cast part
Core
provides internal features of the part. It is placed inside the mold cavity with some support.
Gating System
It is channel through which molten metal flows into cavity from outside of mold
It is channel through which molten metal flows into cavity from outside of mold Consists of a down-sprue, through which metal enters a runner leading to the main cavity
At the top of down-sprue, a pouring cup is often used to minimize splash and turbulence as the metal flows into down-sprue
Gating System
Riser
It is a reservoir in the mold which is a source of liquid metal to compensate for shrinkage of the part during solidification
Most metals are less dense as a liquid than as a solid so castings shrink upon cooling, which can leave a void at the last point to solidify. Risers prevent this by providing molten metal to the casting as it solidifies, so that the cavity forms in the riser and not in the casting
Riser
The Pattern
A full-sized model of the part, slightly enlarged to account for shrinkage and machining allowances in the casting.
Pattern materials:
Wood
Metal
Plastic
Wood
common material because it is easy to work, but it warps
Metal
more expensive to make, but lasts much longer
Plastic
compromise between wood and metal
solid pattern
split pattern
match-plate pattern
cope and drag pattern
Types of Patterns
Solid Pattern (Loose or Single Piece)
Problem in locating the parting line. Locating is skill dependent. Suitable for low production
Split pattern
Relatively easy to locate parting line. Used for low-medium size production
Match-plate pattern
The cope and drag portions of the pattern are mounted on opposite sides of a wood or metal plate conforming to the parting line. Match plates are also integrally cast in which cast pattern and plate are cast as one piece in sand or plaster molds. It is used with some type of molding machine, in order to obtain maximum speed of molding. Advantages of the match-plate patterns are: (a) Costly but good production rate (b) Increase the dimensional accuracy
Cope and Drag pattern
(a)Similar to match-plate pattern but split pattern halves are attached to separate plates.
(b)The pattern contains built-in gating system thus save time for making separate gating system in each mold.