Power Electrical Engineering for Renewables | L2
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
A diode is what type of device?
Uncontrolled.
What type of device is uncontrolled?
Diode.
A thyristor is what type of device?
Half-controlled.
What type of device is half-controlled?
Thyristor.
A transistor is what type of device?
Fully-controlled.
What type of device is fully-controlled?
Transistor.
A converter consists of which two elements?
Power switching semiconductor + energy storage element.
What does the controller do?
Switches on/off the semiconducting devices in the converter.
What are two types of circuits that are present in power electronics?
Information circuit & power circuit.
What circuit interfaces between an information circuit and a power circuit?
A drive circuit.
A diode has how many terminals?
2
How are on/off states determined for a diode?
By power circuit.
A thyristor has how many terminals?
3
How is a thyristor turned on?
Control signal.
How is a thyristor turned off?
Power circuit.
A transistor has how many terminals?
3
How is a transistor turned on/off?
Control signal.
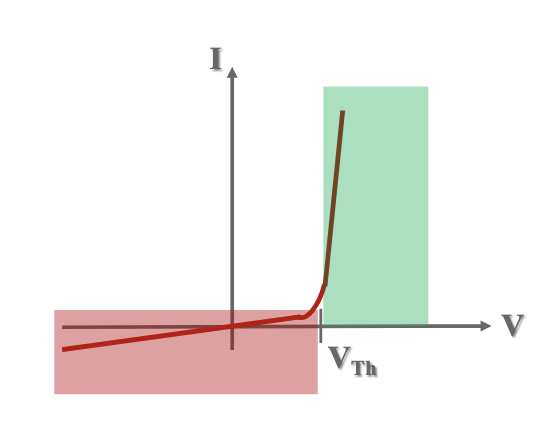
What semi-conductive device is this?
Diode.
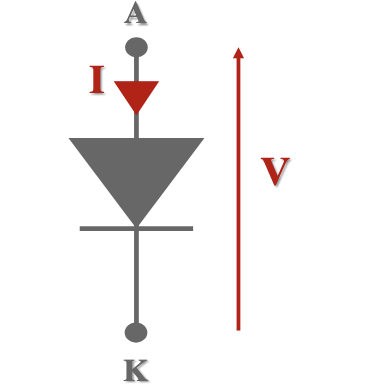
What semi-conductive device is this?
Diode.
What is an N-type semi-conductor?
Electrons are the majority carriers.
What is a P-type semi-conductor?
Holes are the majority carriers.
An equilibrium junction creates a ____________ that results in ________.
charge separation, E (electric field)
In an equilibrium junction, E ________ diffusion of carriers.
stops
The equilibirum junction leads to what condition?
Thermal equilibrium.
What is characteristic of a reverse-biased PN junction?
Ve+ to n & Ve- to p
For a reverse-biased PN junction, what happens if you apply a voltage in circuit?
It will induce an applied electric field.
In a reverse-biased PN junction, do the applied electric field and the E-field within the space-charge region point in the same or opposite direction?
Same
Does the total magnitude of the reverse-biased PN electric field (E_T) increase or decrease compared to the thermal equilibrium value?
Increase
What is the resulting action of the forces in a reverse-biased PN junction?
Increased electric field holds back the holes and the electrons in their proper regions.
What is characteristic of a forward-biased PN junction?
Ve+ to p & Ve- to n
In a forward-biased PN junction, do the applied electric field and the E-field within the space-charge region point in the same or opposite direction?
opposite
Does the total magnitude of the forward-biased PN electric field (E_T) increase or decrease compared to the thermal equilibrium value?
decrease
What is the resulting action of the forces in a forward-biased PN junction?
Diffusion of charges begins and continues as long as a voltage is applied (to induce the required E-field).
What is the relevant meaning of diffusion of charges in a forward-biased pn-junction?
Current.
What is a benefit of a thyristor?
Used in very high power situations.
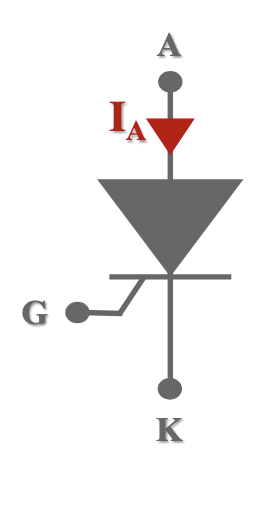
What semi-conductive device is this?
Thyristor.
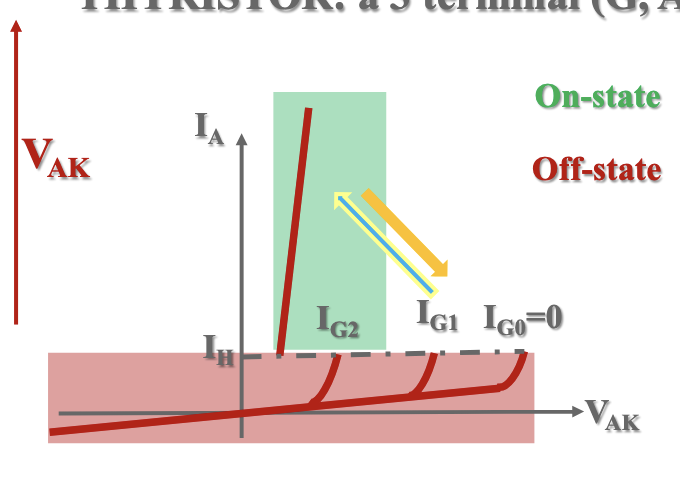
What semi-conductive device is this?
Thyristor.
What semi-conductive device is this?
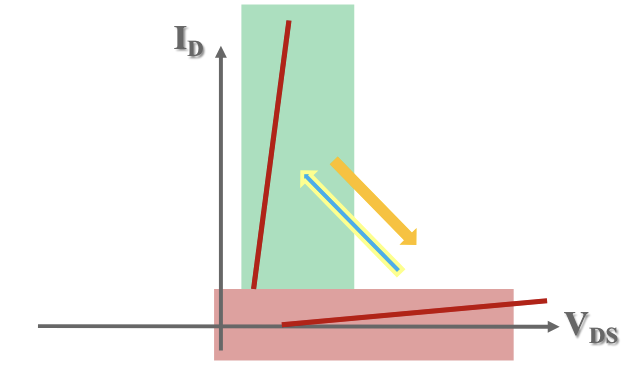
Transistor.
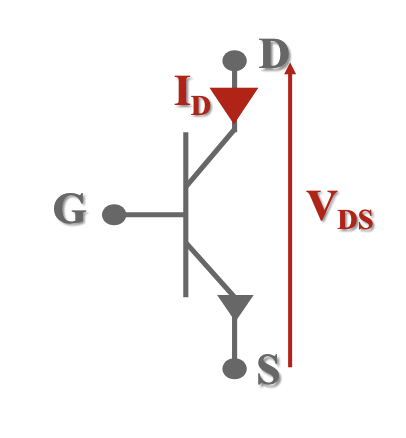
What semi-conductive device is this?
Transistor.