Chapter 2,3,4
1/262
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
263 Terms
Proton
positive charge, inside nucleus, 1 amu
Electron
negative charge, outside nucleus, 0 amu
Neutron
no charge, inside nucleus, 1 amu
Isotopes (nucleus breaks apart and can be radioactive)
Atoms with the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons.
Carbon Dating
a scientific method used to determine the age of an artifact. Carbon-14 > Nitrogen-14 = Older

Energy Levels (K, L, M, N…)
electrons farther from nucleus have more energy

Which energy level has the least energy?
K (Closest to the nucleus)
Valence Shells
outermost electron shell, with unpaired electrons which participates in chemical reactions and bonding

Orbitals/shells
regions around the nucleus which holds up to 2 electrons each

How does an Electron gain energy?
When it absorbs light energy (photons) and moves to a higher energy level
When does and Electron lose energy?
Electrons can lose energy by emitting heat or light and move closer to the nucleus
Ion
forms when an atom gains or loses a electron
Cations
Positively charged ions resulting from the loss of electrons. Protons > Electrons

Anions
negatively charged ions formed by gaining electrons. Electrons > Protons

Molecule
2 atoms or more of the same element bonded together.
What holds a molecule together?
Covalent bond
Compound
a substance made of 2 atoms or more of different elements
What holds a compound together?
Chemical bonds

How are electrons gained?
it is reduced, when an oxidizing agent is added
How are electrons lost?
it is oxidized, when a reducing agent is added
Chemical Bonds
When atoms with incomplete outer shells react to end up with shared electron pairs.
Covalent bond
A chemical bond that involves sharing one or more pair of electrons

Ionic bond
A chemical bond resulting from the attraction between oppositely charged ions.

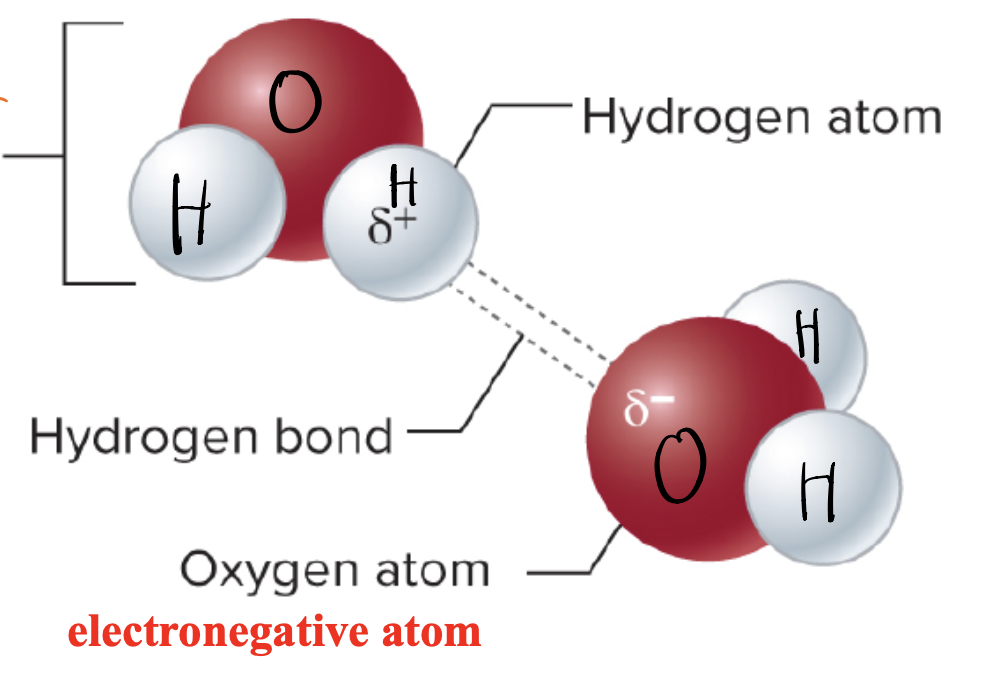
hydrogen bond
3rd weak: weak attraction between a hydrogen atom and another atom

Hydrophobic interactions or hydrophobic forces
4th weak: Interactions between hydrophobic molecules grouping together to avoid water

Van der Waals interactions
individually weak and occur only when atoms and molecules are very close together
polar covalent bond
a covalent bond in which electrons are shared unequally due to different electronegativity

non-polar covalent bond
a covalent bond where electrons are shared equally due to the same electronegativity

What is stronger polar or non polar covalent bonds?
Polar covalent bonds are generally stronger than non-polar covalent bonds due to the unequal sharing of electrons, which creates a dipole moment.
Hydrogen Bonds
form between hydrogen atom of one molecule and an electronegative atom (O, N, or F) of another atom
Chemical Reaction
The formation and breaking of bonds
What can change the rate of a chemical reaction?
Catalysts, Temperature, and Concentration of reactants
What is catalyst
enzyme that speeds up chemical reactions.
what is a type of catalyst?
Homogeneous Catalysts- Acids and bases and transition metals, same phase as a reactant
Heterogeneous Catalysts - Metal catalysts, platinum, different phase as a reactant
Enzymes (biocatalysts) - Protein, Amylase, lipase and protease
The importance of Water (H2O)
Cohesive, adhesive, capillary action, high specific heat, high heat of vaporization, universal solvent, and essential for biological processes.
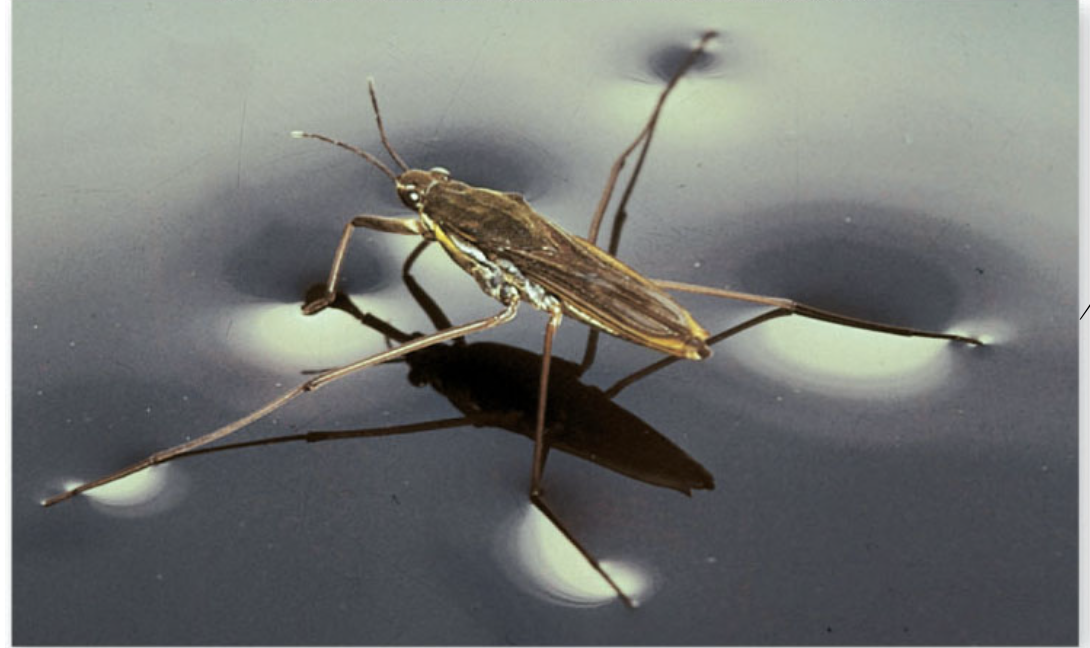
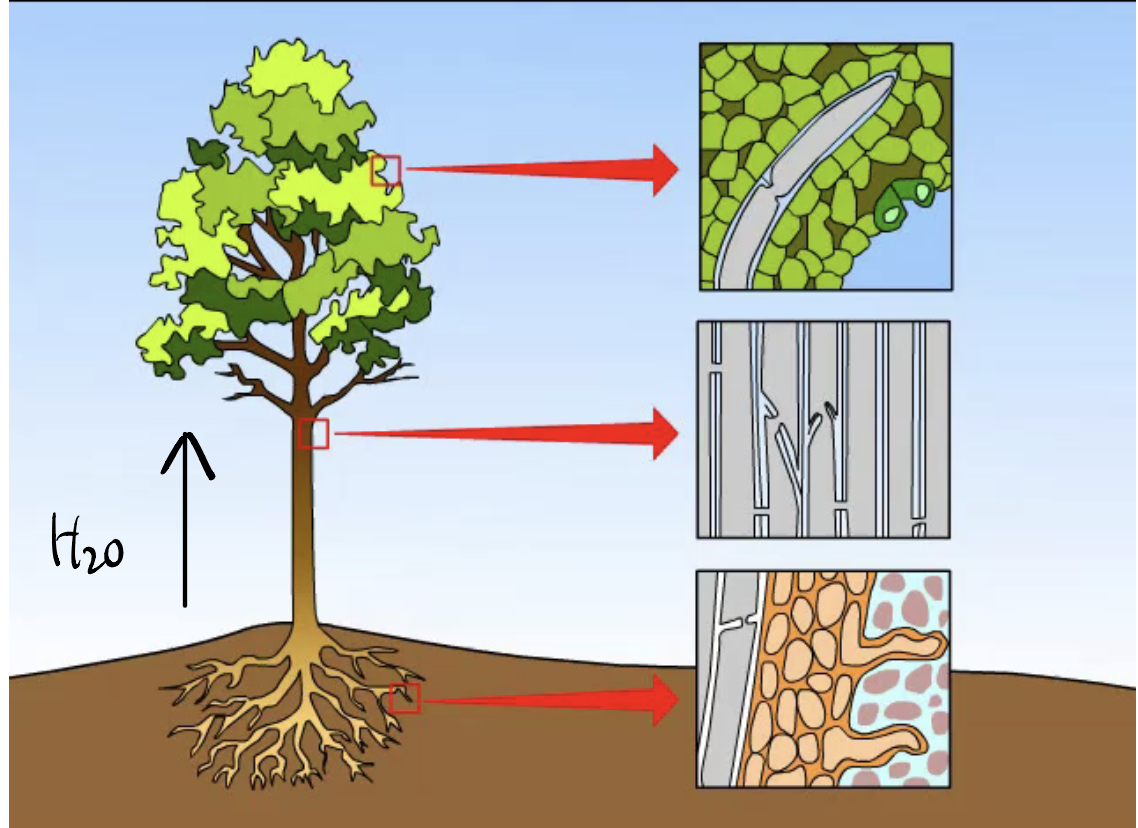
H2O Cohesion
H2O molecules stick together due to hydrogen bonding, allowing for surface tension and the transport of nutrients in plants.

H2O Adhesion
H2O molecules stick to other polar molecules by hydrogen bonding, resulting in capillary action and the ability of water to move through porous materials.
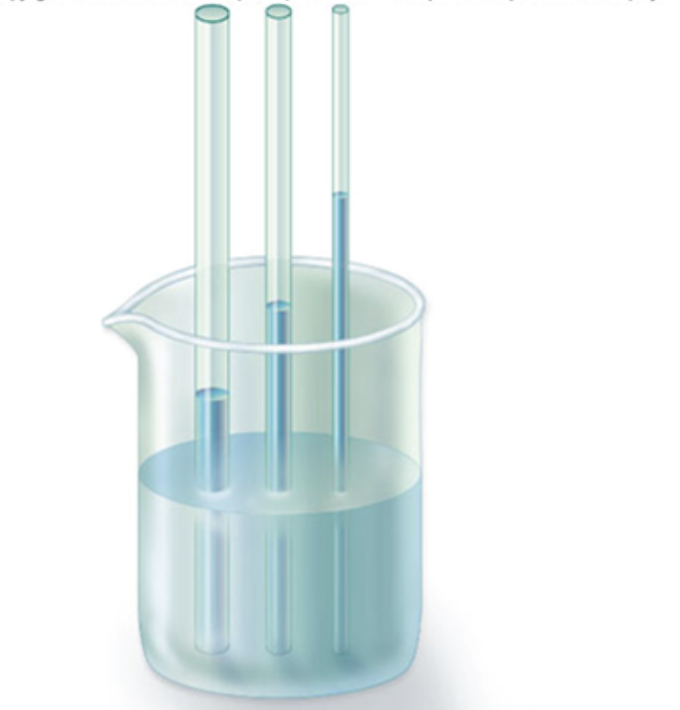

Does water move up or down?
Water ALWAYS moves up as cohesive and adhesive properties of water work together to move water from the roots to the leaves of plants.
H2O has high specific heat, what is it?
a large amount of heat (energy) is needed to raise the temperature of water
H2O has a high heat of vaporization, what is it?
a lot of heat (energy) is necessary to turn liquid water into vapor, which allows living things to release excess body heat via sweating
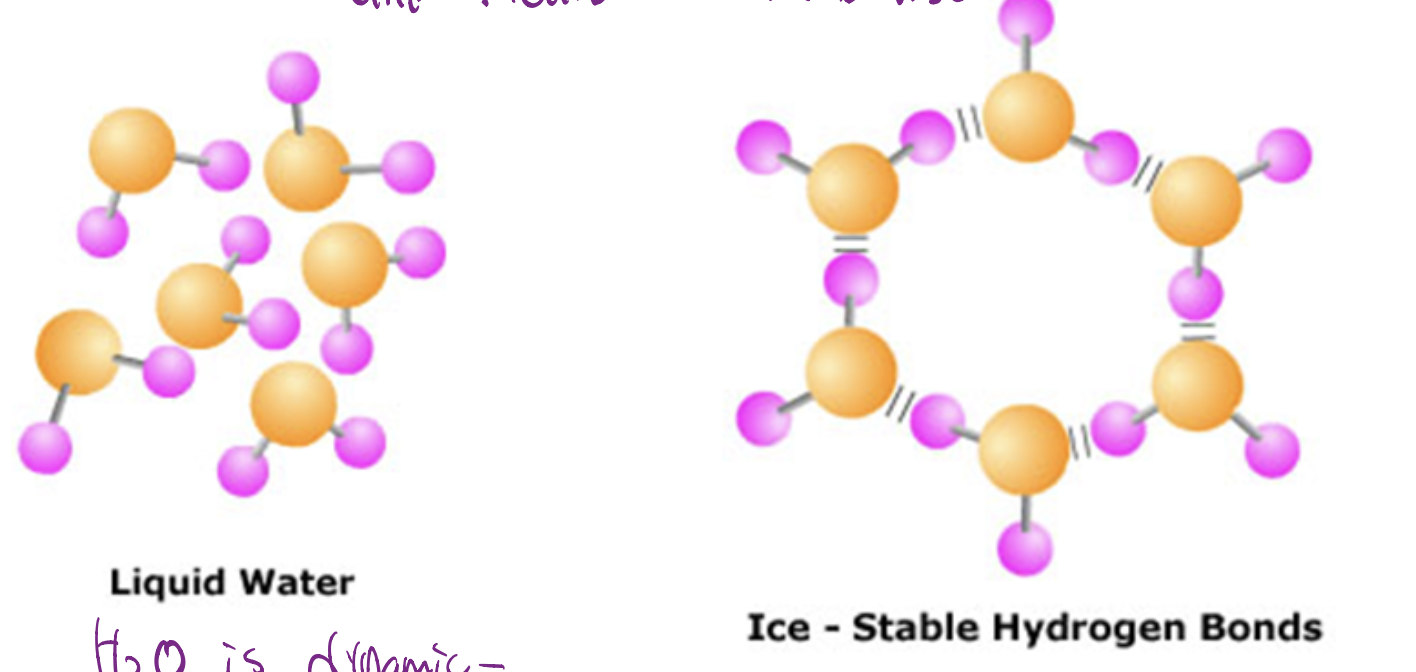
How does H2O freeze?
Bodies of water freeze from the top down, when H2O freezes (ice) is less dense than liquid H2O. But H2O is dynamic and can break and reform
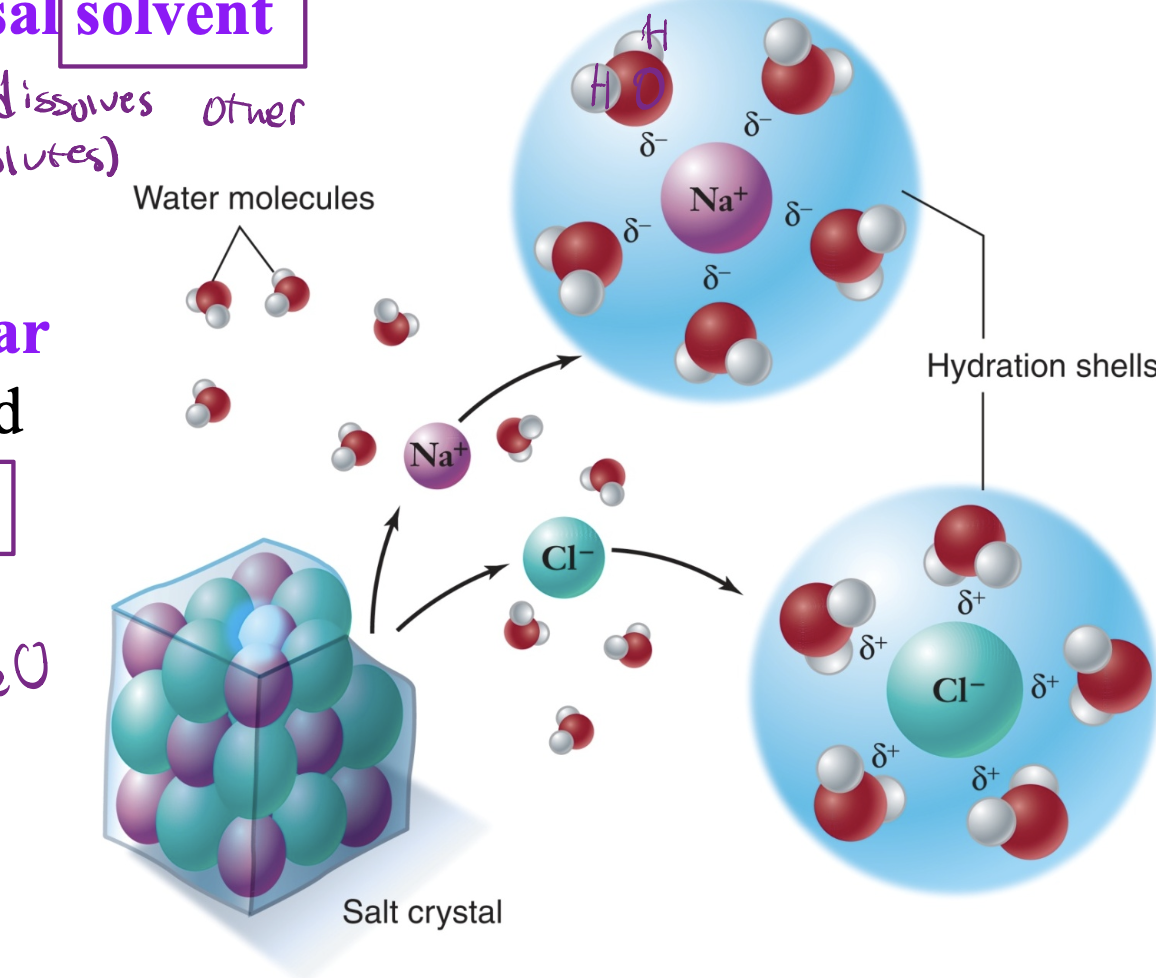
What type of solvent is H2O?
H2O is a universal solvent which dissolves other substances (solutes) which dissolves polar molecules and ions (solutes).
What are solutes
Substances dissolved in a solvent, forming a solution. Examples include salt in water or sugar in coffee.
Hydrophilic
Water loving substances that are usually polar and readily dissolve in water.
Hydrophobic
Water fearing substances that do not dissolve in water, typically non-polar. water causes hydrophobic molecules to aggregate or assume specific shapes.
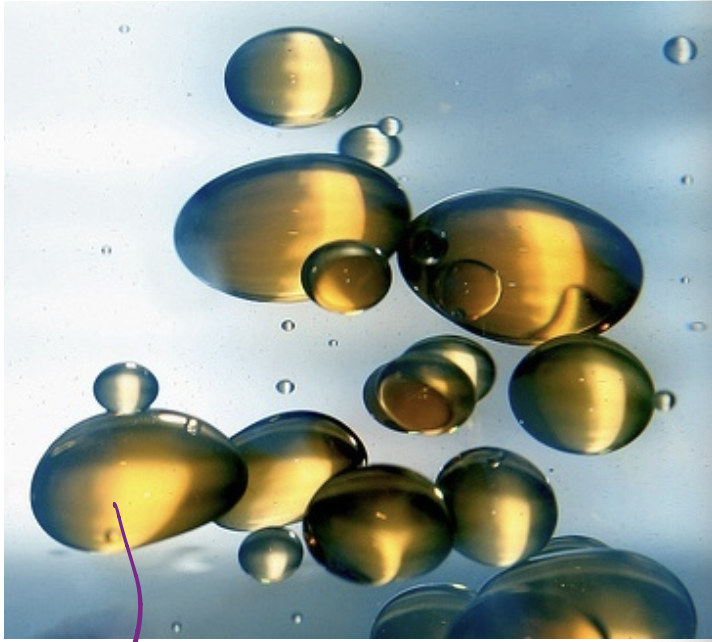

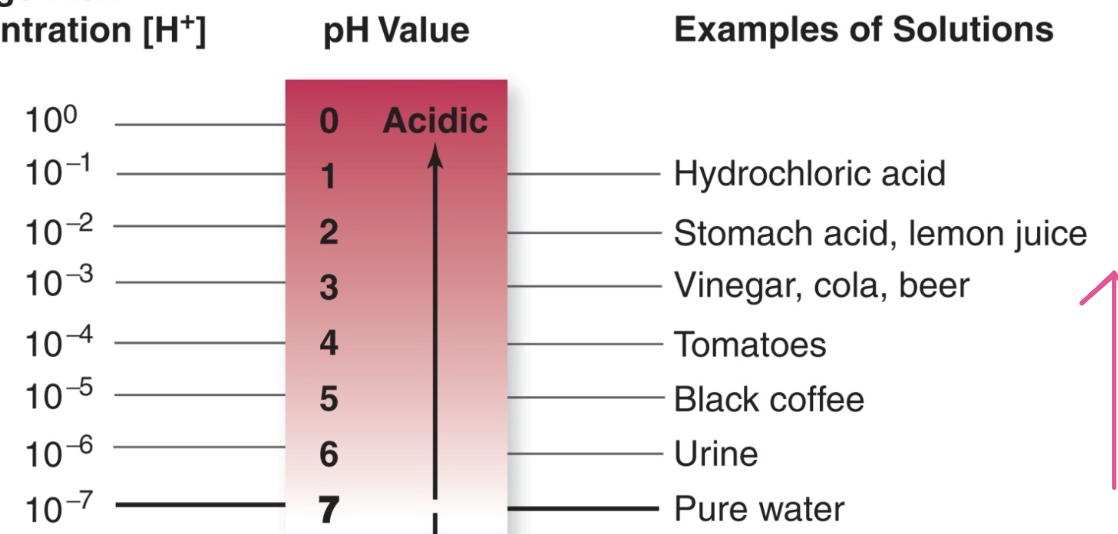
When water forms ions it makes Acids solutions
When there is more hydrogen ion concentration [H+] than the solution is acidic, <7 less pH more acidic
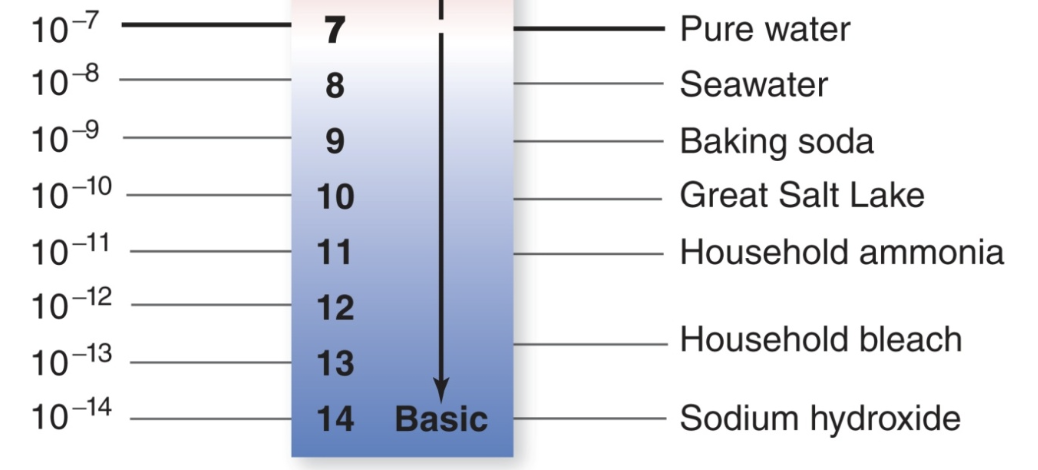
When water forms ions it can turn into basic solution
When there is less hydrogen ion concentration [H+] than the solution is basic, >7 more pH more basic
What is a buffer and why is it needed?
A buffer is a solution that resists changes in pH when an acid or base is added. It is important for maintaining stable pH levels.
How does a buffer work?
A buffer works by either releasing or absorbing hydrogen ions (H+) in response to changes in pH, thus helping to maintain a relatively stable pH in a solution.
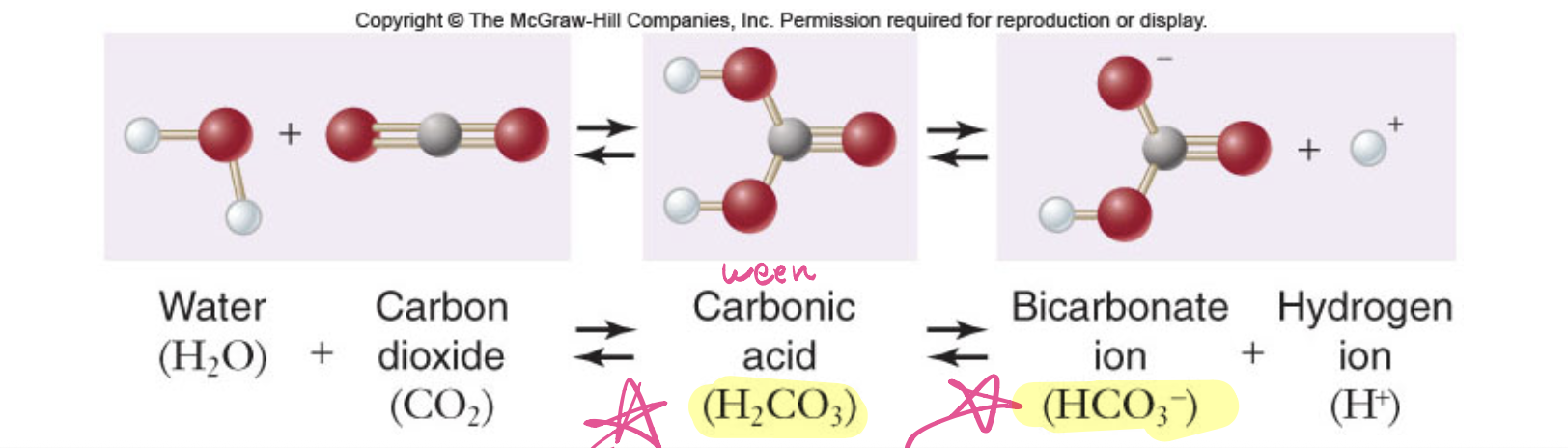
what is the formula of a carbonic acid-bicarbonate buffer
Carbonic acid (H2CO3) ←→ Bicarbonate ion (HCO3 -) + Hydrogen ion (H+)
Acidosis
When blood pH becomes too acidic due to a lot of [H+ ions], occurs when blood pH falls bellow <7.35, all caused by hypoventilation
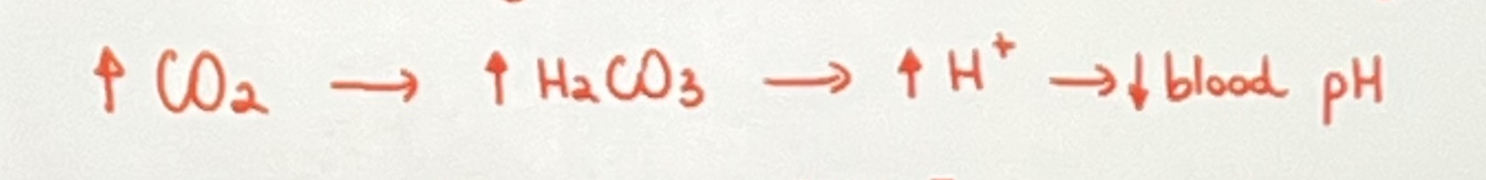
what is hypoventilation?
Hypoventilation is when we breath too little, leading to an increase in carbon dioxide levels and a decrease in blood pH. the respitoray disease is usually pneumonia or emphysema.
How is Acidosis corrected?
Acidosis is corrected by increasing respiration or adding bicarbonate ion (HCO3)
Alkalosis
When blood pH becomes too basic due to not a lot of [H+ ions], occurs when blood pH rises above 7.45, often caused by hyperventilation.

What is hyperventilation?
Hyperventilation is caused when we breathe too much usually from stress and anxiety
How is Alkalosis corrected?
Alkalosis is corrected by adding H2CO3, or putting paper bag over the mouth and short breathing.
What are the 4 Macromolecules?
The four macromolecules essential for life are carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. They are organic compounds due to the presence of Carbon skeletons
Carbohydrates
Organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, serving as a primary energy source for living organisms typically in a ratio of 1:2:1.. They are classified into simple sugars (monosaccharides), disaccharides and complex forms (polysaccharides).
What are the subunits of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides, such as glyctose, glucose and fructose, are the basic subunits that make up carbohydrates.
Glucose
the primary energy source for cells. It’s used in cellular respiration to make ATP. (monosaccharide)
Starch
energy storage in plants, composed of long chains of glucose molecules.(polysaccharide carbohydrate)
Glycogen
a polysaccharide that storage’s form of glucose in animals, especially in liver and muscle cells
Cellulose
a structural polysaccharide carbohydrate in plant cell walls. Humans can’t digest it, but it’s important as fiber.
Chitin
a structural polysaccharide that provides strength and support to fungal cell walls and in the exoskeletons of insects and crustaceans
Gene
Piece of DNA that codes for a protein
Gene expression
The process of when a gene is transcribed and translated
Transcription
The second step in the process of gene expression when DNA is copied to RNA
Translation
The final step of gene expression where RNA is decoded into proteins
Replication
The first step of gene expression where DNA is copied to create identical copies of itself, ensuring each new cell has the same genetic information.
What is the correct order for the gene expression process?
Replication, Transcription, Translation.
What are functional groups?
The certain groups of atoms in macromolecules that determine their chemical function
Hydroxyl
group (-OH), a functional group found in carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids
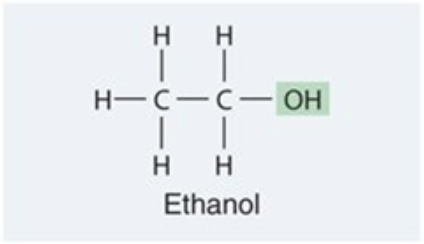
Carbonyl
group (C=O), a functional group found in carbohydrates and nucleic acids that can influence molecular structure and reactivity.

Carboxyl
group (-COOH), a functional group found in amino acids and fatty acids that acts as an acid by donating its [H+] to a solution. And becomes a negatively charged (COO-) ion
![<p>group (-COOH), a functional group found in amino acids and fatty acids that acts as an acid by donating its [H<sup>+</sup>] to a solution. And becomes a negatively charged (COO<sup>-</sup>) ion</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5d5fc62e-e953-43c0-8f1f-d9195cd7fe75.png)
Amino
group (-NH2), a functional group found in amino acids that acts as a base by accepting an [H+] from a solution. And becomes a positively charged (NH3+) ion.
![<p>group (-NH<sub>2</sub>), a functional group found in amino acids that acts as a base by accepting an [H<sup>+</sup>] from a solution. And becomes a positively charged (NH3<sup>+</sup>) ion.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5351b288-0283-49a8-b26e-f2523fbbdaf1.png)
Slufhydryl
group (-SH), a functional group found in some amino acids that can form disulfide bonds, influencing protein structure.
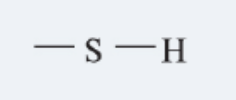
Disulfide bridge
A covalent bond that forms between the sulfur atoms of two cysteine amino acids
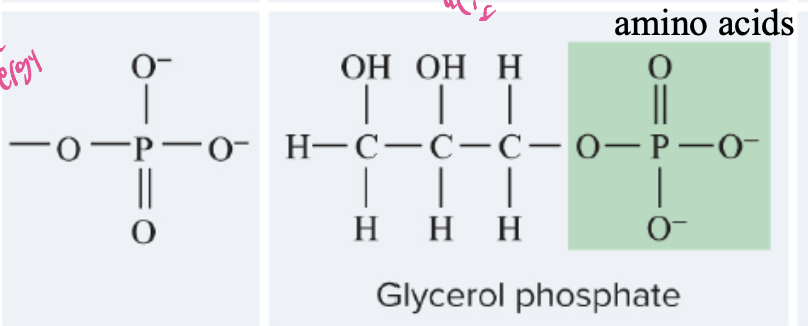
Phosphate
group (O-O—-P-O--O-), a functional group that plays a key role in energy transfer in cells, often found in nucleic acids, ATP, and can attach to other molecules to modify their function.
Methyl
group (-CH₃), a functional group that can affect gene expression and play a role in metabolism. Found in proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. Methyl is non-polar covalent.
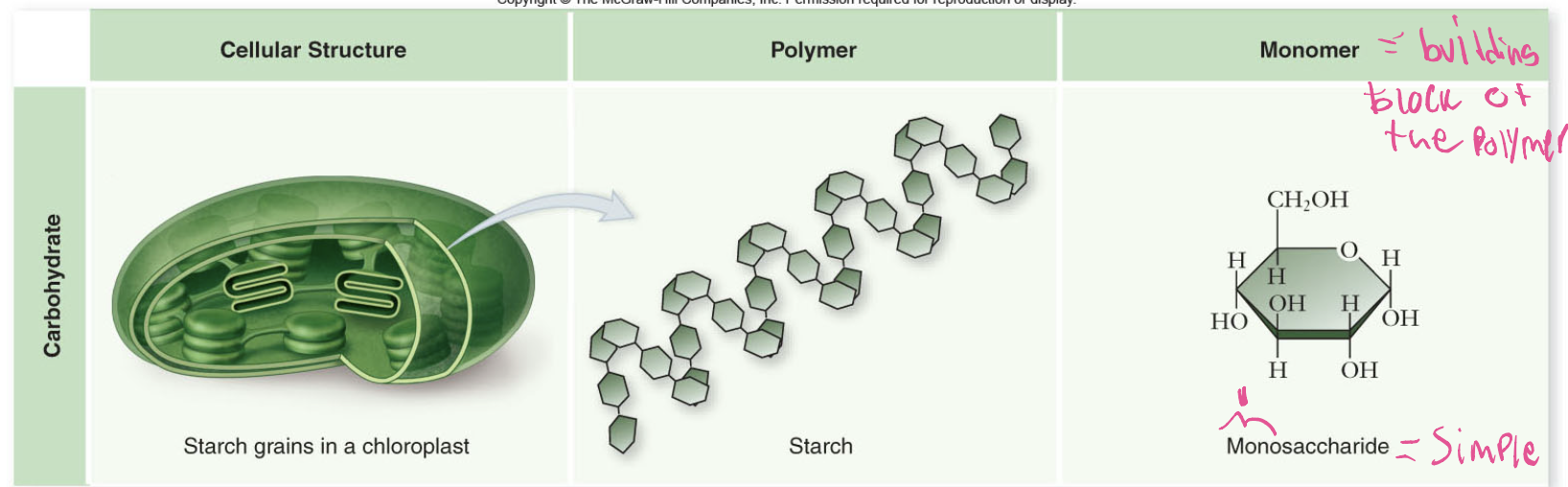
What makes carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are made of monomers called monosaccharides (simple sugars). These link to form polymers like starch in plants (stored in chloroplasts) or glycogen in animals (stored in liver and muscle cells).
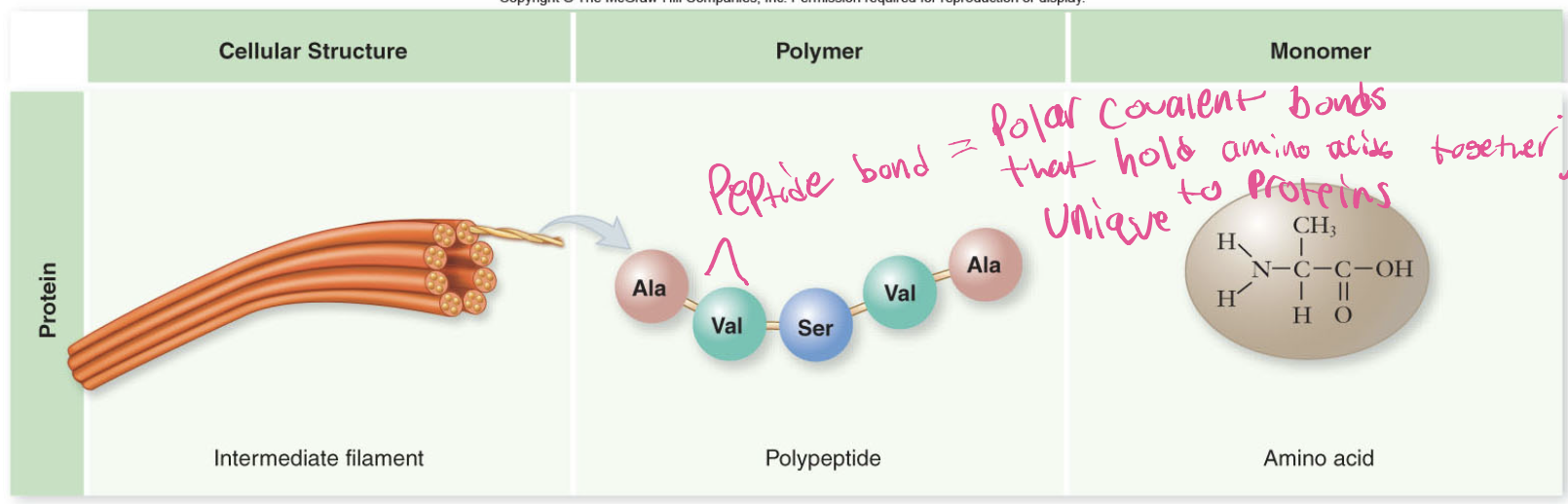
What are Proteins made of?
Proteins are made of amino acids, which are linked by peptide bonds to form dipeptide or polypeptides.
Peptide bond
Polar covalent bond that holds amino acids together; each unique to proteins which determines their structure and function.
What is it called when two amino acids form a dipeptide?
Chains of amino acid held together by peptide bonds.
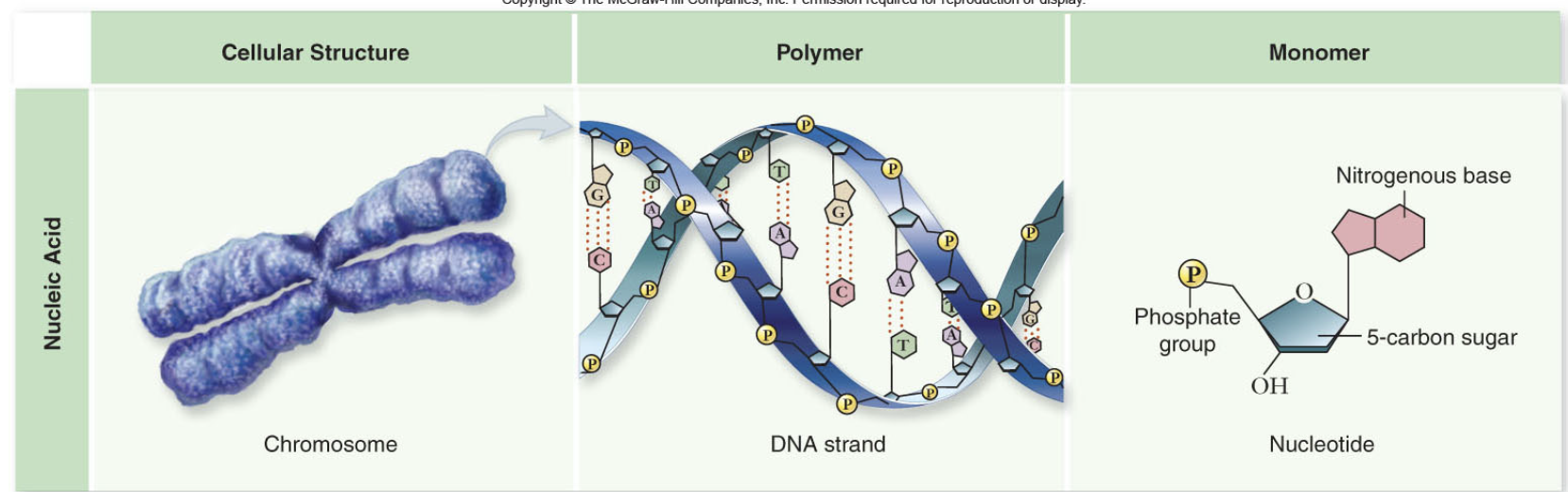
What is DNA made of?
They are formed of nucleotides, which consist of a 5 carbon sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base. Then turned into a dna strand that connects these nucleotides through phosphodiester bonds. And then turned into chromosomes.
What is RNA made of?
They are also formed of nucleotides join through phosphodiester bonds to form a single RNA strand. RNA stays single-stranded and folds into various shapes and carry genetic information in cells.
Whats a nucleotide?
A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids, consisting of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
What are lipids made of?
Lipids are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the form of fatty acids and glycerol. Some also include phosphate groups or ring structures, depending on the type, like phospholipids or steroids.
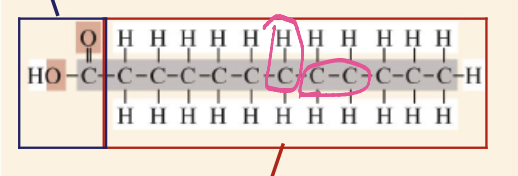
How to make a polymer?
Polymers form through dehydration synthesis when monomers bond by losing a water molecule.
Dehydration synthesis
is a chemical reaction in which two or more molecules combine to form a larger molecule, with the elimination of water. Which forms covalent bonds.
How to break apart a polymer?
Polymers break apart through hydrolysis, which adds a water molecule to split the bonds between monomers. The –H and –OH from water attach to the separate monomers, reversing dehydration synthesis.
What is hydrolysis?
Is when water is added to a molecule to split between monomers. Which breaks apart covalent bonds in the polymer.
Isomers
are compounds that have the same molecular formula but arranged differently, resulting in different properties.
How are disaccharides formed?
When two monosaccharides undergo dehydration synthesis, where a water molecule is removed to bond them together.
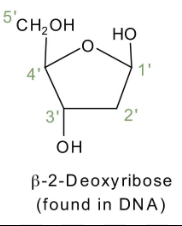
Deoxynucleotides
Are nucleotides that are used to make dna because of a sugar Deoxyribose which has -H attached to its 2’C
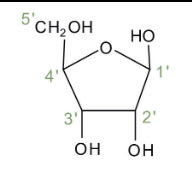
Ribonucleotides
Are nucleotides that are used to make RNA, containing the sugar ribose which has -OH attached to its 2'C.
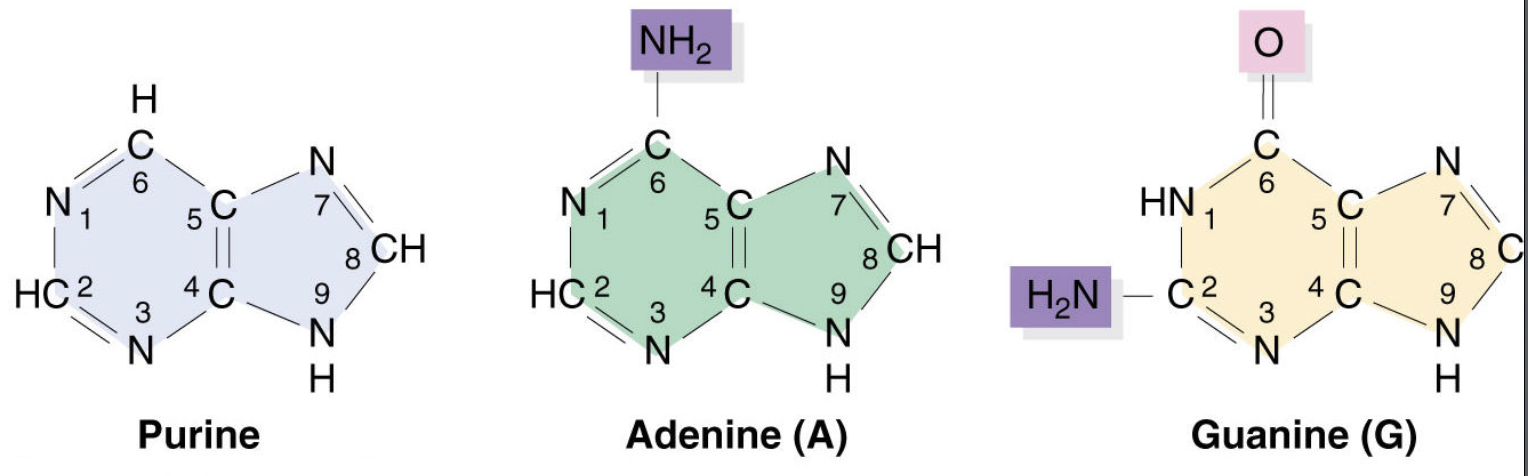
Purines
Are double ringed nitrogenous found in DNA and RNA, including adenine and guanine.
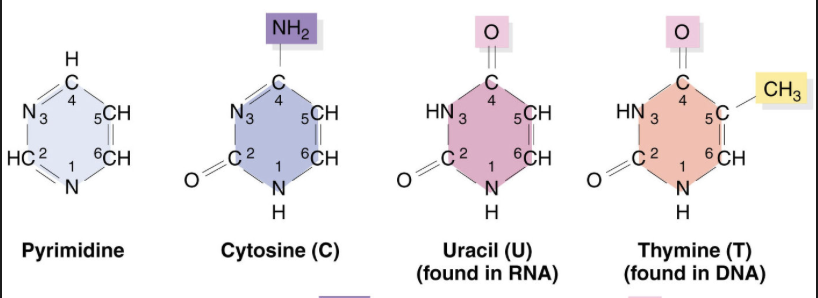
Pyrimidines
Are single ringed nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA, including cytosine, thymine, and uracil.
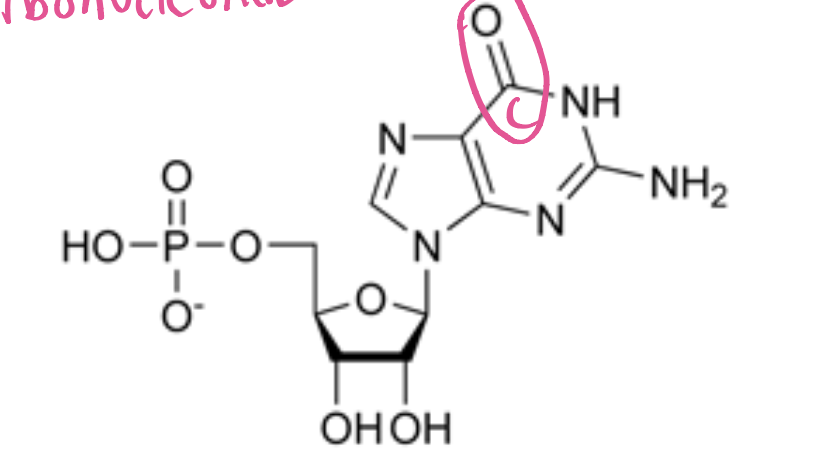
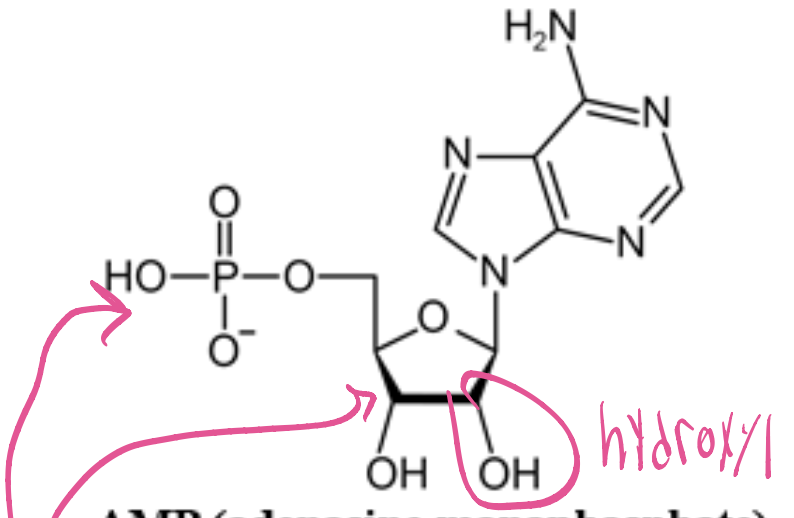
AMP (Adenosine monophosphate)
ribose+adenine+phosphate. It plays a crucial role in energy transfer and signaling within cells. (Purine)
GMP (Guanosine monophosphate)
ribose+guanine+phosphate, a nucleotide that plays a role in cellular signaling and energy transfer. (Purine)