Exam 1 Lecture Cards
1/256
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Topics: Water & Life
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
257 Terms
what substance do all living organisms require the most?
water
what are cells surrounded by?
water
How many percent of a cell is water?
70-95%
How long can a human survive without water?
1 week
How much of earth’s surface is submerged in water?
3/4
What makes earth habitable?
the abundance of water
Life begins in what type of environment?
a watery environment
How many covalent bonds do water molecules contain?
2
What allows water molecules to form hydrogen bonds with one another?
the partial charges
Does water have emergent properties?
yes
what are the four emergent properties of water?
cohesion/adhesion, temperature moderation, density of ice, good solvent
What is cohesion?
the binding together of like molecules, often by hydrogen bonding (a substance being attracted to itself)
does water have a strong or weak cohesion?
a very strong cohesion
what is adhesion?
the attraction between different kinds of molecules
is water adhesive, cohesive, or both?
both
what is transpiration?
the evaporative loss of water from a plant
what is surface tension?
how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid
why does water have an unusually high surface tension?
because of hydrogen bonds
which emergent property of water explains surface tension?
cohesion
how does water moderate air temperature?
by absorbing heat from air that is warmer than water, and releasing stored heat to air that is cooler than water
why is water able to absolve or release a large amount of heat but only slightly change its own temperature?
because it has a high specific heat
what is specific heat?
the amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost for 1 g of a substance to change its temperature by 1 degree C
define “heat of vaporization”
the quantity of heat a liquid must absorb for 1 gram of it to be converted from liquid to gas
does water have a high or low heat of vaporization?
high
define “evaporative cooling”
the process in which the surface of an object becomes cooler during evaporation
what is an example of humans doing evaporative cooling?
sweating
why can’t water molecules break their hydrogen bonds when frozen?
because it loses energy and the molecules aren’t moving fast enough
why does ice float?
because the density of frozen water is less than the density of liquid water
what would happen if ice sank?
If ice didn't float it would form at the bottom of a body of cold water rather than the top. The water would continue radiating heat away from its surface and so would get colder and colder until the water and everything in it had frozen solid from the bottom up.
what is a solvent
the dissolving agent
what does it mean to dissolve something
to make or become liquid
what is a solution?
a liquid that is a homogenous mixture of two or more substances
what is a solute?
the substance being dissolved
what is an aqueous solution?
solution where water is the solvent
what is a hydration shell?
a more or less continuous cluster of water molecules surrounding some other substance that the water molecules are attracted to
what happens when water forms a hydration shell around a molecule?
the molecule dissolves
water can dissolve what type of molecules?
polar molecuels
what does hydrophilic mean
having an affinity for water (water loving)
define hydrophobic
having an aversion to water
are molecules with non-polar covalent bonds more likely to be hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
hydrophobic
what is a colloid?
a mixture made up of a liquid and particles that remain suspended rather than dissolved in that liquid
How many bonds can carbon form?
4 bonds
Why is carbon the perfect backbone for biomolecules?
because it can form 4 STRONG covalent bonds
what is the oversimplified definition of organic chemistry?
the studying of carbon-containing molecules usually found in living things
Can organic molecules come from non-living things?
yes, some non-living things contain carbon
do all organic molecules contain carbon?
yes
are all things containing carbon organic?
no, some are inorganic
If carbon is bound to N,O, or H it’s ____ except for CO2
organic
What is vitalism?
the belief that life in living organisms was caused and sustained by a vital force that is distinct form all physical and chemical forces
can organic molecules be synthesized from inorganic molecules?
yes, we discovered this in a lab
How did Wohler create an organic compound from inorganic molecules? did he continue to believe in vitalism after?
he mixed ammonium ions and cyanate ions which made urea (urea is organic); no
How did Kolbe create an organic compound from inorganic molecules? did he continue to believe in vitalism after?
he synthesized acetic acid from inorganic molecules not sourced from living material; no
what is spontaneous generation
the hypothetical process by which living organisms develop from nonliving matter
what was the miller experiment intending to replicate?
the conditions of earth when it was first created to see if we can get some of these orgional organic molecules
how many amino acids were discovered in the Miller Experiment?
over 20, which is more than the amount that naturally occurs in the genetic code
which of the types of models (molecular formula, structural formula, ball and stick model, and space filling model) is the most accurate?
the space filling model (is less used because its kinda hard to see stuff)
where on the skeletal structure would you find the carbons? where are the hydrogens?
the carbons would be at the ends and at every corner; the hydrogens would fill the remaining spots
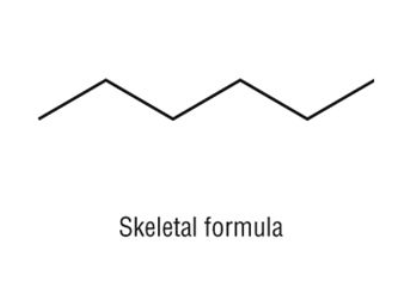
How many carbons would this molecule have?
6
can double bonds rotate?
no
can single bonds rotate?
yes
what are the different ways hydrocarbons can vary?
length, branching, single or double bonds, rings
what is an isomer?
molecules with the same molecular formula, but different physical structures
what is a structural isomer?
isomer with different arrangement of bonds (note: molecules are 3D so flipping something upside or the other way would not count as an isomer!)
what are cis-trans isomers?
isomers that have different arrangements around the double bond
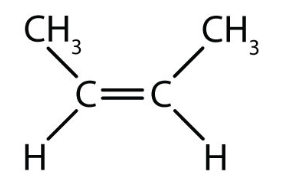
what type of isomer is this?
cis isomer
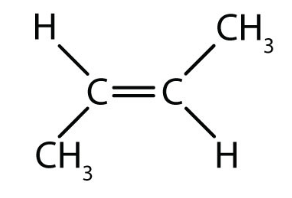
what type of isomer is this?
trans isomer
what are enantiomers? Practice identifying them!
mirror images which are not superimposable
what are hydrocarbons?
a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon
carbon skeletons serve as a backbone for _____ to attach and branch off
functional groups
what are functional groups? practice identifying them
small molecules which are directly involved in chemical reactions
which functional groups do we need to know?
-OH (hydroxyl)
>C=O (carbonyl)
-COOH (carboxyl)
-NH2 (amine)
-SH (sulfhydryl)
-OPO3 (phosphate)
-CH3 (methyl)
compounds with hydroxyl groups are called ______
alcohols
what do the names of compounds with hydroxyl groups end with
“ol”
why do hydroxyl groups mix well with water?
because they tend to be polar compounds
what are the two names for compounds with carbon groups?
aldehydes and ketones
where is the carbonyl group for aldehydes?
the end
where is the carbonyl group for ketones?
the middle
what are the names of compounds that have carboxyl groups?
carboxylic acids or organic acids (has both an CO group and OH group)
compounds with amine groups are called ____?
amines
amines act as a _____
base
sulfhydryl functional groups are called?
thiols
sulfhydryl functional groups form _____ in hair proteins
cross links
compounds with phosphate functional groups are called
organic phosphates
what do phosphate functional groups do?
make up the backbone of DNA and stores energy in ATP
what are compounds with methyl functional groups called?
methylated compounds
what do methylated compounds do?
change the expression of genes
what are the four types of macromolecules?
carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids
which of the four macromolecules is heavily debated to be classified as a macromolecule?
lipids
what do carbohydrates do?
give cells fuel (like sugar) and gives cells simple structures (like cellulose)
what do proteins do?
make up most of the complex structures in cells
are lipids hydrophobic or hydrophillic?
hydrophobic
lipids make up (3 things)
fats, cell membranes (phospholipids), and hormones (steroids)
what are the two types of nucleic acids?
DNA and RNA
what do nucleic acids do?
stores, moves, and processes genetic information
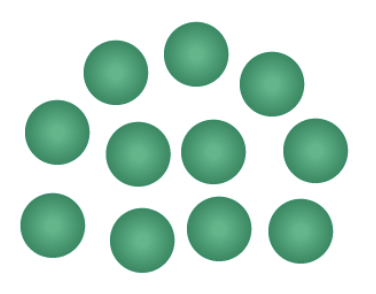
are these monomers or polymers?
monomers
are these monomers or a polymer?
polymer
when monomers or polymers fuse together, it is called a ______
dehydration synthesis
during a dehydration synthesis, is water removed or created?
removed
when monomers or polymers split apart, it is called a _______
hydrolysis reaction
during a hydrolysis reaction, is water removed or added?
added