Blood Bank Lecture Exam I
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MLS 4130
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Serum
the liquid remaining after blood clots that contains antibodies
Plasma
the liquid remaining after blood centrifugation that contains clotting factors
Unexpected antibody
any detectable antibody against an RBC antigen that is not ABO, can only be formed after exposure
Affinity
the binding strength of a single antibody and antigen
Avidity
the binding strength of all serum antibodies with their respective antigens
Valency
the number of binding sites on a single antibody
Fab region
the binding portion of an antibody
Prozone
excess of antibody, causes a false positive
Postzone
excess of antigen, causes a false negative
High titer low avidity (HTLA) reaction
Weak (1+) reaction for a highly diluted solutions due to weak bonds, not typically considered clinically significant unless masking clinically significant reactions
Centrifugation reduces the zeta potential, which is the negative-charge repulsion between the cells.
Why does centrifugation enhance agglutination?
6.5-7.5
Ideal pH for agglutination reactions
22ºC
Ideal spin phase temperature
37ºC
Ideal AHG phase temperature
IgG
Which antibody requires the use of potentiators to visualize reactions?
IgM
Which antibody reacts easily in saline without the use of potentiators?
Anti-IgG and anti-C3d
What is in polyspecific antihuman globulin?
Polyspecific AHG is used to begin the DAT in all people except infants (lack of production) because it contains both anti-IgG and anti-C3d. A positive on polyspecific AHG needs identification of if it is due to IgG or C3d.
When is a polyspecific AHG used versus a monospecific AHG?
Gamma heavy chain, infrequently the light chain
What is anti-IgG specific to?
For identification of a variety epitopes
When is polyclonal AHG more useful than monoclonal?
Warm
Does anti-IgG identify cold or warm agglutinins?
Cold
Does anti-complement identify cold or warm agglutinins?
It is an “indirect” way of detecting IgM due to its ability to bind complement.
Why is anti-complement used rather than anti-IgM?
False negative due to inability of reagent AHG to bind to the correct regions.
Does a lack of or poor quality washing cause a false positive or negative?
Check cells identify if negative results are due to the patient being negative for the respective factor OR if the reagents are bad. If the patient is negative for the factor and reagents are good, the check cells should cause agglutination.
What is the role of check cells?
1+
What would the anti-C3 or anti-IgG reaction look like in a acute or delayed hemolytic transfusion reaction?
Drug-induced immune hemolytic anemia, paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria, cold agglutinin disease
Potential conditions for a positive anti-C3 with 2-4+ reaction
Acute or delayed hemolytic transfusion reaction, passively acquired antibody, ABO hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn
Potential conditions for a postiive anti-IgG with a 1+ reaction
Rh or other hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn, drug-induced immune hemolytic anemia, warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Potential conditions for a positive anti-IgG with a 2-4+ reaction
Drug-induced immune hemolytic anemia and warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Potential conditions for a positive anti-IgG and anti-C3 with a 2-4+ reaction
ABO, Hh, and Se
What are the three genes that affect ABO inheritance?
Type 1 chain
glycolipid with a beta 1-3 linkage, primarily found in secretions
Type 2 chain
glycolipid with a beta 1-4 linkage, primarily found on the RBC surface
H antigen
the precursor structure that A and B are built upon
alpha-2-L-fucosyl transferase
What does the H antigen elicit production of?
L-fucose
What does the H antigen cause the transfer of?
Type 2 chains
What kind of chain does L-fucose transfer to?
Type 1 chains
What chain does the secretor gene elicit the transfer of L-fucose to?
alpha-3-N-acetylgalactoseaminyl transferase
What does the A antigen elicit production of?
N-acetyl-D-galactoseamine (GalNAc)
What does the A antigen cause the transfer of?
a-3-D-galactosyl transferase
What does the B antigen elicit production of?
D-galactose (GAL)
What does the B antigen cause the transfer of?
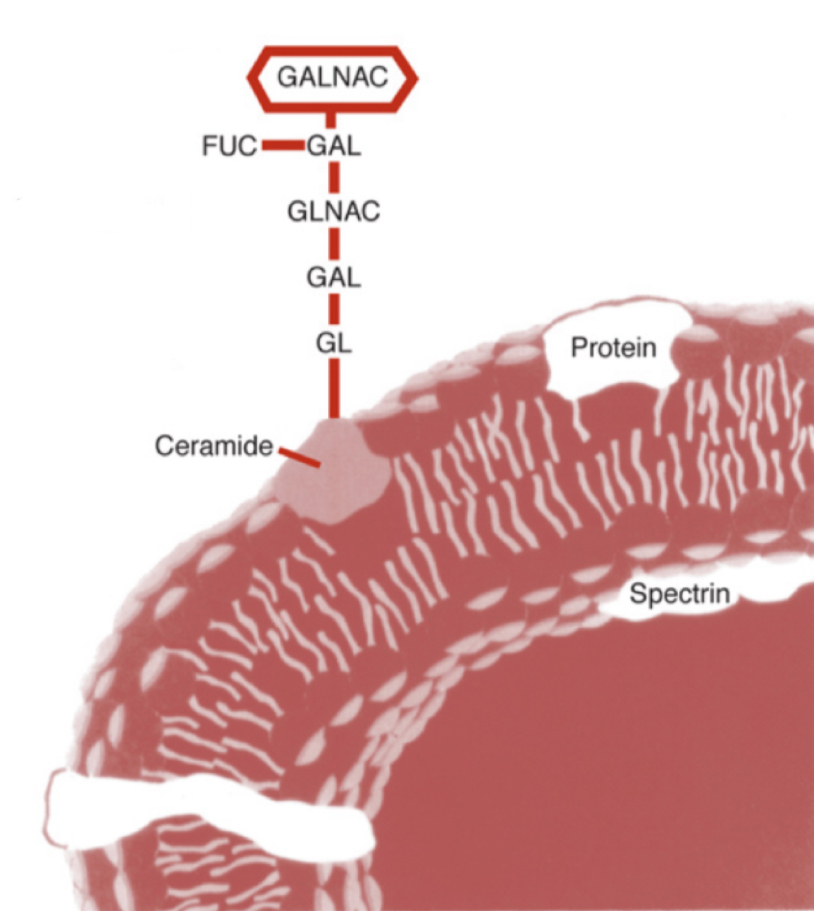
Blood type A
What blood type does this image represent?
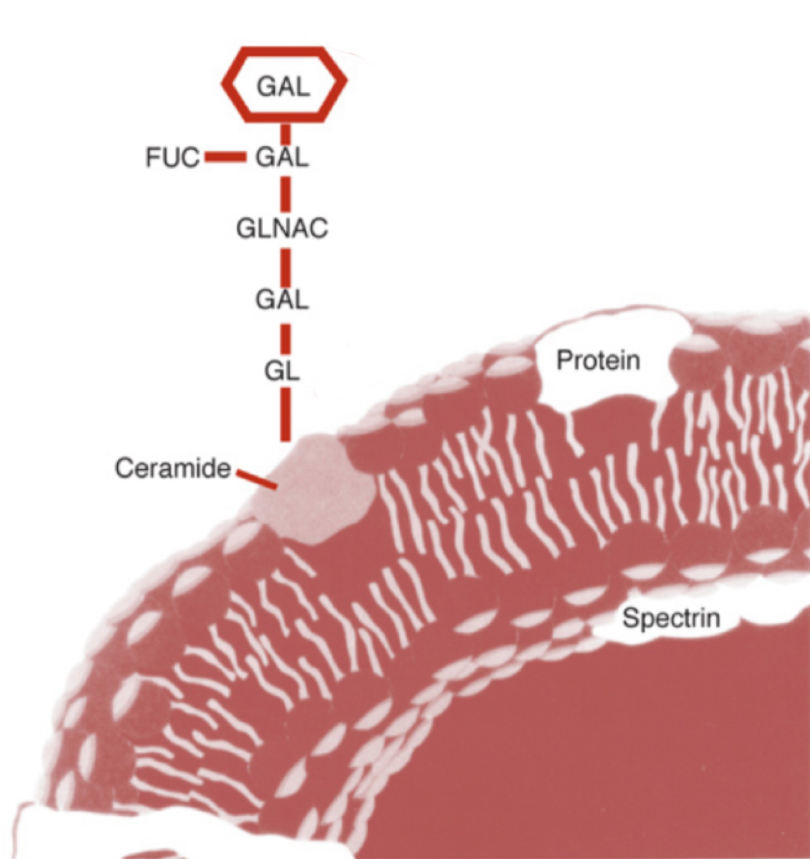
Blood type B
What blood type does this image represent?
Monoclonal IgM
In ABO blood typing, the reagents are predominantly composed of what?
Identifying donor types
What is anti-AB used for?
45%
What is the frequency of phenotype O in white people?
50%
What is the frequency of phenotype O in black people?
40%
What is the frequency of phenotype A in white people?
26%
What is the frequency of phenotype A in black people?
11%
What is the frequency of phenotype B in white people?
20%
What is the frequency of phenotype B in black people?
4%
What is the frequency of phenotype AB in white and black people?
Dolichos biflorus
lectin used for agglutination of A1
Bandeiraea simplicifolia
lectin used for agglutination of B
Ulex europaeus
lectin used for agglutination of H
O>A2>B>A2B>A1>A1B
What is the order of blood type strength of Ulex europaeus agglutination from strongest to weakest?
A1B due to having A1, A, and B antigens
Which blood type bears the least amount of H antigen on the cell?
A1 antigen
What antigen does A1 blood type have that A2 does not?
Bombay phenotype
the lack of H antigen due to inheritance of hh
O blood group
What blood group do Bombay and para-Bombay individuals belong to?
Group I discrepancy
The discrepancy of a weak or missing reactions on the reverse type due to low affinity/avidity or lack of antibodies
The mixture of patient cells with patient serum to test for autoagglutination
What is an auto-control?
Group I due to lack of antibodies, incubate the sample and retry with auto and O cell controls
An elderly woman presents with a forward type of O but does not react to A cells or B cells, what discrepancy is most likely and what should be done?
Group II discrepancy
The discrepancy of an unexpected reaction in the front type
Acquired B syndrome
GalNAc cleavage due to enteric bacteria deacetylase, creating a molecule more antigenically similar to GAL
Group III discrepancy
The discrepancy due to plasma abnormalities or excess protein
Washing six times and/or saline replacement
How should suspected group III discrepancies be resolved?
Group IV discrepancy
The discrepancy due to cold autoantibodies, unexpected alloantibodies, and/or unexpected ABO isoagglutinins
A1 and A
Most common ABO isoagglutinin
Washing, DAT, autocontrol, autoantibody screen
How should suspected group IV discrepancies be resolved?
Rhesus macaques
What monkey was the D antigen discovered in?
RhAG
What antigen must be present for the expression of RhD and/or RhCE?
85%
D antigen frequency in white people
70%
C antigen frequency in white people
80%
c antigen frequency in white people
30%
E antigen frequency in white people
98%
e antigen frequency in white people
Antigens are determined by 3 pairs of genes, each complex determines D/d, C/c, and E/e, and are inherited in a linked fashion as a haplotype.
What is postulated by the Fisher-Race theory?
Antigens are determined by two genes, one on each chromosome pair, that controls the expression of Rh and production of agglutinogens.
What is postulated by the Wiener theory?
Antigens are number 1-3 in order of discovery and are negative if they are recessive.
How does Rosenfield code the antigens?
Weak D
RBCs not immediately agglutinated by anti-D must be tested for what?
C in trans to D, partial D, and few antigen sites
What are the three mechanisms of weak D?
Rhnull
blood type defined as a lack of Rh antigen sites that causes stomatocytosis and hemolytic anemia
The Rh antigen is a non-glycosated protein that resides on transmembrane proteins. It is important for RBC structure.
Why does Rhnull cause hemolytic anemia?
Rhmod
weakened expression of Rh and LW due to RHAG gene mutations
G
Genes that code for D and C also code for which antigen?
Anti-D and anti-C
Anti-G activity cannot be separated from what two antibodies?
Cw
rare variant Rh antigen that is caused by an amino acid change in the RhCe protein
f
What antigen is also expressed if a person is ce?
rhi
What antigen is also expressed if a person is Ce?
D > c > E > C > e
What is the order of immunogenicity of the Rh group antigens?
Positive DAT, IAT, & antibody screens; unexplained fever; elevated bilirubin; low hemoglobin and haptoglobin
What are the clinical signs of a transfusion reaction?
IgG1 and IgG3
What kinds of IgG are the most common cause of a transfusion reaction?
Dosage effect
an increase in immunogenicity against homozygous individuals versus heterozygous individuals
Extravascular
Is a transfusion reaction primarily intravascular or extravascular hemolysis?
Anti-c
R1R1 people with anti-E most always also make what?
Anti-G
Anti-D serum may also contain what?
Anti-D
Anti-C is rare but usually accompanies what?
Anti-c
Anti-f typically accompanies what?