BCS 111 Lecture 9
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Is language essential for problem solving?
-
Not really needed
Satisfying basic biological needs
Needs language
tasks that require verbal skills (e.g., verbal analogy, sudoku, etc.)
Language not necessarily needed but could help the thinking process
tasks that don’t require verbal skills (rotate a magic cube, card sorting, etc.)
What do we need for problem solving?
Goal setting
Attention
Memory
Experience
Knowledge about the problem itself: problem-specific
Well-defined vs. ill-defined problems
-
Well-defined problems
Clear goal/narrower scope
Narrower set of actions
Easier to plan ahead than the ill-defined ones
Ill-defined problems
Open-ended
Unclear actions needed to achieve the goal
May generate some well-defined problems while solving the ill-defined ones.
Common strategies in problem-solving
-
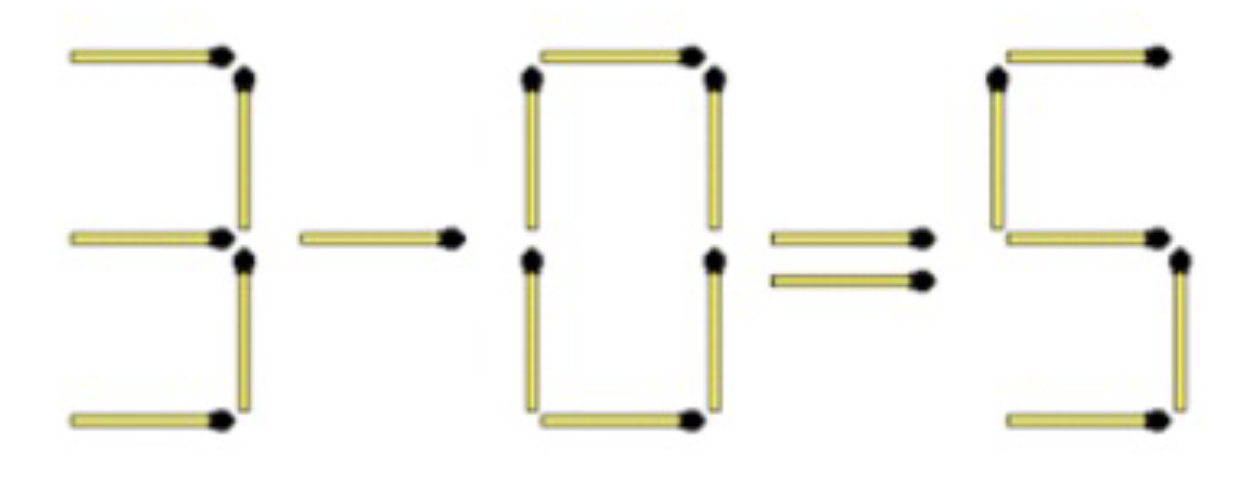
Generate-and-test (trial-and-error approach)
Add two matches to correct the equation
Working backward
know what the solution should look like
Perform last step first
Planning of moves
Tower-of-Hanoi
Rules:
One disk at a time
Smaller disk on top of bigger disks
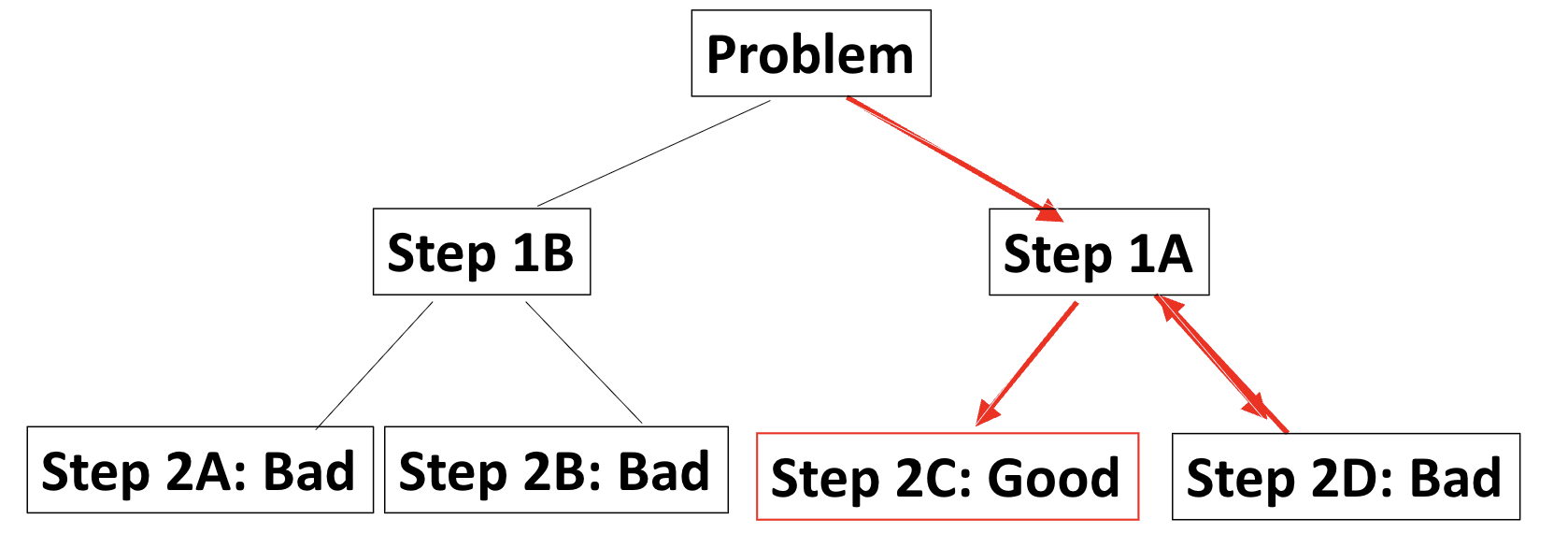
Backtracking
step back to track the root of the problem
Commonly used in coding and debugging
Are these strategies used independently? Can we use some combinations of them? Of course!
Can you use the Tower-of-Hanoi task (or any other examples) to illustrate the following strategies are being used to solve one single problem?
Generate-and-test
Working backward
Backtracking
Tower-of-Hanoi task (cont)
Ideally, only working backward needed if no mistakes are made.
But practically:
Generate-and-test: move a peg and see if it works
Backtracking: moved a few pegs and found it didn’t work; reversed a few steps back to see where it began to get wrong.
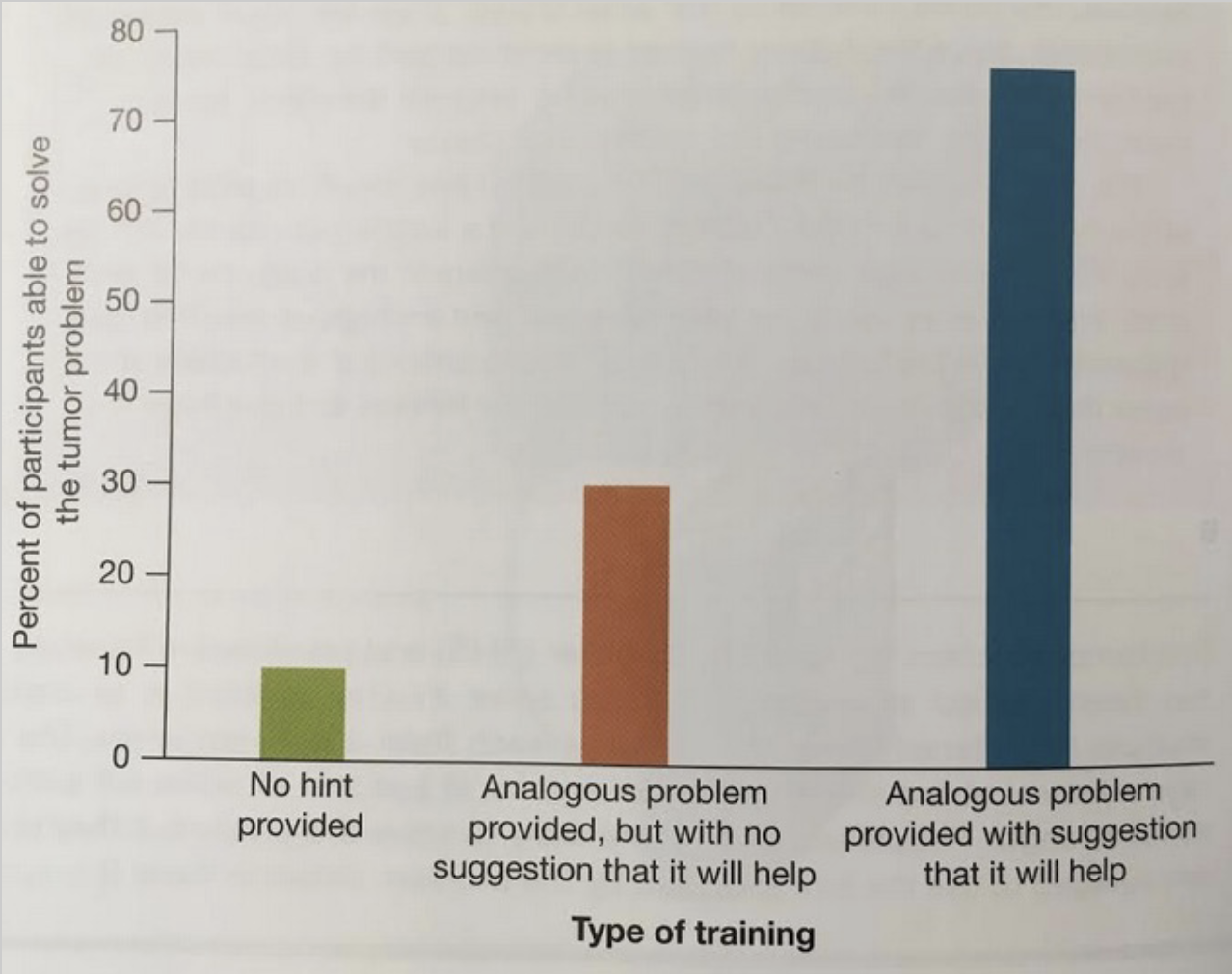
Analogy
Analogy helps with the tumor problem!
How mental set limits our creativity?
Mental set: one’s strategy/preference to approach a problem e.g., positive vs. negative thinking
Nine-dot problem
How functional fixedness blocks our creativity?
Functional fixedness: a fixed mental set for the function of an object
The two-string problem
Functional fixedness
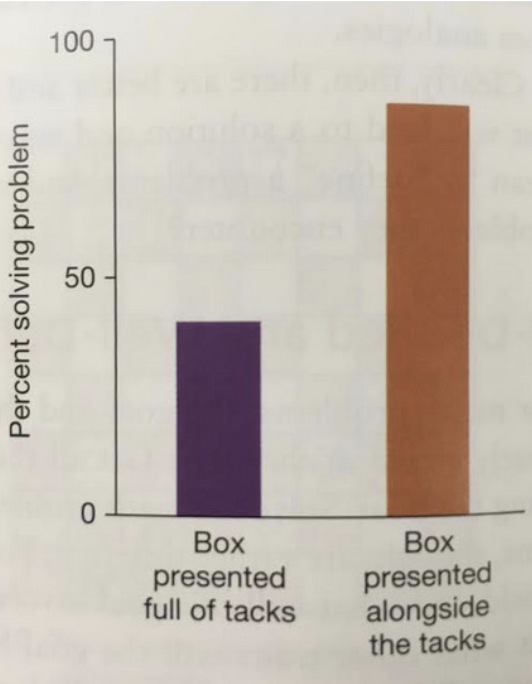
The candle problem (Duncker 1945)
How would you attach the candle to the wall so that the wax doesn’t fall when the candle is lit?
Functional fixedness – Think outside the box!
The candle problem
Context or available cues also matter!
Where the tacks are placed
Divergent thinking
Think outside the box: think in more than one direction
The plier in the two-string problem
The box in the candle problem
The parking lot problem
Most brain teasers
Convergent thinking
The ability to associate irrelevant concepts
Try to find a word that can be combined with each of the three words in the set to create another new set of three words or phrases (The Remote Associates Test)
1. Snow, down, out
2. Cross, rain, tie
3. Opera, hand, dish
4. Sense, courtesy, place
Problem-solving and intelligence
-
Fluid intelligence
Ability to solve new problems
Crystallized intelligence
Ability to solve similar problems that you encountered before
How do we measure Intelligence?
Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC): sample question to test verbal IQ
Question: How are morning and afternoon alike?”
Question (to test vocab size): Select the picture that matches the word you heard
Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC): sample question to test spatial skills/visual imagery
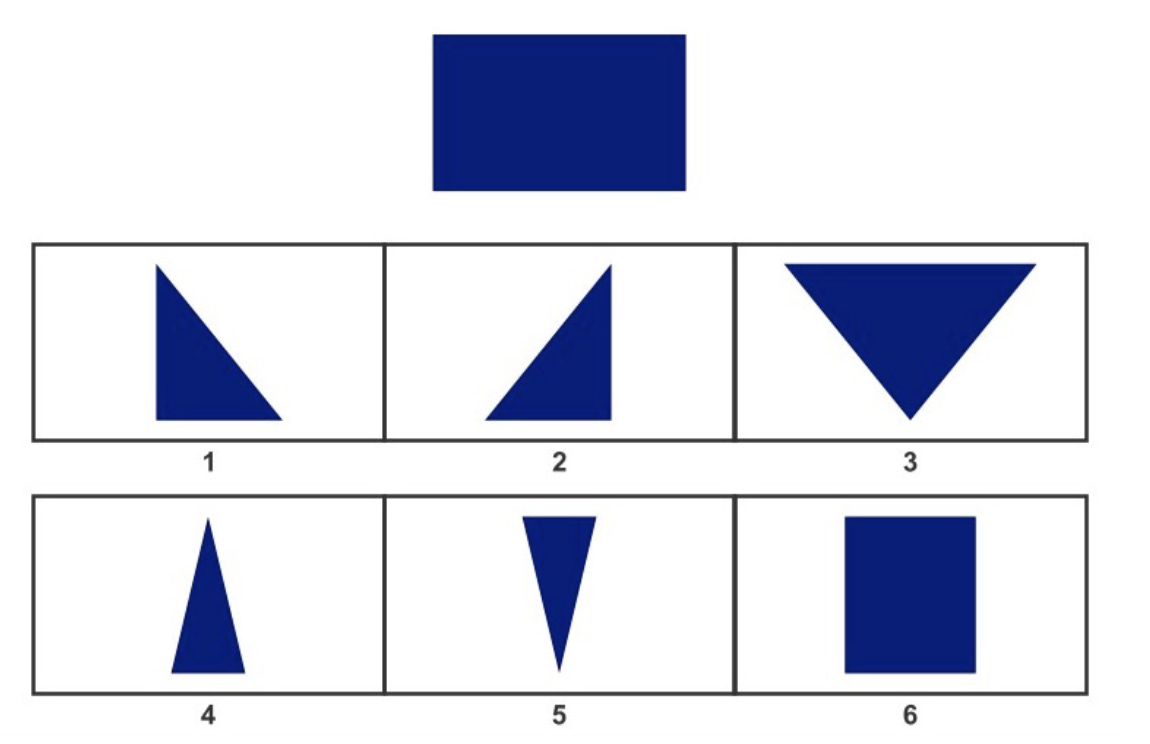
Which shapes on the bottom panel do you need in order to form the large shape on the top?