3.3 - compression
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
inward
compression is a ____________ directed mechanical force that increases pressure on the body
prevent DVT
facilitate healing of venous ulcers
residual limb shaping
scar control
control of peripheral edema
primary clinical applications for compression (5)
circulatory system
lymphatic system
interstitial spaces between cells
what are the 3 major pathways that fluid travels through
hydrostatic; osmotic
fluid exchange at the capillary occurs via _________ and ________ pressures
90;10
about ______% of fluid travels through arterial and venous pathways and about ______% of fluid travels through the lymph system
edema
prevention of DVT
venous statis ulcers
lymphedema
indications for Intermittent pneumatic compression (4)
true (ex. congestive heart failure and cirrhosis)
T/F: we do not treat systemic diseases with compression
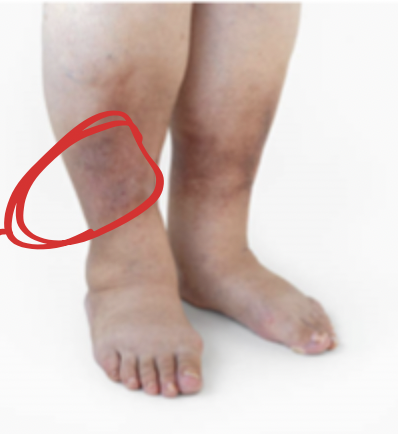
venous
hemosiderin staining is a result of _________ insufficiency
anthropometric measurement (taken at reproducible landmarks)
volumeter (water displacement)
pitting edema
3 ways to measure edema
1+
where does this fall on the pitting edema scale:
barely detectable impression when finger is pressed into skin
2+
where does this fall on the pitting edema scale:
slight indentation, 15 sec to rebound
3+
where does this fall on the pitting edema scale:
deeper indentation, 30 sec to rebound
4+
where does this fall on the pitting edema scale:
more than 30 seconds to rebound
15
a grade 2+ pitting edema takes ________ seconds to rebound
30
a grade 3+ pitting edema takes ________ seconds to rebound
>30
a grade 4+ pitting edema takes ________ seconds to rebound
osmotic
the theory of compression for edema is applying compression to change pressure and have an external force to increase ________ pressure so fluid return into venous/lymph systems
80
_____% of patients undergoing orthopedic sx will develop VTE without prophylactic interventions
bed ridden/not moving
who is most at risk for getting a DVT
inc; dec; dec
intermittent pneumatic compression:
(dec or inc) blood flow
(dec or inc) venous statis
(dec or inc) opportunity for clot to form
physical activity with muscular contractions
what method is the best to return venous/lymph fluid
venous
compression is recommended with venous or arterial ulcers
prolonged immobility
obesity
calf muscle pump dysfunction
pregnancy
what are the 4 risks of developing venous stasis ulcers
true
T/F: compression can improve the rate of healing venous statis ulcers
false (multilayer is better)
T/F: multilayered compression has the same effect as a single layer for treating venous statis ulcers
mod-high (40-60mmHg)
what level of compression is recommended to treat venous statis ulcers?
used after amputation
residual limb reduction and shaping
prepare limb for prosthetic
what circumstances is compression used for limb shaping
collagenase
compression can reduce scar formation by increased ________ activity
20-30mmHg; 23 hours a day
what is the recommended compression intensity and duration for hypertrophic scar treatment
true (limits ROM and function tho)
T/F: compression can treat hypertrophic scars by decreasing contractures
<0.06
0.06-0.80
>0.80
contraindications for compression with arterial insufficiency:
ABI ______ = contraindicated
ABI ______ = reduced compression 23-27mmHg
ABI ______ = full compression 30-40mmHg
Arterial insufficiency
ABI <.06 = Contraindicated
ABI .06-0.80 = reduced compression 23-27 mmHg
ABI >0.80 = full compression 30-40 mmHh
Uncontrolled HTN
Thrombosis: DVT or PE
Obstructed venous return
CHF
Acute pulmonary edema
Malignancy
Acute trauma/Fracture
Arterial revascularization
contraindications for intermittent pneumatic compression
Recent skin graft
Acute local dermatologic infections
Impaired sensation
Impaired mentation
precautions for intermittent pneumatic compression
increased edema
impaired circulation
ischemia
peripheral nerve injury
increased cardiac load
potential adverse effects of compression (5)
milking
sequential intermittent compression is thought to provide more effective “_________” than single chamber compression sleeves
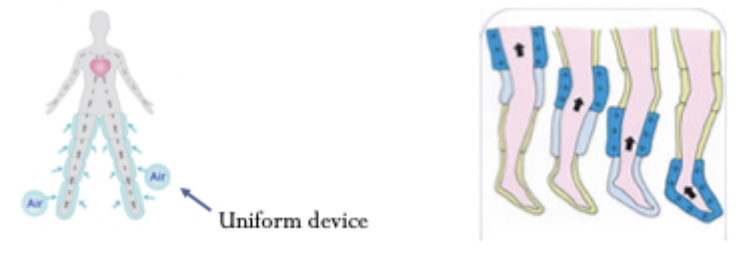
sequential = goes in sequence
uniform = all at once
what is the difference between sequential and uniform compression
resting; working
bandages apply _________ or ___________ pressure
resting
resting or working bandage pressure:
exerted by elastic when it is put on stretch
working
resting or working bandage pressure:
produced by active muscles pushing against inelastic bandages
mobility
working pressure bandages only work if the patient has some ___________
Long stretch
short stretch
multilayered
semi-rigid
what are the types of bandages used for compression
resting
resting or working bandage pressure:
use high-stretch bandages
working
resting or working bandage pressure:
use low-stretch bandages
resting
resting or working bandage pressure:
most effective on immobile patients
resting
resting or working bandage pressure:
examples: tubigrip, ace wrap
working
resting or working bandage pressure:
example: durelast
resting
resting or working bandage pressure:
provides greatest resting pressure
working
resting or working bandage pressure:
provides high working pressure
working
resting or working bandage pressure:
little elasticity
both
thrombo-embolic stockings/garmets provide moderate (resting or working) pressure
24 hours per day
what is the duration recommendation for wearing thrombo-embolic stockings/garmets