Assessing the Ears
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
External parts of the ear
Auricle, helix, fragus, lobule
Middle parts of the ear
Malleus, incus, stapes
Inner parts of the ear
Cochlea, semicircular canals
Cranial nerve VIII
Hearing and balance
Audiometric testing
Hearing evaluation to assess sensitivity of hearing at high and low frequencies
Tympanometry
Use of air pressure in the ear canal to test for disorders of the middle ear
Sequence of assessment
Inspecting the ears, palpating the ears, assessing hearing, assessing the internal ear
Inspecting the ears normal findings
Color same as face, equal size and shape bilaterally, normal size (4-10cm), symmetrical, no deformities, inflammation, nodules, or drainage, angle of attachement <10 degrees
Inspecting the ears abnormal findings
Color is blue, white, red, or pale; asymmetrical, lesions drainage, cauliflower ear
Cauliflower ear
Ear deformity caused by destruction of underlying cartilage of the outer ear

Palpating the ears normal findings
No tenderness, firm consistency
Palpating the ears abnormal findings
Swelling, tenderness, lumps, nodules
Conductive hearing loss
Sound is not conducted through outer ear canal to eardrum and ossicles
Sensorineural hearing loss
Occurs when there is drainage to the inner ear (cochlea) or nerve pathways from inner ear to the brain
Mixed hearing loss
Includes conductive and sensorineural hearing loss
Whisper test
Assesses for impaired or high-frequency of hearing
Normal whisper test
Pt reports at least 3 of 6 letters or numbers correctly
Abnormal whisper test
Pt repeats < 3 of 6 letters or numbers correctly or did not hear what you whispered
Weber test
Assesses unilateral hearing loss
Unilateral hearing loss
Hearing loss in one ear
Normal Weber test findings
Sound quality is heard equally in both ears
Abnormal Weber test findings
Sound will be perceived as louder in the good ear and softer in the bad ear (sensorineural hearing loss); sound will be perceived as louder in the bad ear (conductive hearing loss)
Rinne test
Assesses bone conduction vs air conduction
Normal Rinne test findings
Positive Rinne: air conduction is heard twice as long as bone conduction
Abnormal Rinne test findings
Negative Rinne: bone conduction is heard longer than air conduction
Otoscope
Instrument used for visual examination of the ear

Assessing ear using otoscope normal findings
External ear canal patent; no inflammation or drainage; small amount of pale yellow, moist ear wax; tympanic membrane intact, pearly gray color, translucent, contour slightly conical; bony landmarks visible, cone of light present
Assessing ear using otoscope abnormal findings
Excessive ear wax, otitis externa, otitis media, serous otitis media, scarred tympanic membrane, perforated tympanic membrane
Otitis externa
Infection of the outer ear (ear canal)
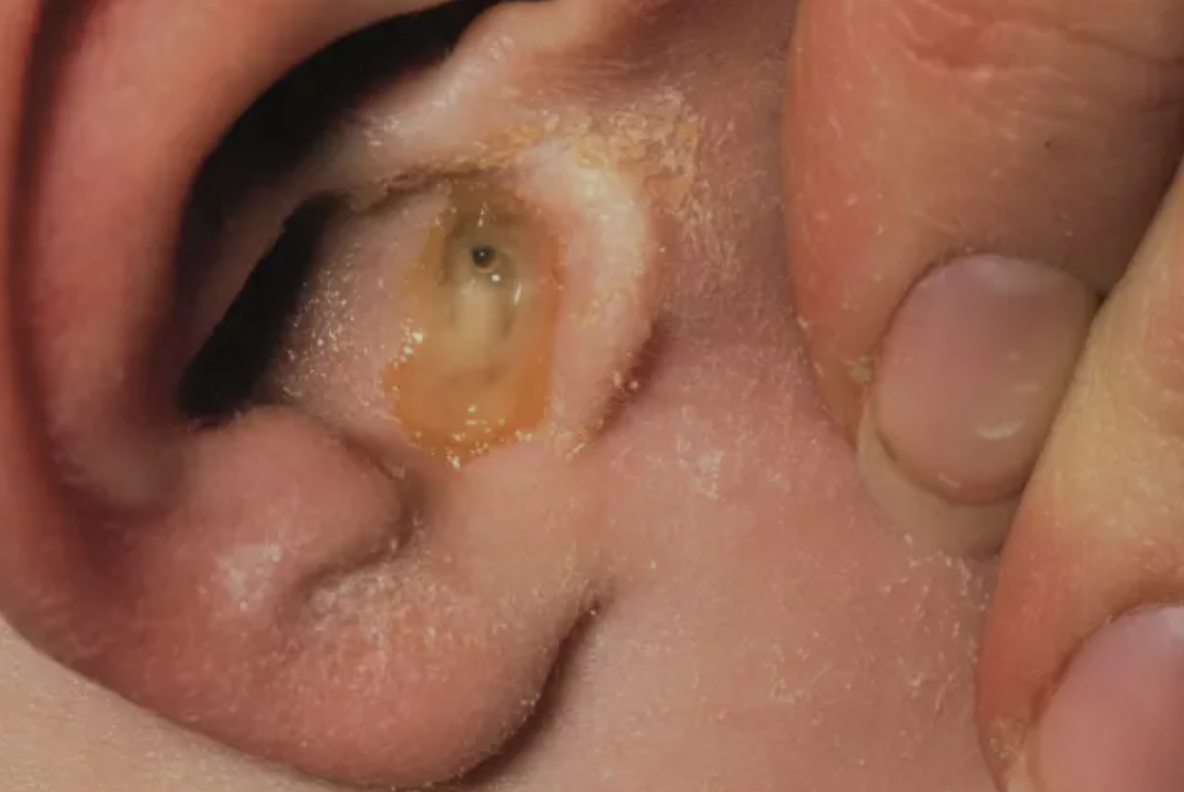
Otitis media
Infection of the middle ear
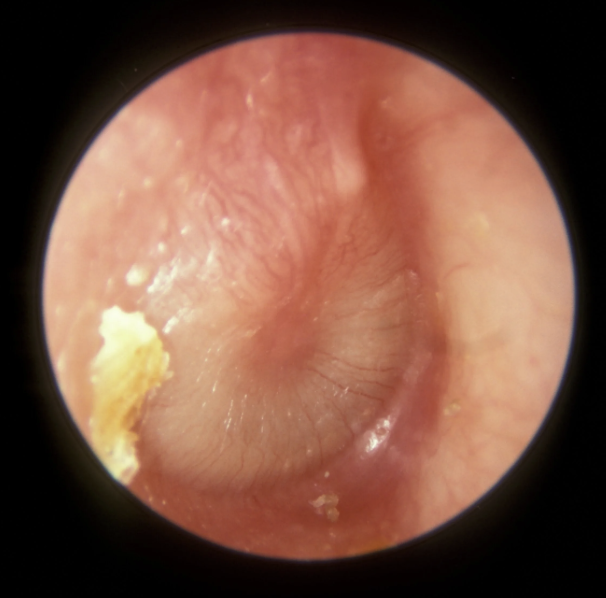
Serous otitis media
Fluid buildup in the middle ear that can follow acute otitis media or caused by obstruction of the Eustachian tube
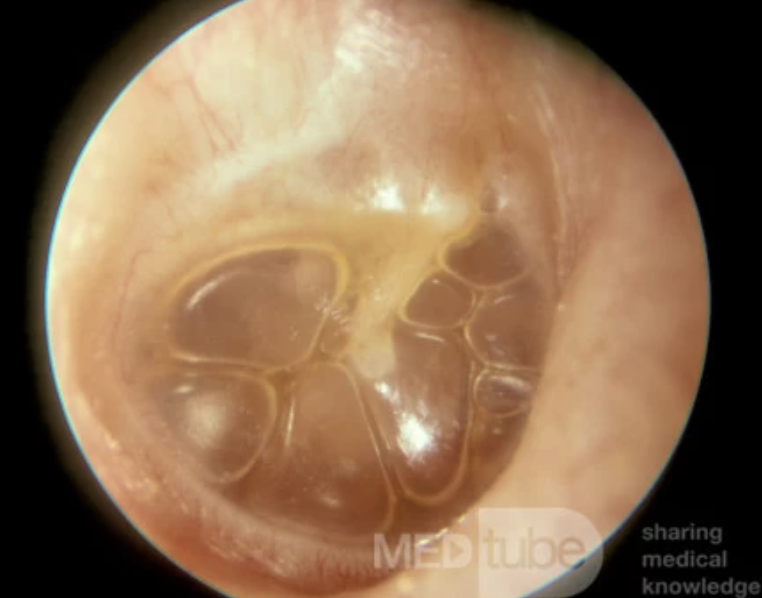
Perforated tympanic membrane
Ruptured tympanic membrane; a dark oval, hole will be present in the membrane
Tinnitus
Ringing or buzzing in the ears
Vertigo
Dizziness