Nervous System and Ventral Cavity
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Somatic and Autonomic
What are the divisions of the peripheral nervous system (PNS)?
Skeletal muscle
The somatic nervous system innervates
Smooth muscle, Cardiac muscle, and Glands
The autonomic nervous system innervates
SNS- one neuron system
ANS- two neuron system (preganglionic neuron and postganglionic neuron)
How many neurons do the somatic and autonomic nervous systems use?
Acetylcholine (ACh), always excitatory
Somatic NS releases what neurotransmitter?
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Autonomic NS Preganglionic fibers all release what neurotransmitter?
Norepinephrine(most); exictatory
ANS Postganglionic sympathetic fibers release what neurotransmitter?
Ach; inhibitory
ANS Postganglionic parasympathetic fibers release what neurotransmitter?
Craniosacral, brain stem CN 3, 7, 9, 10 and S2-S4
Parasympathetic origin
Thoracolumbar, T1-L2
Sympathetic origin
Parasympathetic: Long pre, short post
Sympathetic: Short pre, long post
Relative lengths of fibers
Parasympathetic, in/near visceral effector organs (intramural)
Sympathetic, paravertebral (chain) and prevertebral (splachnic on branches of the aorta)
Location of ganglia
CN III, Oculomotor
Innervates smooth muscles in eye
CN VII, Facial
Innervates nasal, lacrimal, submandibular, and sublingual glands
CN IX, Glossopharyngeal
Innervates parotid gland
CN X, Vagus
Innervates heart, lungs, liver, gallbladder, stomach, small intestines, pancreas, and proximal 1/2 of large intestines
Pelvic Splanchnic nerves (S2-S4) Lateral gray matter of spinal cord
Sacral parasympathetics
Innervates distal 1/2 of large intestines, urinary bladder, ureters, and reproductive organs
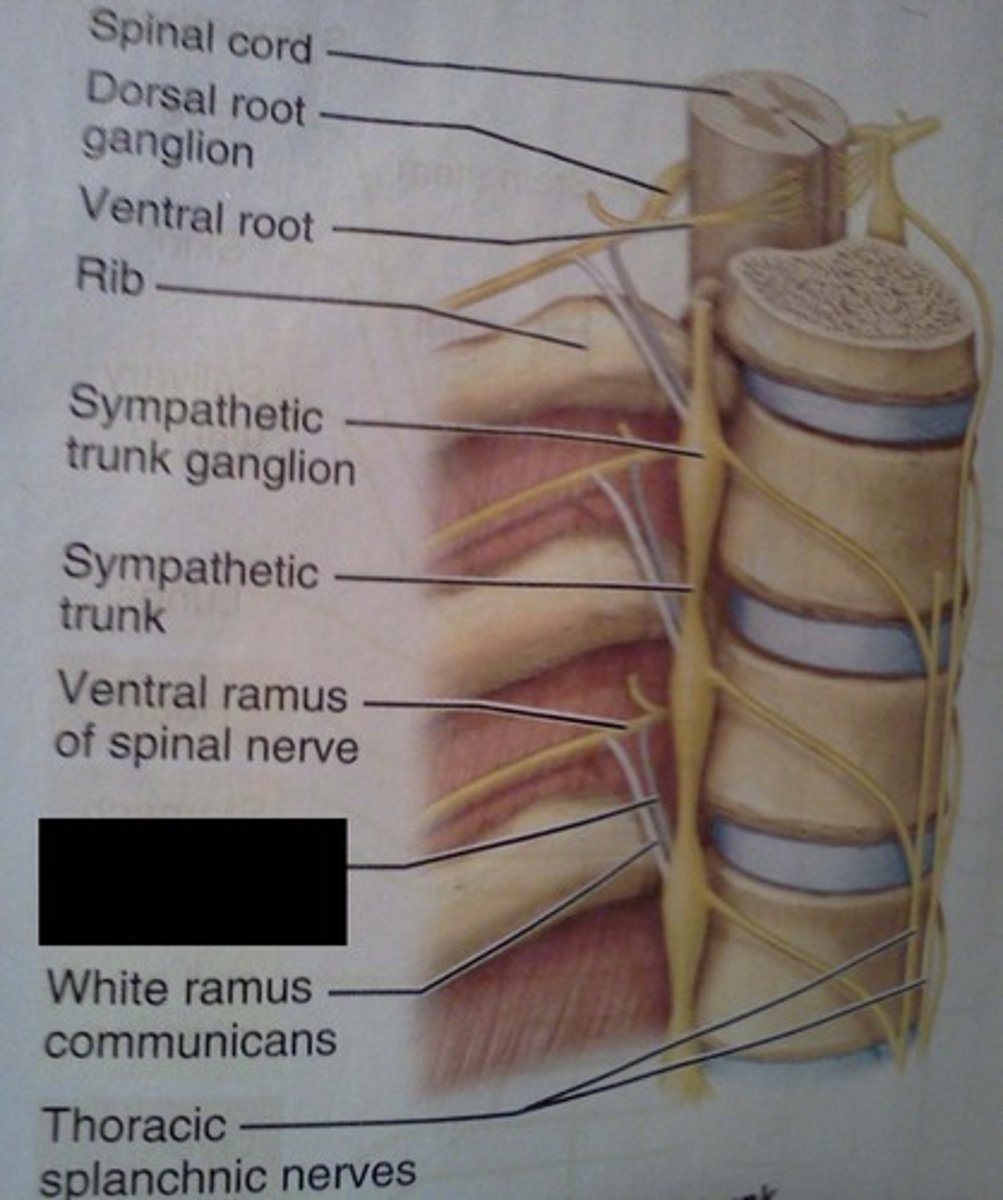
Leave the spinal cord through the ventral root, pass into spinal nerve, travel through white rami communicans into paravertebral ganglion on the sympathetic chain then can
1) Synapse with postganglionic neuron that exits the chain through the gray ramus communicans and enters either the ventral or dorsal ramus of the adjoing spinal nerve
2) Ascend or descend in the sympathetic chain and synapse with postganglionic neuron in a different paravertebral ganglion, fiber exits the sympathetic chain through the gray ramus communicans and enters either the ventral or dorsal ramus of the adjoining spinal nerve
3) Leaves the sympathetic chain without synapsing and forms a splanchnic nerve, goes to visceral organs
3 pathways of sympathetics
White ramus communicans
Myelinated
Preganglionic
Only found at T1-L2
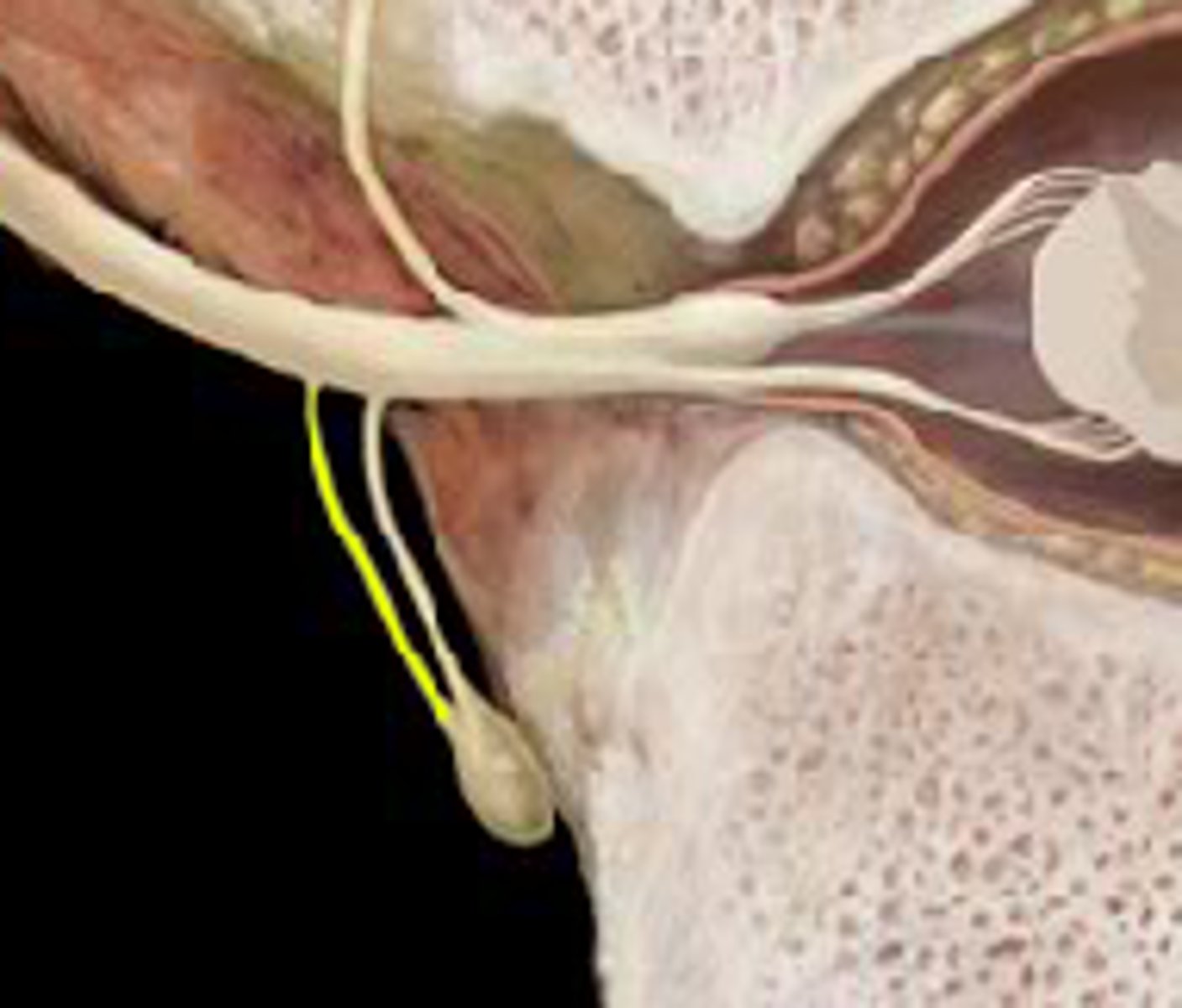
Gray ramus commincans
Unmyelinated Postganglionic
Found all along spinal cord
Visceral organs
What typically receives dual innervation (sympathetic and parasympathetic)?
Cardiac muscle of the heart and smooth muscle of the digestive and urinary tract organs
What typically receives dominate innervation from the parasympathetic, but can be overridden by sympathetic during stress?
Blood vessels (mediates body temperature)
Adrenal medulla, sweat glands of skin, arrector pili muscles of skin, and kidneys
What typically receives only sympathetic innervation?
Thoracic (Right and left Pleural cavity and Mediastinum which holds the pericardial cavity)
Abdominopelvic (Abdominal and Pelvic cavities)
Cavities of the Ventral body cavity
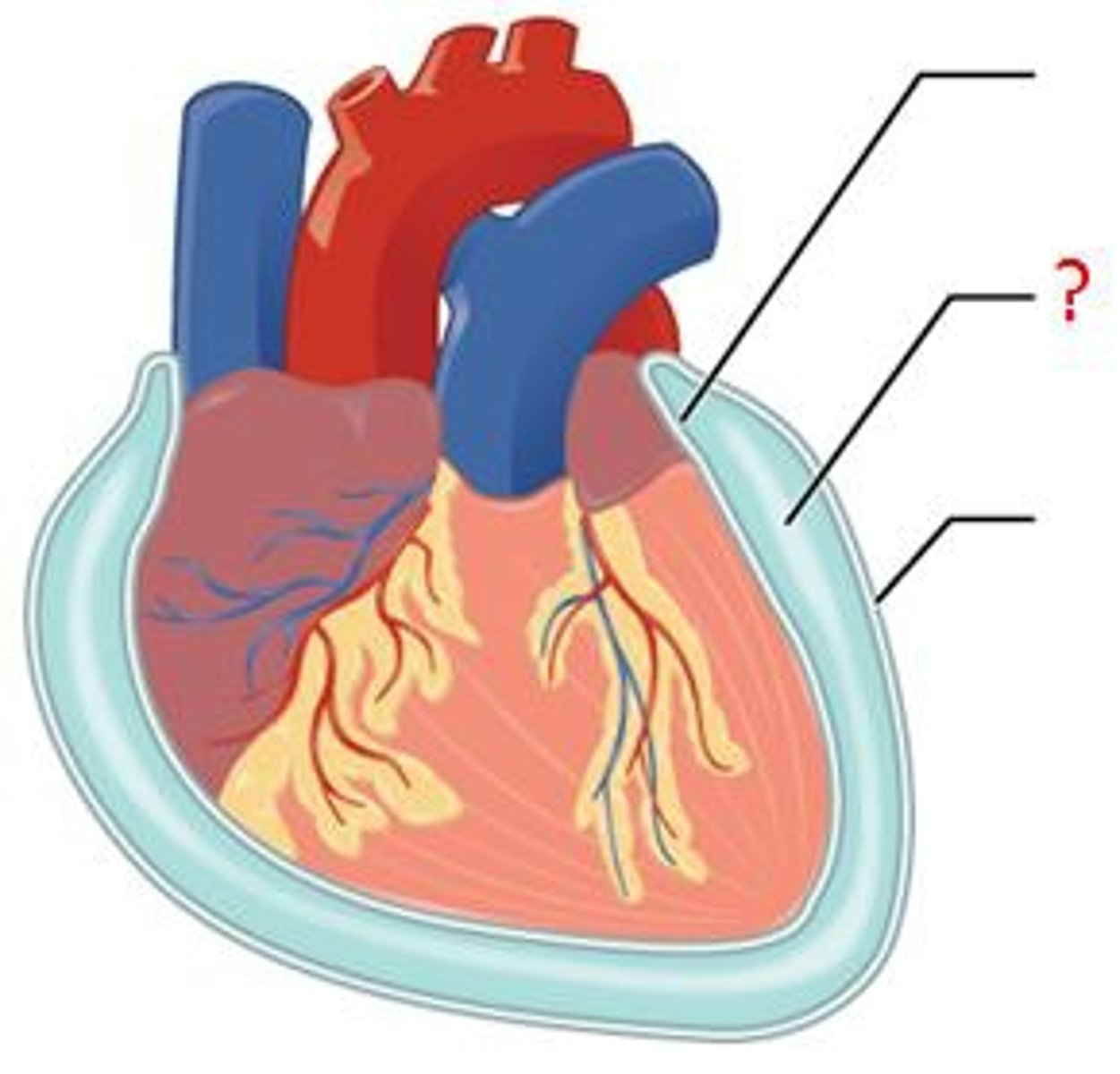
Parietal layer
lines the walls of the cavity
Visceral layer
adheres to the surface of the organ
Serous fluid
A thin layer of fluid located between the parietal and visceral layers
Reduces friction when the viscera move
Parietal/ visceral pleura
Found around the lungs
Parietal/ visceral pericardium
Found around the heart
Parietal/ visceral peritoneum
Found in the abdominopelvic cavity