Chapter 11- Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Sexual reproduction
Sharing of genetic info to get a devil.
Common among diploid (2n) organisms-2 copies of each gene
Recombination
mixing of genetic material from two genetically different individuals(parents)
mixing dna from different parents
3 types of recombination
Crossover, independent assortment, fertilization(more recombo during this)
Cross over
Parts of DNA are swapped between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes
Exchange of genetic sequences b/t homologous chromosomes
"trading" sections of DNA, leading to new combinations of alleles, contributing to genetic variation in offspring
independent assortment (allele definition)
The allele a gamete receives for one gene does not affect the allele received for another gene.
the alleles of two (or more) different genes get sorted into gametes independently/randomly of one another.
The random sorting of allele during the making of gametes.
fertilization
the process of a sperm and egg uniting to create a zygote, which then develops into an embryo (2 cells meet)
Sperm + egg = zygote—> embryo (due to mitosis)
gametes
sex cells, haploid, n,
How are meiosis and mitosis similar?
both have interphase b/t karyokinesis events
Both processes divide nucleus in eukaryotic cells
chromosomes form in same manner
both have same phases
How are meiosis and mitosis different?
mitosis has one karyokinesis event (single division) while meiosis has two karyokinesis event(two division-meiosis I and meiosis II)
meiosis results in 4 genetically unique daughter cells(n)-(reduce ploidy: 2n—>n)while mitosis results in 2 genetically identical daughter cells(2n) of parents cells.
Only in meiosis is there crossover b/t sister chromatids in tetrads and indep assortment of chromosomes during both anaphases produce genetically unique cells
What does meiosis maintain?
genetic diversity
Why is genetic diversity good?
helps species adapt to environmental changes, which is critical for their survival
Phases of meiosis
prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I and cytokinesis, prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II, cytokinesis
Prophase 1
tetrad formation (homologous chromosomes pair up)
Crossover (first recombination event-only b/t two in middle, random as in where the crossing over occurs)
Loci(location), length & number of crossovers(where, how many times, length of each crossover) are random
Result in parental-look like parents-chromosomes(the non-recombinant, didn’t cross over ones on outside) (2) and recombinant homologous chromosomes(2) (ones in the middle that cross over)
Are recombinant chromosomes unique?
genetically unique due to crossing over
What is the result of meiosis I in terms of chromosomes?
Homologous chromosomes separate(sister chromatids still attached together, meaning the X shape is still present)
What happens to the chromosomes in meiosis II?
Sister chromatids separate, so they are now the sticks again and half a X
What is the result of meiosis?
Daughter cells(4)– all genetically unique & haploid (n)
Tetrad
homologous chromosomes are paired up and back to back (connected at the chiasmata)
My def: two X are connected together to ensure crossing over happens
Recombinant chromosomes
chromosomes that have undergone recombination(crossing over in this case)
Synapsis of chromosomes
forming of the tetrad
Non recombinant chromsomes
chromosomes that have not undergone genetic recombination during meiosis, meaning they retain the original allele combinations from the parent cells
Synaptonemal complex
The protein structure that facilitates this pairing(tetrad), allowing for crossover to occur between non-sister chromatids.
important in forming tetrads
Chiasmata
Points of crossover where non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material during prophase I
The only structures holding the homologous chromosomes together at metaphase I.
Meiosis Interkinesis
Brief resting phase that occurs between the first and second meiotic divisions (meiosis I and meiosis II)
Meiosis
form haploid cells for sexual reproduction
recombination at several levels: crossover, independent assortment, fertilization(2 cells meet)
Crossing Over results
Results in new, genetically unique recombinant chromosomes. Random alleles
When does independent assortment occur?
Meiosis I and meiosis II-metaphase and anaphase areas
how one homo aligns/lines up during metaphase and splits(anaphase) doesn’t affect how the other homo aligns- TOTALLY RANDOM
Whichever side of the cell each parental homologous chromosome with its recombinant end up is random.
What does independent assortment produce?
Random combinations of parental and recombinant homologous chromosomes in each new cell
Independent assortment(meiosis def)
Alignment and separation of homologous pairs are random during M1 and M2
Whichever side of cell each parental homologous chromosome with its recombinant ends up is random
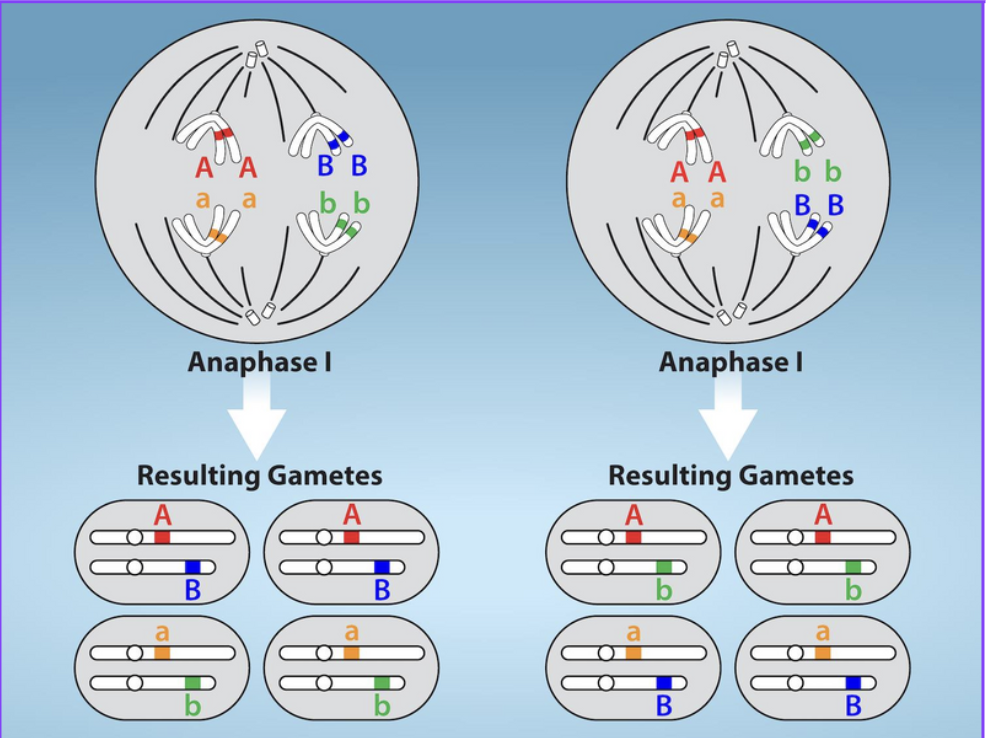
Mitosis vs meiosis: DNA synthesis
Meiosis: occurs in S phase of interphase
Mitosis: occurs in S phase of interphase
Mitosis vs meiosis: synapsis of homologous chromosomes
Meiosis: during prophase I
Mitosis: does NOT occur in mitosis
Mitosis vs meiosis: crossover
Meiosis: during prophase I
Mitosis: does NOT occur in mitosis
Mitosis vs meiosis: homologous chromosomes(tetrad) line up at metaphase plate
Meiosis: during metaphase I
Mitosis: does NOT occur in mitosis
Mitosis vs meiosis: sister chromatids line up at metaphase plate
Meiosis: during metaphase II
Mitosis: during metaphase
Prometaphase I
homologous chromosomes(in tetrad) are attached to spindle microtubules at the fused kinetochore shared by the sister chromatids
chromosomes continue to condense
nuclear envelope completely disappears
Metaphase I
homologous chromosomes randomly assemble at the metaphase plate, where they have been maneuvered in to place by the microtubules
Anaphase 1
spindly microtubules pull the homologous chromosomes apart
the sister chromatids are still attached at the centromere
Telophase I and Cytokinesis
sister chromatids arrive at the poles of the cell and begin to decondense.
A nuclear envelope forms around each nucleus
cytoplasm is divided by a cleavage furrow
Cyto-result is two haploid cells, each containing one X(each cell contains one duplicated copy of each homologous chromosome pair)
Prophase II
sister chromatids condense
new spindle begins to form
nuclear envelope starts to fragment
Prometaphase II
nuclear envelope disappears
spindle fibers engage the ind kinetochores on the sister chromatids
Metaphase II
sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate
Anaphase II
sister chromatids are pulled apart by the shortening of the kinetochore microtubules.
Non-kinetochore microtubules lengthen the cell
Telophase II and Cytokinesis
Chromosomes arrive at the poles of the cell and decondense
nuclear envelopes surround the four nuclei.
cleavage furrows divide the two cells into four haploid cells
Meiosis I vs. Meiosis II
M1: Homologous pairs of chromosomes are held together at the chiasmata, microtubules attach to the FUSED kinetochores of the sister chromatids
Homologous pairs or chromosomes are pulled apart by microtubs attached to the kinetochore, sister chromatids remain attached at the centromere
M2: Sister chromatids are held together at the centromere, microtubs attach to the ind kinetochores of the sister chromatids
sister chromatids are pulled apart by microtubs. attached to the kinetochore
germ cells
reproductive cells in humans that develop into eggs or sperm
Specialized diploid, 2n number of chromosomes, cells and undergo meiosis to form gamete in which the number of chromosomes is half and mitosis to keep alive the germ cell line
Also germ cells are the only cell which can undergo meiosis as well as mitosis
Where are germ cells produced?
gonads(testes and ovaries)
evolutionary success: asexual reproduction
producing clones of genetically successful parents(genetic clones of the parents). This means that the kids are same as parents.
can quickly become established (since no partner is needed)
little genetic diversity—>less adaptable to environmental changes
evolutionary success: sexual reproduction
requires mate
constant recombination breaks up genetically successful lineage(genes well-suited to your environment). This means that there is a lot of variation in well suited genes.
more genetic diversity —> more likely to adapt to env. changes
Life cycles: diploid-dominant life cycle(ex:humans)
Germ cells(2n)—> meiosis—> gametes(n)—> fertilization—> zygote(2n)—> mitosis—> new ind (2n)
only haploid cells are gametes
Fertilization
fusion of two gametes, usually from diff ind, to restore diploid state
Life cycles: Haploid-dominant life cycle (fungi and algae)
ind (n)—> specialized cells fuse—> zygote(2n)—> meiosis—> spores(n)—> mitosis—> new individuals(n)
Describe the haploid dominant life cycle in steps
Determined if: Body of organism is haploid
haploid cells that make up the tissues of the dominant multicell stage are formed by mitosis
during sex reprodu, sepcialized haploid cells from two ind(designated (+) and (-) mating types) join to form a diploid zygote
Zygote undergoes meiosis to form four haploid cells called spores(contains new genetic combo from parents)
Spores form multicellular haploid cells through many rounds of mitosis
Life cycles: alternation of generations(moss, ferns, angiosperms, gymno)
Sporophyte(2n) asexual stage—> meiosis—> spores(n)
gametophyte(n) sexual stage—> mitosis—> gametes(n)
Together: gametophyte(n)—> gametes(n)—> zygote(2n)—> mitosis—> sporophyte(2n)—> sporangia—> meiosis—> spores(n)—> mitosis
gametophyte
haploid multicellular plants that produce gametes from specialized cells.
meiosis not involved in prod of gametes bc organism that produces gametes already haploid
sporophyte
diploid multicellular plant(formed when zygote undergoes many rounds of mitosis)
Describe the alternation of generations in steps
Determined if: have a blend of haploid and diploid in life cycle
Haploid multicellular plants(gametophyte) produce gametes from specialized cells.
fertilization b/t gametes(egg and sperm) forms a diploid zygote
Zygote undergoes many rounds of mitosis and gives rise to a diploid multicellular plant(sporophyte)
Specialized cells of the sporophyte undergoes meiosis and produce haploid spores'
Spores will then develop into gametophytes
Law of segregation
Each gamete (sperm or egg cell) made by an organism will get just one of the two gene copies present in a parent organism, and gene copies are randomly allocated to the gametes.
Ex: If an organism has a genotype of Aa, half of its gametes will contain an A allele, and the other half will contain an a allele.
mycelium
fungus body(underground)
Spores
reproductive cells that are produced by certain organisms, like plants
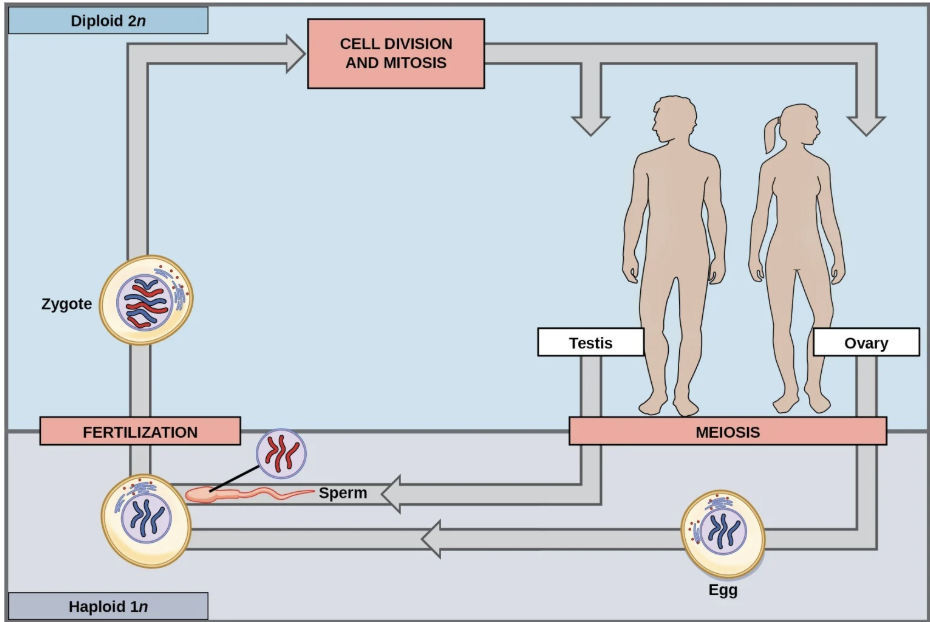
describe it
do it.

Describe it
Spores grows into the mycellium through mitosis, gills have things on them that produces spores through meiosis
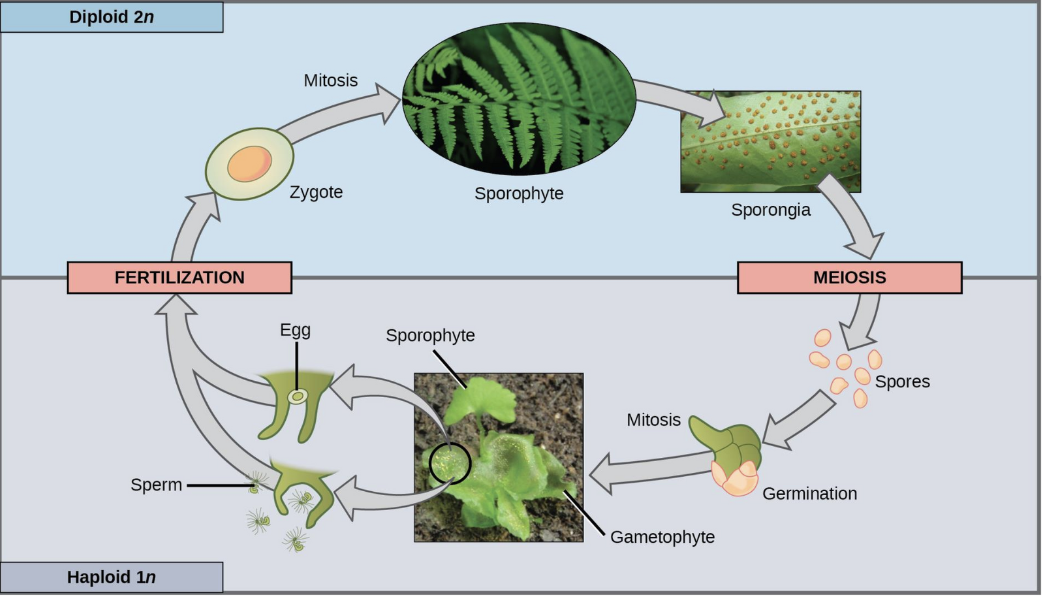
Describe it.
do it.