AP Biology - Metabolism, enzymes, and cellular respiration unit 2
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism
metabolic pathways
a series of chemical reaction that either build up complex molecules or break down complex molecules
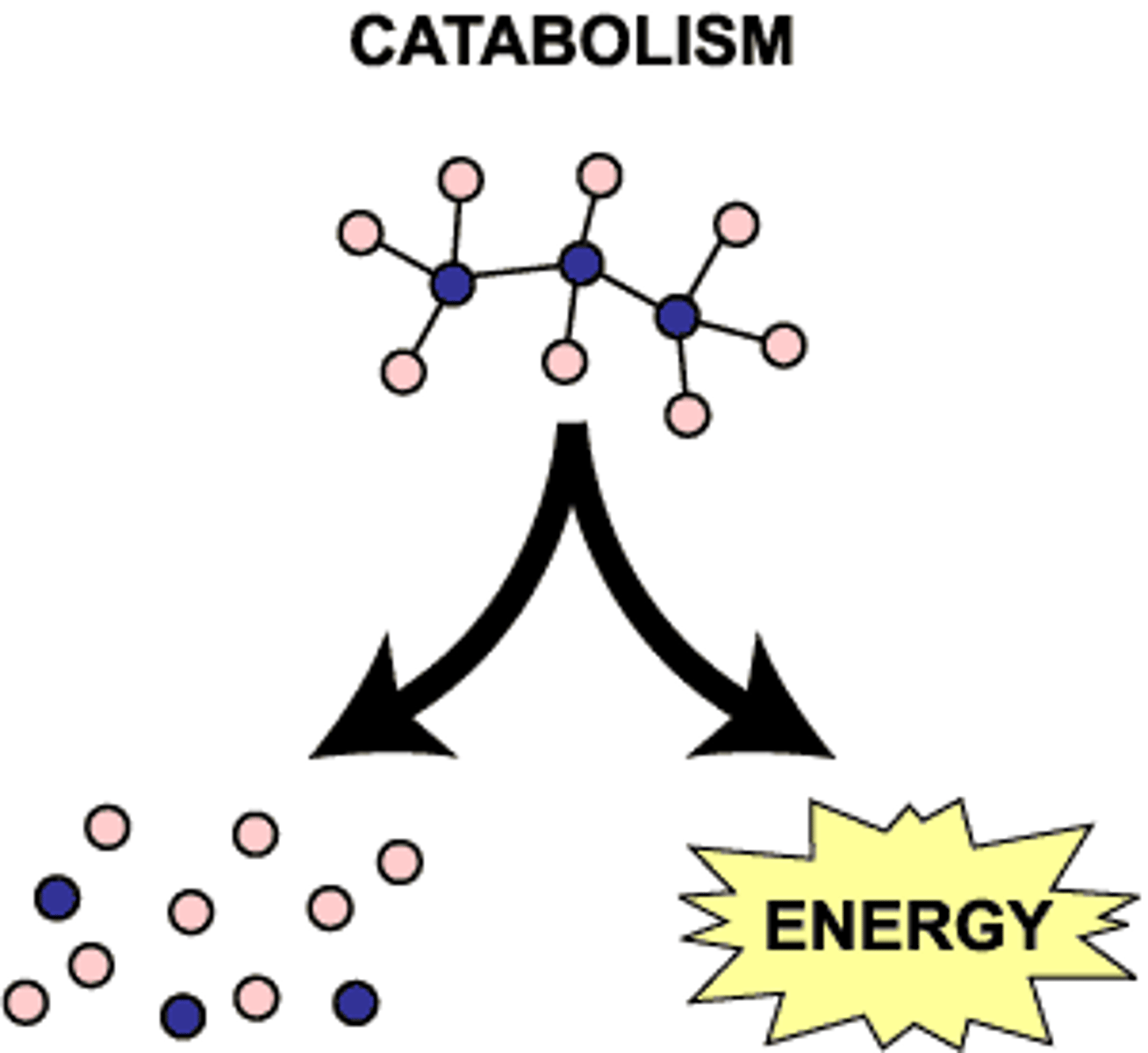
Catabolic pathways
pathways that release energy by breaking down complex molecules into simpler compounds
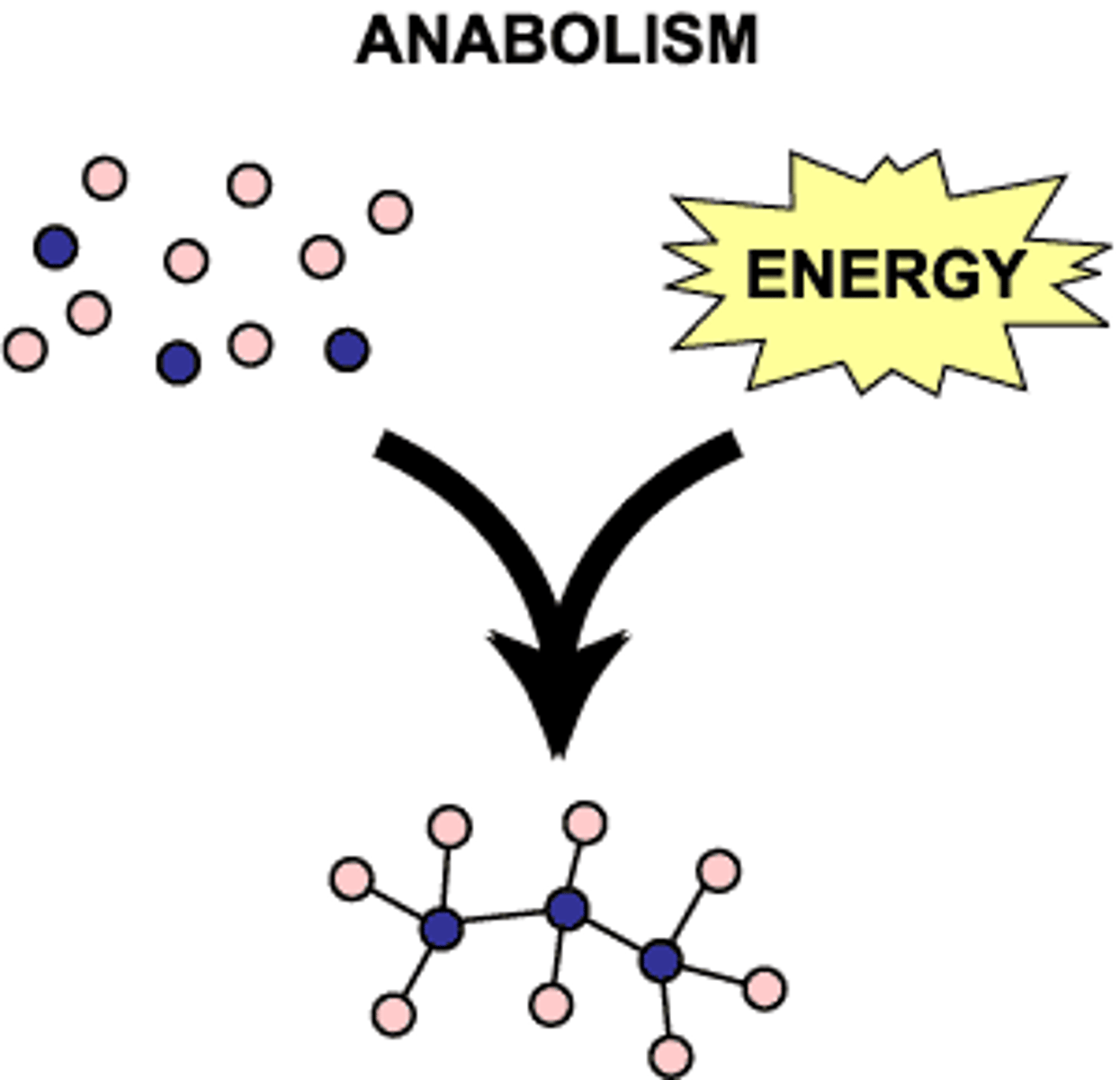
Anabolic pathways
pathways that consume energy to build complicated molecules from simpler compounds
Energy
the ability to do work
Kinetic energy
energy associated with motion
Thermal energy
energy associated with the movement of atoms or molecules
Potential energy
stored energy
Chemical energy
potential energy stored in chemical bonds
1st law of thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed only transformed or transferred
2nd law of thermodynamics
Every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy of the universe and during some energy transfer transformations some is unstable and lost as heat
Entropy
measure of disorder
Free energy
used to determine the likelihood of reactions in organisms or if the reaction is energetically favorable
equation of free energy
∆G = ∆H - T∆S
∆G
change in free energy
∆H
change in total energy
T
absolute temperature in K
∆S
change in entropy
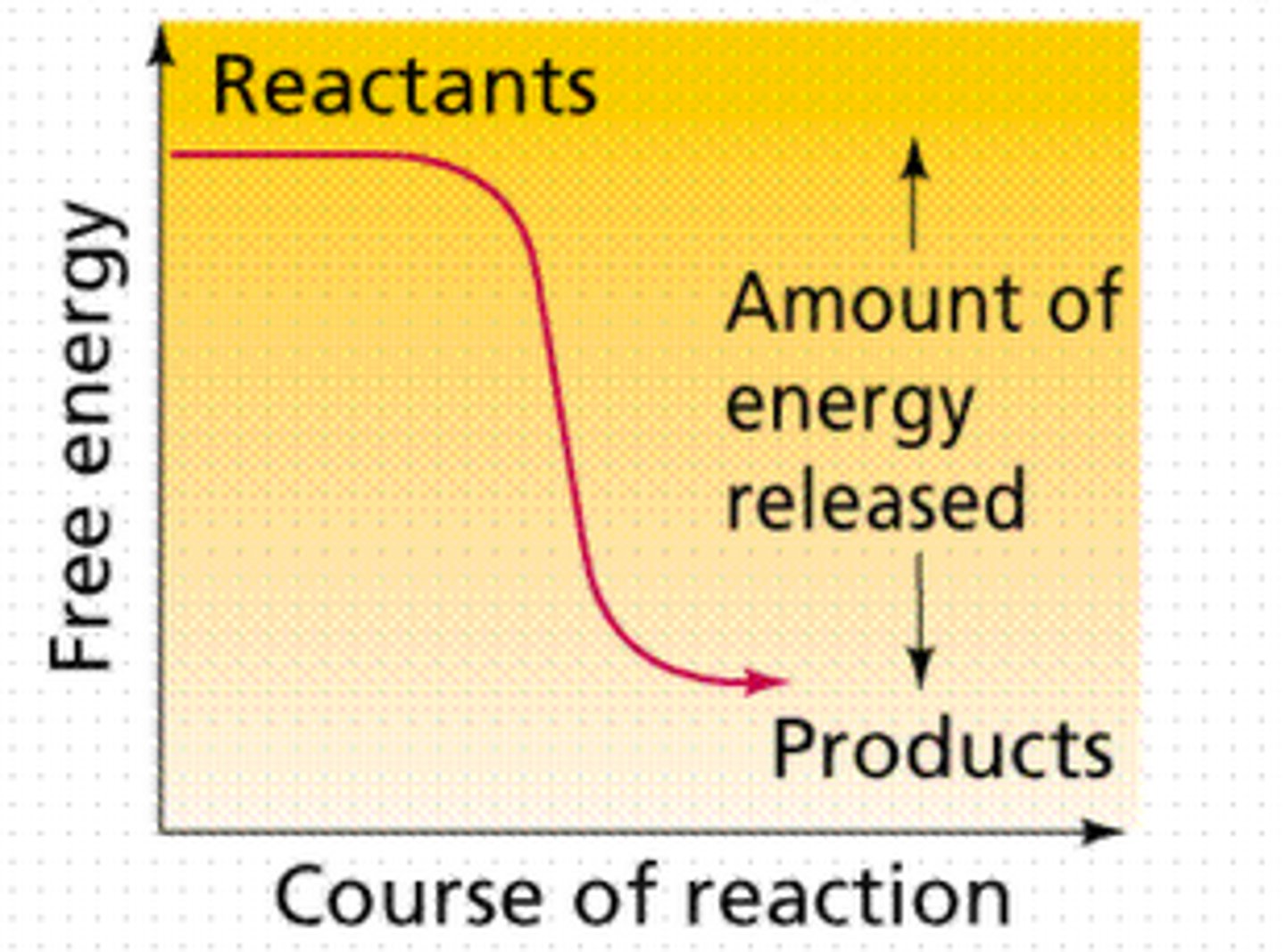
Exergonic reactions
release energy, spontaneous, ∆G is less than zero
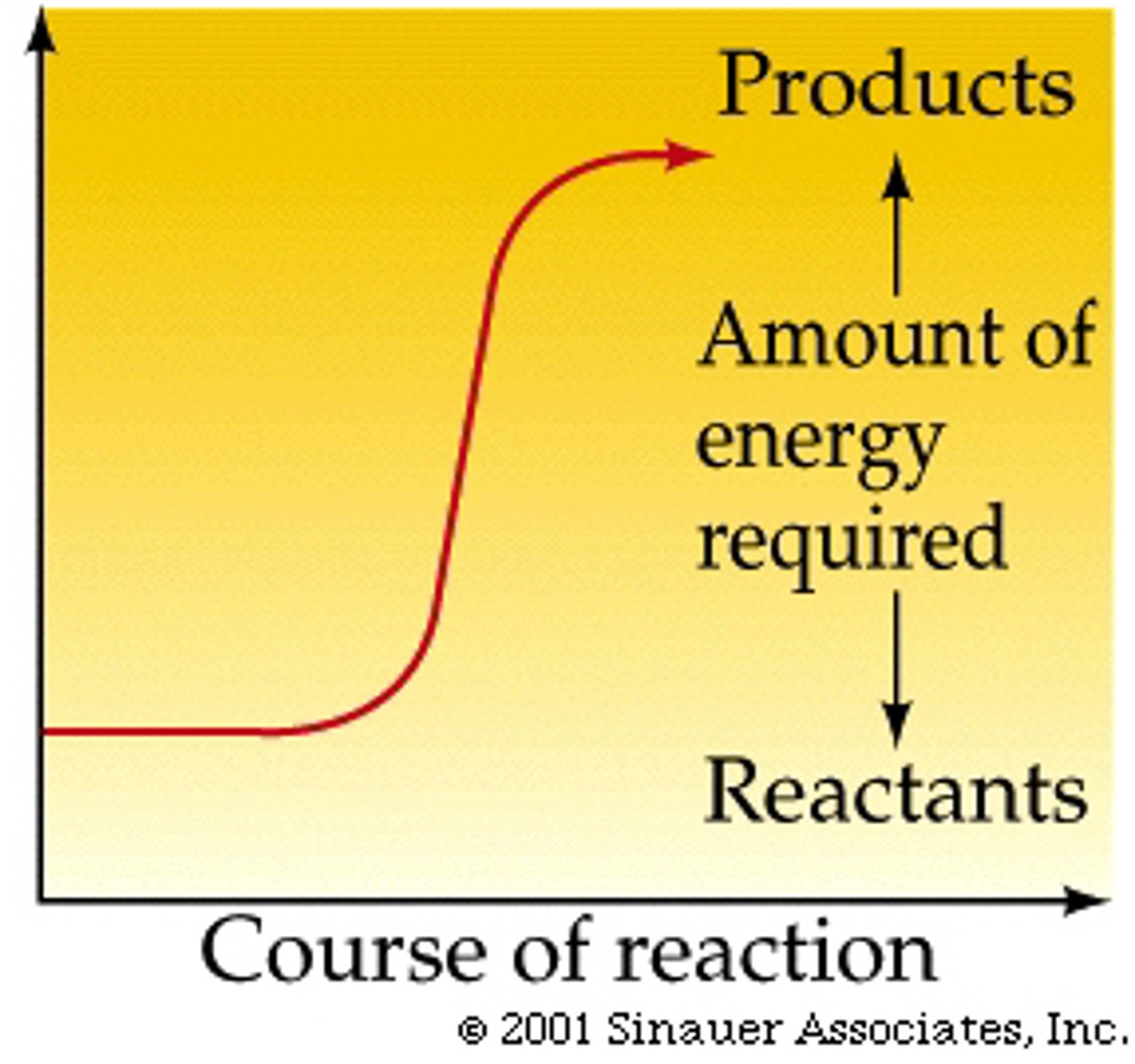
Endergonic reactions
absorb energy, not spontaneous, ∆G is greater than zero
Exergonic drives what?
Endergonic reactions
What are the three types of work cells can perfrom?
mechanical, transport, chemical
Mechanical work
movement
Transport wok
pumping of substances across membranes
Chemical work
synthesis of complex molecules
ATP
main energy source that cells use for most of their work
Phosporylation
the released phosphate moves to another molecule to give energy
Regeneration of ATP
ADP can be regenerated to ATP via the ATP cycle
Oxidation
loss of electrons
Reduction
gain of electrons
To catalyze
to speed up
Activation energy
the minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction
Enzymes
macromolecules that catalyze reactions by lowering the activation energy
Active site
The part of an enzyme or antibody where the chemical reaction occurs
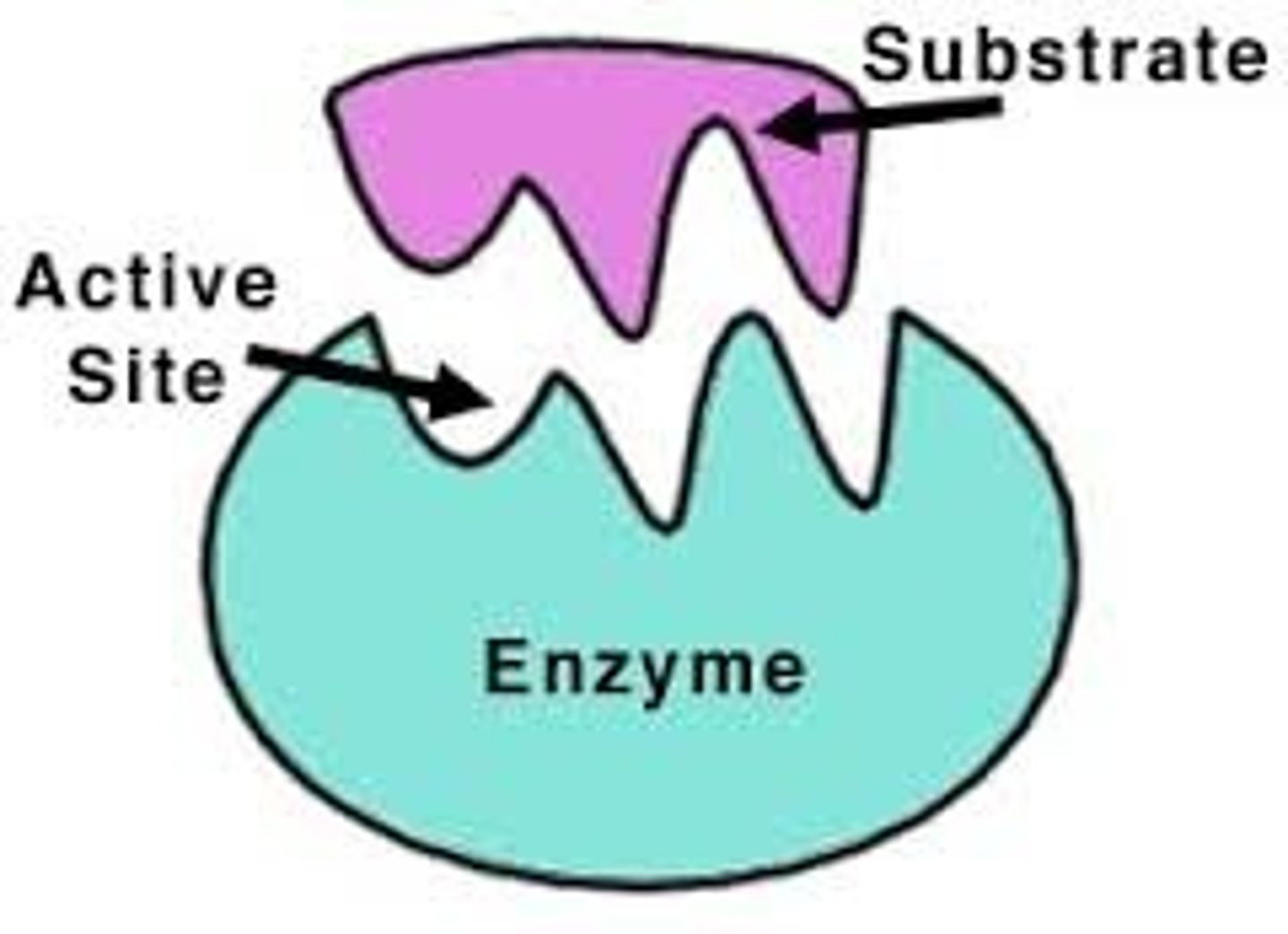
Substrate
A specific reactant acted upon by an enzyme
Induced fit
The change in shape of the active site of an enzyme so that it binds more snugly to the substrate, induced by entry of the substrate.
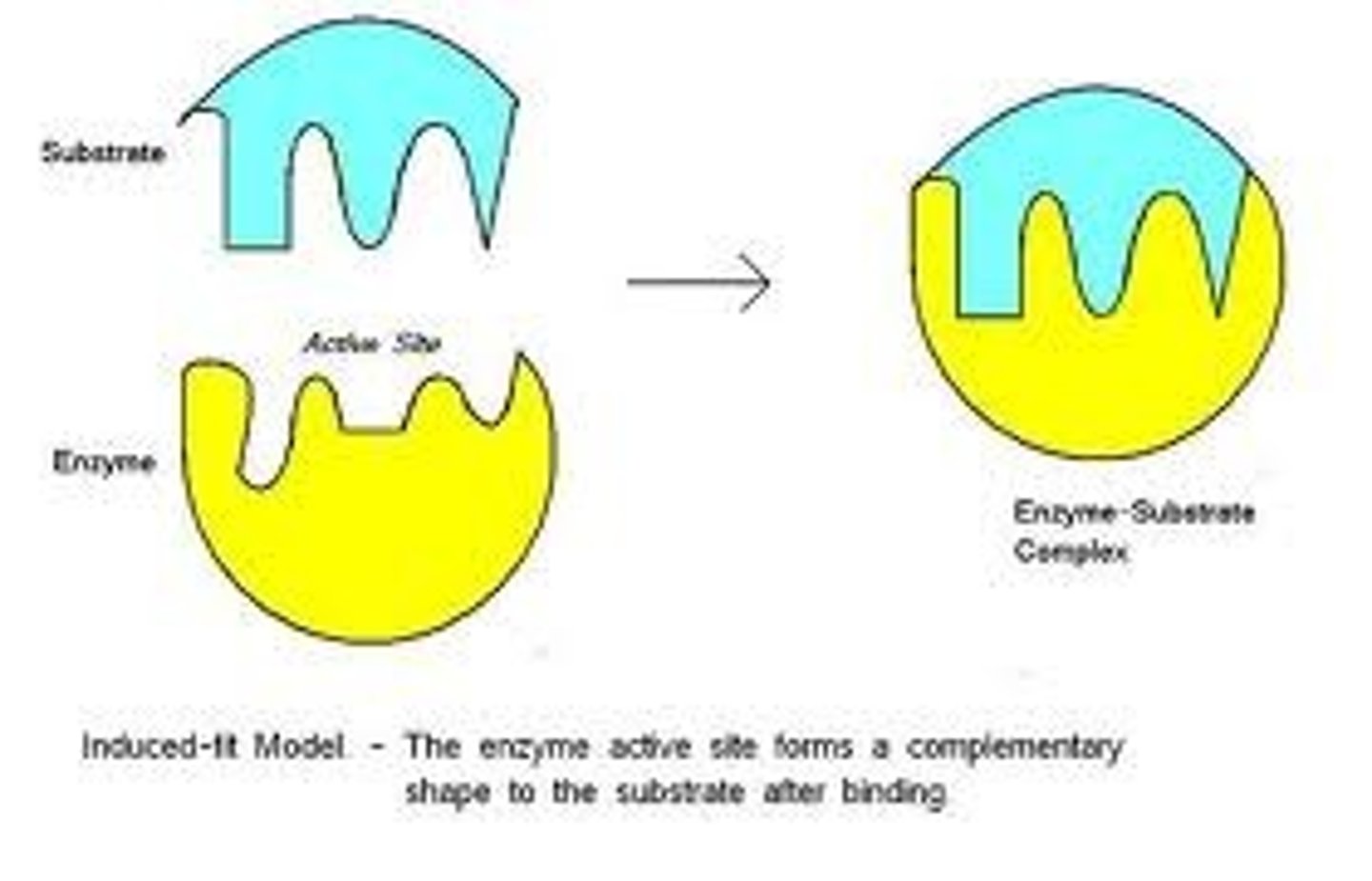
Enzyme-substrate complex
enzyme binds to its substrate
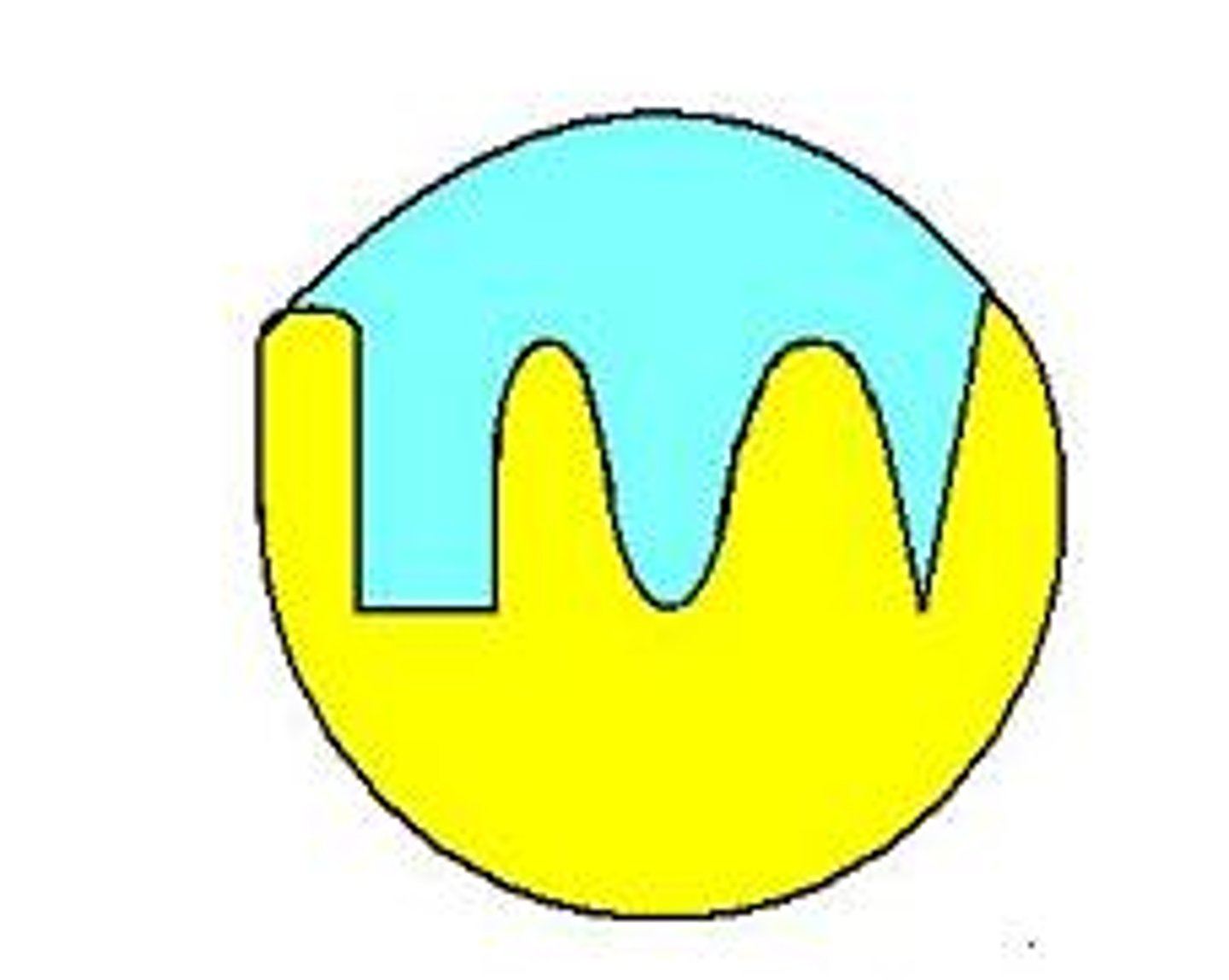

Enzyme catabolism
enzyme helps break down complex molecules
Enzyme anabolism
enzyme helps build complex molecules
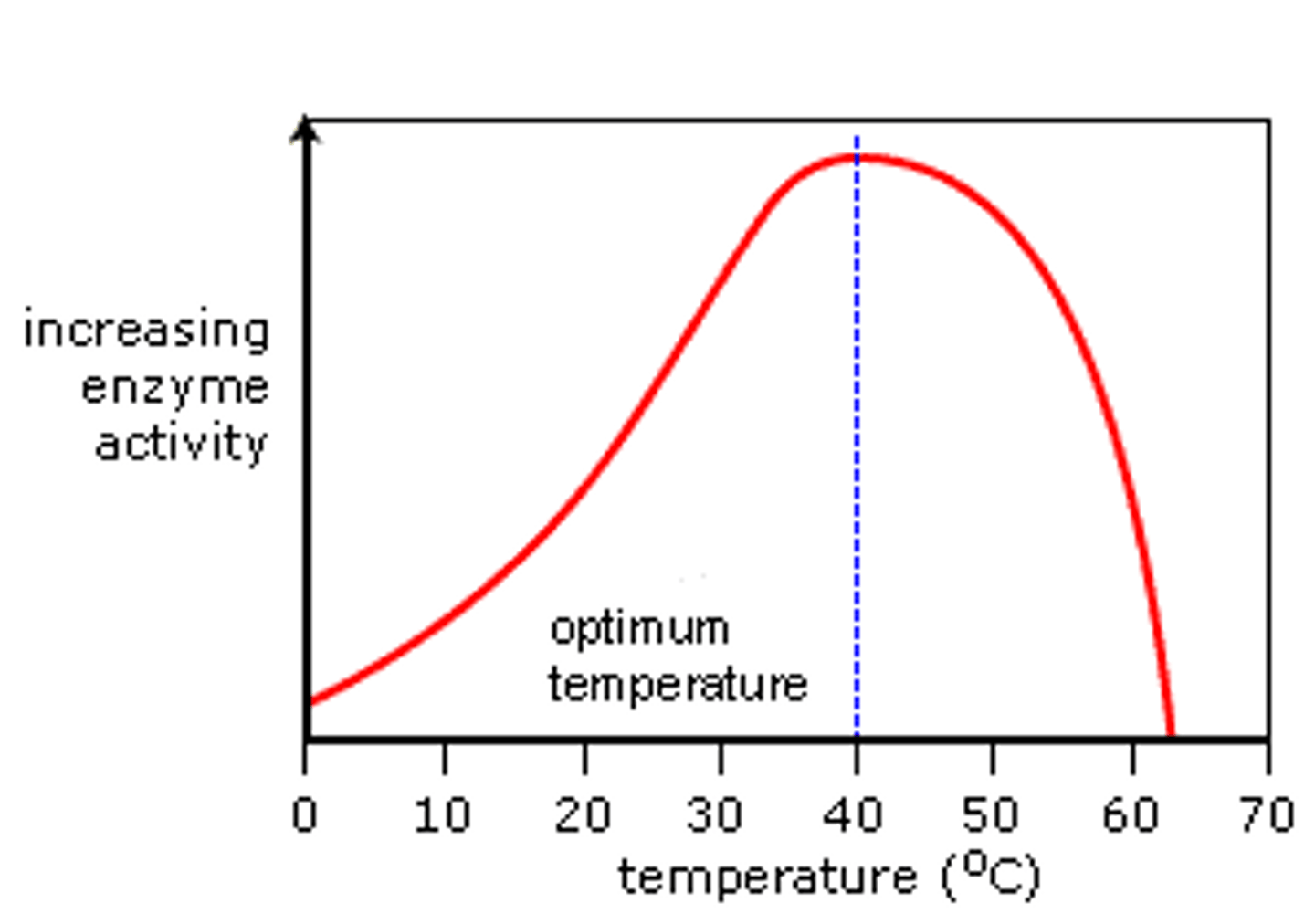
Does the rate of enzyme activity increase or decrease with an increase in temperature?
Increase up to a certain point due to collision
What happens when an enzyme is outside it's optimal ph?
Hydrogen bonds break denaturing the enzyme
Cofactors
nonprotein enzyme helpers
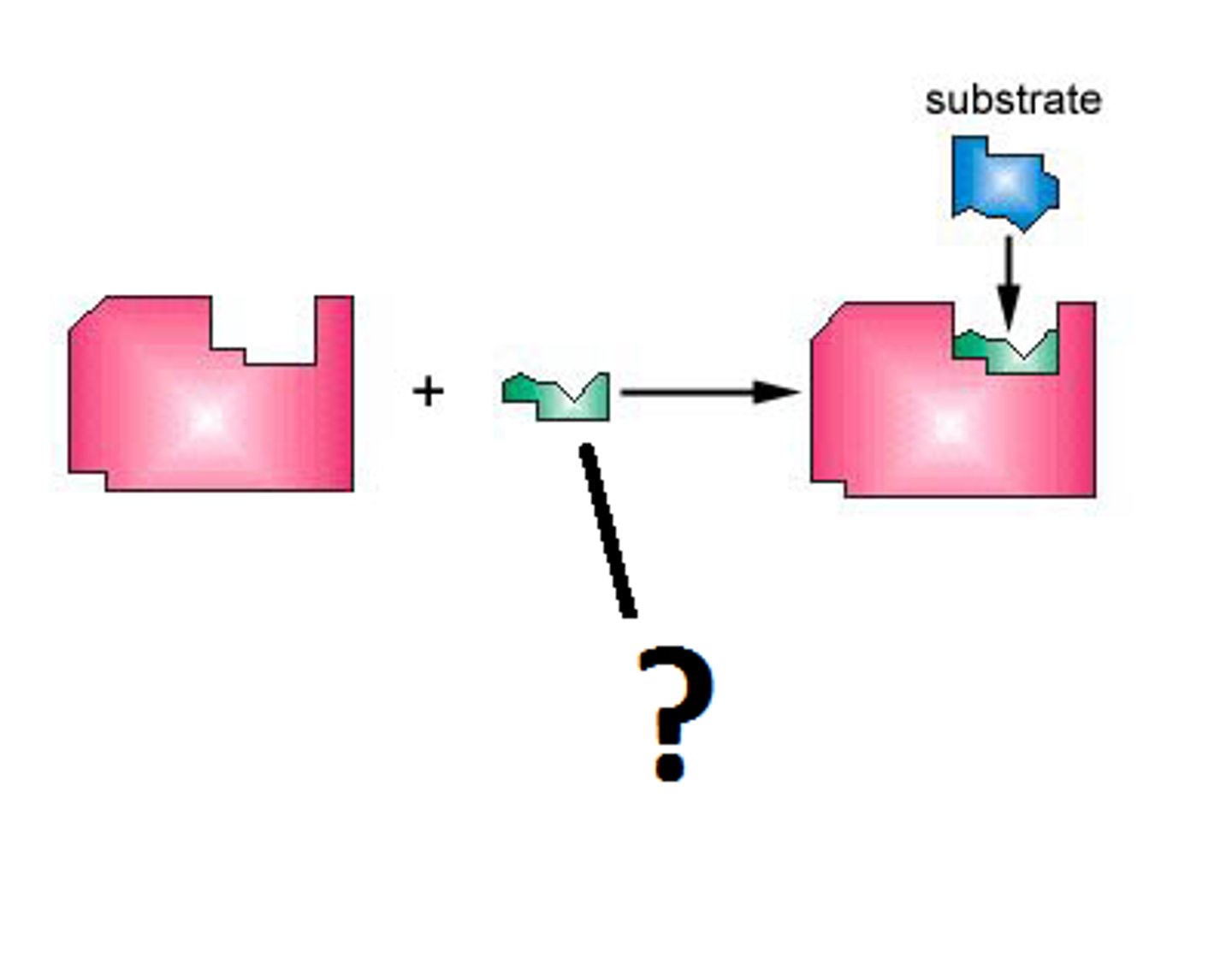
Two types of cofactors
metals and minerals
Coenzymes
organic cofactors

Example of coenzyme
vitamins
Enzyme inhibitors
reduce the activity of specific enzymes
Competitive inhibitors
reduce enzyme activity by blocking substrates from binding to the active site
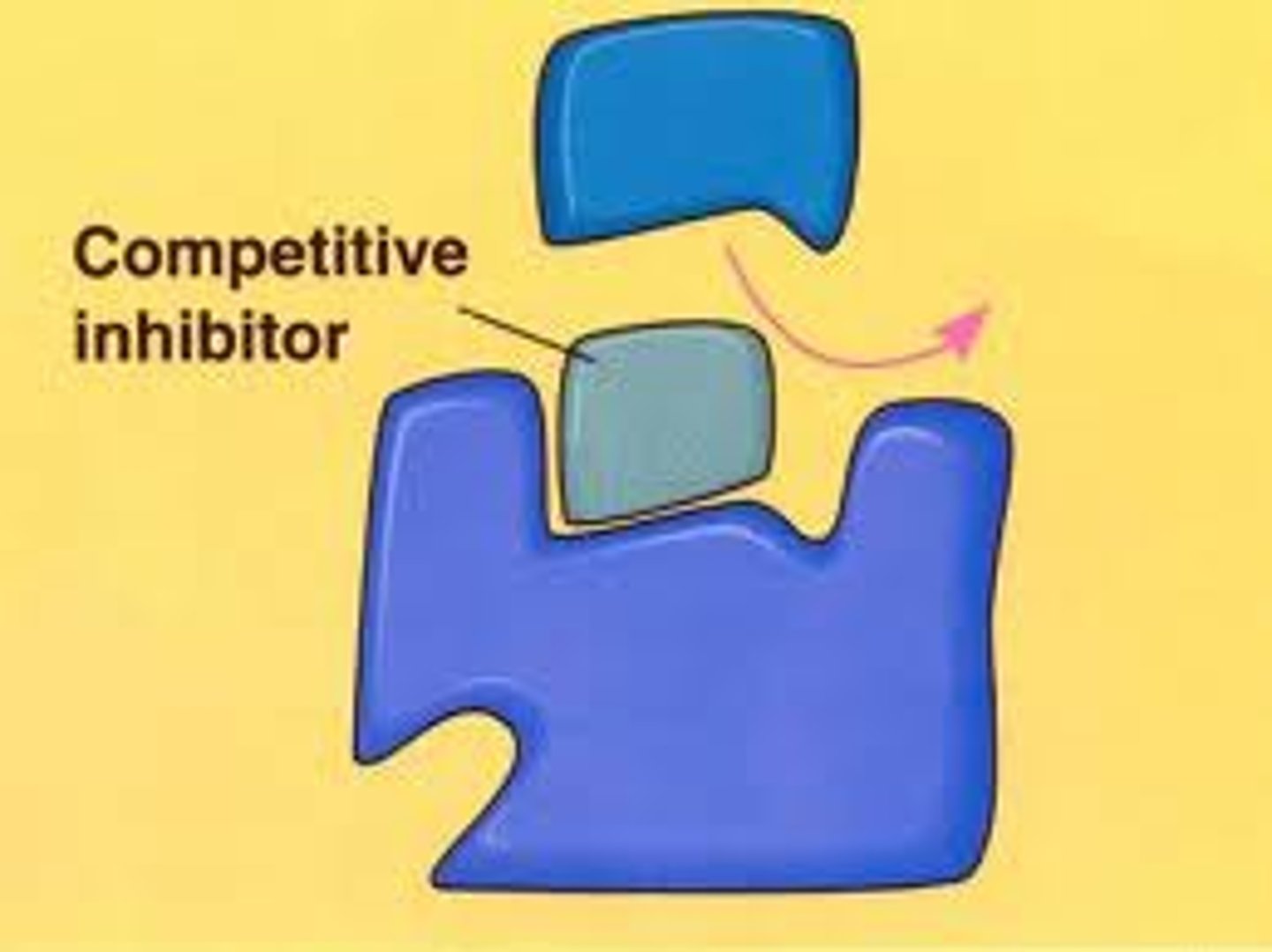

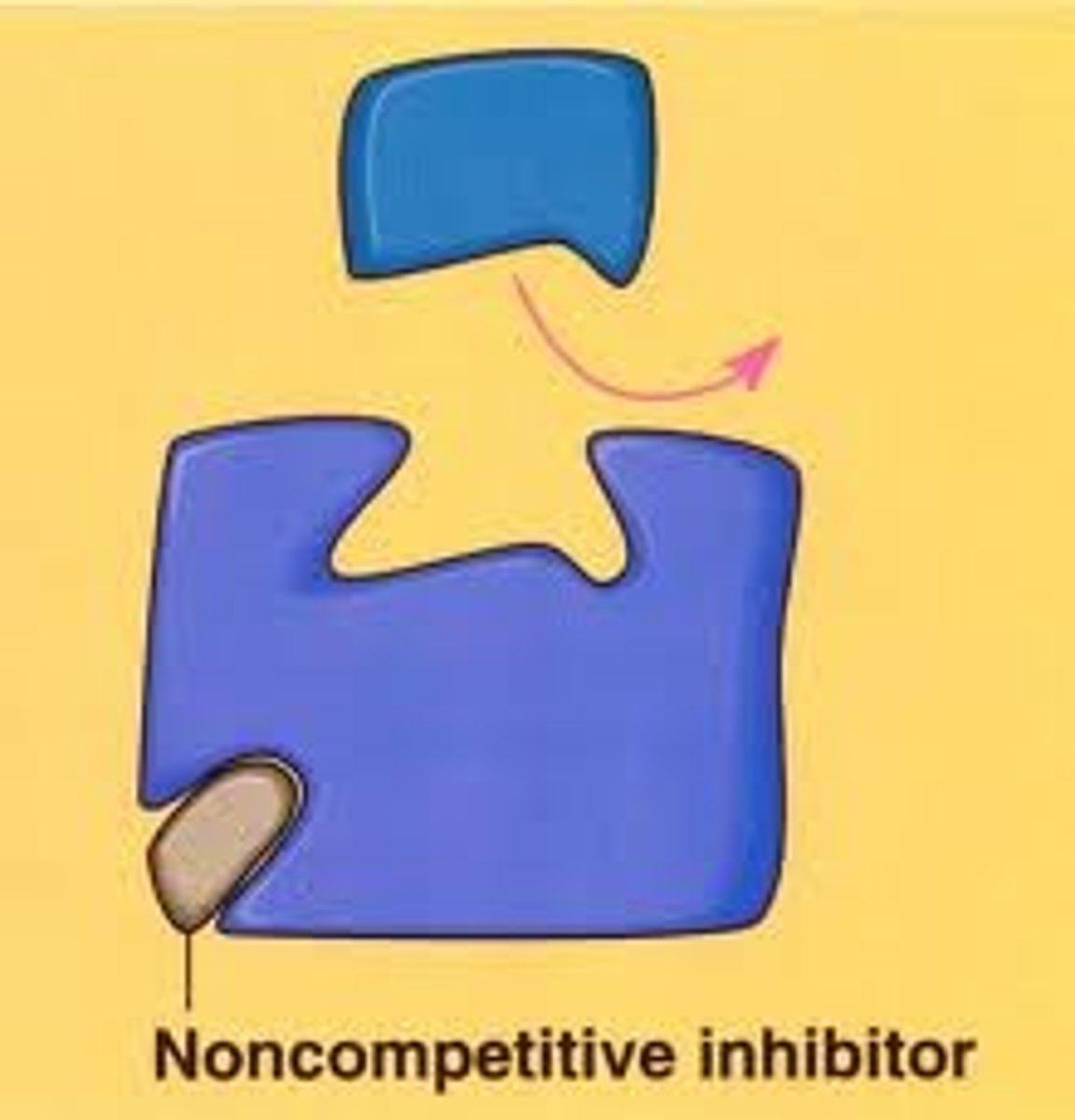
non-competitive inhibitor
bind to an area other than active site (allosteric site) which changes the shape of the active site preventing substrate from binding
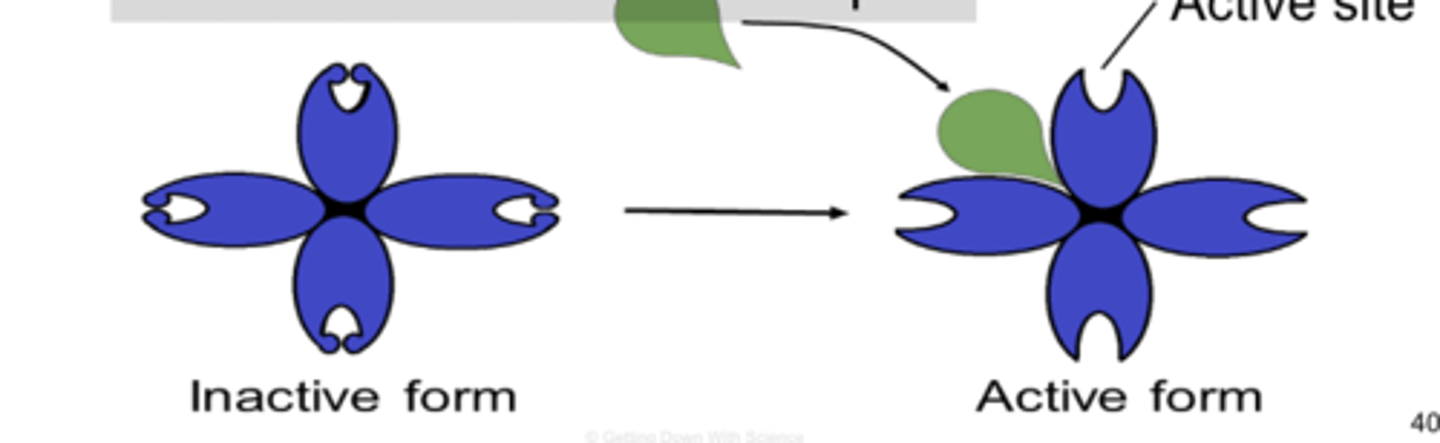
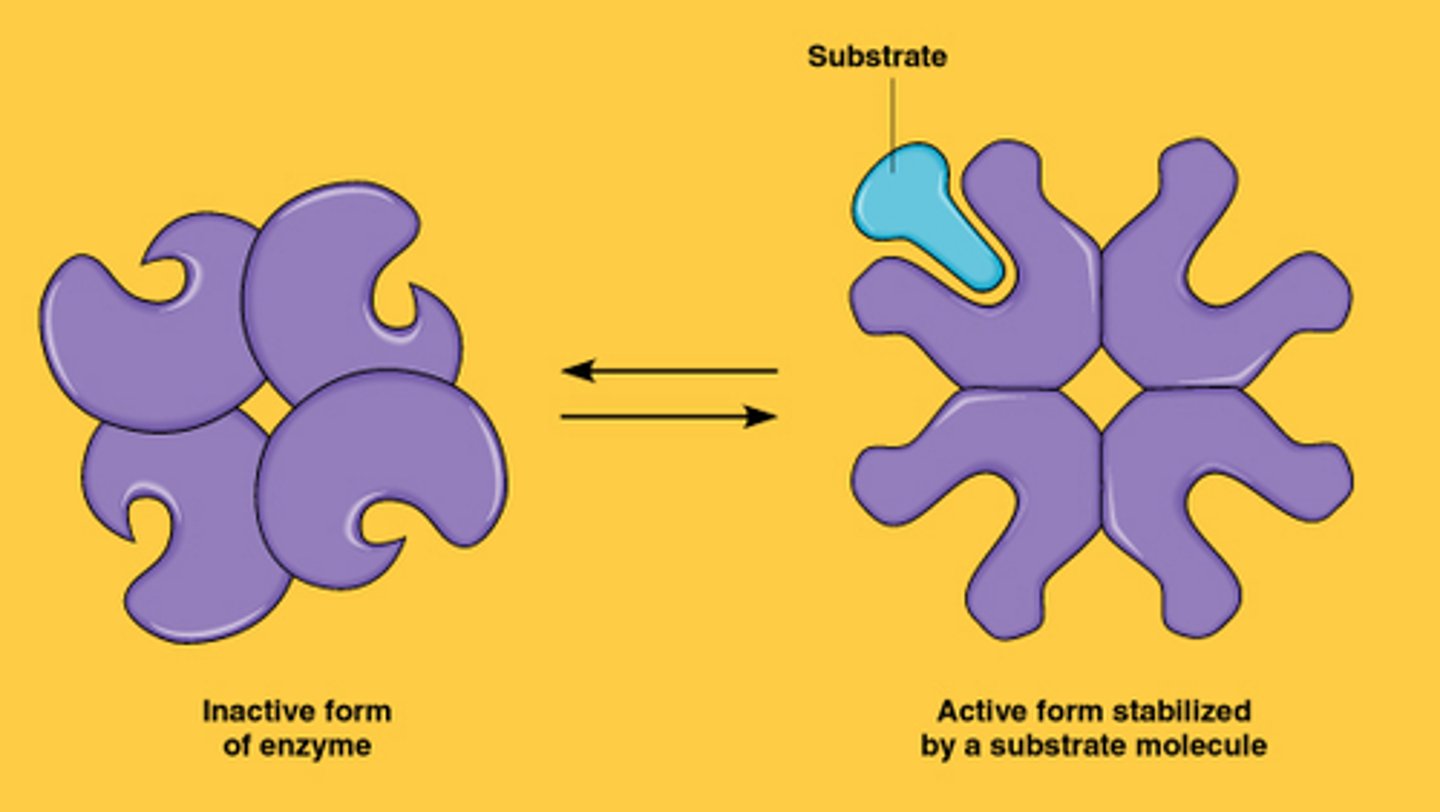
Allosteric enzymes
two binding sites
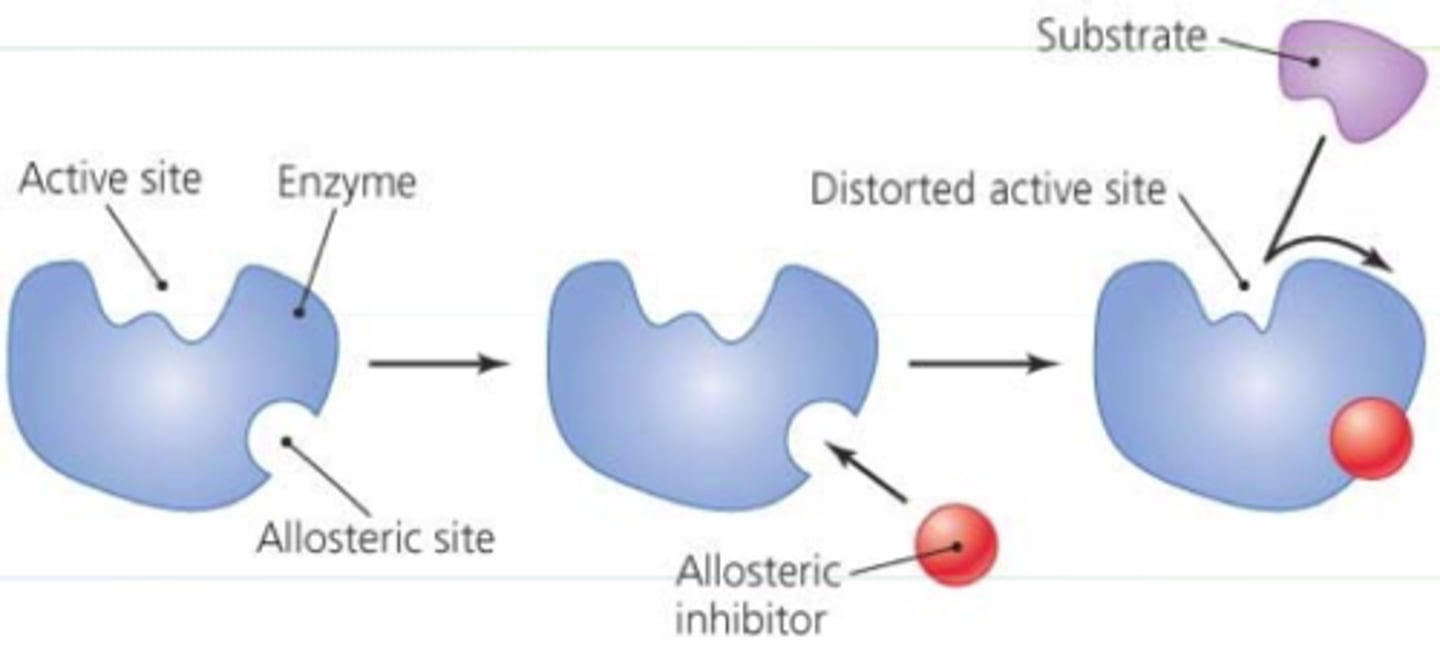
Allosteric regulation
molecules bind to an allosteric site which changes the shape and function of the active site
Allosteric activator
binds to allosteric site and increases enzyme activity by opening it or unlocking it
Allosteric inhibitor
substrate binds to allosteric site and stabilizes the enzyme shape so that the active site remains closed
Cooperatvity
is a form of allosteric regulation that can amplify enzyme activity
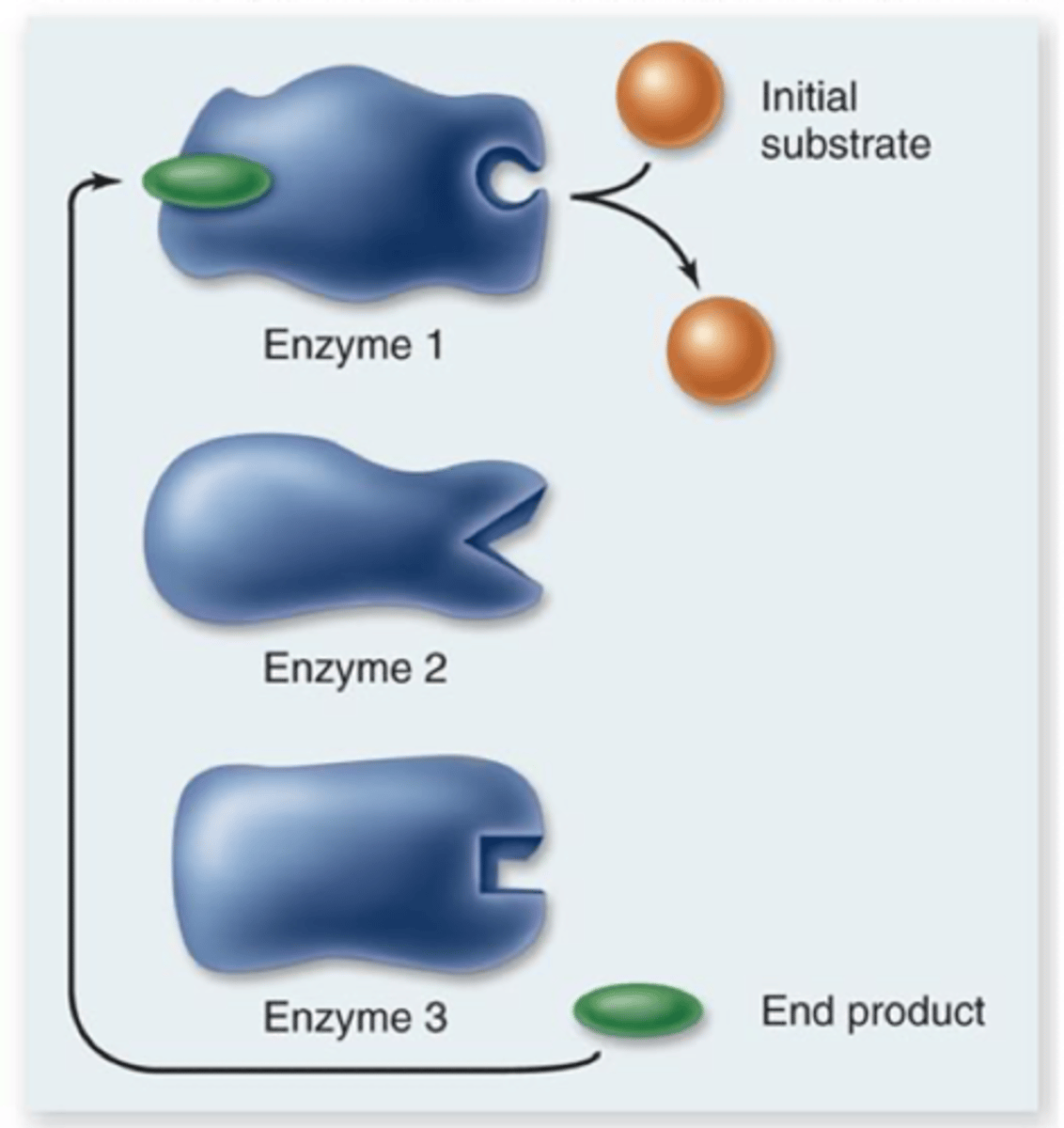
Feedback inhibtion
sometimes end product of metabolic pathway can act as an inhibitor to an early enzyme in the same pathway
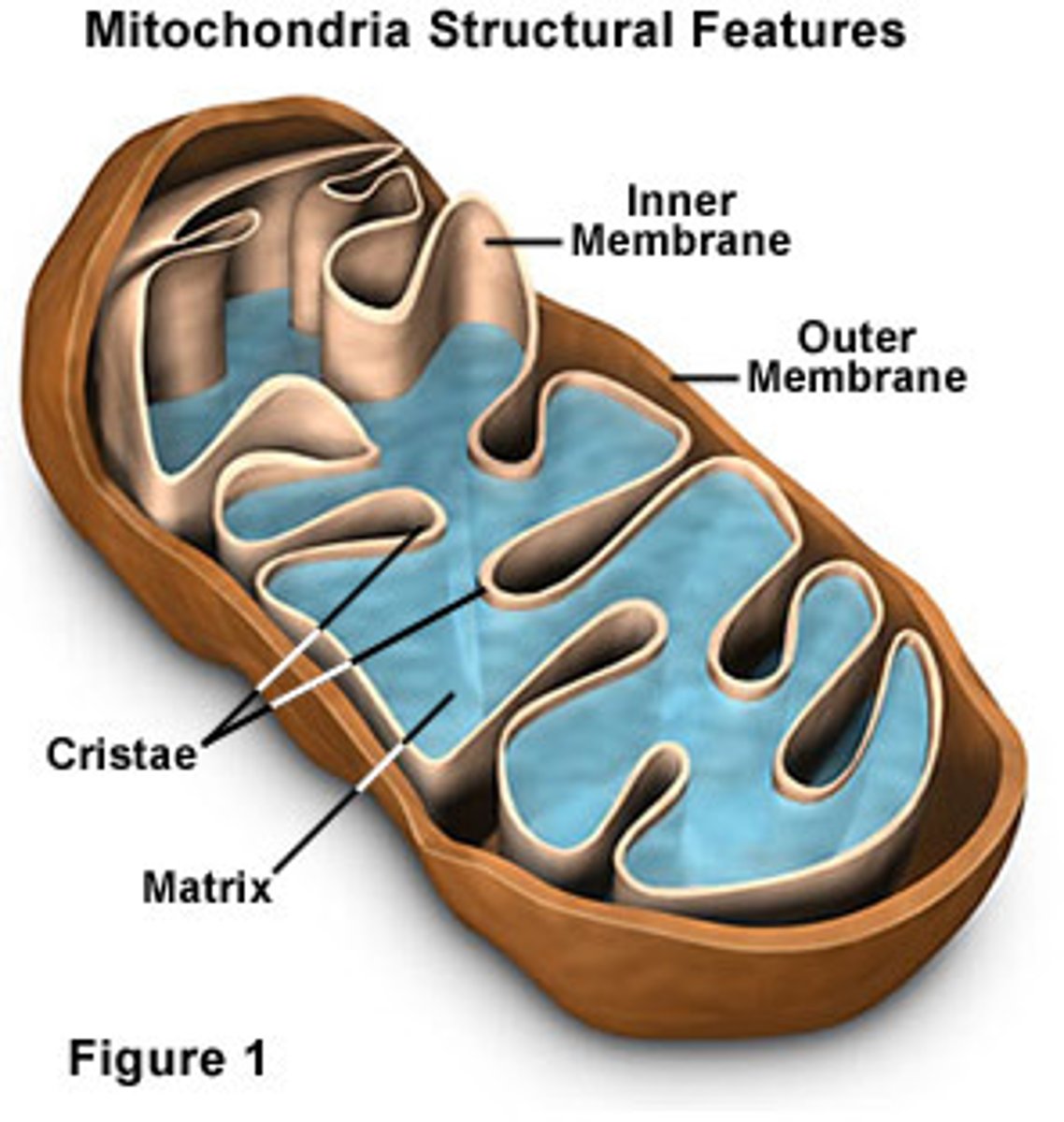
Cristae
folds in the inner membrane of mitochondria
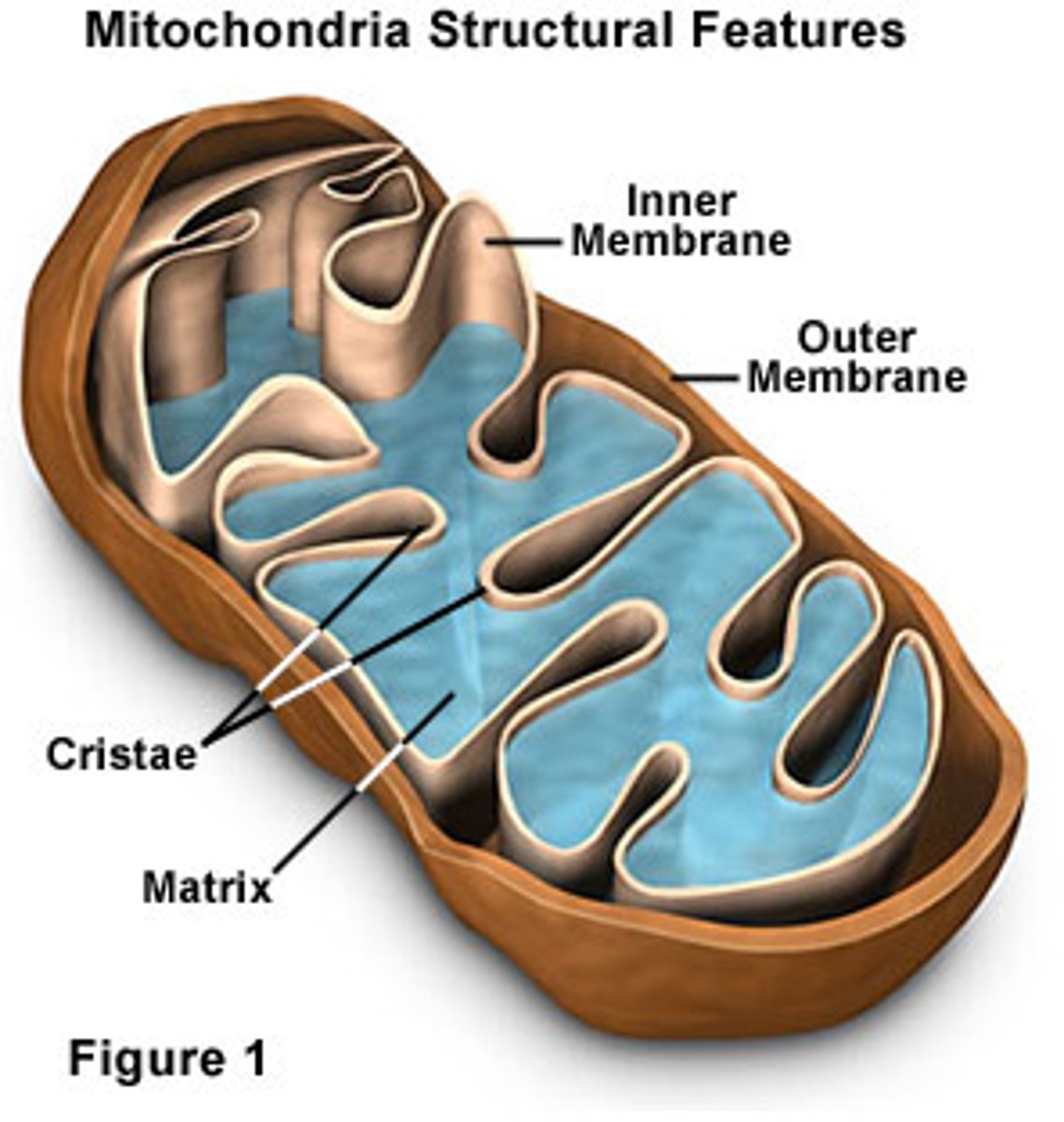
Matrix
cytoplasm inside mitochondria
Equation of cellular respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
What is oxidized in cellular respiration
glucose to Co2
What is reduced in cellular respiration
O2 to H20
Electron pathway in CR
glucose to NADH to ETC to oxygen
Where does glycolysis occur
cytoplasm
Inputs of glycolysis
1 glucose
Outputs of glycolysis
2 pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 NADH
Stage 1 of glycolysis
Energy investment - cell uses ATO to phosphorylate compounds of glucose
Stage 2 of Glycolysis
Energy payoff - energy is produced by substrate level phosphorylation
Inputs of pyruvate oxudation
2 pyruvate
outputs of pyruvate oxidation
2 acetyl CoA, 2 CO2, 2 NADH
pyruvate oxidation
pyruvate is oxidized to acetyl CoA and then acetyl CoA is used make citrate for citric acid cycle
Inputs of citric acid cycle
2 Acetyl CoA
Outputs of citric acid cycle
4 CO2, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, 2 ATP
Where does the citric acid cycle occur?
mitochondrial matrix
Citric acid cycle...
turns CoA into citrate, release Co2, synthesizes ATP, electrons transferred to NADH and FADH2
Inputs of oxidative phosporylation
10 NADH, 2 FADH2
outputs of oxidative phosphorylation
32 ATP
two parts of oxidative phosphorylation
electron transport chain and chemiosmosis
ETC
a sequence of membrane proteins that shuttle electrons down a series of redox reactions

What does the ETC do?
release energy to make ATP and transfers e- to o2 to make H20
Where is the ETC located?
inner mitochondrial membrane
Biggest function of ETC
create a proton (H+) gradient across the membrane
final electron acceptor of ETC
oxygen
Chemiosmosis
the use of energy in a H+ gradient to drive cellular work
ATP synthase
the enzyme that makes ATP from ADP and P
When H+ binds...
the rotor spins
Anaerobic Respiration
generates ATP using an ETC in the absence of oxygen
Final electron of anaerobic
sulfates or nitrates
Fermentation
generates ATP without an ETC, an extension of glycolosis
2 types of fermentation
alcoholic and lactic acid
Alcohaulic fermentation
pyruvate is converted to ethanol
Lactic acid fermentation
pyruvate is reduced directly by NADH to form lactate
How many ATP is produced in fermentation
2 ATP
When lactate is built up in blood....
it lowers the ph
facultative anaerobes
can live with or without oxygen