u3 ch14 study guide THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
SNS
somatic nervous system
ANS
autonomic nervous system
autonomic nervous system (ANS): overview
consists of motor neurons that innervate: smooth muscle, cardiac muscle and glands
general visceral motor system: responsible for regulating involuntary body activities like heart rate, digestion and breathing
SNS and ANS: similarities
both are composed of motor neurons
SNS and ANS: differences
effectors, efferent pathways and ganglia, neurotransmitters, response to the neurotransmitters
SNS effector
skeletal muscle (voluntary)
ANS effector
Cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, glands (involuntary)
efferent pathways: SNS
uses single neuron
extends from CNS to skeletal muscle
cell body → in the CNS
axon → heavily myelinated fiber (thick)
efferent pathways: ANS
uses two neuron chain
preganglionic neuron and postganglionic neuron
ANS efferent pathways two neuron chain: Preganglionic neurons
extends from CNS to the ganglion
cell body → in CNS
axon → lightly myelinated fiber (thin)
ANS efferent pathways two neuron chain: Postganglionic neuron
extends from ganglion to the effector organ
cell body → outside CNS
axon → nonmyelinated fibers (thinnest)
Neurotransmitters and effects: SNS
all somatic motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh)
effects are always stimulatory
Neurotransmitters and effects: ANS
preganglionic fibers release ACh
postganglionic sympathetic fibers release norepinephrine
postganglionic parasympathetic fibers release ACh
effect is either stimulatory or inhibitory, depending on type of receptors
ANS preganglionic fibers release
ACh
Postganglionic sympathetic fibers release
norepinephrine
postganglionic parasympathetic fibers release
ACh
divisions of ANS: sympathetic division
‘fight or flight’ system
mobilizes the body during activity, promotes adjustments during exercise/threat
diverts blood from abdominal viscera and skin to skeletal and cardiac muscles and brain when necessary
originates in thoracolumbar region
divisions of ANS: parasympathetic division
‘rest and digest’ system
promotes maintenance activities, conserves body energy
promotes adjustments when a person is relaxing or reading after a meal
90% of all parasympathetic fibers are derived from → cranial nerve X (vagus)
originates in craniosacral region
ANS fibers/neurot: CHOLINEREGIC FIBERS
releases acetylcholine (Ach)
all preganglionic axons (sympathetic and parasympathetic)
all parasympathetic postganglionic axons
ANS fibers/neurot: ADRENERGIC FIBERS
releases norepinephrine (NE)
most sympathetic postganglionic axons (sweat glands exception)
how is action of neurotransmitter decided?
on the receptor it binds to
receptors of neurotransm: general
action of neurot depends on receptors
each neurotransm binds to 2(+) types of receptors
allows neurotransmitter to exert DIFFERENCE effects at different targets
receptors for neurotransmit: CHOLINERGIC RECEPTORS
binds to ACH
two types:
Nicotinic receptors
Muscarinic receptors
receptors for neurotransmit: ADRENERGIC RECEPTORS
binds to NE
two types:
alpha adrenergic
beta adrenergic
Cholinergic receptors: Nicotinic receptors
found on:
cell bodies and dendrites of all postganglionic neurons of sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers
sarcolemma of skeletal muscle cells at neuromuscular junction
effect on ACh on nicotinic receptors is always stimulatory
Cholinergic receptors: Muscarinic receptors
found on: effector cells stimulated by parasympathetic fibers
subclasses: M1, M2, M3, M4, M5
effect depends on subclass of receptors on target organ
stimulatory (mostly)→ M1, M3, M5 (ex: smooth muscles and GI tract glands)
inhibitory (some) → M4 (ex: cardiac)
Cholinergic receptors: muscarinic receptors STIMULATORY ONES
M1, M3, M5
cholinergic receptors: muscarinic receptors INHIBITORY
some
M4 (heart)
what is M4 for
cardiac
Adrenergic receptors: general
responds to NE or epinephrine
found on effector cell stimulated by sympathetic fibers
effects depend on subclass of receptor predominating the target one
2 classes: alpha (a1, a2) and beta (B1, B2, B3)
Adrenergic receptors: Stimulatory
a1, B1, B3
Adrenergic receptors: Inhibitory
a2, B2
what does NE binding to cardiac muscle B1 receptors cause
increase in heart rates
epinephrine binding to B2 receptors cause…
bronchial relaxation
interactions of autonomic divisions: DUAL INNERVATION
most visceral organs have both SYMPATHETIC and PARASYMPATHETIC innervation
interactions of autonomic divisions: ANTAGONISTIC INTERACTIONS
works in opposite to each other, allows for precise control of vsiceral activity
Antagonistic interaction example: Sympathetic division
increases heart and respiratory rates
inhibits digestion and elimination
dilation of pupils for far vision
Antagonistic interaction example: Parasympathetic division
decrease heart and respiratory rates
allows for digestion and discarding of waste
constriction of pupils
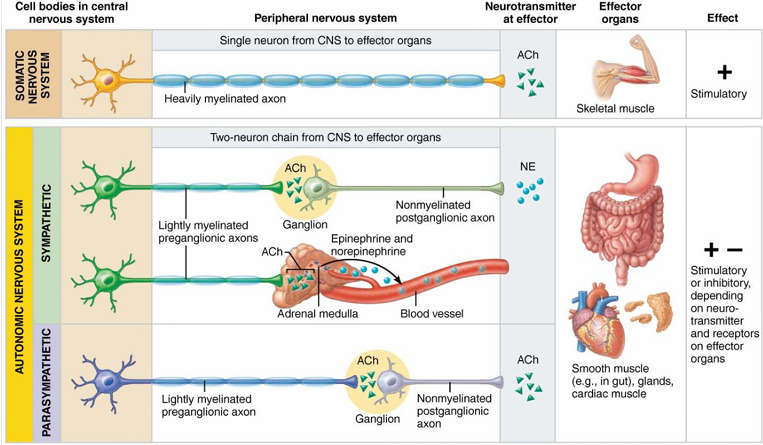
important
SNS vs ANS
What division of the ANS uses NE as the neurotransmitter?
sympathetic division
ANS Sympathetic
two neuron chain preganglionic neuron and postganglionic
effectors: cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, glands
postganglionic fibers release norepinephrine NE
adrenergic fibers
ANS Parasympathetic
two neuron chain preganglionic neuron and postganglionic
effectors: cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, glands
postganglionic fibers release ACh
cholinergic fibers
The ACh effect on what receptors is always stimulatory?
cholinergic: NICTOTINIC receptors
What ACh receptor is always stimulatory EXCEPT for the cardiac muscle?
cholinergic: MUSCARINIC receptors
inhibitory for → M4 (cardiac muscle)
what receptor responds to NE or epinephrine and what division does it belong to?
ADRENERGIC receptors and sympathetic division
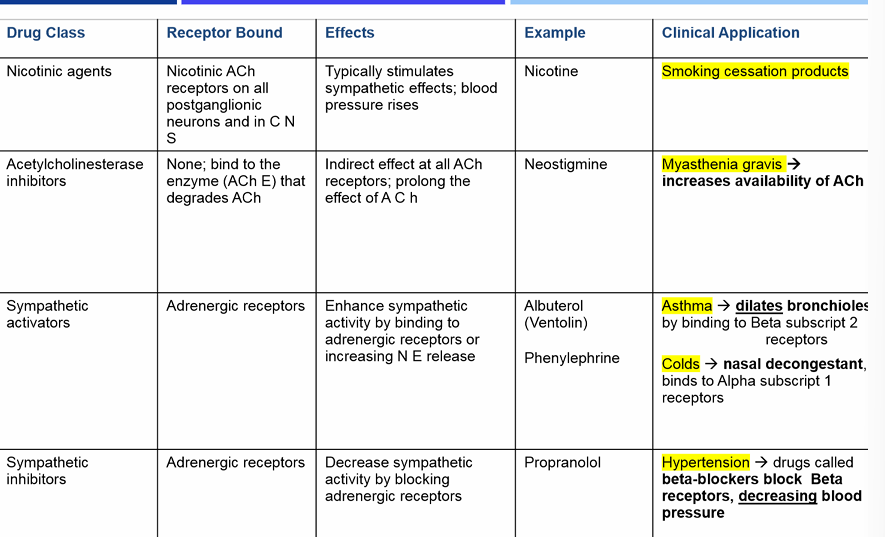
drug table
note: asthma, hypertension, myasthenia gravis
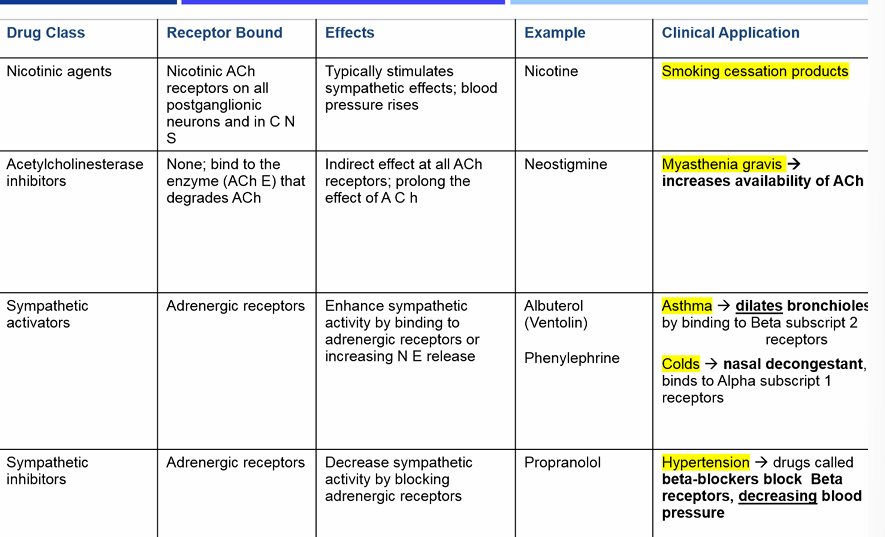
What drug class and process dilates the bronchioles by binding to B2 receptors for asthma?
drug class: sympathetic activators
receptor bound: adrenergic receptors
effects: enhance sympathetic activity by binding to adrenergic receptors or increasing NE release
ex: albuterol
what drug class and process use beta-blockers and decrease the blood pressure during hypertension?
drug class: sympathetic inhibitors
receptor bound: adrenergic receptors
effects: decrease sympathetic activity by blocking adrenergic receptors
ex: propranolol
what drug class and receptor bound increases availability of ACh for myasthenia gravis?
drug class: acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
receptor bound: NONE, binds to enzyme (ACh R) that degrades ACh
effects: indirect effect at all ACh receptors; prolong effects of ACh
ex neostigmine
effects of ans (local vs diffused): PARASYMPATHETIC division
short lived, highly localized control over effectors because
ACh is quickly destroyed by acetylcholinesterase
effects of ans (local vs diffused): SYMPATHETIC division
long lasting, body-wide effects because:
NE and epinephrine are secreted into the blood as part of sympathetic response
control of ANS functioning: CNS , hypothalamus
main integrative center of ANS activity
cerebral input → may modify ANS but foes so subconsciously
other controls → brain stem, spinal cord, cerebral cortex
how does the brain stem influence ANS activity?
regulates pupil size, heart, blood pressure, airflow, salivation
how does the spinal cord influence ANS activity?
reflexes for urination, defecation, erection and ejaculation
Series of events in sympathetic pathway
thoracolumbar origin, short preganglionic fiber, ACh release at ganglion, long postganglionic fiber, NE release at effector
What is an effect of norepinephrine binding to beta 2 adrenergic receptors?
vasodilation
does the somatic or autonomic NS have ganglia in motor pathways?
autonomic only
what receptor would you target to get an inhibitory effect on the heart (reduce heart rate)
muscarinic receptors
Sympathetic responses generally are widespread because
NE and epinephrine are secreted into the blood as part of the sympathetic response
Drugs called beta-blockers
decrease heart rate and blood pressure
Sympathetic division excitation causes
increased blood glucose, decreased GI peristalsis, and increased heart rate and blood pressure
Which of the following drug classes would be useful for smoking cessation
products?
nicotinic agents