Body fluids Final review
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Reasons to analyze CSF
Meningitis
CVA
MS
Leukemia, tumors, lymphoma
hydrocephalus
X-ray dye
CSF is created by the
Choroid plexus
Purpose of the CSF
to cushion and exchange nutrients and wastes
In CSF, the amount of cells, protein, and glucose is controlled by the
Blood brain barrier
Normal WBC in CSF
0-5
Normal RBC in CSF
none
Normal protein in CSF
15-45mg/dL
Normal glucose in CSF
2/3 of blood glucose
Tube 1 of CSf goes to ____ for ______. if it can’t be analyzed w/in 2 hrs you _______ it
chem
protein/glucose
freeze
Tube 2 of CSF goes to ____ for ______. if it can’t be analyzed w/in 2 hrs you _______
micro
culture and gram stain
leave it at rm temp
Tube 3 of CSF goes to ____ for ______. if it can’t be analyzed w/in 2 hrs you _______
heme
Diif/cell count
put it in the fridge
Tube 4 of CSF goes to ____ for ______. if it can’t be analyzed w/in 2 hrs you _______
extra
serology/special tests
put in the fridge
Normal CSF looks
like water
CSF from a meningitis patient is
cloudy
CSF from a CVA patient is
bloody/yellow
CSF from a bad tap is
bloody but clear
How doe you distinguish CVA from a bad tap
RBC in 1 vs 3 (Bad tap)
Xanthochromia (CVA)
clot (CVA)
Meningitis has what CSF results
inc. WBC
inc. CSF protein
dec. CSF glucose
inc. CSF lactate
Viral meningitis has what CSF results
inc WBC
Inc. lymphs
CSF protein norm
CSF glucose norm
What cell type is found in CSF for a CVA pt.
Erythrophage
expected CSF results for a CVA
inc. WBC
Inc. macrophages and RBC
inc CSF protein (damage from blood brain barrier)
norm CSF glucose
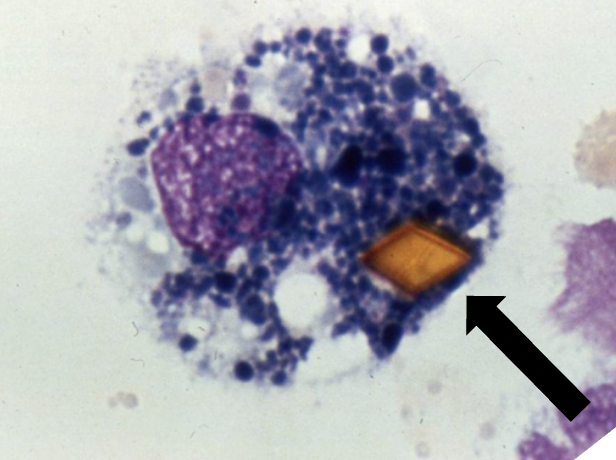
What two things are in this macrophage and when does this happens?
Hematoidin crystal and hemosiderin
CVA
What will happen if someone sees blasts in a CSF
Chemo to the (spinal) cord
what does it mean when lymphoblasts are seen in CSF
leukemia metastisized
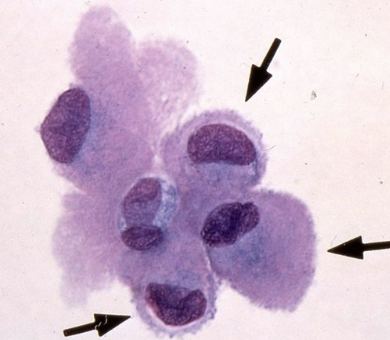
What do these cells indicate
inflammation of the pleural lining (mesothelial cells)
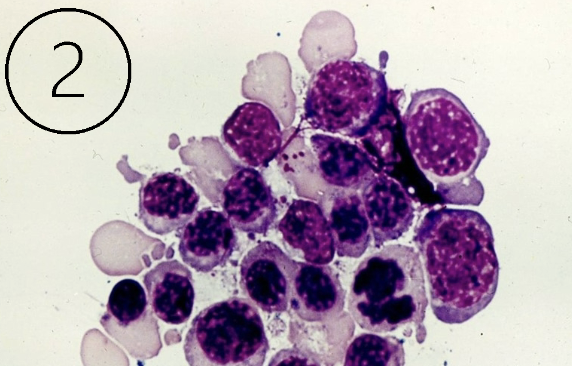
What do these cells indicate in a body fluid
Bone marrow contamination (b/c nucleated RBCs)
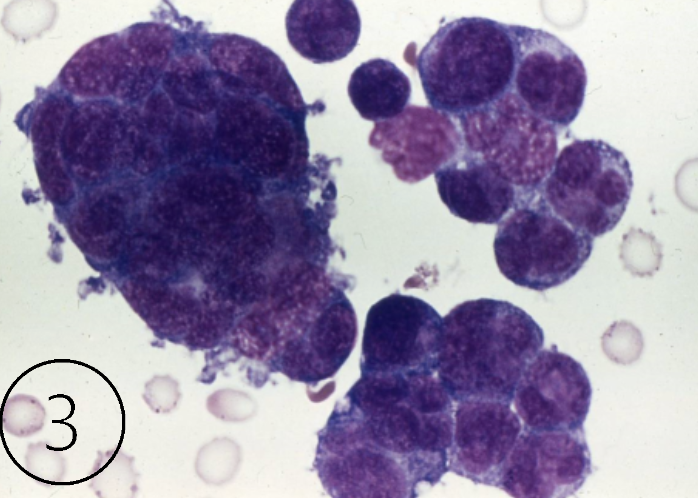
What do these cells indicate?
malignancy
When the ratio of CSF albumin to serum albumin is <9, indicates
normal CSF
When the ratio of CSF albumin to serum albumin is >9, indicates
damage to the BBB
the Presence of oligoclonal bands in CSF means
MS
MS has the presence of what protein in CSF
Myelin basic protein
Calculation of Ig index
[CSF IgG/serum IgG] / [CSF albumin/serum albumin]
hyperphosphorylated tau proteins in the CSF indicate
Alzheimers, parkinsons, or encephalopathy
Tau proteins are good for
stabilizing the internal structure of neurons
Effusion
build up of fluid btw 2 serous membranes
Transudate
Build up of fluid due to pooling btw membranes
Exudate
build up of fluid due to disruption of membranes
Chylous
milky fluid due to increased triglycerides
Pseudo-chylous
Milky fluid due to an increased cholesterol
Transudates are caused by:
CHF
chronic kidney failure
liver failure
transudates look like
clear yellow
cell count of pleural fluid is
<1000
Cell count of ascites and peritoneal is
<500
Transudates fluid:serum protein ratio is
<0.5
Transudates fluid:serum LD ratio
<0.6
Exudates are caused by
malignancy
trauma
infection
Exudates appear
yellow cloudy/bloody
Fluid:serum protein ratio of exudate is
>0.5
Fluid: serum LD ratio of exudates is
>0.6
The viscosity of synovial fluid is due to
hyaluronic acid
How do you pre treat synovial fluid
Hylauronidase
Mixing synovial fluid with acetic acid causes he fluid to
gell as it lyses RBC
What are the three M’s too look for in body fluids
macrophage
Mesothelial
Malignant cells
What are the five categories of joint disorders
Hemmorhagic, RBC
Septic, bacteria
crystal induced, urate/calciumphosphatedehydrogenase
Atoimmune related
degenerative disorders, decreased WBC
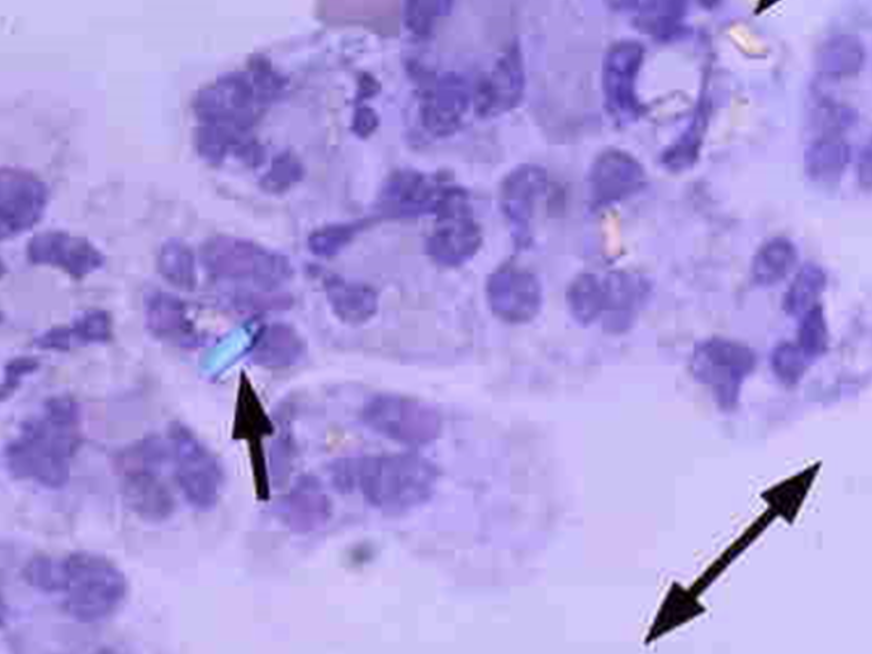
____ has ____ birefringence and is blue when parrallel; yellow when perpendicular
CPPD, +
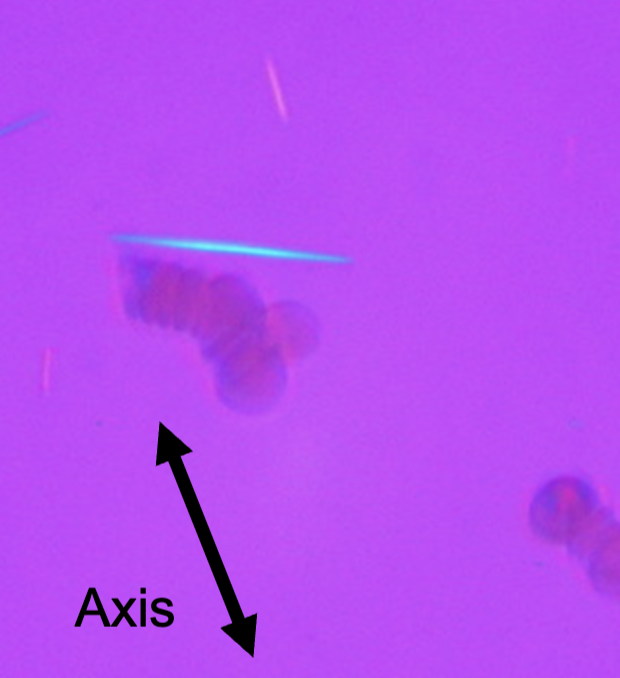
______ has ____ birefringence and is yellow when parallel; blue when perpendicular
Gout, -
Semen analysis should be done within
1 hrs
the first part of the ejaculate has
the most sperm
semen sample should be kept at
room temp
what are other tests you can do on semen
fructose and spermviability
preliminary info for sperm
volume
viscosity
ph
if liquefaction occurs with in 30-60 min
40x sperm
look for agglutination, round cells, motility
grading is different btw WHO 4th and 5th
sperm dilution on 20x
immobolize sperm in fomalin/phos to count
count 5 RBC squares
number counted is multiplied by 1 million, is the serm concentrated
multiply number x volume in ml to get absolute count
how long is a sperm count needed post vas
2 months post vas and isnt called clear until 2 months in a row
to be sure no sperm are present what do you do to the specimen
centrifuge
Amniotic fluid must be
kept from light
Amniotic appears
colorless and hazy
What conditions are tested for in amniotic fluid
open neural tube defects
hemolytic disease
fetal lung maturity
Nueral tube defects are indicated by what in amniotic fluid and maternal serum
AFP
How do you monitor hemolytic disease of a fetus
OD 450 Scan
liley graph (23wks on)
Queenan graph for early pregnancy
What are indicators of fetal lung maturity
Lecithin to sphingomyelin >2.5
Phosphatidyl glycerol in amniotic fluid
Lamellar body count >50
Fetal fibronectin can signal
pre-term labor
APT test hemolysate mixed with NaOH adult hgb _____/ fetal hgb ______
denatures
remains pink
What is a ROM test
to see if fluid is amniotic or not
Fern test
bedside test to see if fluid is vaginal or amniotic
Maternal serum quad scree screens for birth deects by looking for
high AFP (neural tube defects)
Low estriol (downs)
High DIA (downs and edwards)
High HCG (in downs and multiple babies)
Sweat chloride is used to diagnose
CF
High levels of chloride in sweat obtained by
pilocarpine iontophoresis
Steatorrhea means
fatty feces
Fecal fat measurement done to assess pancreatic enzyme deficiency where patient is unable to break down fats; condition is called
pancreatic insufficiency
Eosinophils in the urine detect
drug induced interstitial nephritis