MidTerm Econ Macro
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Which of the following is a topic studied in macroeconomics?
A. The impact of higher prices for gasoline on the number of SUVs people buy
B. The impact of labor unions on wages
C. The pricing decisions in the computer hardware industry
D. The effect on economic growth if the government raises taxes
E. How the wheat industry determines how much wheat to grow
D. The effect on economic growth if the government raises taxes
When all other influences on work plans remain the same, the
A. lower the real wage rate, the smaller the quantity of labor demanded.
B. lower the real wage rate, the greater the quantity of labor supplied.
C. lower the real wage rate, the smaller the quantity of labor supplied.
D. lower the real wage rate, the larger the labor force participation.
E. higher the real wage rate, the greater the quantity of labor demanded.
C. lower the real wage rate, the smaller the quantity of labor supplied.
Suppose the market basket of consumer goods and services costs $180 using the base period prices, and the same basket of goods and services costs $300 using the current period prices. The CPI for the current year period equals
A. 66.7.
B. 160.0.
C. 60.0.
D. 300.0.
E. 166.7
E. 166.7
To find the market demand curve for in line skates, we must−
A. take account of the skate buying plans of all actual and potential buyers in all possible situations.
B. add the quantities demanded at every price and every income by every buyer of in line skates.
C. sum horizontally the individual demand curves of all the buyers.
D. add the quantities demanded at prices that all buyers can afford to pay.
E. None of the above answers is correct because we need also to take account of the supply of in line skates
C. sum horizontally the individual demand curves of all the buyers.
Which factor of production does human capital enhance?
i. land
ii. labor
iii. capital
A. i only.
B. ii only.
C. iii only.
D. i and ii.
E. i, ii, and iii.
B. ii only.
Capital, as a factor of production, refers to
A. the production technology used by firms.
B. the production factors imported from abroad.
C. money, stocks, and bonds.
D. the physical goods used to produce other goods and services.
E. stocks, and bonds but not money
D. the physical goods used to produce other goods and services.
Which of the following is an example of the unfairness of rent ceilings?
A. Newcomers have a more difficult time finding apartments.
B. Voluntary exchange is encouraged by rent ceilings.
C. Too many people rent apartments.
D. Rich people do not get apartments in these markets.
E. Racial discrimination in renting is discouraged by rent ceilings.
A. Newcomers have a more difficult time finding apartments.
When production efficiency does NOT occur,
i. an economy is producing at a point within its PPF.
ii. there are unemployed resources.
iii. allocative efficiency can not occur.
A. i and iii
B. iii only
C. i only
D. i, ii, and iii
E. i and ii
D. i, ii, and iii
When a nation imports a good, its ________ surplus decreases and its ________ surplus increases.
A. consumer; consumer
B. producer; producer
C. total; consumer
D. consumer; producer
E. producer; total
E. producer; total
The point that each glass of lemonade consumed on a hot day brings lower and lower levels of satisfaction is known as the principle of
A. increasing opportunity cost.
B. increasing marginal cost.
C. decreasing marginal benefit.
D. decreasing marginal price.
E. total benefits
C. decreasing marginal benefit.
In a housing market with a rent ceiling set below the equilibrium rent, as time passes the supply of apartments
A. does not change.
B. decreases.
C. increases.
D. increases while the demand for apartments decreases.
E. becomes fixed by the government
B. decreases.
New York City, which has had a rent ceiling law for more than seventy years, has many abandoned apartment buildings throughout the city. Which of the following explains this?
A. Few workers with jobs in the city want to live there because of pollution.
B. Once any building gets so old, it is abandoned.
C. Landlords have no incentive to finance maintenance and remodeling of apartment buildings.
D. Rent ceilings make the construction of new buildings so profitable that old buildings are simply abandoned.
E. No building permits for new apartment buildings have been issued for over seventy years.
C. Landlords have no incentive to finance maintenance and remodeling of apartment buildings.
Scarcity
A. leads to higher prices.
B. is not something that affects very rich people.
C. is the inability to satisfy all our wants.
D. applies only to people living in poverty.
E. used to exist everywhere but has been eliminated in advanced economies.
C. is the inability to satisfy all our wants.
Scarcity means that
A. what we can produce with our resources is greater than our material wants.
B. governments must make up for shortages in resources.
C. resources are unlimited.
D. choices made in self interest cannot be the same as those made in the social interest.−
E. wants are greater than what we can produce with our resources.
E. wants are greater than what we can produce with our resources.
In recent years, which of the following has been negative?
A. government expenditure on goods and services
B. investment
C. net exports of goods and services
D. wages
E. consumption expenditure
C. net exports of goods and services
Suppose that the government imposes a price ceiling on gasoline that is below the equilibrium price. The black market for gasoline is ________ market in which the price ________ ceiling price.
A. an illegal; is less than the
B. a legal; exceeds the
C. an illegal; equals
D. a legal; is less than the
E. an illegal; exceeds the
E. an illegal; exceeds the
Market demand curves are obtained by
A. averaging the quantities every consumer is willing to buy at each different price.
B. observing the prices and quantities sold in a market over time and plotting those price quantity combinations in a graph.−
C. summing the quantities every consumer is willing to buy at each different price.
D. determining the price each consumer is willing to pay for the good and summing those prices across all consumers.
E. observing the behavior of an individual consumer in a market
C. summing the quantities every consumer is willing to buy at each different price.
Allocative efficiency is achieved when the production is such that
A. the marginal benefit exceeds the marginal cost by as much as possible.
B. marginal cost equals zero.
C. marginal benefit is equal to marginal cost.
D. the production point is on the PPF.
E. None of the above is true.
C. marginal benefit is equal to marginal cost.
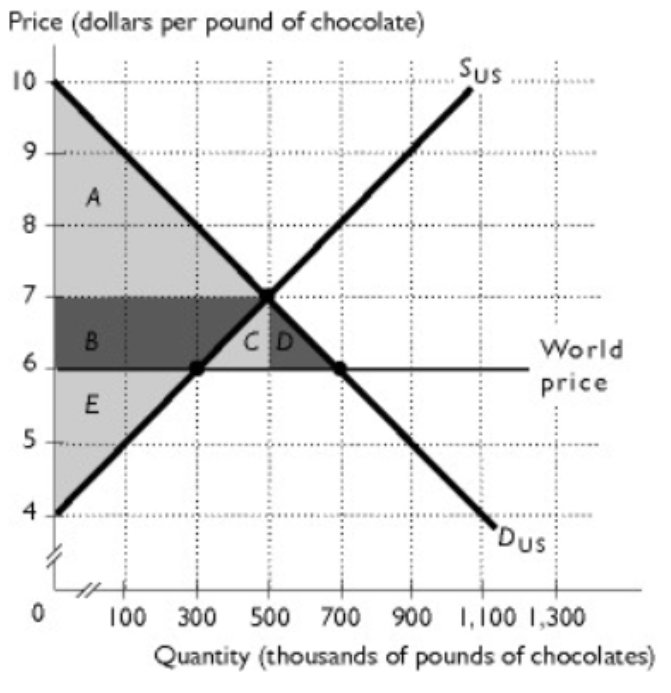
The figure shows the U.S. market for chocolate. With
international trade, ________ is the transfer of surplus from producers to consumers.
A. area E
B. area A
C. area B +area C + area D
D. area B
E. area C + area D
D. area B
Because human wants are insatiable and unlimited while available resources are limited, people are said to face the problem of
A. microeconomics.
B. scarcity.
C. macroeconomics.
D. why to produce.
E. social interest versus self interest
B. scarcity.
The concept of human capital describes
A. the number of workers per operating machine.
B. human skills, that is, the quality of labor.
C. human population, that is, the quantity of labor.
D. the number of machines (capital) that have been produced by people (humans).
E. the number of machines per employed worker.
B. human skills, that is, the quality of labor.
Involuntary part time workers are not working more hours due to−
A. an increase in the labor force.
B. family reasons.
C. a lack of training and skills.
D. educational commitments.
E. economic reasons.
E. economic reasons.
In order to efficiently allocate goods and services, we have to compare
A. marginal benefit to price.
B. price to marginal cost.
C. total cost to price.
D. total cost to marginal benefit.
E. marginal cost to marginal benefit.
E. marginal cost to marginal benefit.
To achieve allocative efficiency, one must compare the
A. marginal benefit of a good to its marginal cost.
B. opportunity cost to the attainable point on the production possibilities frontier.
C. point of production efficiency to the point of allocative efficiency.
D. marginal cost to the production efficiency cost.
E. marginal cost of a good to its opportunity cost
A. marginal benefit of a good to its marginal cost.
If a country had a CPI of 105.0 last year and a CPI of 102.0 this year, then
A. the quantity of consumer goods and services produced decreased between last year and this year.
B. the average quality of goods and services decreased between last year and this year.
C. there was an error when calculating the CPI this year.
D. the average prices of goods and services increased between last year and this year.
E. the average prices of goods and services decreased between last year and this year.
E. the average prices of goods and services decreased between last year and this year.
Human capital can be increased through
A. investment in new machinery.
B. education, on the job training, and work experience.−
C. decreases in population.
D. increasing the nation's production of consumption .
E. investment in new technology.
B. education, on the job training, and work experience.−
When demand increases,
A. consumers buy more of the good only if its price rises.
B. consumers are willing to buy more at any price.
C. the demand curve shifts leftward.
D. consumers buy more of the good only if its price falls.
E. the price is lower at any level of quantity demanded.
B. consumers are willing to buy more at any price.
A rent ceiling creates a deadweight loss
A. if it is set below the equilibrium rent.
B. if it is set equal to the equilibrium rent.
C. if it set above the equilibrium rent.
D. if it decreases the taxes the government collects in the housing market.
E. never, because if it did create a deadweight loss, the government would not impose it.
A. if it is set below the equilibrium rent.
In 2009 in the United States, consumption expenditure was $9,996 billion, investment was $1,559 billion, government expenditures goods and services were $2,927 billion, and total exports were $1,492 billion. GDP equaled
A. $14, 415 billion.
B. $10,120 billion.
C. $12,641 billion.
D. $11,488 billion.
E. some amount, but there is not enough information given to calculate GDP
E. some amount, but there is not enough information given to calculate GDP
Which of the following is a macroeconomic topic?
i. China increases interest rates to slow its economic growth.
ii. Congress lowers tax rates to try and lower the unemployment rate.
iii. Nissan decides to produce more electric Leaf models and fewer Altima sedans.
A. i and iii
B. iii only
C. i, ii and iii
D. ii and iii
E. i and ii
E. i and ii
After a nation starts importing a good from overseas, the domestic price of the good
A. falls.
B. might change, but more information about what else the country imports is needed to determine if the price rises, falls, or does not change.
C. rises.
D. might change, but more information about what the country exports is needed to determine if the price rises, falls, or does not change.
E. stays the same
A. falls.
In general, the marginal benefit curve
A. has a negative slope.
B. is concave.
C. is horizontal.
D. is vertical.
E. has a positive slope.
A. has a negative slope.
If consumption was 70 percent of GDP and both investment and government expenditure were 18 percent each, then we see that
A. exports must be less than imports.
B. GDP can be over 100 percent because it is "gross" rather than "net."
C. exports must be more than imports.
D. the error is due to rounding.
E. we must subtract depreciation from investment so that the components of GDP do not exceed 100 percent.
A. exports must be less than imports.
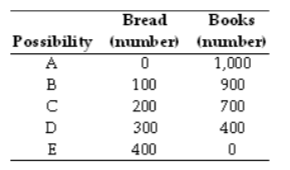
The table above shows a production possibilities frontier for an economy. Which of the following combinations is unattainable?
A. 0 loaves of bread and 0 books
B. 200 loaves of bread and 800 books
C. 0 loaves of bread and 800 books
D. 100 loaves of bread and 800 books
E. 300 loaves of bread and 200 books
B. 200 loaves of bread and 800 books
Holding all other influences constant, the quantity of labor supplied in a given time period depends
A. inversely on the real wage rate so that a higher real wage decreases the quantity of labor supplied.
B. directly on the quantity of labor demanded.
C. inversely on the quantity of labor demanded.
D. on the money wage rate not the real wage rate.
E. directly on the real wage rate so that a higher real wage increases the quantity of labor supplied
E. directly on the real wage rate so that a higher real wage increases the quantity of labor supplied
Jan is attending college and studying to be an investment broker. To improve her chances of employment following college, she has interned at a top brokerage firm during the last two summers. Jan's internship has increased her
A. consumption services.
B. entrepreneurship capital.
C. human capital.
D. natural labor.
E. natural resources
C. human capital.
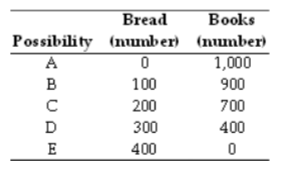
The table above shows a production possibilities frontier for an economy. If the economy tried to produce a combination of 250 loaves of bread and 800 books,
A. there is full employment.
B. it cannot produce this combination because it lacks enough resources or technology.
C. the tradeoff between bread and books is inefficient.
D. there is some unemployment.
E. it is enjoying a free lunch.
B. it cannot produce this combination because it lacks enough resources or technology.
The principle of decreasing marginal benefit explains why the marginal benefit curve
A. is upward sloping.
B. is vertical.
C. has an infinite slope.
D. is horizontal.
E. is downward sloping
E. is downward sloping
As the real wage rate rises, the opportunity cost of
A. leisure rises.
B. saving rises.
C. leisure falls.
D. working rises.
E. buying goods and services rises
A. leisure rises.
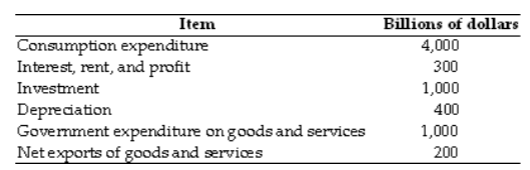
The table gives data for a nation. What is the amount of the country's GDP?
A. $6,000 billion
B. $6,900 billion
C. $6,600 billion
D. $6,200 billion
E. $5,800 billion
D. $6,200 billion
When a nation imports a good or service, the nation's consumer surplus ________, its producer surplus ________, and its total surplus ________.
A. decreases; decreases; decreases
B. increases; increases; increases
C. decreases; decreases; increases
D. increases; decreases; increases
E. increases; decreases; decreases
D. increases; decreases; increases
When a nation starts importing a good or service, domestic employment in that industry
A. increases.
B. might change, but more information about what the country exports is needed to determine if employment increases, decreases, or does not change.
C. decreases.
D. stays the same.
E. might change, but more information about what else the country imports is needed to determine if employment increases, decreases, or does not change
C. decreases.
Scarcity requires that we
A. make choices about what goods and services to produce.
B. learn to limit our wants.
C. have unlimited resources.
D. produce efficiently.
E. have the most rapid economic growth possible.
A. make choices about what goods and services to produce.
If a rent ceiling is imposed that is less than the equilibrium rent, which of the following outcomes is most likely to occur?
A. a building boom
B. reduced search activity
C. a housing surplus
D. black market activity
E. None of the above answers is correct because to have an impact the rent ceiling must be above the equilibrium rent
D. black market activity
Human capital ________ as you work. As a result, the ___________ of goods and services ________.
A. decreases; quantity; decreases.
B. does not change; quality; does not change.
C. improves; quality; does not change.
D. increases; quantity; increases.
E. declines; quality; increases
D. increases; quantity; increases.
Car insurance and cars are complements. If the price of car insurance increases, the
A. demand for cars increases.
B. quantity of cars demanded increases.
C. demand for cars decreases.
D. quantity of cars demanded decreases.
E. More information is needed to determine if the demand increases or decreases
C. demand for cars decreases.
When Jamie purchases a classic 1968 Plymouth Cuda convertible from Shane, GDP
A. does not change, because the car was not produced this year.
B. increases, because the car is a durable good and increases investment.
C. increases, because the car is a durable good and increases consumption.
D. does not change, because Jamie did not buy the car from a dealership.
E. increases, because this expenditure decreases saving
A. does not change, because the car was not produced this year.
The United States possesses a large amount of human capital. As a result of this fact, in the United States there is a
A. large number of kind and generous humans.
B. large number of people and a great deal of land.
C. large amount of machinery (capital) that is run by people (humans).
D. highly skilled and educated labor force.
E. large amount of machinery and equipment
D. highly skilled and educated labor force.
Production efficiency is represented by ________ a production possibilities frontier.
A. all points outside
B. a movement along
C. all points on
D. all points inside
E. only one point on
C. all points on
The marginal benefit of the first hotdog consumed is ________ the marginal benefit of the fifth hotdog consumed.
A. less than
B. greater than
C. equal to
D. equal to 5 times
E. the inverse of
B. greater than
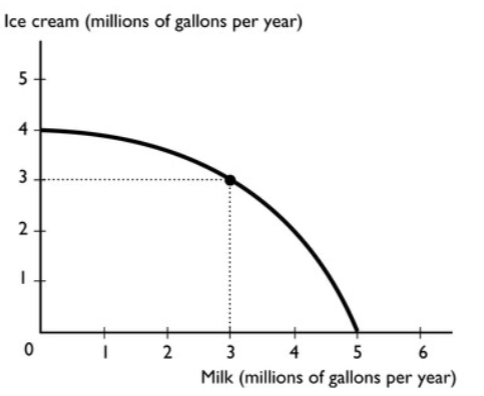
The figure above shows the production possibilities frontier for a country. A combination of 3 million gallons of milk and 3 million gallons of ice cream is
A. attainable and production inefficient.
B. unattainable.
C. attainable and production efficient.
D. unattainable and production efficient.
E. More information is needed to determine if the point is attainable or not
C. attainable and production efficient.
The phrase "a change in demand" refers to a
A. movement along the quantity curve.
B. movement along a demand curve.
C. change in the quantity demanded of a good.
D. movement along the price curve.
E. shift of the demand curve
E. shift of the demand curve
Which of the following is true regarding the measurement of GDP?
A. Wages and consumption are used in the expenditure approach to GDP.
B. Investment and wages are expenditures , and are therefore are used in the expenditure approach to GDP.
C. Wages and profit income are used in the income approach to GDP.
D. Government expenditure is only counted in the income approach to GDP.
E. Consumption and investment are used in the income approach to GDP
C. Wages and profit income are used in the income approach to GDP.
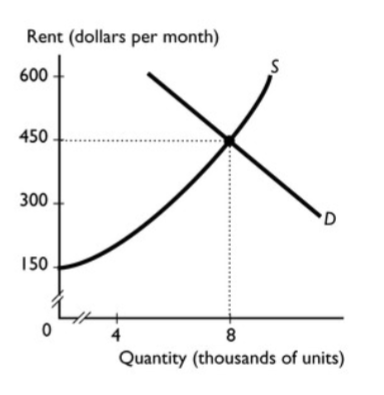
The graph shows the market for rental housing in Little Rock. The market for apartments is efficient when ________.
A. there is no rent ceiling
B. the quantity of apartments demanded is 12,000 a month
C. the quantity of apartments supplied is 6,000 a month
D. the rent charged is less than $450
E. the rent ceiling is set at $300 a month
A. there is no rent ceiling
In a country with a working age population of 200 million, 140 million people are employed and 20 million are unemployed. The size of the labor force is
A. 120 million.
B. 20 million.
C. 200 million.
D. 160 million.
E. 140 million
D. 160 million.
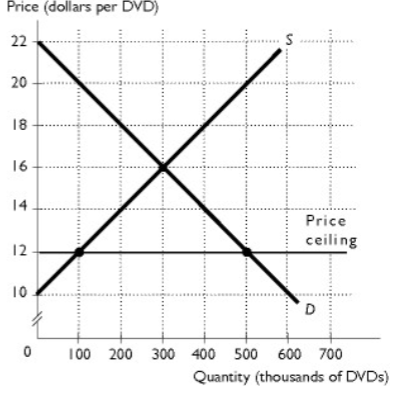
The figure shows the market for DVDs. The government decides that all citizens deserve to watch affordable DVDs so a price ceiling of $12 per DVD is placed on DVDs. After this price ceiling is in effect, producer surplus equals ________.
A. $400,000
B. $200,000
C. $900,000
D. $1,800,000
E. $100,000
E. $100,000
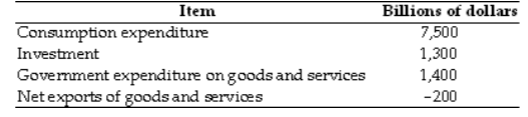
Based on the data in the table above, what does GDP equal?
A. $10,400 billion
B. $10,000 billion
C. $9,800 billion
D. $8,900 billion
E. $10,200 billion
B. $10,000 billion
The market demand curve for mousetraps is
A. found by summing the quantities of mousetraps demanded at each income level by each buyer.
B. found by summing the prices of mousetraps at each quantity of mousetraps demanded by each buyer.
C. the horizontal sum of the individual demand curves for mousetraps of all the buyers.
D. Both answers B and C are correct.
E. Both answers A and C are correct.
C. the horizontal sum of the individual demand curves for mousetraps of all the buyers.
The quantity of labor supplied increases as the real wage rises because
A. the opportunity cost of leisure rises.
B. the opportunity cost of working increases.
C. higher real wages mean that nominal wages have increased.
D. labor force participation decreases so that only serious workers are left in the labor force.
E. the quantity of labor demanded increases.
A. the opportunity cost of leisure rises.
Scarcity exists because
A. the costs of production are high.
B. some people make bad economic decisions.
C. human wants exceed the resources available to satisfy them.
D. people take too much leisure time.
E. some individuals have low income
C. human wants exceed the resources available to satisfy them.
Suppose Jennifer derives $100 in marginal benefits from her first skiing trip and $80 from her third trip. Her marginal benefit from her second trip is likely to be
A. between $79 and $51.
B. between $100 and $80.
C. more than $100.
D. less than $51.
E. some amount that cannot be calculated without additional information
B. between $100 and $80.
Spending on financial assets ________ counted as part of GDP ________.
A. are not; because their purchase is not spending on goods or services
B. may be; as long as their value increases
C. are not; because interest must be paid on them
D. are; because the cash exchanged represents an expenditure
E. are; as long as their purchase produces income
A. are not; because their purchase is not spending on goods or services
The quantity of labor demanded definitely increases if the
A. nominal wage rate falls.
B. real wage rate falls.
C. real wage rate rises.
D. nominal wage rate rises.
E. supply of labor decreases.
B. real wage rate falls.
When a nation imports a good, its ________ surplus decreases and its ________ surplus increases.
A. consumer; consumer
B. producer; consumer
C. producer; producer
D. total; consumer
E. consumer; producer
B. producer; consumer
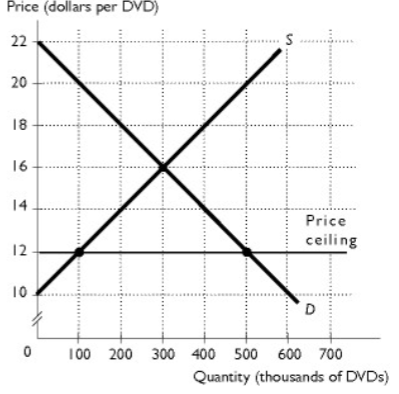
The figure shows the market for DVDs. The government decides that all citizens deserve to watch affordable DVDs so a price ceiling of $12 per DVD is placed on DVDs. After this price ceiling is in effect, deadweight loss equals ________.
A. $1,800,000
B. $800,000
C. $400,000
D. $200,000
E. $1,600,000
B. $800,000
When you make the decision to spend your time attending class, which economic question are you answering?
A. Why?
B. How?
C. What?
D. Social interest
E. For whom?
C. What?
If a price ceiling is introduced in the market for milk below the market equilibrium price, then the producer surplus made by dairy farmers ________.
A. will decrease
B. will not change
C. will increase
D. might increase or decrease depending on whether the demand for milk increases or decreases
E. might increase or decrease depending on whether the supply of milk decreases or increases
A. will decrease
Capital is a factor of production. Which of the following is an example of capital?
i. $1,000 in money
ii. 100 shares of Microsoft stock
iii. $10,000 in bonds issued by General Motors
iv. A drill press in your local machine shop
A. ii and iii.
B. iv only.
C. ii only.
D. i and ii.
E. iii only.
B. iv only.
A change in the demand for apples could result from any of the following EXCEPT
A. a change in income.
B. increased preferences for fresh fruit consumption for health reasons.
C. a change in the number of buyers.
D. a change in the price of an apple.
E. a change in the price of a banana
D. a change in the price of an apple.
Which of the following is a macroeconomic issue?
A. The National Football League signs a new television contract.
B. Utilities are required to install more anti pollution devices.−
C. The Iowa corn harvest is smaller than normal.
D. The number of jobs and production in Zimbabwe increase.
E. The price of a ticket to Walt Disney World in Orlando is increasedI
D. The number of jobs and production in Zimbabwe increase.
Involuntary part time workers are workers who−
A. work less than 35 hours by choice.
B. work less than 35 hours but would like to work full time.
C. work have lost their jobs within the last four weeks and are seeking another job.
D. have withdrawn from the labor market.
E. work more than 35 hours but would like to work less than 35 hours
B. work less than 35 hours but would like to work full time.
In measuring the unemployment rate, part time workers are ________ and discouraged workers are ________.−
A. excluded; excluded
B. included as employed; included as unemployed
C. included as unemployed if they are involuntary part time workers; excluded−
D. excluded; included as unemployed
E. included as employed; excluded
E. included as employed; excluded
The supply of labor curve has a ________ slope because as the real wage rate rises, ________.
A. negative; households work more hours
B. negative; firms hire fewer workers
C. positive; firms offer more jobs
D. positive; the opportunity cost of leisure falls
E. positive; the opportunity cost of leisure rises
E. positive; the opportunity cost of leisure rises
When a nation exports a good or service in which it has a comparative advantage, employment in that industry
A. increases.
B. decreases.
C. stays the same.
D. might change, but more information about what else the country exports is needed to determine if employment increases, decreases, or does not change.
E. might change, but more information about what the country imports is needed to determine if employment increases, decreases, or does not change
A. increases.
The purchase of 500 shares of Honda stock by the California State Employees' Pension fund
A. is counted as investment in the GDP accounts.
B. is counted as part of export expenditure in the GDP accounts because Honda is a foreign firm.
C. is counted as consumption expenditure.
D. is not counted as part of GDP.
E. Is counted as part of import expenditure in the GDP accounts because Honda is a foreign firm.
D. is not counted as part of GDP.
The period for which the Consumer Price Index is defined to equal 100 is called the
A. beginning period.
B. base period.
C. starting point.
D. zero period.
E. reference base period
E. reference base period
In the United States, the inflation rate since 1999 generally was
A. much higher than between 1985 to 1995.
B. higher than in the 1980s.
C. lower than between 1979 to 1981.
D. negative.
E. higher than between 1979 to 1981
C. lower than between 1979 to 1981.
The total value of capital in the United States is around
A. $60 trillion.
B. $79 trillion.
C. $10 trillion.
D. $145 trillion.
E. $100 trillion
A. $60 trillion.
The labor force participation rate
A. is one of the major reasons that firms pay efficiency wages.
B. decreases as the real wage increases.
C. increases as the real wage increases.
D. increases as the opportunity cost of working increases.
E. has nothing to do with the real wage rate
C. increases as the real wage increases.
If an economy cannot produce more of one good without producing less of another good, this implies that which of the following has been achieved?
A. PPF efficiency
B. minimum marginal cost
C. allocative efficiency
D. production efficiency
E. maximum marginal benefit
D. production efficiency
Two brands of water, Natural Water and Mountain Water, are close substitutes. If the price of Mountain Water decreases, the fall in price
A. shifts the demand curve for Natural Water leftward.
B. shifts the demand curve for Natural Water rightward.
C. increases the demand for Mountain Water.
D. increases the price of Natural Water.
E. More information is needed to determine if the demand curve for Natural Water shifts
rightward or leftward
A. shifts the demand curve for Natural Water leftward.
Since 1305, the inflation rate has been greater than 2 percent per year and reaching its highest peaks
A. primarily between 1700 and 1900.
B. primarily between 1500 and 1700.
C. primarily after 1900.
D. primarily between 1400 and 1500.
E. primarily before 1400
C. primarily after 1900.
There are five hundred buyers in the market for cheese. If we know each individual's demand curves, to find the market demand, we must
A. average the price each buyer is willing to pay for each given quantity.
B. add the prices that each buyer will pay at every quantity.
C. add the quantities that each buyer will purchase at every price.
D. multiply the price times quantity for each buyer and then add the resulting products together.
E. give up because there is no way to find the market demand
C. add the quantities that each buyer will purchase at every price.
The unemployment rate at full employment is
A. the natural unemployment rate.
B. equal the amount of unemployment caused by job search.
C. undefined because the economy is never at full employment.
D. zero.
E. equal to the rationed rate of unemployment
A. the natural unemployment rate.
The production function graphs the relationship between
A. real GDP and capital.
B. real GDP and the quantity of labor employed.
C. real GDP and the supply of labor.
D. nominal GDP and real GDP.
E. nominal GDP and the quantity of labor employed
B. real GDP and the quantity of labor employed.
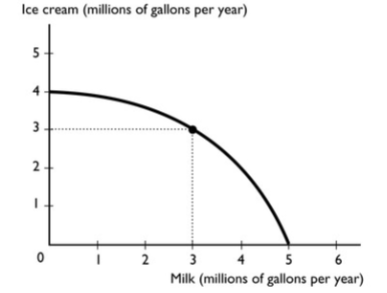
The figure above shows the production possibilities frontier for a country. A combination of 4 million gallons of milk and 4 million gallons of ice cream is
A. attainable and production inefficient.
B. attainable and production efficient.
C. unattainable.
D. unattainable and production efficient.
E. More information is needed to determine if the point is attainable or not.
C. unattainable.
Allocative efficiency is achieved when the marginal benefit of a good
A. is less than its marginal cost.
B. exceeds the marginal cost by as much as possible.
C. exceeds the marginal cost regardless of how much the difference is.
D. is equal to its marginal cost.
E. equals zero
D. is equal to its marginal cost.
When a nation exports a good, its consumer surplus ________, and its producer surplus ________.
A. increases; increases
B. increases; decreases
C. decreases; increases
D. decreases; decreases
E. does not change; increases
C. decreases; increases
Which of the following is a macroeconomic topic?
A. The effect of floods in agricultural areas on the price and quantity of wheat.
B. Why did production and jobs expand rapidly in 2017?
C. General Motors decides what prices to set for its new models.
D. The county government's decision to increase the sales tax for your county.
E. The federal government's decision to spend more on environmental protection
B. Why did production and jobs expand rapidly in 2017?
Suppose the CPI last year was 82.3 and this year is 90.9. Based on this information, we can calculate that the inflation rate in 1981 was
A. 82.3 percent.
B. 9.09 percent.
C. 90.9 percent.
D. 8.6 percent.
E. 10.4 percent
E. 10.4 percent
We allocate resources efficiently when
A. marginal benefit is greater than marginal cost by any amount.
B. total benefit is greater than total cost.
C. marginal cost is greater than marginal benefit.
D. marginal benefit is greater than marginal cost by as much as possible.
E. marginal benefit is equal to marginal cost.
E. marginal benefit is equal to marginal cost.
Which of the following is NOT directly related to human capital?
A. knowledge of computer programing
B. an understanding of real estate markets
C. a college education
D. a summer internship
E. an MRI machine
E. an MRI machine
Recently, the government made adjustments to how GDP is calculated that included placing software purchases into the category of
A. net exports of goods and services because most software is written abroad.
B. net operating surplus.
C. intermediate goods because software is not a final good.
D. inventory and now software purchases are not directly counted as part of GDP.
E. investment and now directly counts software purchases as part of GDP
E. investment and now directly counts software purchases as part of GDP
f a society moves from a period of time with significant unemployment to a time with full employment, its production possibilities frontier will
A. not shift because the society moves from one point on the frontier to a point outside the frontier.
B. shift rightward.
C. not shift because the society moves from one point on the frontier to a point inside the frontier.
D. shift leftward.
E. not shift because the society moves from a point inside the frontier to a point on the frontier
E. not shift because the society moves from a point inside the frontier to a point on the frontier
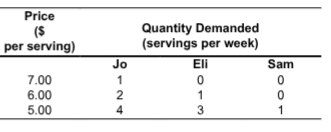
The following table shows the market for frozen yogurt and the
three people who make up the market. If the price is $6 per serving, __________ each week.
A. there will be a shortage of frozen yogurt
B. there will be a surplus of frozen yogurt
C. the market demand is 7 servings
D. the market supply is 3 servings
E. the market demand is 3 servings
E. the market demand is 3 servings
When a nation exports a good or service, employment in that industry
A. stays the same.
B. decreases.
C. increases.
D. might change, but more information about what else the country exports is needed to
determine if employment increases, decreases, or does not change.
E. might change, but more information about what the country imports is needed to determine if employment increases, decreases, or does not change
C. increases.
Production efficiency occurs
A. at only one point on the production possibilities frontier.
B. when the total cost of production is minimized.
C. at all points on the production possibilities frontier.
D. anywhere inside or on the production possibilities frontier.
E. at all points inside the production possibilities frontier
C. at all points on the production possibilities frontier.
When a nation exports a good or service in which it has a comparative advantage, production of the good or service
A. decreases.
B. stays the same.
C. increases.
D. might change, but more information about what the country imports is needed to determine if production increases, decreases, or does not change.
E. might change, but more information about what else the country exports is needed to
determine if production increases, decreases, or does not change.
C. increases.
Julie works part time for economic reasons. She would be considered−
A. a discouraged worker.
B. an involuntary part time worker.−
C. unemployed as calculated by the Bureau of Labor statistics.
D. not in the labor force.
E. a job seeker
B. an involuntary part time worker.−
If there is unemployment in an economy, then the
A. production possibilities frontier will shift outwards.
B. economy is producing at a point inside the production possibilities frontier.
C. economy is operating at an unattainable point.
D. production possibilities frontier must be bowed inward.
E. production possibilities frontier will shift inwards
B. economy is producing at a point inside the production possibilities frontier.