Lecture 1 -- Anatomy and Physiology of Birds
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
What classification kingdom do birds belong to?
Animalia
What is the phylum for birds?
Chordata
To which class do birds belong?
Aves

Which group of birds does the bird shown in the picture belong to? What are they also called? What are its features?
Passerines
= Songbrids/ Perching birds
Four toed, one pointing backwards
What are commonly kept songbirds?
Finches, canaries, and mynah birds.
What is the order for parrots?
Psittaciformes (Psittacines)
List three types of small parrots that are commonly kept
Budgies, lovebirds and cockatiels
List three types of big parrots that are commonly kept
African grey, Amazon and Cockatoo
Raptors are divided into three orders. What are these orders, and what birds are included in each?
Accipitriformes - Diurnal birds e.g. Hawks 鷹, Buzzards
Falconiformes - Diurnal birds e.g. Flacons
Strigiformes - Nocturnal birds e.g. Owls
What types of birds belong to the order Anseriformes?
Duck
Geese 鵝
Swans 天鵝
What types of birds belong to the order Galliformes?
Chicken
Turkey
Peacock
Quail 鵪鶉
What types of birds are classified as ratites? Why those birds are classified as ratites?
Ostrich + Rheas
They are flightless birds with no keel
What is the order for chickens and turkeys?
Galliformes.
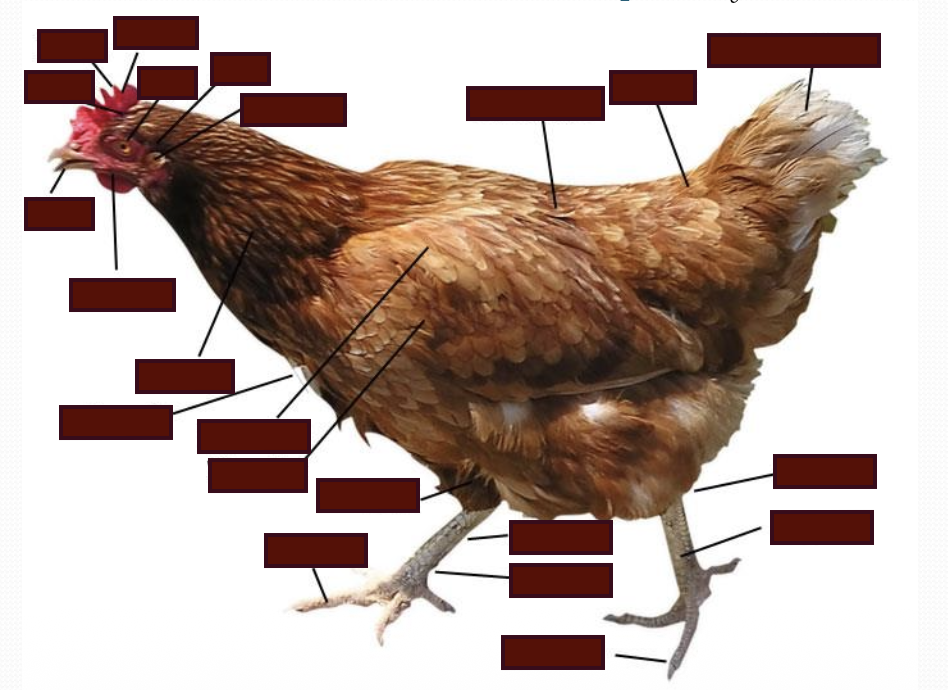
List the anatomy of the chicken
Ratites not being strictly a taxonomic term.
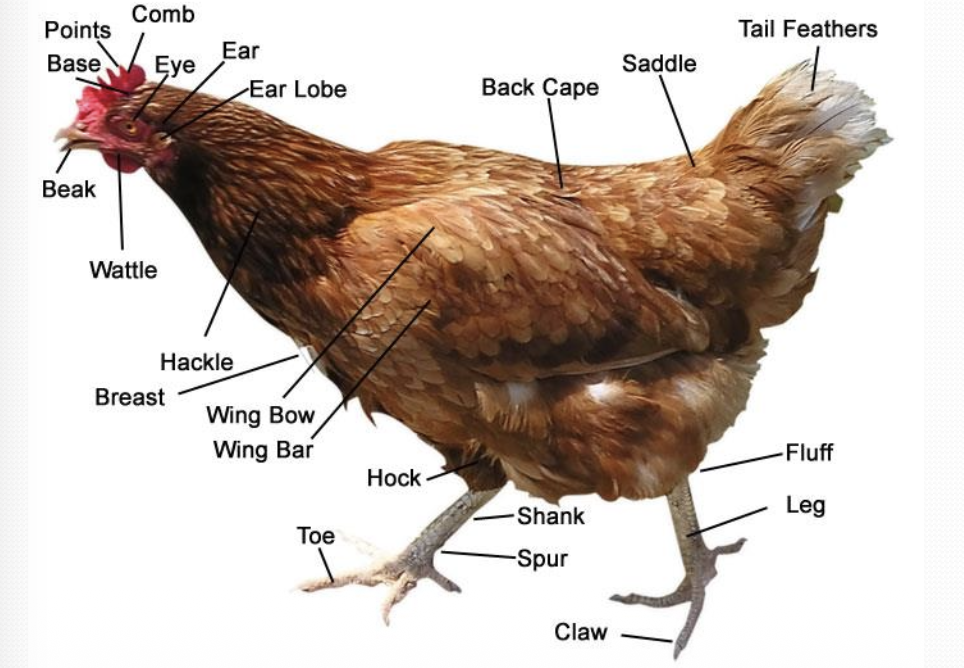
Try to list out all the features of bird’s eyes
Huge eyes (Up to > 50% cranial volume in some birds)
Have sclerotic rings to support the eye balls
Have ability recognise UV → Enhance vision for communication, behaviour and hunting
Rarely blink → Eyelids only closed when sleeping
Have third eyelid, which functions as blinking
No meibomian gland → Harderian and lacrimal gland are the main source of tear production
Thinner cornea + Softer lens → Allow more movement in the lens, which allow for visual activity
Thick and avascular retina
Have pecten (Out-folding of retinal surface)
What features of the eyes in birds are similar to those in mammals?
Have anterior and posterior chamber as in mammals
Which eye feature is absent in birds?
No meibomian gland (Harderian and Lacrimal gland)
What structures support the eyeball in the eye socket of a bird?
Sclerotic ring
What is the function of the third eyelid in birds? Why?
Blinking as they rarely blink (They only close their eyelids when sleeping)
What are the major differences in the cornea, lens, and retina between chickens and mammals?
Retina is thicker and avascular
Lens is softer (Allow more movement), Cornea is thinner
What are the adaptations found in the eyes of raptors (birds of prey)?
They have the ability to recognise UV/ polarised light → Important in communication, behaviour and hunting
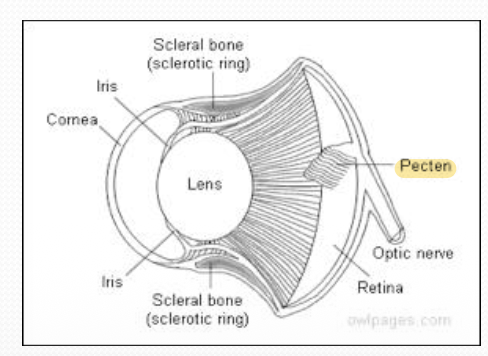
What is the pecten in the eyes of birds? What are its function?
Pecten is out-folding of the retinal surface
Rich blood supply
Function: 1. Retinal nourishment 2. Acts as a sunshade → Reduce light reaching the retina
What features of the ears in birds are similar to those in mammals?
Comprises outer, middle and inner ear
What feature of the ear in birds is absent in their outer ear?
No external pinna
If birds lack an external ear (pinna), what protects their outer ear, and what are the other functions of this protective feature?
Protected by auricular feathers
Act to funnel sound towards ear
Compared to mammals, are the glands present in birds increased or reduced?
Greatly reduced
No sweat glands, no sebaceous gland
What glands are present in birds but not in mammals? Where is it located? What is its function?
Uropygial gland (Preen gland)
Located at the dorsal surface of tail
Produces lipid rich secretion for feather waterproof and maintenance
What types of birds have a uropygial gland, and which species do not?
Largest in aquatic birds
Not present in ostrich, emu, some pigeons and some parrots
Compared to mammals, what are the special features of the integumentary system in birds?
Skin of most birds is thin and inelastic, especially in the strigiformes (owls)
Modified on limbs → Scales can be observed in their limbs
For bird species that do not have a uropygial gland, what adaptations do they have instead?
The birds who don’t have the uropygial gland have a slightly different type of feather (power down feather) → They produce a lot more dust on their feathers and that helps with the waterproofing and feather maintenance
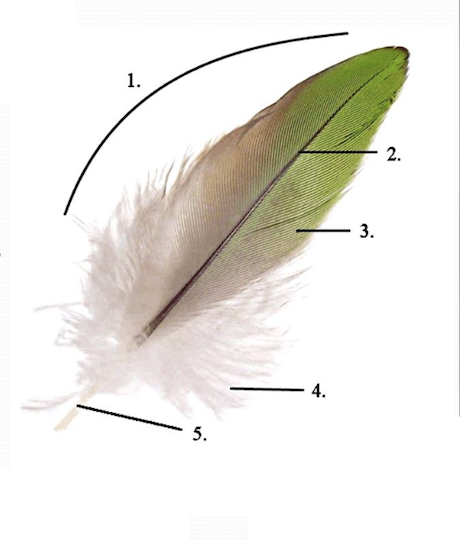

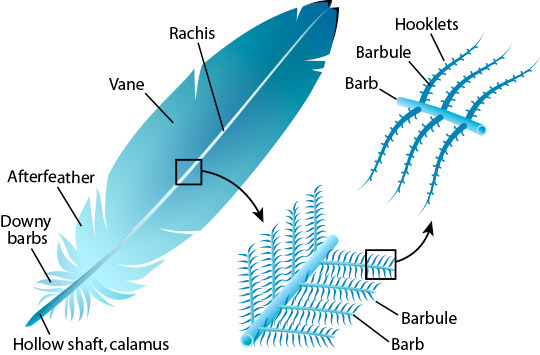
Name all the features of a feather.
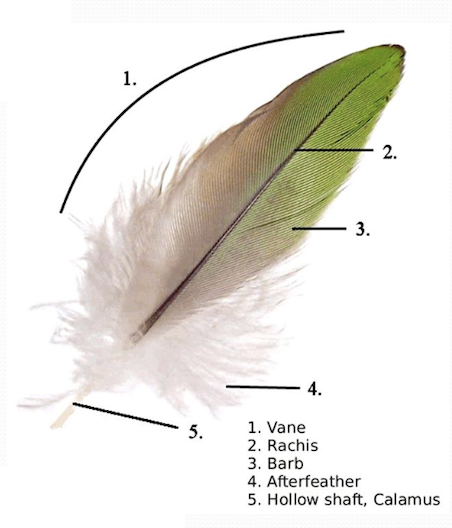

What are the features of rachis?
Contains capillaries during growth phase → Loses them and becomes hollow as feather matures
What are the features of calamus?
Hollow → Anchors feather into follicle
What are the features of vane?
Vane = Either side of central rachis
Consist of series of barbs with interlocking barbules
List the different types of feathers in birds, along with their location and features.
Contour feather (Outermost feathers) → Give colour and “contour” and protect from the elements
Semiplumes (Under contour feathers) → Loose structure that provide insulation
Down feathers → Very loose structure with no barbs that provide insulation
Power down feather → Specialised down feather where tips of barbules disintegrate during preening → Provide a waterproofing effect
What are the three types of contour feathers, and what are their functions?
Coverts - Small contour feathers of the wing
Remiges - Large contour “flight feather” of the wing
Retrices - Tail feathers
What types of birds tend to have powder down feathers?
Can mostly seen in birds with reduced or absent preen gland
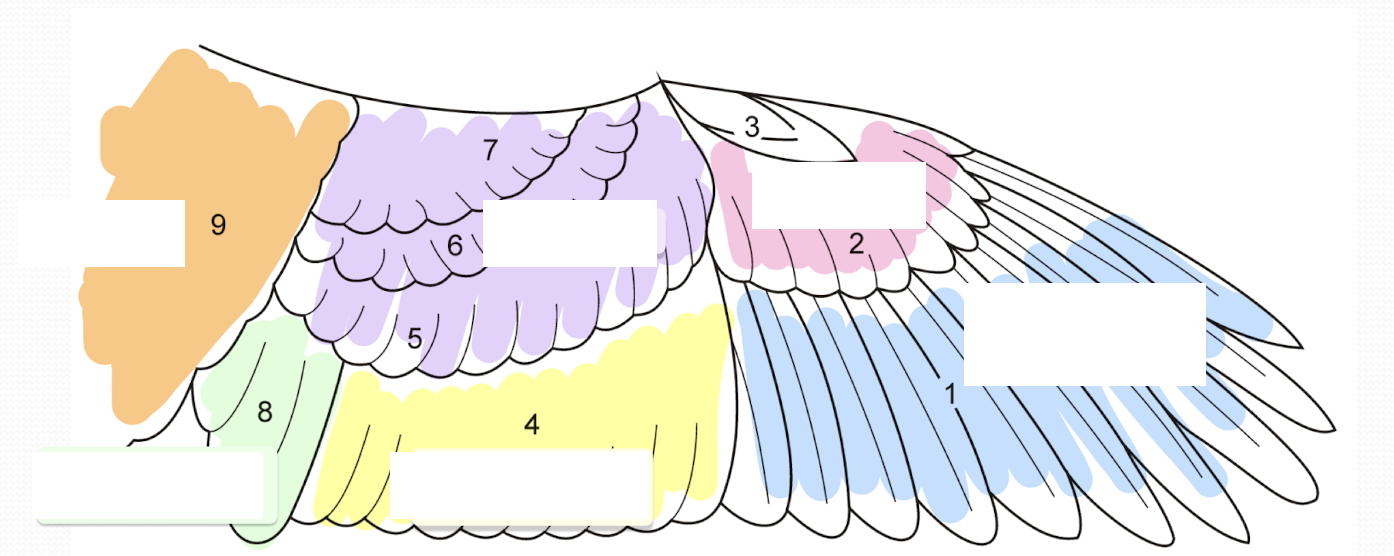
Name different regions of a wing feather
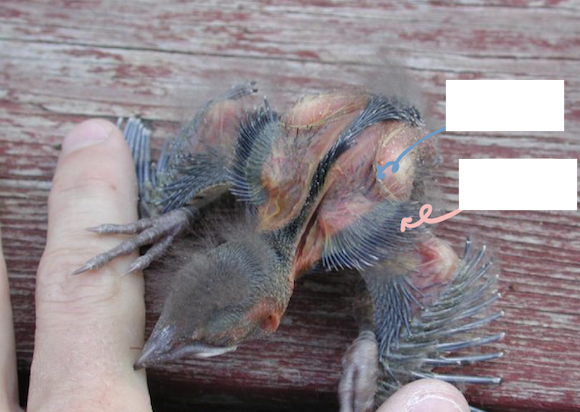
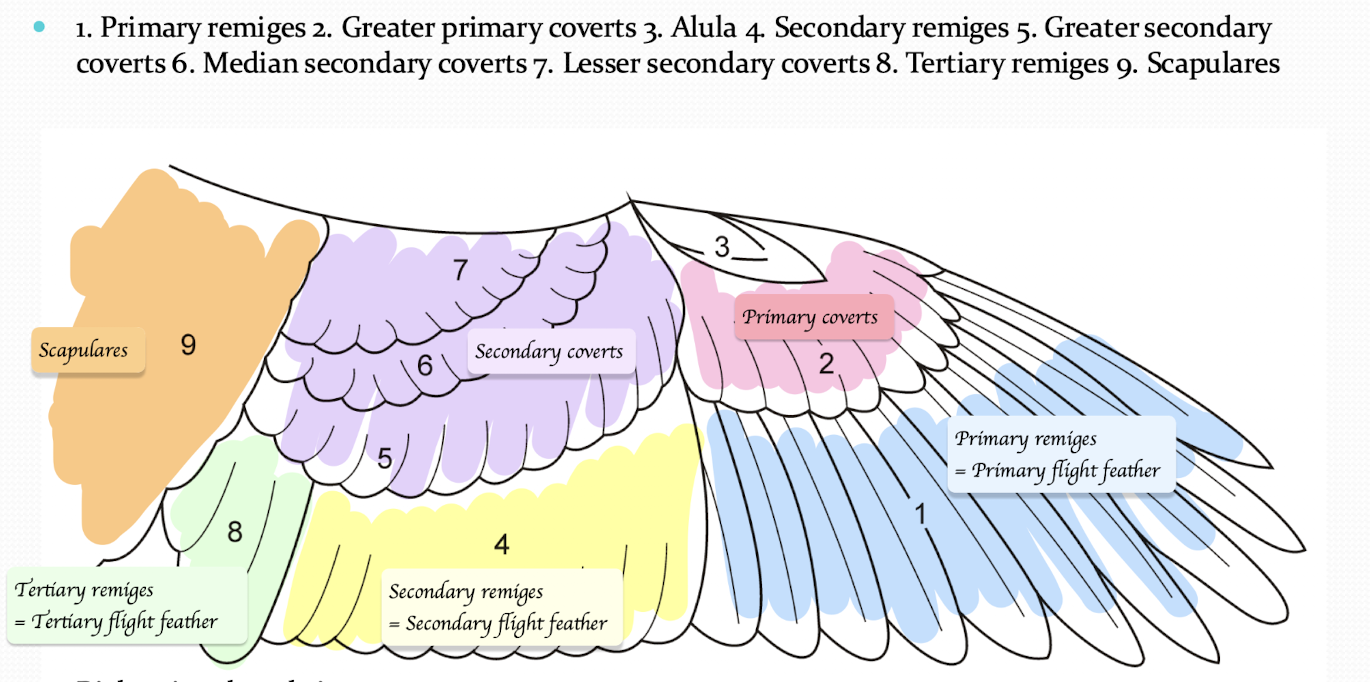

Name the areas in the below pictures
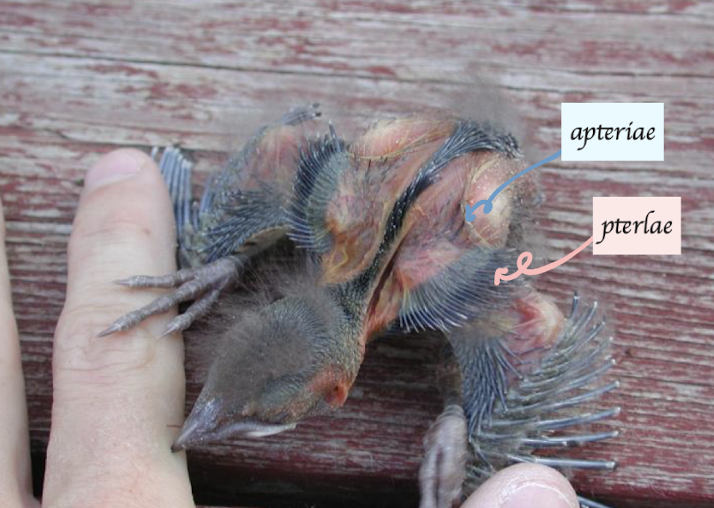

What are pterylae?
Feather follicles confined to well defined areas
What are apteriae?
Area that has no feather follicles
What are the characteristics of blood feathers?
Growing feathers with a huge blood supply and nerve supply
What happens if a blood feather is broken?
It bleeds and does not grow back until the next moult.
How frequent does birds moult?
Generally once a year (some species might be slightly different)
What factors affect moulting?
Season, temperature and nutrition factors
What is required for moulting in birds?
Increased energy intake
If feathers are damaged during handling, when will they grow back ?
Next moult because the shaft is still left in
If feathers are plucked when will they grow back?
Immediately
Why wing clipping is controversial?
Wing clipping affect bird’s behaviour, ability to fly and well-bing
What is the aim of wing clipping?
To reduce ability for vertical lift , not stop them flying completely
What are the different techniques of wing clipping?
Bilateral vs Unilateral
Primary vs Secondary feathers
All (Complete primary feathers) vs some (Part of the primary feathers)
What is the effect of unilateral wing clipping?
Imbalance → Crashes landing
What are the main functions of skeletal system provided in birds
Flight
Egg production
Respiration
How does the skeletal system support flight in birds?
By reducing weight
Fused bone e.g. Fused area of spine, fused pelvis, fused lumbar vertebrae and fused leg bones
Lightweight structure
Small skull relative to body size
No teeth (They’ve modified teeth into beak)
By providing attachment points for flight muscle
Keel
Coracoid → Stick up with the scapula → Stop the thorax being compressed by those strong wing muscle when they are flying = Prevent chest compression
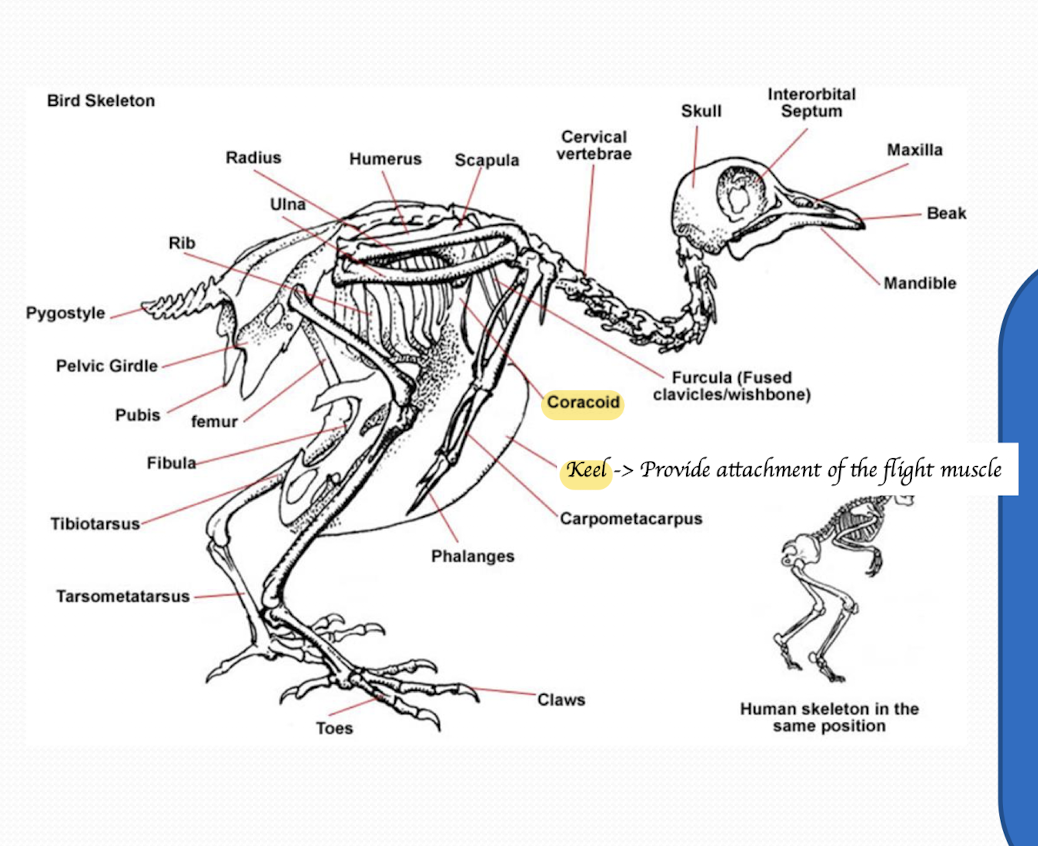
How does the skeletal system support respiration in birds?
Some of the bones are hollow and house extensions of the air sacs
How does the skeletal system support egg production in birds?
Medullary bone provides a source of stored calcium during times of peak egg production
What is unique about the bird skull?
No teeth
Sclerotic rings supporting globes
→ Help them to reduce the thickness and the weight of bone in the skull
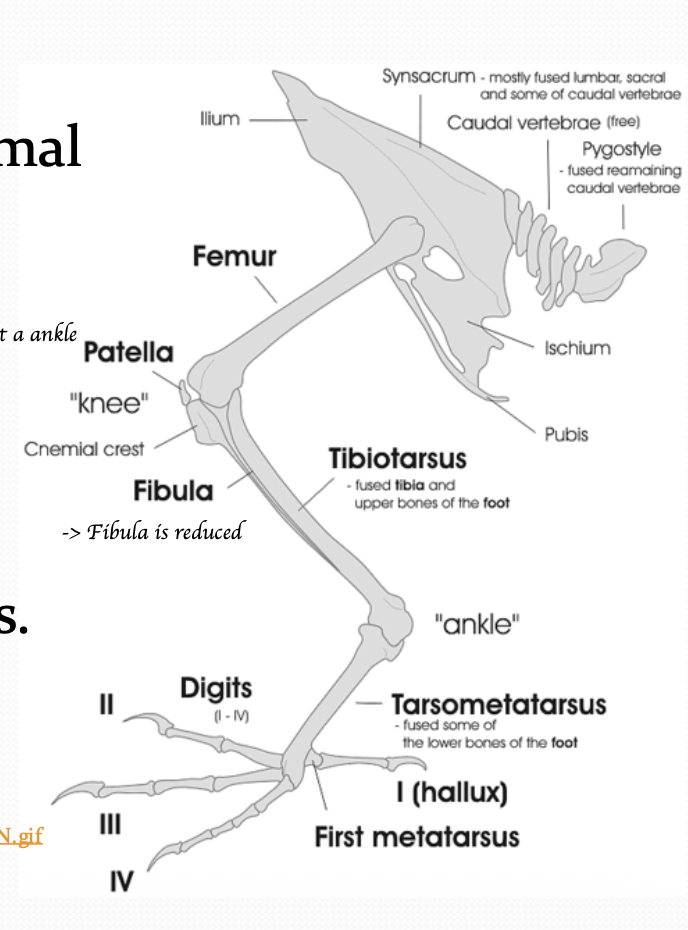
How many cervical vertebrae do birds have?
11 to 25 cervical vertebrae.
Most vertebrae in birds are fused. Which ones are they?
Cervical vertebrae - No fused
Thoracic vertebrae - Fused as notarium
Lumbar, sacral and some caudal vertebrae - Fused as synsacrum
Final few caudal vertebrae - Fused as pygostyle
What is the function of the fused thoracic vertebrae (notarium) in birds?
Resist twisting forces of flight
What is the function of pygostyle in birds?
Attachment of tail feathers and musculature
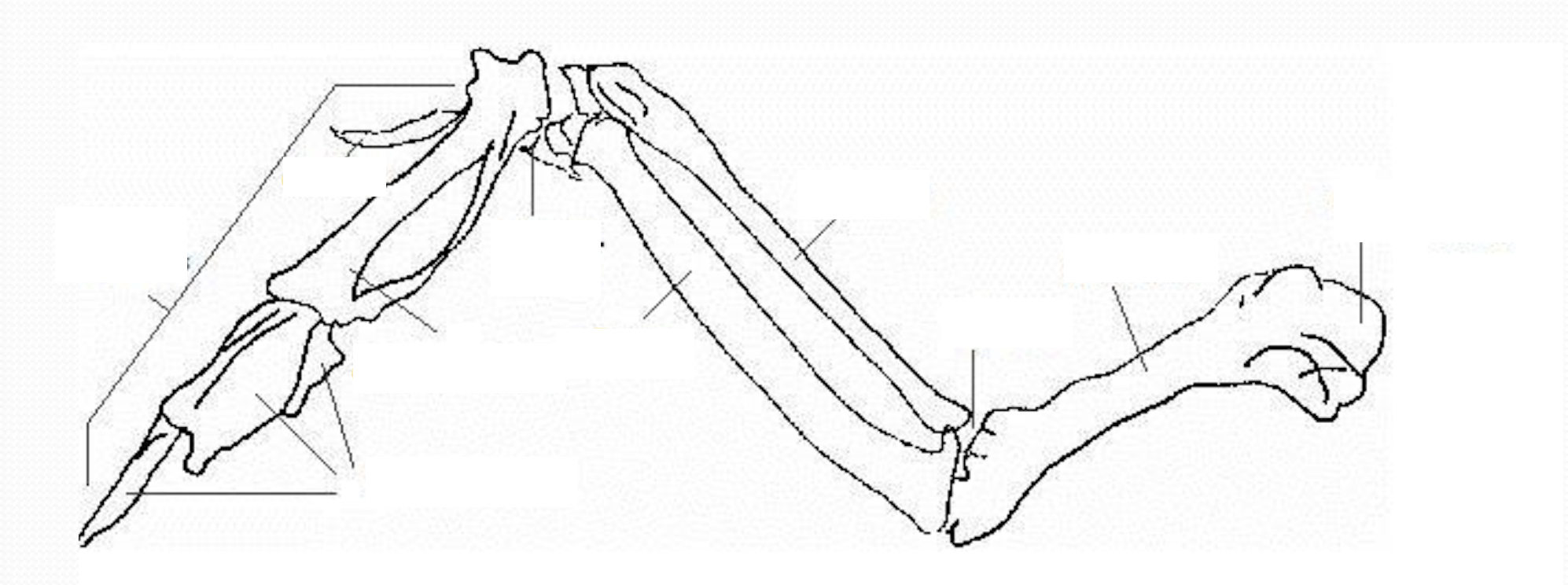
Name the anatomy of the forelimb = wing
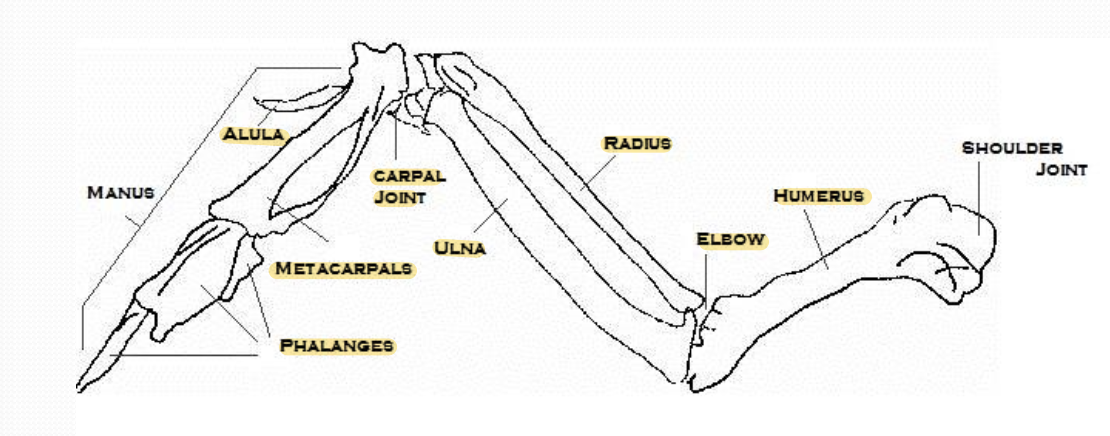
What is the “thumb” in a bird? Where is it located, and what is its function?
Alula is the first digit of chicken
Located on the carpometacarpal joint
Support small stiff feather to aid in flight stability
What is the function of the humerus of birds?
Humerus is a pneumatic bone, which contains extension of cervical air sac
What bones support the primary flight feathers?
Carpal bone
What bone supports the secondary flight feathers?
Ulnar bone
What is the third major part of wing, apart from humerus, ulna and radius
Carpometacarpus (Phalanges, metacarpus and alula)
What are the differences between the ulna and radius in birds compared to mammals?
Ulnar > Radius
What bones in the hindlimb are fused together in birds?
Tibia and part of the tarsus fuse together = Tibiotarsus
Some lower bones of the feet fuse = Tarsomatatarsus
From what bone downward do birds have scaly legs, and what controls the digits?
From about the tibiotarsus downwards, the birds only got that scaly legs
Control of digits via long tendons (Muscles located high up limb(
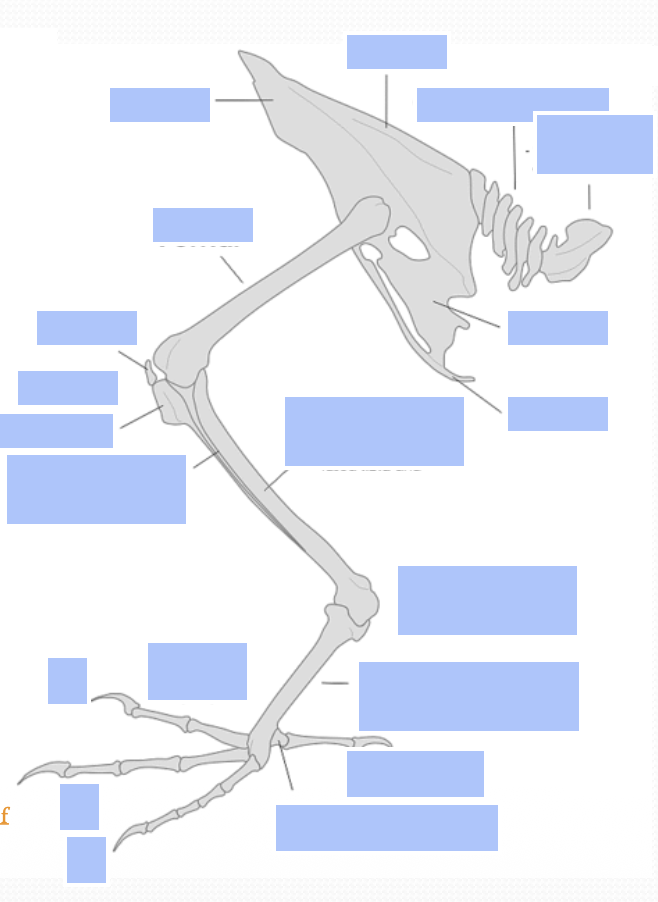
Name the anatomy of birds’ hindlimbs

Anatomy of foot dependent on lifestyle. What type of bird’s foot is shown in the picture below? What are its functions? In which types of birds is it typically seen?
Type: Swimming
Ducks
Function: Paddle through the water more efficiently

Anatomy of foot dependent on lifestyle. What type of bird’s foot is shown in the picture below? What are its functions? In which types of birds is it typically seen?
Type: Grasping
Predatory birds e.g. hawks 鷹
Function: Claw-like feet help grab their prey

Anatomy of foot dependent on lifestyle. What type of bird’s foot is shown in the picture below? What are its functions? In which types of birds is it typically seen?
Climbing
Woodpeckers 啄木鳥 → Climb trees
Sharp nails for digging into the wood + Back toes prevent the bird toppling 倒下 backward

Anatomy of foot dependent on lifestyle. What type of bird’s foot is shown in the picture below? In which types of birds is it typically seen? What are the special features in this type of foot?
Type: Scratching
Chicken or other birds that scratch in the dirt for insect
Feature: Have strong nails for digging into the ground

Anatomy of foot dependent on lifestyle. What type of bird’s foot is shown in the picture below? What are its functions? In which types of birds is it typically seen?
Type: Perching 棲息在高處
Birds like blud jays
Feature: Feet with four toes, one of which is in the back
Function: Birds can wrap their toes on tree branches to help balance

Anatomy of foot dependent on lifestyle. What type of bird’s foot is shown in the picture below? What are its functions? In which types of birds is it typically seen?
Type: Running
Emus
Features: Three toes, al of which face forward
Function: Help them to run quickly
What bones make up the pectoral girdle of a bird?
Scapula
Clavicle
Coracoid
Keel = Sternum
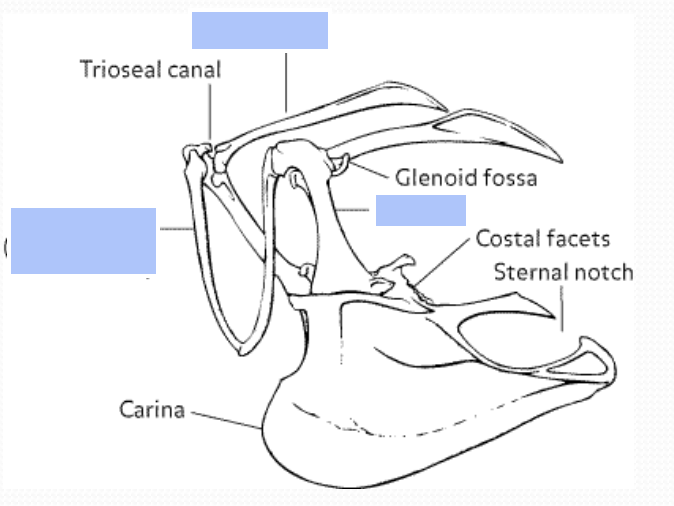
Name the anatomy of pectoral girdle
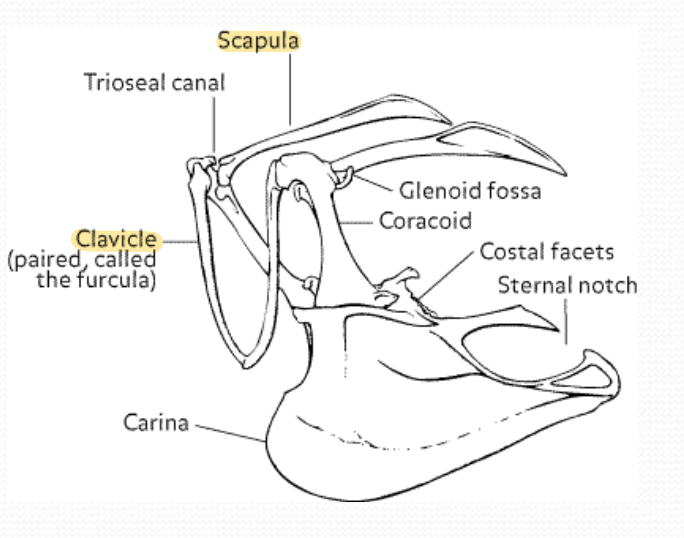
Which bone of the pectoral girdle is fused?
Clavicle is fused to form the "wishbone" or furcula.
What is the pelvic girdle in birds?
Innominate bones (Ileum, ischium and pubis) fuse dorsally with synsacrum, making a single unit
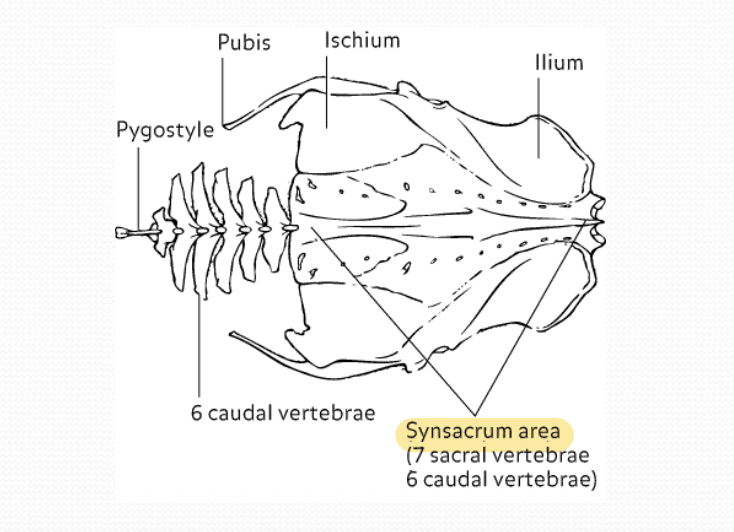
Name the anatomy of pelvic girdle
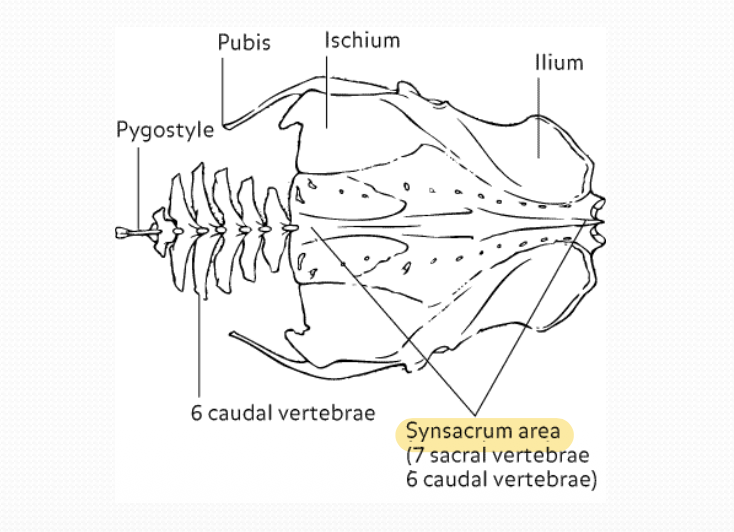
What is the innominate bone in birds?
Fused bone that forms the pelvic girdle in birds
Comprises of fused ileum, ischium and pubis
What muscles are adapted for flight in birds?
Pectoralis (Wing depressor)
Supracoracoideus (Wing elevator)
What is the function of deltoideus in birds?
Flexes shoulder and rotates wing outward
What type of muscles can be used for IM injections
Pectoral muscles
Which types of birds cannot use the pectoral muscles as a site for intramuscular (IM) injections? Why?
Ratites - Because ratites do not have a kneel, which there is nothing to stop our needle going right into the thoracic area
Nestlings (Young birds) - Because at that stage, the keel have not calcified yet = Cartilage, which is way to put a needle right through into the chest
Why should we avoid the thigh and leg muscles for intramuscular (IM) injections in birds?
Renal portal system
→ Blood draining to hindlimb goes straightly to the kidney without going through the circulation first
= If we put certain drugs in the thighs or leg muscle, those will go straight to the kidney, potentially causing toxicity or damage.

What species of bird is this?
Canaries
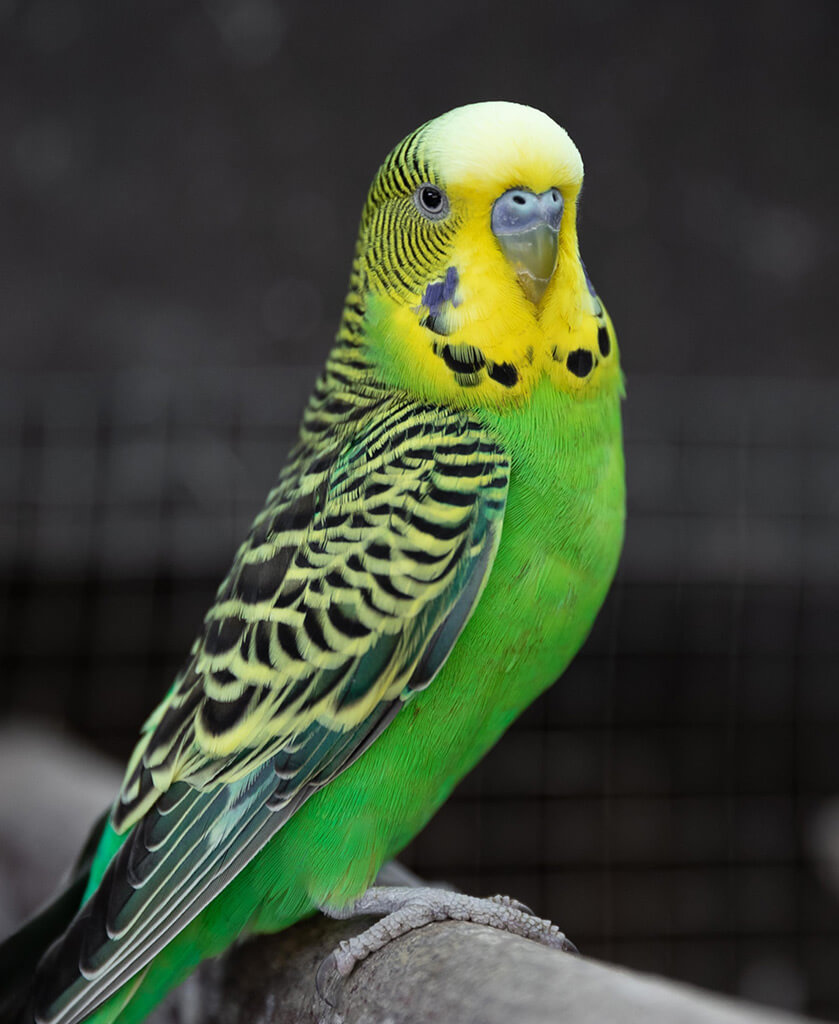

What species of bird is this?
Budgies
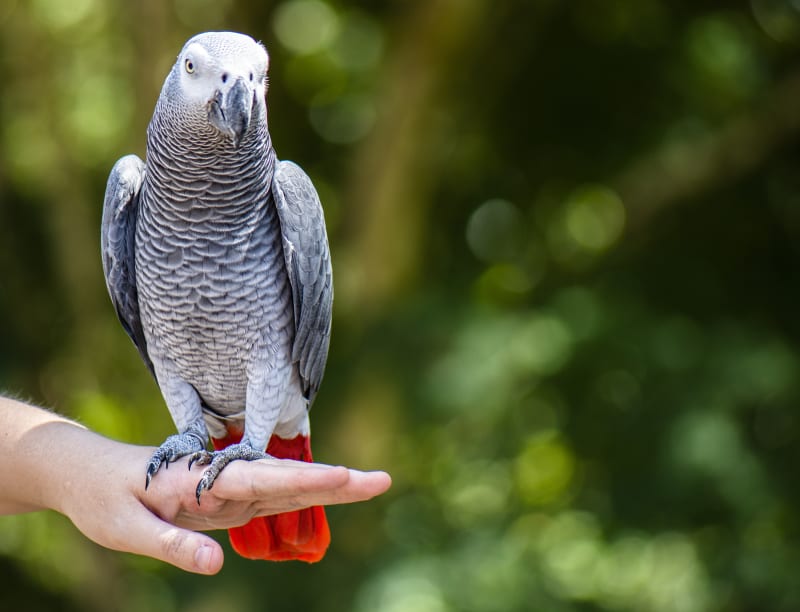

What species of bird is this?
African grey
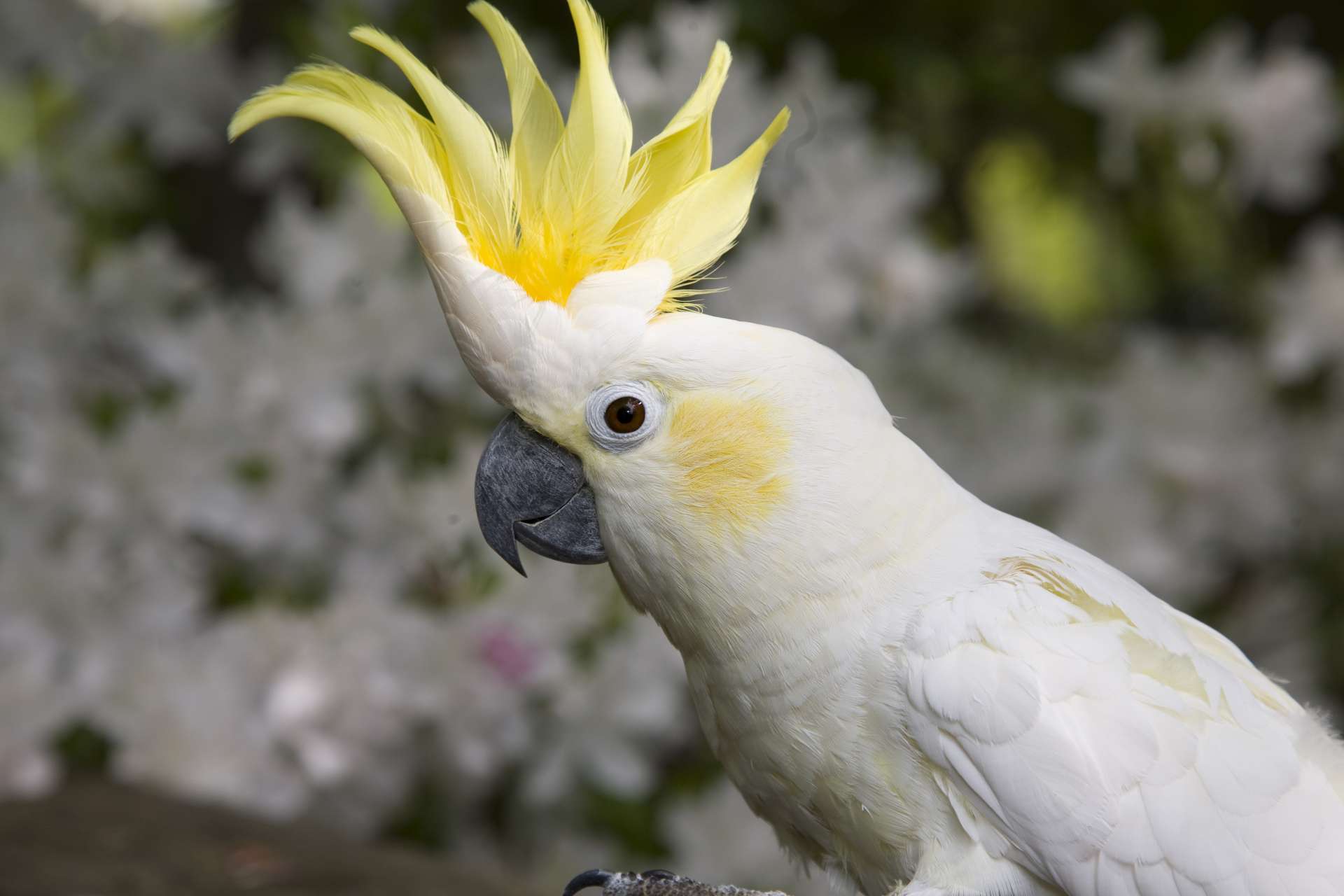

Cockatoo

Lovebirds
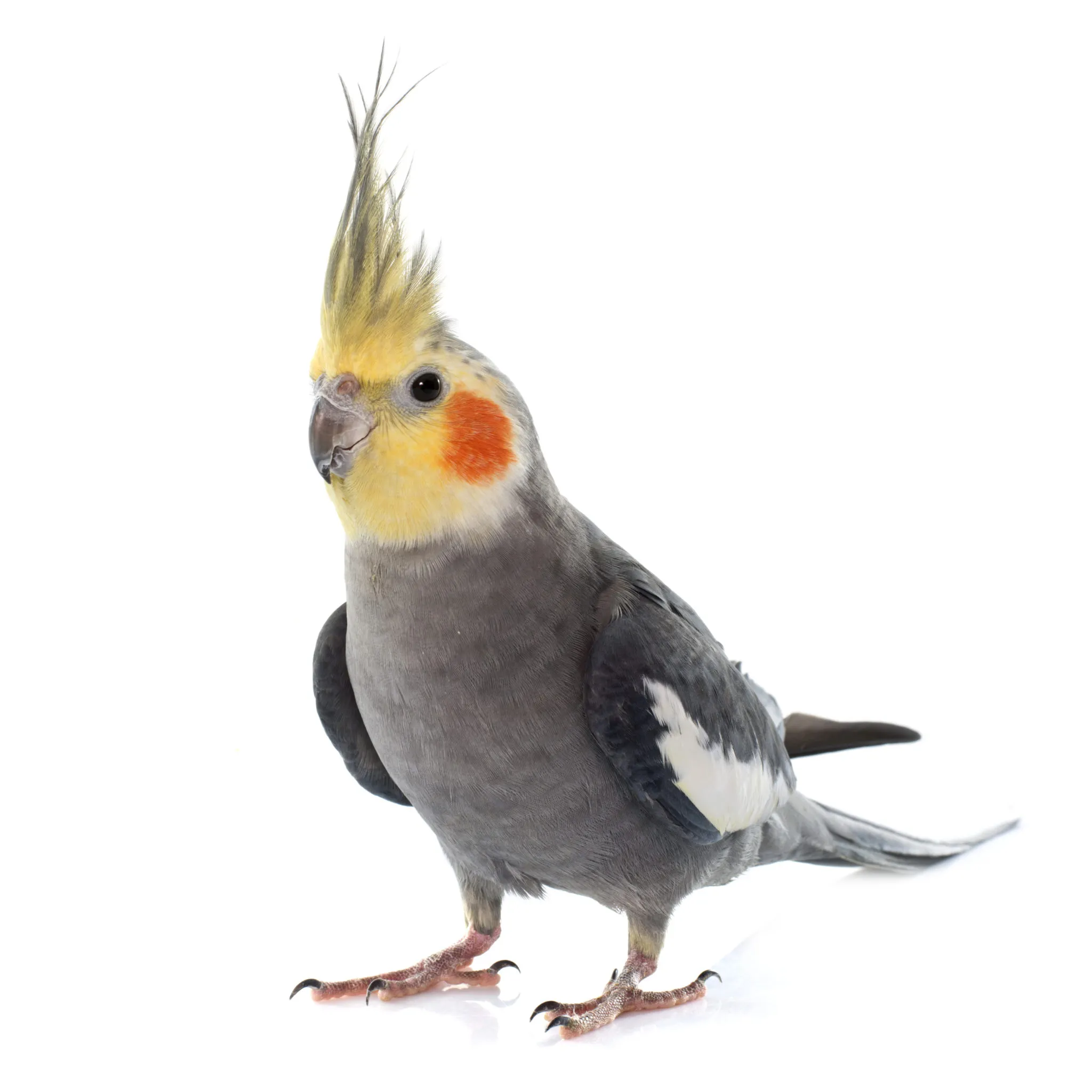

Cockatiels
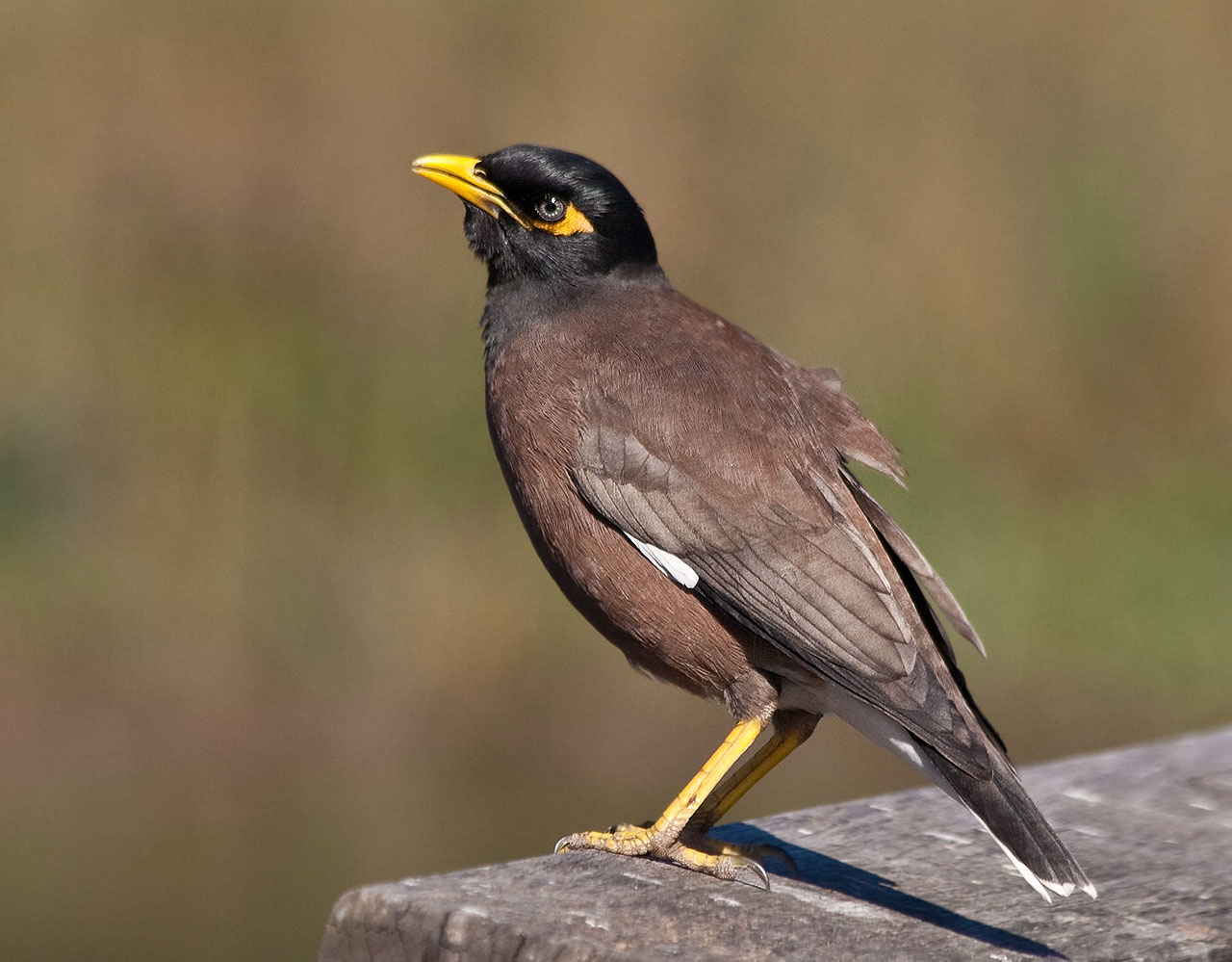

What species of bird is this?
Mynah bird
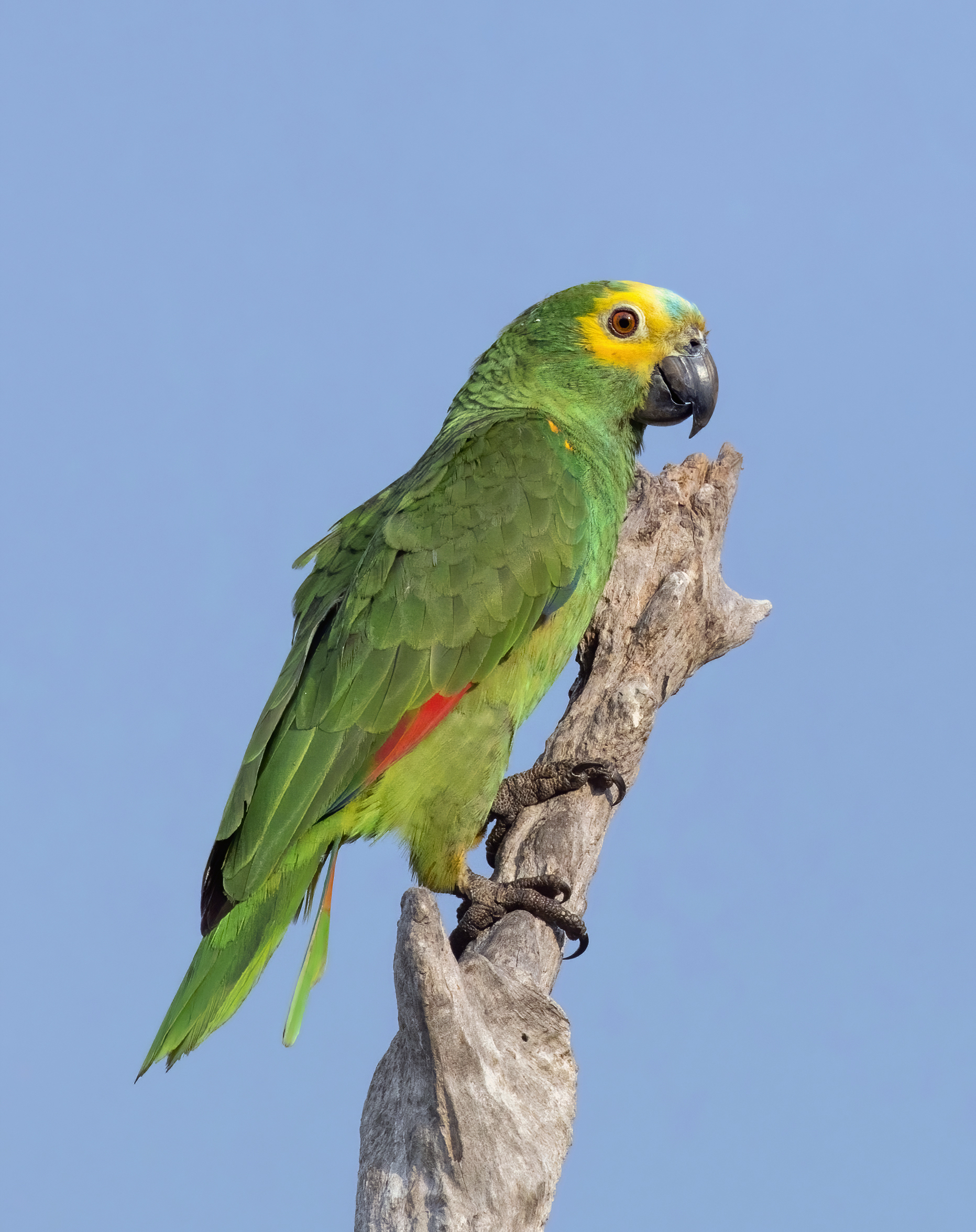

What species of bird is this?
Amazon
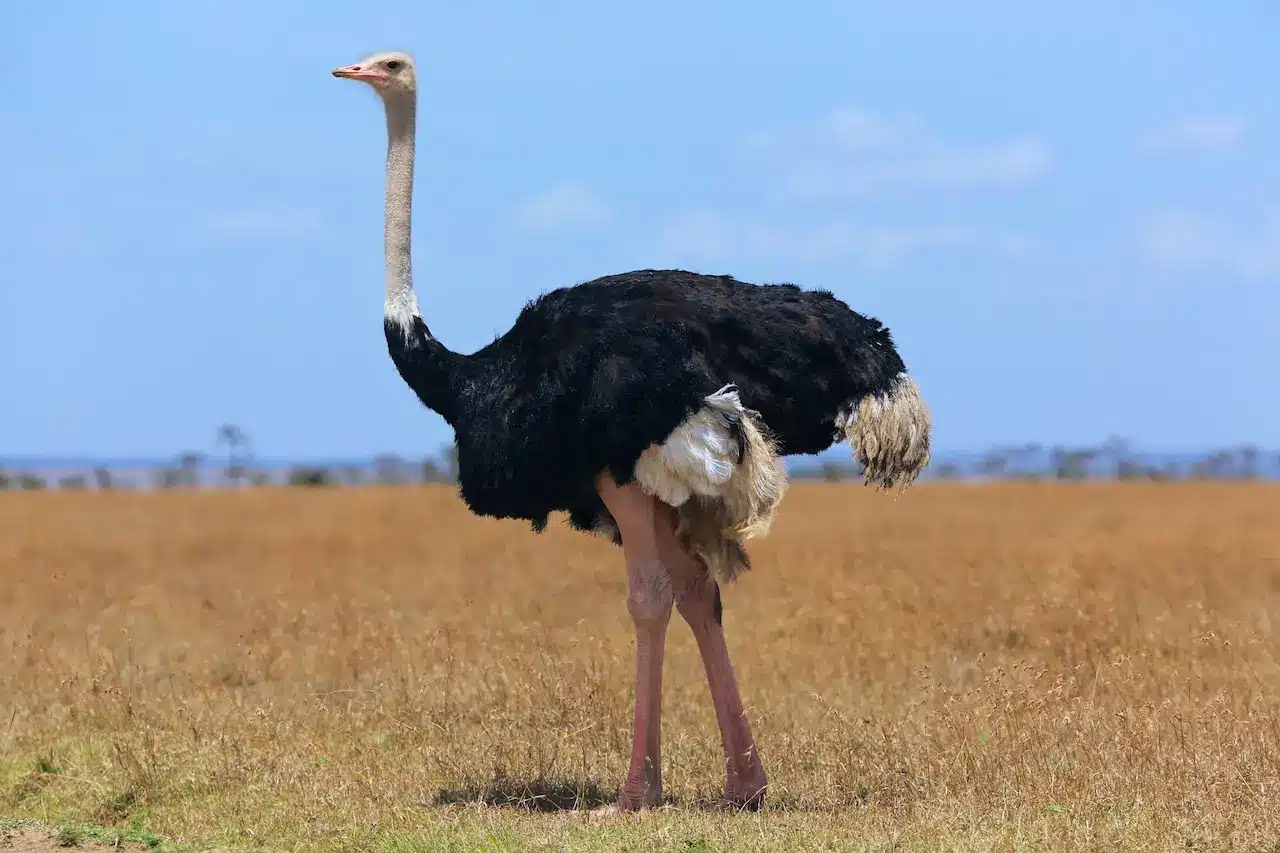

What species of bird is this?
Ostriches
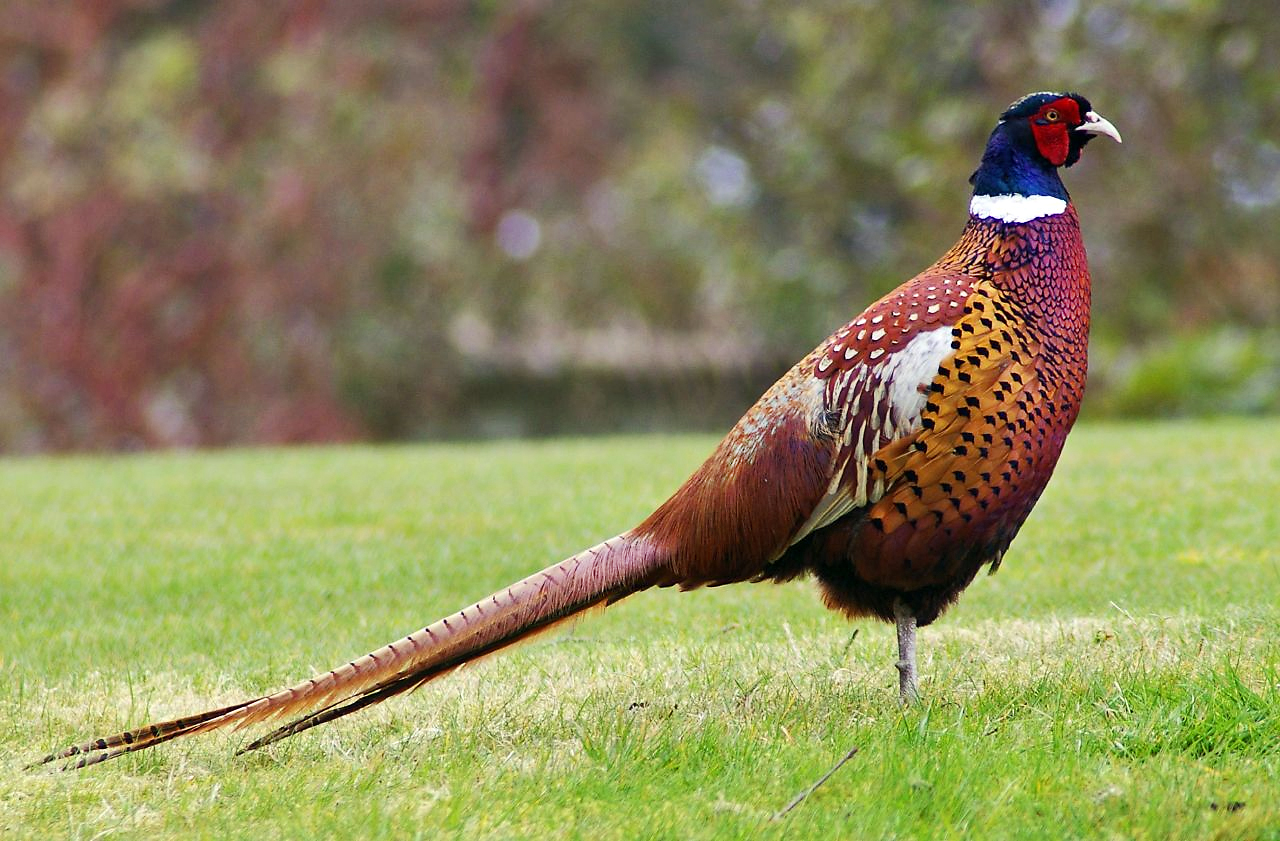

What species of bird is this?
Pheasants
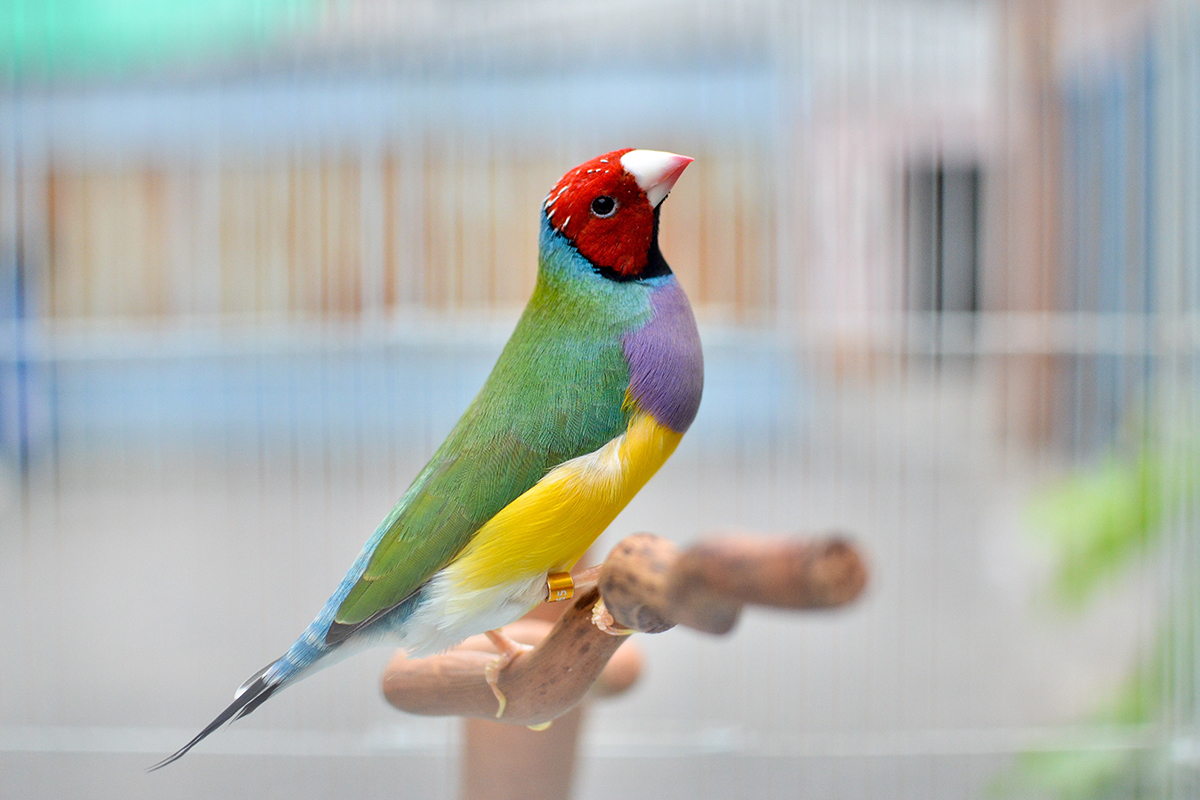

What species of bird is this?
Finches