ANAPHY LEC (NERVOUS SYSTEM)
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
2 divisions of the nervous system
CNS
Key decision maker
receives information from and sends information to the body.
PNS
Messenger detects stimuli in and around the body and sends the information to the CNS and communicates messages from CNS
to the body.
neurons
fundamental unit of the nervous
system that receive and transmit
signals to different parts of the
body.
sensory

motor

interneuron

astrocytes

Ependymal cells

Oligodendrocytes

Microglia

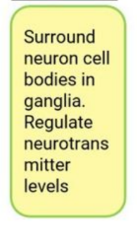
satellite cells
Schwann cells

Leak Ion Channels
Always open, allowing ions to diffuse across the membrane.
Gated Ion Channels
Open or close in response to specific signals, regulating ion
flow.
Ligand-Gated Channels
Open when specific molecules
(e.g., neurotransmitters) bind to receptor sites.
Voltage-Gated Channels
Open in response to changes
in membrane potential.
Mechanically Gated Channels:
Open due to physical
stimuli like pressure or stretch.
Resting Membrane Potential
The result of K+ diffusion through leak channels and the
electrochemical gradient.
Resting membrane potential
Voltage-gated Na+ channels (pink) and most, but not all, voltage-gated K+
channels (purple) are closed. Outside of the plasma membrane is
positively charged compared to the inside.
Depolarization
Voltage-gated Na+ channels open.——results because the
inward movement of Na+ makes the inside of the membrane more
positive
Repolarization
Na+ movement into the cell stops, and K+ movement out of the
cell increases, causing —-
End of repolarization and
afterpotential
Diffusion of K+ through open voltage-gated channels
produces the——.
resting membrane potential
The —— is reestablished by the Na+/K+
pump after the voltage-gated K+ channels close. Na+ is pumped
out of the cell and K+ is pumped into the cell.
Cerebrospinal Fluid
forms a watery cushion
to protect the brain and
spinal cord; and provides
nutrients.
choroid plexus
is produced by the
— of each
ventricle.
Cerebrum
what section of the brain is responsible for: Interpret sight, sounds, touches; regulates emotions, reasoning, learning
Cerebellum
what section of the brain is responsible for: Posture; Balance;
Coordination of movement
Brainstem
what section of the brain is responsible for: Consciousness; Breathing;
Heart rate
Frontal
what lobe of the brain is responsible for: Movement; Problem-solving;
Concentrating; Thinking;
Behavior, personality, mood
Parietal
what lobe of the brain is responsible for: Sensation; Language;
Perception; Body Awareness;
Attention
Temporal
what lobe of the brain is responsible for: Hearing; Language; Memory
Occipital
what lobe of the brain is responsible for: Vision; Proprioception
Right
(Creativity)
what hemisphere of the brain is responsible for:
Receives info from and
controls L side of the
body.
• (Dancer) spatial,
Kinesthetic, body
image, hand-eye,
holistic process.
• (Creative) imaginative,
express feelings,
understand music.
what hemisphere of the brain is responsible for:
Left
(Analysis)
• Receives info from and
controls R side of the
body.
• (ACADS) language,
logical, math, leader,
analytical rational,
written and spoken
words.
• Sequence and perform
movement.
Dura Mater
meninges; Outermost layer; form folds that separate
right half of the brain from the left.
Arachnoid Mater
meninges; Middle layer; fragile layer that covers the
entire brain.
Pia Mater
Innermost layer; contains blood vessels
that runs into the brain’s surface
Thalamus
The switchboard of the CNS; relays sensory
information to the cortex from the rest of the body.
Hypothalamus
Regulates hormonal functions, autonomic function,
hunger, thirst and sleep.
Pituitary Gland
Sends out hormones to different organs in the
body.
Basal Ganglia
Group of nuclei in the cerebrum; controls
movement, including motor learning and planning.
The Brain
Homunculus
portrays the anatomical divisions of the primary motor cortex and the
primary somatosensory cortex.
Dyskinesia
General term for movement problems; often
involves basal nuclei.
Parkinson's
disease
Muscle rigidity, slow movement, resting
tremors, and shuffling gait; linked to basal
nuclei lesions.
Huntington
Disease
Hereditary disorder causing involuntary
movements and degeneration of basal
nuclei.
Cerebral Palsy
Caused by brain damage during pregnancy
or birth; includes muscle tone issues,
tremors, and difficulty speaking or moving.
Cerebellar
Lesions
Jerky, ataxic (uncoordinated) movements
and tremors when trying to control
movements.
Alzheimer
Disease
Dementia with memory loss, confusion, and
disorientation; caused by neuron loss in the brain.
Tay-Sachs
Disease
Hereditary lipid-storage disorder; leads to paralysis, blindness, and death in infants.
Epilepsy
Seizures due to abnormal electrical activity in the
brain, causing convulsions.
Headaches
Pain caused by inflammation, muscle tension, or
unknown factors.
Dyslexia
Reading difficulties due to impaired ability to
recognize letters and words.
Stroke
Caused by blood supply loss to the brain;
symptoms include paralysis and speech loss.
31
pairs of spinal nerves,
which exit the vertebral column
through intervertebral and
sacral foramina.
Cervical Enlargement
Nerve fibers supplying
the Upper limbs enter/exit.
Lumbosacral Enlargement
Nerve fibers supplying the Lower
limbs enter/exit.
Conus Medullaris
tip is the inferior end of the
spinal cord; extends to L2.
Cauda Equina
Horse’s tail; lumbosacral roots
Filum Terminale
Prolongation of pia mater
Reflex Arc
an automatic response to a stimulus; unconscious thought.
Monosynaptic
Polysynaptic
—- Reflexes- without interneurons
—- Reflexes- has interneurons
Stretch Reflex
reflex contraction of muscles in response to stretching of that same muscle.
(1) the endoneurium -
(2) the perineurium -
(3) the epineurium - binds the
nerve fascicles together to form a
nerve
There are three layers of
connective tissue:
endoneurium
surrounds each axon, or nerve
fiber, and its Schwann cell sheath
perineurium
surrounds
groups of axons to form nerve
fascicles
epineurium
binds the
nerve fascicles together to form a
nerve
Ascending Pathways
Carry sensory
information to the brain.Body to Brain
Descending Pathways
Carry motor commands from the
brain to the body. Brain to Body
Spinal
Stenosis
Narrowing of the spinal canal compressing nerves; causes
pain, numbness, or weakness in the neck or lower back.
Encephalitis
Brain inflammation caused by viruses or, less commonly,
bacteria; symptoms include fever, coma, and seizures.
Meningitis
Inflammation of meninges due to infection; symptoms include
stiff neck, headache, fever; severe cases lead to paralysis or
death.
Rabies
Viral disease from animal bites; affects brain and nerves,
causing aggression, paralysis, and death if untreated.
Tetanus
Bacterial toxin affects motor neurons, causing rigid muscles
("lockjaw"); can lead to fatal respiratory spasms.
Multiple
Sclerosis
Autoimmune disease damaging nerve sheaths; symptoms
include tremors, speech issues, and exaggerated reflexes.
Anesthesia
Loss of sensation, either pathological or induced for
medical procedures.
Neuritis
Inflammation of nerves; can cause motor function loss
(motor nerves) or loss of sensation (sensory nerves).
neuralgia
Nerve pain with spasms or stabbing sensations; often
due to inflammation or nerve damage.
Sciatica
Pain radiating down the back of the leg from the sciatic
nerve; often caused by a herniated lumbar disk.
Leprosy
Bacterial disease causing skin and nerve damage; leads
to disfiguring lesions and tissue death.
Herpes
Virus causing painful skin sores (e.g., cold sores,
shingles); different forms can attack sensory ganglia.
Poliomyelitis
Viral CNS infection damaging motor neurons;
causes paralysis and muscle atrophy.
Diabetic
Neuropathy
Nerve damage from high blood sugar levels;
affects extremities with pain, numbness, and
weakness.
Charcot-Marie-To
oth Disease
Hereditary disorder causing progressive nerve
damage and muscle weakness.
Neurofibromatosis
Genetic condition causing benign tumors in
nerve tracts and skin growths.
Myasthenia
Gravis
Autoimmune disorder affecting nerve-muscle
communication; leads to fatigue and paralysis.
Somatic Nervous System
Voluntary control from
cerebral cortex, with
contributions from basal
ganglia, cerebellum, brain
stem, and spinal cord.
Autonomic Nervous System
Involuntary control from
hypothalamus, limbic system, brain
stem, and spinal cord; limited
control from cerebral cortex.
Autonomic tone:
The balance between sympathetic and
parasympathetic activity; regulated by the hypothalamus.
Sympathetic response:
“Fight or flight,” happens during physical
and emotional stress. Favors body functions that support
vigorous physical activity over the storage of energy.
Parasympathetic response:
“Rest and digest,” supports body
functions that conserve and restore body energy during times of
rest and recovery.