AP Bio Unit 1: Chemistry of Life
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Polarity
Difference in atomic electronegativity in a molecule
Electronegative
Oxygen is slightly _______
Covalent
This type of bond between atoms is created when they chare electrons
Hydrogen bond
A weak bond between negative and positive regions of separate molecules
Cohesion
A property of water when it is attracted to itself
Adhesion
A property of water when it is attracted to other molecules
Surface Tension
Higher bonding at the surface of water
Capillary Action
the process of a liquid flowing in a narrow space in opposition to or at least without the assistance of any external forces like gravity.
Law of Conservation of Energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed
Carbon
This element allows the creation of large, complex molecules that are used to store energy and form basic cell structures
Macromolecules
a molecule containing a very large number of atoms, such as a protein, nucleic acid, or synthetic polymer.
Organic Molecules
These are molecules that are made of carbon and hydrogen, and can include other elements
Dehydration Synthesis
The process of combination of two molecules with the elimination of a water molecule
Hydrolysis
The process of splitting apart a polymer into monomers with the addition of a water molecule
Monomer
A molecule that can be bonded with others of its kind to create a polymer
Monosacchride
Monomer of a carbohydrte
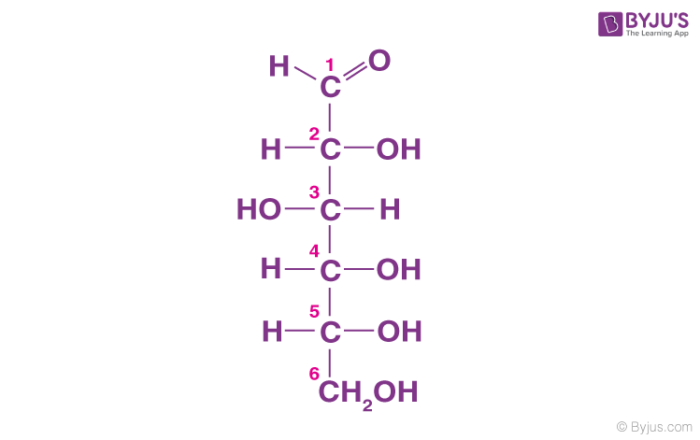
Carbohydrate
This macromolecule is a major fuel and building material
Made of sugar monomers strung together
Lines, rings, and branches
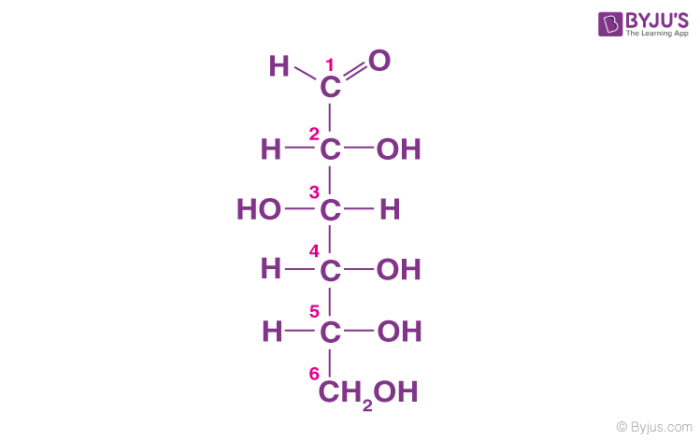
Starch
This carbohydrate has easily breakable bonds and is a source of sugar and energy
Cellulose
This carbohydrate bonds in alternate directions and is not easy to break, so it is used as structural support for plants
1:2:1
Ratio of CHO in Carbohydrates
C, H, O
Elements in a carbohydrate
Proteins
These macromolecules are composed of amino acids. They serve as structural support, biochemical catalysts, hormones, enzymes, building blocks, and initiators of cellular death
Amino Acids
Monomers of proteins
C, H, O, N
Elements of protein
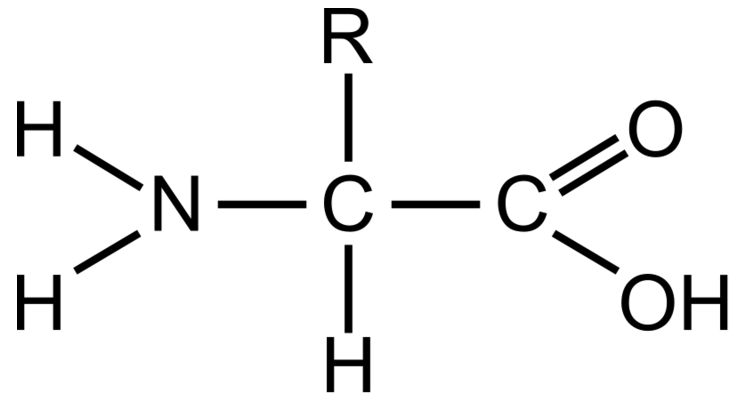
Amino Group
This part of a amino acid is basic
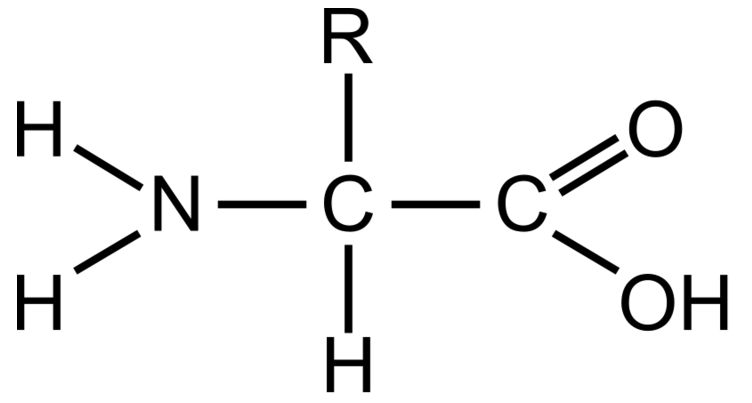
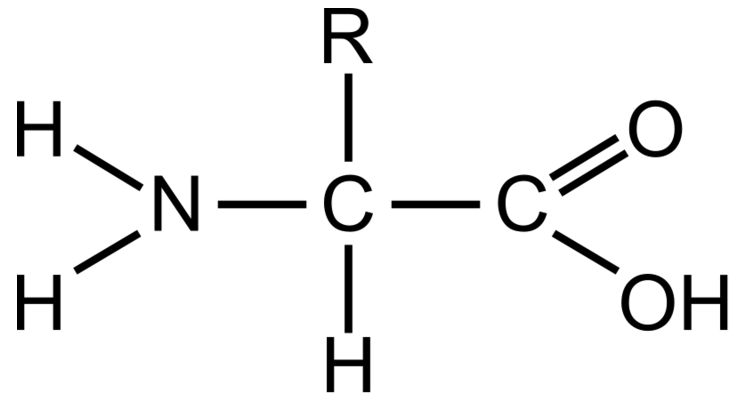
Carboxyl Grou
This part of an amino acid is acidic
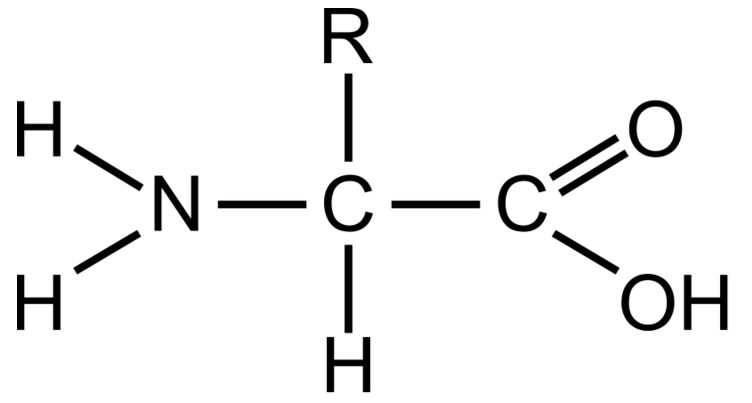
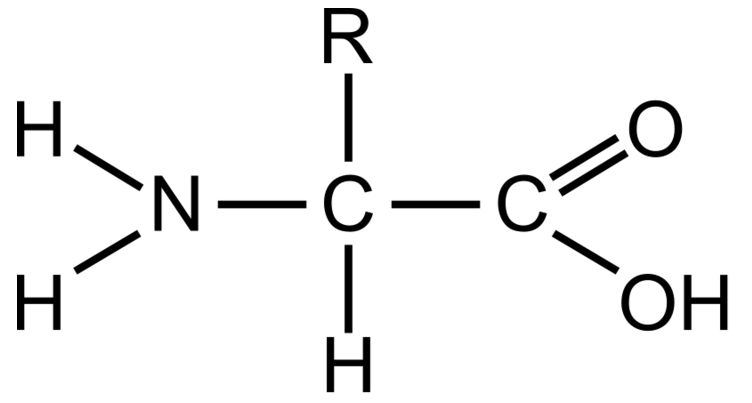
R-Group / Sidechain
This gives each amino acid proteins specific characteristics, including size, polarity, and pH
It can be hydrophobic, hydrophilic, or ionic
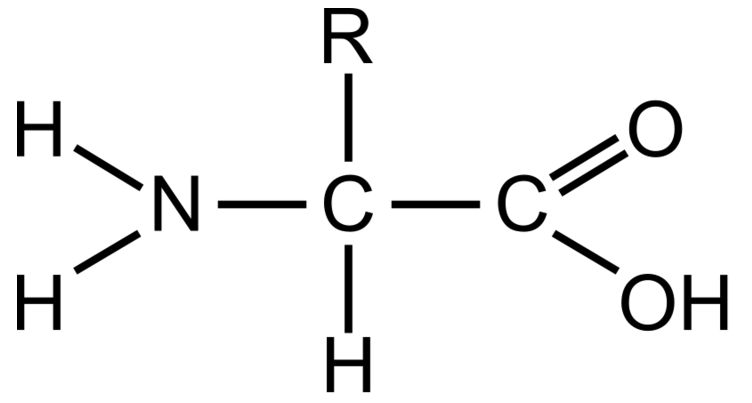
Polypeptide
The primary structure of all proteins. It is a specific order of amino acids and determines the overall shape
Primary
This structure of proteins is a linear chain. New amino acids are added at the carboxyl terminus and it is held together by covalent (peptide) bonds
Carboxyl Terminus
Amino acids are added to a polypeptide chain from this end
Secondary
This structure of a protein is comprised of local folding: alpha helices and beta-sheets
Tertiary
This is the overall 3D shape of a protein and is very stable and rich in potential energy
This is where disulfide bridges, hydrogen bonding, covalent bonding, and hydrophobicity/hydrophilicity play a part
Quaternary
This protein structure is when sometimes, several proteins need to combine in order to function
Lipid
Fats (storing energy, signaling, etc.)
Fats composed of hydrocarbons
No long, stringy molecules
Nonpolar macromolecules → Not a polymer through dehydration synthesis
Differences in saturation determine structure + function
Saturated Fatty Acid: only single bonds in the chain → pack closely together → butter is solid at room temperature
Unsaturated Fatty Acid: Double bonds that change the direction of the macromolecule: cannot pack as closely together → oil is liquid at room temperature
Energy rich
Triglycerols: 3 molecules of fatty acids
Hydrocarbons
Monomers of lipids
C,H,O, P
elements of lipids
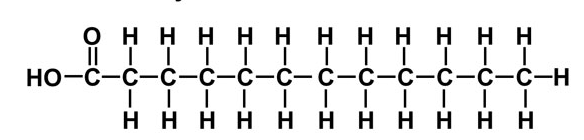
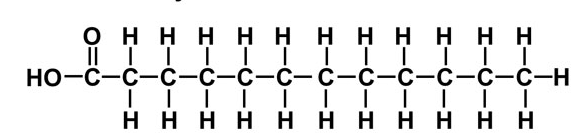
Saturated
This fatty acid has only only single bonds in the chain → pack closely together → butter is solid at room temperature
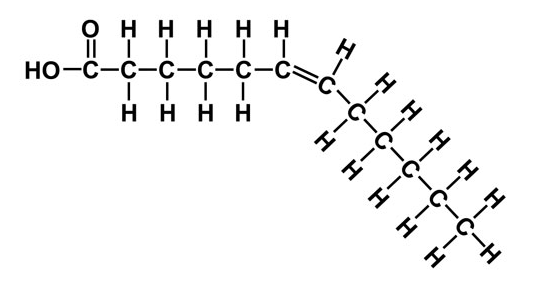
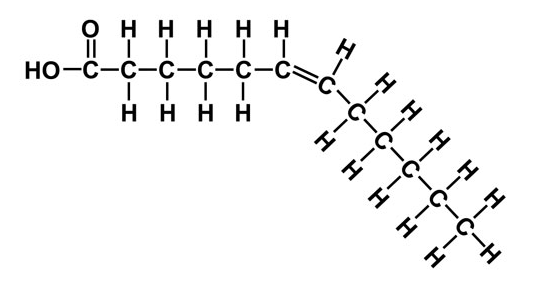
Unsaturated
This fatty acid has Double bonds that change the direction of the lipid: cannot pack as closely together → oil is liquid at room temperature
Phospholipids
These lipids are in membranes and have polar and nonpolar regions
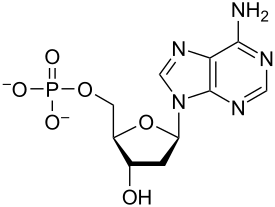
Nucleic Acids
These macromolecules are Large, complex organic molecules
Store + transfer information
DNA: contains info + determines characteristics
Directs cell activities
Missing oxygen
(Adenine, Thymine); (Cytosine, Guanine)
RNA: store + transfer info from DNA to manufacture proteins
Acts as enzymes
2 hydroxyls
(Adenine, Uracil);(Cytosine, Guanine)
Made of nucleotides (1000s of linked monomers)
Phosphate +nitrogenous base + pentose sugar
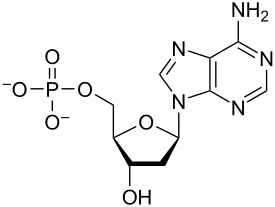
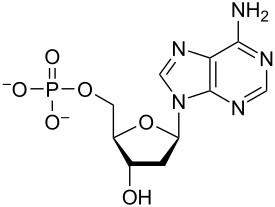
C,H,O,N,P
Elements of nucleic acids
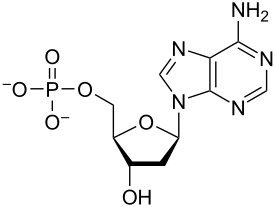
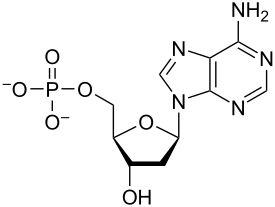
Nucleotides
Monomers of nucleic acids
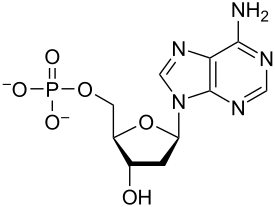
Deoxyribose
This is the type of sugar in the nucleotide monomer for DNA: double-stranded sugar phosphate
Ribose
This is the type of sugar in the nucleotide monomer for RNA: single-stranded sugar phosphate
Ionic Bond
Yoink