Chapter 11 - Chemical Equilibrium
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
dynamic equilibrium
Rate of forward reaction will occur at the same rate as that of the reverse reaction
No
Once equilibrium is reached, do the forward and reverse reactions stop?
Not necessarily
Do concentrations of reactants and products have to be equal at the time of equilibrium?
Gibbs' free energy formula including equilibrium constant
∆G° = -RTln(Keq)
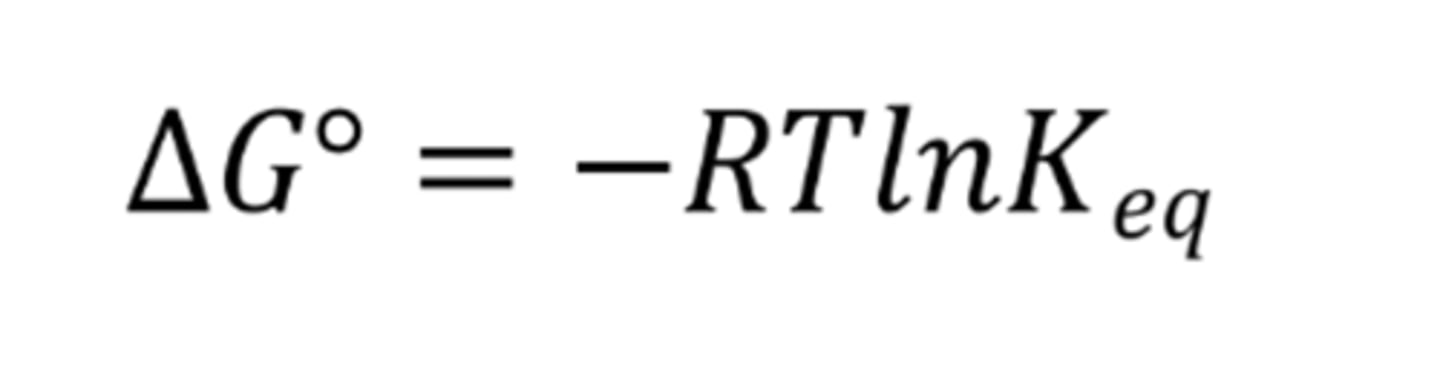
Keq < 1
Greater concentration of reactants than products at equilibrium
Keq = 1
Ratio of products to reactants at equilibrium is equal
Delta G is positive, more reactants
When Keq < 1, is ΔG° positive or negative?
Delta G = 0
When Keq = 1, is ΔG° positive or negative?
ΔG° is negative, there are more products
When Keq > 1, is ΔG° positive or negative?
Equilibrium Constant
Based off of concentrations once reaction has reached equilibrium
Reaction quotient
ses concentrations at any point in time during a reaction other than equilibrium
Q < Keq
There is a higher concentration of reactants than there would be at equilibrium, as such the system shifts more towards the forward reaction to reach equilibrium
Q = Keq
The reaction is in dynamic equilibrium
Q > Keq,
There is a higher concentration of products than there there would be at equilibrium, as such the system more towards the reverse reaction to reach equilibrium
Liquid and solids
What type of reactants and products are excluded from calculating equilibrium constant?
Le Châtelier's principle
A system will shift in a direction that restores the equilibrium state in the presence of changes in concentration or in the temperature of the system
forward
If reactants are added, what direction would the reaction shift?
Reverse
If reactants are removed, what direction would the reaction shift?
Reverse
If products are added, what direction would the reaction shift?
Shift towards the side with less moles
If pressure is added to a system resulting in a decrease in volume, how would the equilibrium shift?
Shift towards the side with greater moles
If pressure is removed from a system resulting in an increase in volume, how would the equilibrium shift?
Reactant
If a reaction is endothermic in the forward direction, would heat be considered a reactant or a product?
Product
If a reaction is exothermic in the forward direction, would heat be considered a reactant or a product?
Shift Left
If you lower the temperature in an endothermic forward reaction, what direction would the system shift?
Shift Left
If you increase the temperature in an exothermic forward reaction, what direction would the system shift?
solubility product constant (Ksp)
Used to figure out direction in which reaction will proceed, but also the saturation of the solution and whether or not precipitation will occur
Q = Ksp
What relationship between Q and Ksp would suggest a saturated reaction mixture?
Q > Ksp
What relationship between Q and Ksp would suggest a supersaturated reaction mixture?
Q < Ksp
What relationship between Q and Ksp would suggest an unsaturated reaction mixture?
Precipitation
Q > Ksp. Reaction is currently supersaturated and will proceed in reverse reaction to result in _________
amphoteric
A substance that can act as both an acid and a base, depending on what it is reacting with
Acidic dissociation constant (Ka) formula
Ka = [H+][A-]/[HA]
Basic dissociation constant (Kb) formula
Kb = [OH-][HB+]/B]
Shift left
How would the following reaction shift if HCl is added? HA (aq) + H2O (l) ⇄ H3O+ (aq) + A- (aq)
Shift right
How would the following reaction shift if NaOH is added? HA (aq) + H2O (l) ⇄ H3O+ (aq) + A- (aq)
shift right
How would the following reaction shift if HA is added? HA (aq) + H2O (l) ⇄ H3O+ (aq) + A- (aq)
Shift left
How would the following reaction shift if A- is added? HA (aq) + H2O (l) ⇄ H3O+ (aq) + A- (aq)
Positive
Keq < 1, then ln(Keq) is negative, making the ΔG° _______
Equal
Keq = 1, then ln(Keq) is zero, making the ΔG° ____ to zero
Negative
Keq > 1, then ln(Keq) is positive, making the ΔG° ______ (spontaneous)
Reactants
ΔG° > 0, formation of ______ is favored at equilibrium.
Products
ΔG° < 0, formation of ______ is favored at equilibrium.
Irreversible Reactions
Denoted by a unidirectional arrow
Reversible Reactions
Denoted by a bidirecitonal arrow; meaning reactants can convert into products and products can convert into reactants
Dynamic Equilibrium
When the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction
Same
In a dynamic equilibrium, the forward and reverse reactions proceed at the _____ rate
Do not
The forward and reverse reactions _____ stop once equilibrium is reached
Not always
The concentrations of the reactants and products are ________ equal at the equilibrium
Law of Mass Action
States that the rate of the forward and reverse reaction is proportional to the product of the concentrations of the reactants and products
Equilibrium constant
Allows us to quantify the concentrations of reactants and products for a system in equilibrium under constant temperature
kp
Represents the equilibrium constant of gaseous systems, expressed in partial pressures
Keq < 1
There is a greater concentration of reactants than products
Keq > 1
There is a greater concentration of products than reactants
Keq = 1
Ratio of reactants to products is equal at equilibrium
Positive
When Keq < 1, delta G will be ________
0
When Keq = 1, delta G will be equal to ______
Negative
When Keq > 1, Delta G will be ________
Reactants
When Q < Keq, there is a higher concentration of _______ than there is at equilibrium
Equilibrium
Q = Keq, the reaction is in dynamic _______
Products
When Q > Keq, there is a higher concentration of _______ than there is at equilibrium
Inert Gas
Part of noble gases; it does’t have that much power to do anything
More soluble
Higher Ksp
Less soluble
Lower Ksp