Biology 111 - Chapter 5
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Carbohydrate
Sugars
Monomer
Monosaccharides
Oligosaccharides
Few sugars
Polysaccharides
Many sugars
Carbohydrate formula
(CH2O)n
Purpose of Glucose
Important for cellular respiration and making ATP
Four ways carbohydrates differ
Hydroxyl
Carbonyl
Number of Carbons
Linear and Ring Formations
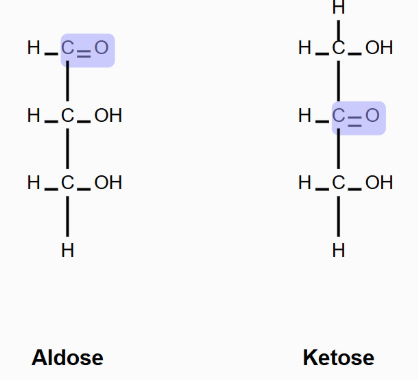
Two configurations of carbonyl group
Aldose (carbonyl group at the end of the carbon chain)
Ketose (carbonyl group in the middle of the carbon chain)
Cell are in aqueous environment
Cell are in aqueous environment
Polysaccharides(long chains of monosaccharides) are formed by polymerization. During this process, monosaccharides are linked together by glycosidic linkages.
Polysaccharides(long chains of monosaccharides) are formed by polymerization. During this process, monosaccharides are linked together by glycosidic linkages.
Purpose of Starch
Energy storage in plant cells
Purpose of gyclogen
Animal storage of sugar
Cellulose
Structural polymer found in plants
Chitin
Structural polymer for crustaceans, insects, and other arthropods
Purpose of peptidoglycan
Structure in bacterial cell walls
What is not a polymer?
Glucose
Purpose of cellular respiration
When a cell needs energy, it breaks down glucose to make ATP.
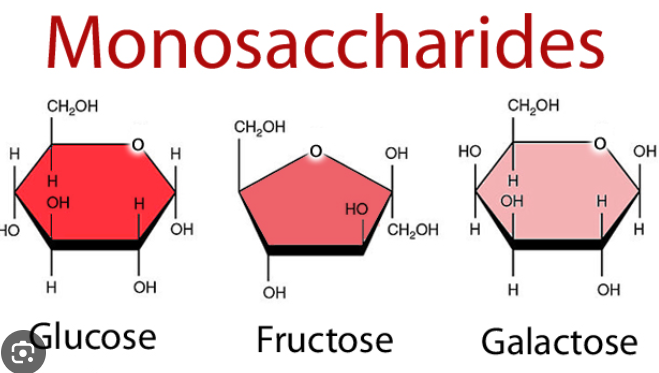
Types of monosaccharides
Glucose
Galactose
Fructose
Carbohydrates relation towards water
Polar and hydrophilic
Triose
3 Carbons
Pentose
5 Carbons (important for DNA + RNA)
Hexose
6 Carbons
Glycosidic linkage
Similar to a peptide bond in proteins
Types of Polysaccharides
Starch
Glycogen
Cellulose
Chitin
Peptidoglycan
Starch
Energy storage in plant cells
Function: store energy
Glucose polymer components:
Alpha glucose monomers
Forms a helix
Amylose
Alpha 1,4
No branching
Amylopectin
Alpha 1,6
Branches once in every 30 monomers
Glycogen
Stored in liver and muscle
Can be broken into glucose monomers for energy
Glucose polymer components:
Highly branched alpha glucose polymer, nearly identical to starch
Branches once in about 1 out 10 monomers
Cellulose
Major component of cell wall
Function: structure & support
Glucose polymer components:
Beta 1,4 linkage, linear molecule
Insoluble fiber
Cellulose on food packages
Beta 1,4 Glycosidic linkage
Organized into fibers and sheets, provides strength and elasticity
Glycoproteins
Proteins with attached carbohydrates
Glycolipids
Lipids with attached carbohydrates
Function of Carbohydrates
Serve as precursors to other molecules such as nucleotides or amino acids
Provide fibrous structural material
Indicate cell identity
Store chemical energy
Monosaccharides differ from one another in whether they contain a ketose or an aldose group
Monosaccharides differ from one another in whether they contain a ketose or an aldose group
Soil pH affecting plant height
Soil pH is independent, plant height is dependent