Biology 102: Unit 3 Test
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Acoelomate
Animal without a body cavity
Bilateral Symmetry
Type of symmetry with only one plane of symmetry
Blastopore
Opening into the archenteron during gastrulation
Blastula
16-32 cell stage of animal embryo development
Body Plan
Defining shape or morphology of an organism
Coelom
Lined body cavity
Determinate Cleavage
Cleavage pattern with tightly defined blastomere fate
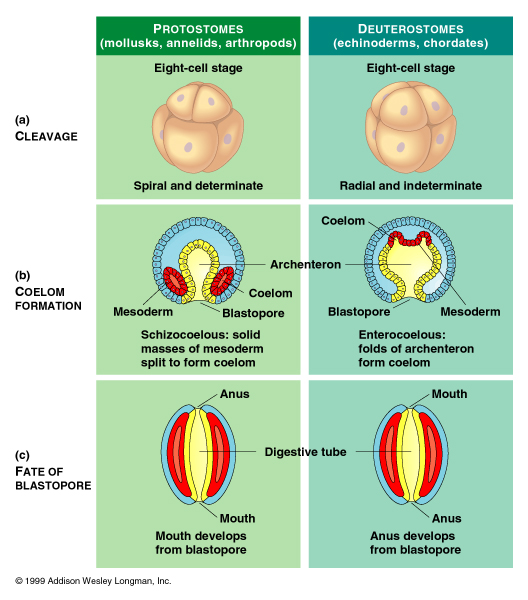
Deuterostome
Blastopore develops into the anus; determinate (fate of each cell already determined), radial structure
Diploblast
Animal developing from two germ layers
Eucoelomate
Animal with a body cavity lined with mesoderm
Gastrula
Stage characterized by digestive cavity formation
Germ Layer
Cells forming during embryogenesis for body tissues
Hox Gene
Master control gene in embryogenesis for gene transcription
Indeterminate Cleavage
Cleavage pattern with blastomeres as stem cells
Organogenesis
Organ formation in animal embryogenesis
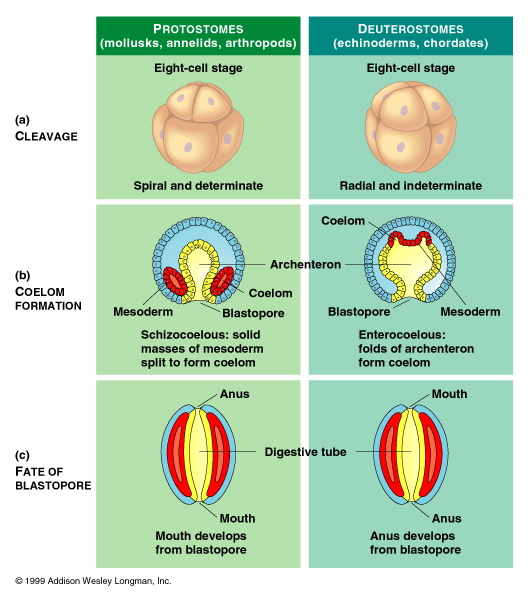
Protostome
Blastopore develops into the mouth, spiral structure
Pseudocoelomate
Animal with a body cavity between mesoderm and endoderm
Radial Cleavage
Cleavage axes parallel or perpendicular to polar axis
Radial Symmetry
Symmetry with multiple planes around a central disk
Spiral Cleavage
Rotation or misalignment of embryo cells
Triploblast
Animal developing from three germ layers
Amoebocyte
Sponge cell with multiple functions
Annelida
Phylum of vermiform animals with metamerism
Archenteron
Primitive gut cavity in the gastrula
Arthropoda
Phylum of animals with jointed appendages
Notochord
Flexible, rod-shaped support structure in embryonic chordates
Osteichthyes
Bony fish class
Pharyngeal slit
Opening in the pharynx
Primates
Order including lemurs, monkeys, apes, and humans
Sebaceous gland
Skin gland producing sebum
Stereoscopic vision
Produces depth perception from overlapping fields of vision
Swim bladder
Gas-filled organ controlling fish buoyancy
Tetrapod
Organism with a four-footed evolutionary history
Theropod
Dinosaur group ancestral to birds
Vertebral column
Backbone made of separate bones
Vertebrata
Chordates with a backbone
Acclimatization
Body system response to environmental change
Alteration
Change of set point in homeostasis
Asymmetrical
Animals with no body symmetry
Basal metabolic rate (BMR)
Resting metabolic rate in endotherms
Cartilage
Connective tissue with chondrocytes and fibers
Columnar epithelia
Tall cells specialized in absorption
Connective tissue
Tissue with cells, matrix, and fibers
Cuboidal epithelia
Cube-shaped cells for glandular functions
Dorsal cavity
Body cavity on the back of an animal
Ectotherm
Animal unable to maintain constant body temperature
Endotherm
Animal maintaining constant body temperature
Epithelial tissue
Tissue lining organs or tissues
Fibrous connective tissue
Tissue with high fiber concentration
Frontal (coronal) plane
Plane separating front and back body portions
Roughage
Low-energy, high-fiber food component
Ruminant
Animal with a four-compartment stomach
Salivary amylase
Enzyme in saliva converting carbs to maltose
Secretin
Hormone stimulating bicarbonate secretion in small intestine
Somatostatin
Hormone halting acid secretion in empty stomach
Sucrase
Enzyme breaking down sucrose into glucose and fructose
Trypsin
Pancreatic protease breaking down protein
Villi
Folds in small intestine increasing absorption area
Vitamin
Organic substance vital in small quantities for life
Acetylcholine
Neurotransmitter in central and peripheral nervous systems
Action potential
Self-propagating change in neuron membrane potential
Amygdala
Limbic system structure processing fear
Astrocyte
Glial cell providing nutrients and structural support
Autonomic nervous system
Peripheral system controlling bodily functions
Axon
Structure propagating signals from neuron cell body
Axon hillock
Structure integrating signals from multiple connections
Axon terminal
End structure forming synapses with other neurons
Basal ganglia
Brain cells involved in movement and motivation
Brainstem
Brain portion controlling basic functions
Cerebellum
Brain structure for posture and motor coordination
Cerebral cortex
Outer brain tissue for higher functions
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Liquid surrounding brain and spinal cord
Corpus callosum
Fiber bundle connecting cerebral hemispheres
Dendrite
Structure receiving messages from other neurons
Depolarization
Change to less negative membrane potential