2.10 Liver and pancreas pathology
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Liver blood flow
75% portal vein (poorly oxygenated)
25% hepatic artery (oxygenated)
How does blood and bile travel in the hexagonal lobule?
Blood travels from portal tracts into central vein (edge to center)
Bile travels from central hepatocytes into peripheral bile ducts (center to edge)
3 hepatic lobule zones (outer to inner)
Periportal
Midzonal
Centrolobular (surrounds central vein)
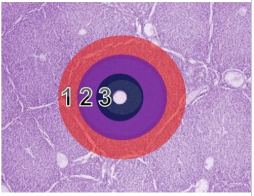
List 2 pathologies that the centrilobular zone is most prone to.
Hypoxic injury → blood travels from peripheral to center
Toxicity → contains lots of enzymes (cytochrome P450s)
Bile duct epithelium type
Cuboidal or columnar
Connective tissue holding portal triad together
Limiting plate
Why does portosystemic shunt cause liver atrophy?
Liver receives growth factors from blood nutrients
Describe how acquired portosystemic shunts are formed. (3) How does it look microscopically? (2) What pathology does it result in? (1)
Older animals → secondary to fibrosis
Blood cannot get into liver → resistance in fibrotic sinusoids
Formation of lots of thin walled capillaries connecting portal vein and rest of venous circulation
Thick pink walls of multiple small hepatic arterioles in microscopy
Distorted structure, cannot see thick portal vein
Hepatic encephalopathy → ammonia bypasses liver
Other than portosystemic shunts, name 5 developmental disorders of the liver.
Congenital cysts (most commonly biliary)
Displacement of liver → portal vein twists → necrosis
Tension lipidosis (attached to body wall) → restricts blood flow
Telangiectasia (dilation of blood vessels)
dark spots → focal sinusoidal dilation
mistaken for melanosis
Capsular fibrosis
How do you distinguish between hepatocytomegaly and congestion causing liver enlargement?
Hepatocytomegaly - dry cut surface
Congestion - blood pours out of it
How does hydropic vacuolation happen in the liver?
Failure of energy supplying pumps (hypoxia, mild toxic damage, metab stress)
Nonspecific and reversible
Name the most common cause of glycogen accumulation.
Endogenous/exogenous glucocorticoids
Cushing’s
Steroids
List 5 causes of liver lipidosis.
Starvation (most common cause in horse)
Massive energy demand (pregnancy or lactation)
Metabolic diseases (diabetes → ketosis, pregnancy toxaemia)
Obesity (less common)
Abnormal hepatocyte function
Cytology of lipidotic liver
Crisp, well defined lipid vacuoles that displace nucleus to edge of cell
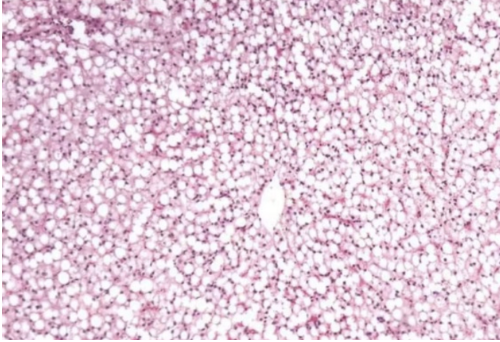
How do you grossly detect hepatic lipidosis?
Liver floats in formalin due to lots of fat
How do you detect amyloidosis in the liver? (3)
Large, pale orange, friable liver
Microscopically - homogenous acidophilic material between hepatocytes
Congo red → apple green birefringence under polarisation
What is zonal liver injury often associated with?
Ischaemia or toxic damage
What is focally extensive liver injury often associated with?
Bacterial injury (big infection)
What are random white nodules of liver injury often associated with?
Viral or bacterial damage
white nodules are small pockets of inflammatory cells
How is the liver different in acute V chronic necrosis?
Acute - liver is soft and friable
Chronic - liver is firm and fibrotic
How is lymphoma mediated cholangitis different from lymphocytic cholangitis?
Lymphocytic → bile duct is regenerating
Lymphoma → bile duct is destroyed
4 ways of hepatitis progression
Regeneration (complete resolution)
Repair (fibrosis + scarring)
Encapsulation by abscessation
Persistence
3 causes of viral hepatitis
Adenovirus (canine infectious hepatitis)
Herpesvirus (EHV1, IBR/P/V, Aujeskys)
FIP (mutated coronavirus)
List the signs of infectious canine hepatitis. (4)
Adenovirus infection
Intranuclear dark marginal bodies
Widespread haemorrhage
Virus has tropism for endothelium
Enlarged, reddened lymph nodes and tonsils
Recovering animals - immune mediated uveitis + corneal opacity
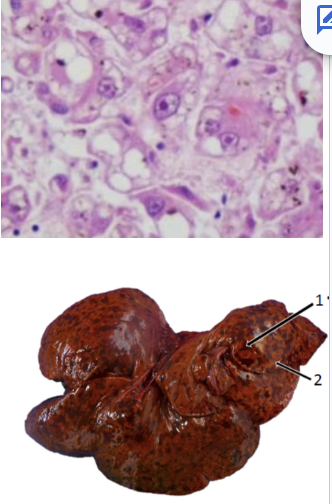
Describe the microscopic lesions seen in hepatic herpesvirus infections.
Pink mass of protein with nuclear fragments, with intranuclear inclusion bodies outside the lesion
Congealing of dying hepatocytes
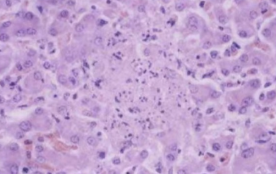
Pathogen causing Tyzzer’s disease and 3 species affected
Clostridium piliforme (piliformis)
Foals (1-4 weeks)
Rodents
Immunosuppressed smallies
Tyzzer’s disease 2 microscopic lesions
Intracellular bacteria (unusual for clostridium)
Wheat sheaf colonies when stained with silver
Cattle specific salmonellosis
S. dublin
How does salmonella spread from gut to liver? What does it look like macroscopically and microscopically? What other pathology can be seen? (4)
Macrophages carry salmonella from gut to liver
Pale pinpoint white foci of liver necrosis - paratyphoid nodules
Necrosis and mixed mononuclear cells
Haemorrhagic or fibronecrotic ileitis
List 2 signs and 2 causes of acute liver intoxication.
Decreased clotting factor synthesis → haemorrhage
Icterus
Cyanobacteria
Iron and cresols
What does chronic liver intoxication normally cause? List 4 causes.
Fibrosis and biliary hyperplasia
Ragwort
Megalohepatocytosis - inhibition of mitosis
Alflatoxins
Copper
Drugs
Primidone
Sulfonamides
Paracetamol
What does nodular hyperplasia look like and what animals does it commonly affect?
Spherical nodules in liver - varied in colour, similar to rest of liver
Benign hyperplasia in older dogs
Liver primary tumour
Hepatocellular adenoma or carcinoma
Biliary epithelium tumour and description
Cholangiocellular carcinoma most common
White, firm, umbilicate (pit in center), may resemble normal parenchyma
If malignant - haemorrhage and necrosis
4 common metastatic tumours in the liver
Carcinoma
Sarcoma
Haemangiosarcoma
Lymphoma
Melanoma
Where does haemangiosarcoma metastasis in the liver usually originate from, what does it look like and what animals is it prevalent in?
Spleen and right auricle
Dark red and blood filled
Large breeds of dogs