PSCI 150C - Week 2, Clinical Interviewing + IQ and Neuro Assessment
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Intake interviews
The first meeting where a therapist gathers a client’s information to thoroughly assess and treat the client.
Diagnostic interviews
Interviews used to develop a comprehensive mental health diagnosis.
Mental status exam (MSE)
Interviews used to evaluate how a client is functioning.
Established after intake interview
Problem-referral interviews
Interviews used to answer problem-referral questions.
Crisis interviews
Interviews used to address an urgent problem and identify if immediate intervention is needed.
What kind of assessment techniques are used for assessments and interviews?
Validity
Reliability
Clinical utility
Rapport
The positive, comfortable relationship between interviewer and client.
What are the three interview formats?
Unstructured
Semistructured
Structured
What are the two key components of an interview?
Rapport and technique
What are the four types of interviews?
Intake interviews
Diagnostic interviews
Mental status exam
Problem-referral interviews
Crisis interviews
What are the main skills and techniques for clinical interviews?
Open-ended and close-ended questions
Ask clarification questions
Confrontation
Paraphrasing
Reflect empathy
Summarize what you’ve learned about the client
What is the main goal of intake interviews and what are the main aspects of them?
Main Goal: What is the best treatment for this patient?
Important aspects:
Providing rapport and resources
Gathering information
Identify problems
Address any symptom
Case formulation
What is the main goal of diagnostic interviews and what are the main aspects of them?
Main Goal: Provide a comprehensive assessment of diagnoses
Important aspects:
Semi-structured interview format
Evaluation and gathering of background information
Close-ended questions
Why is empathy important in clinical psychology?
Building a personal + professional rapport/relationship with the client
Every clients’ experience with diagnosis is different
Compassion is needed therefore clients will want to return to therapy
What are the key dos with interviewing and expressing empathy toward a client?
Asking clarifying questions
Reflecting emotions
Express empathy
Why is empathy important in clinical psychology?
Building a personal + professional rapport/relationship with the client
Every clients’ experience with diagnosis is different
Compassion is needed therefore clients will want to return to therapy
Validity
The measure of accuracy and truthfulness.
What kind of responses are needed to contribute with showing empathy toward a client?
Verbal and non-verbal responses
What are the key don’ts with interviewing and expressing empathy toward a client?
Minimizing the client’s feelings and experiences
Giving straightforward advice
Unstructured Interview
An interview that is flexible and uses open-ended questions.
Advantages: Allows more rapport between the clinician and client
Disadvantages: Important topics might not be addressed
Semi-structured Interview
An interview that uses a balance of guiding questions and specific questions.
Advantages: Rapport, coverage of important topics
Disadvantages: Not reliable for research purposes
Structured Interviews
An interview that uses a specific set of questions in a set order.
Advantages: Systemic, less prone to error
Disadvantages: Can make the client feel alienated.
What are tests?
A systematic procedure for observing and describing a person’s behavior in standard situations.
What are referral questions and what is the importance of them?
Referral questions are questions that have a specific reason to get help
Needed to select the right tests
Recommendations for treatment
Intelligence tests
The measurement of intellectual abilities.
Achievement tests
The measurement of accomplishments in academic areas.
Neuropsychological tests
The measurement of focus on cognitive dysfunction (especially from brain injury or illness).
What is the purpose of psychological tests?
To evaluate different aspects of cognitive functioning
What are the three types of psychological tests?
Intelligence tests
Achievement tests
Neuropsychological tests
General intelligence theory (Spearman, 1904)
The theory of intelligence that states that one underlying factor of intelligence accounts for different intellectual tasks
Multiple intelligences theory
The theory of intelligence that states that different kind of intelligence exist rather than one singular one.
Hierarchal model of intelligence
The theory of intelligence that states that intelligence is organized into levels which combines general intelligence and multiple intelligences; cognitive abilities are organized in layers which help define the “g”
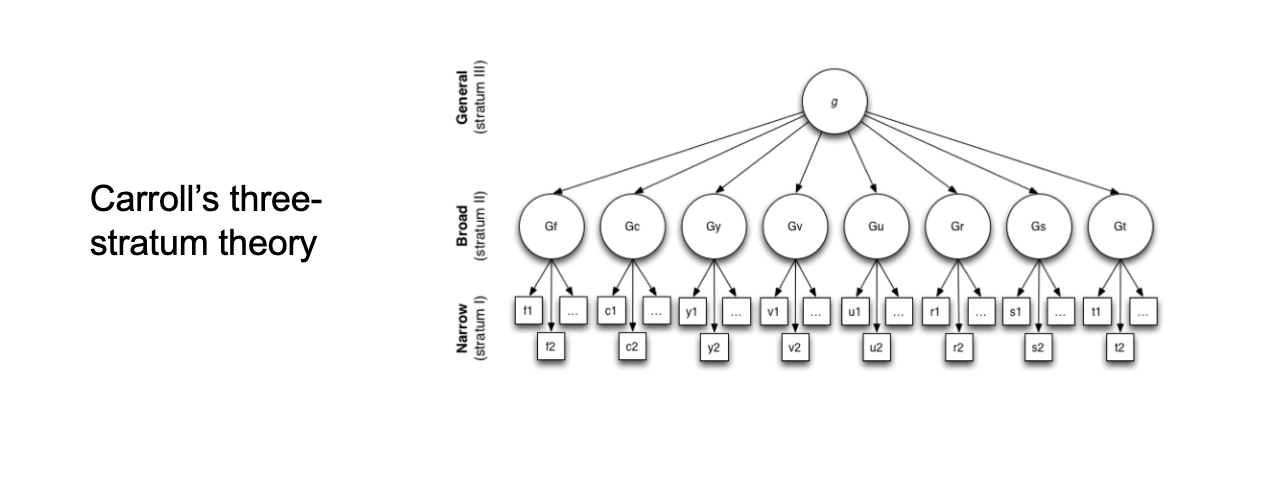
Fluid Intelligence
The ability to solve new problems without relying on knowledge from previous experiences.
Crystallized intelligence
The knowledge that is acquired through one’s own personal skills and experiences.
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)
An IQ test that uses subtests and four different index scores and is designed for adults ages 16-90.
Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC-V)
An IQ test for children ages 5-15 years old that uses subtests and is based on five factor scores.
Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence Fourth Edition (WPPSI-VI)
An IQ test for children ages 2 years 6 months to 7 years 7 months including different index scores.
What are the 4-5 index scores that are on the Wechsler intelligence tests?
Verbal comprehension
Perceptual organization
Working Memory
Processing Speed
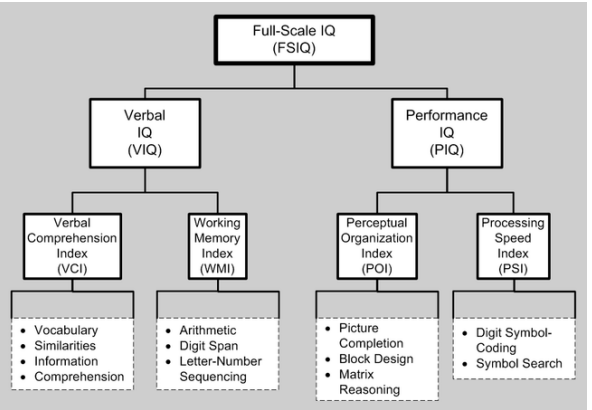
What is the scoring and interpretation of the Wechsler tests?
Full-scale IQ
Index scores
Set of normative data
Stanford–Binet Intelligence Scales
An IQ test that measures overall intellectual ability functioning across the entire lifespan.
How does the Stanford–Binet Intelligence Scales differ from the Wechsler scales?
The Stanford-Binet scale measures across an entire lifespan
Measures both low and high intelligence
Factors/index scores are different
Fluid Reasoning
Knowledge
Quantitative reasoning
Visual-Spatial processing
Working memory