BCS 111 Lecture 13
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Cognitive style
Your preferred ways of solving problems and making decisions
Also associated with personality (e.g., conservative vs. riskier decision)
Can be influenced by external factors (e.g., alcohol, substance abuse)
Cognitive styles
Field-dependent vs. Field independent (FD vs. FI)
When manifested in perceptual processing: Context-dependent vs. Context-independent
When manifested in personality: Dependent vs. Autonomous
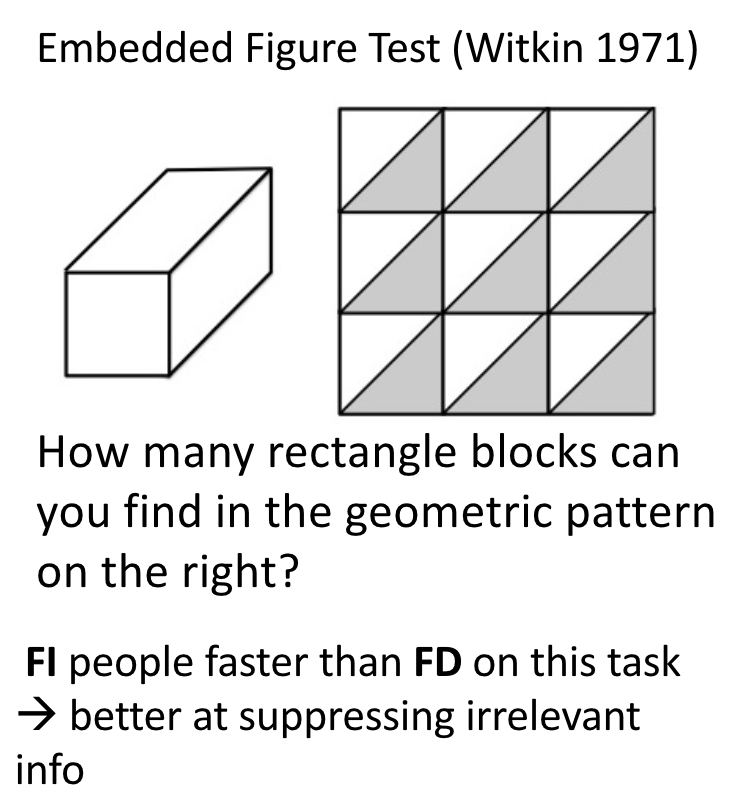
Framed-Line Test: Individual difference in cognitive styles – cultural effect
Contexual information in perception
Cultural differences:
Japanese: field dependent
American: field independent (FI style)
Task: Framed-Line Test (FLT)
Absolute task: re-drawn line should be of the same length as the original
Relative task: keep the same ratio Length of new line / height of new box = Length of the original line / height of the original box
Americans (FI style) should perform better in absolute than in relative task
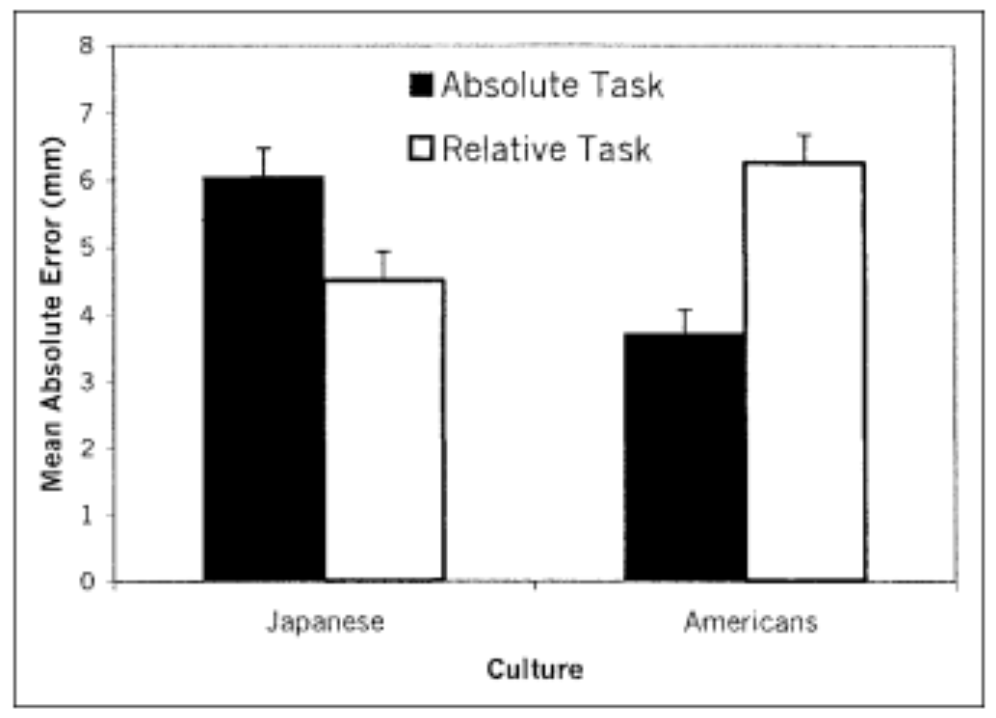
Results
strong cultural effect
Japanese did better in the relative task than in the absolute task → FD style (context-dependent)
Opposite pattern for Americans → FI style (context-independent)
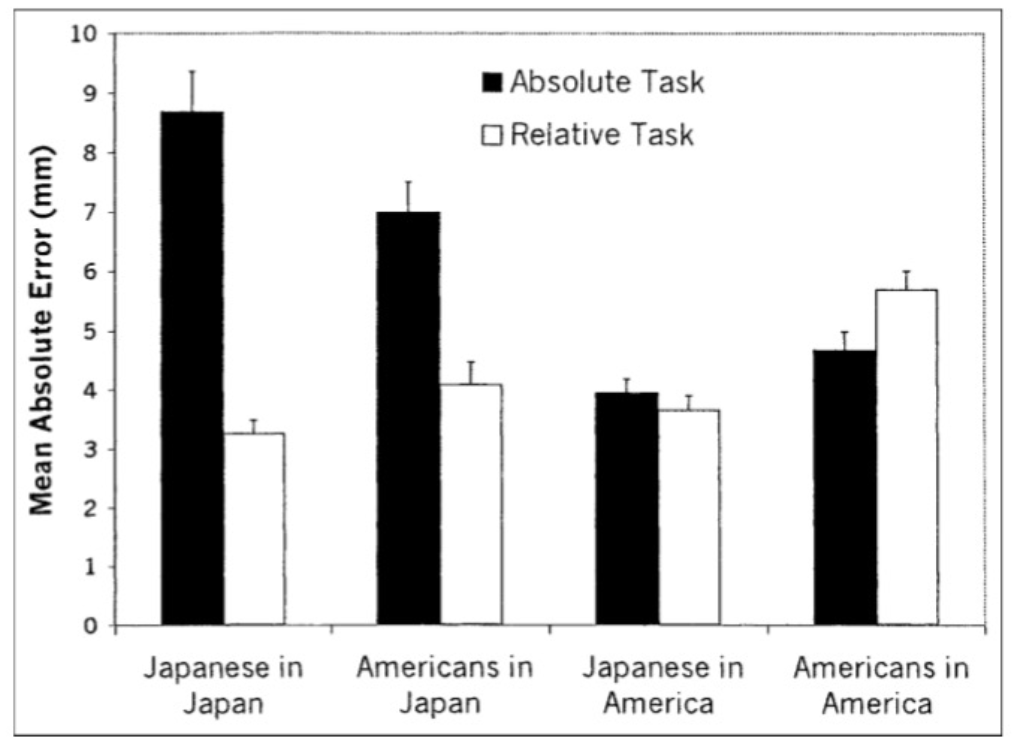
Results (experiment 2)
Location/environment also matters!!
Americans in Japan perform more like Japanese.
Japanese living in the US perform less similarly to those living in Japan
Reflectivity
careful in making decisions (slow but more accurate)
Impulsivity
fast but lots of errors
Cognitive styles
Matching Familiar Figure Test
Measurement: The time it takes to give the first response
Fast but inaccurate resp: impulsivity
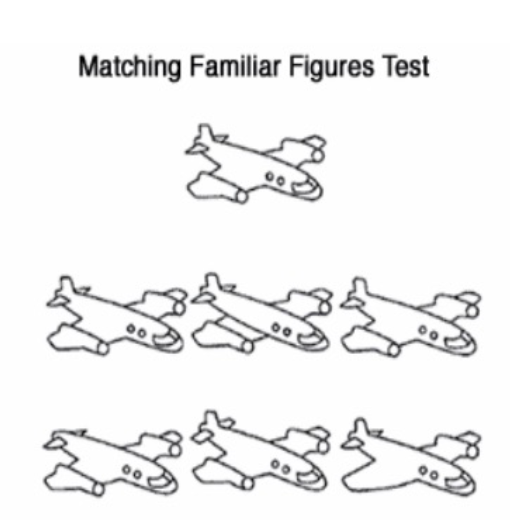
Reflectivity/Impulsivity
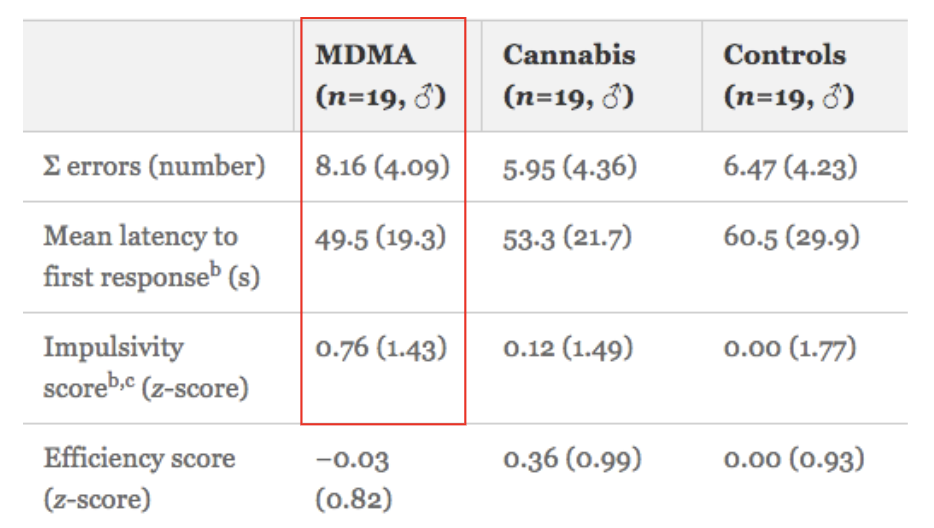
Substance users vs. Control group in Matching Familiar Figure Test:
MDMA users made a lot more errors but faster responses than the other two groups → Evidence for impulsivity
Cognitive styles
Reflectivity/Impulsivity assessed by Matching Familiar Figure Test
BUT: Does it only measure reflectivity and impulsivity?]
What else does it measure?
What else does the matching familiar figure test measure?
What else does it measure?
Visual search/perception
Attention
Decision making
Search strategy: self-terminating vs. exhaustive
Similar to memory search
Cognitive aging: one example – decline of inhibitory control in bilinguals
Inhibitory control: being aware of the stimulus change and shift attention accordingly
Cognitive aging in bilinguals: one
example - inhibitory control
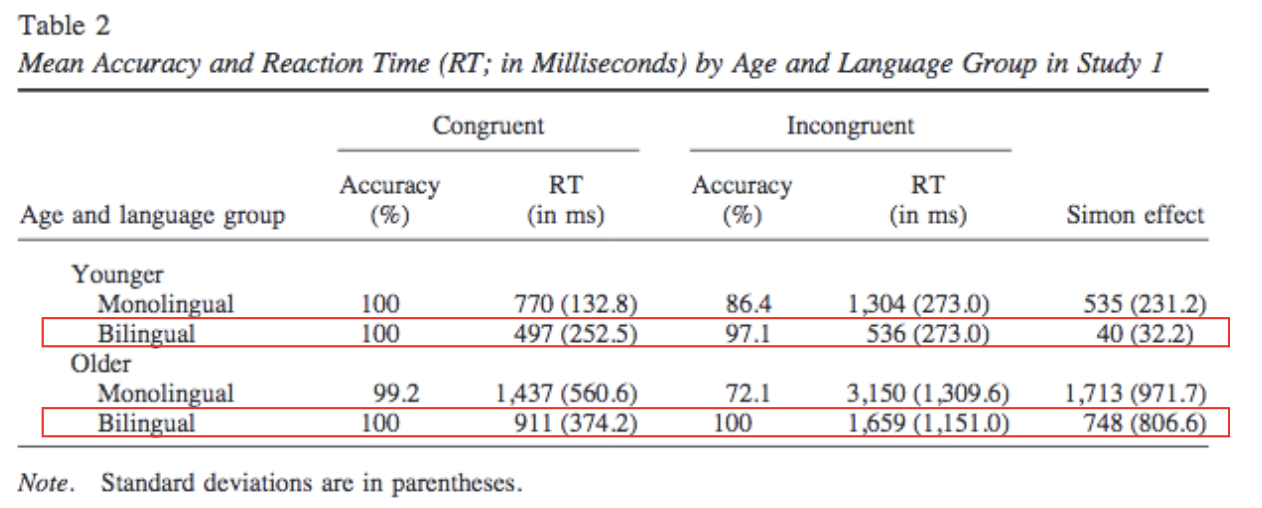
Summary of Simon Task
Ss see one dot on the screen each time.
The dot on either left of right edge
If Red dot, press their right-hand key
If Blue dot, press their left-hand key (Respond based on colors, not location!)
Two conditions:
Congruent: red dot on right edge
Incongruent: red dot on left edge → inhibitory control required
Cognitive aging in bilinguals: one example - inhibitory control
Simon effect = RT (incongruent) – RT (congruent)
Large effect indicates poorer inhibitory control
Simon effect (old) > Simon effect (young): poorer inhibitory control in the older groups
Monolinguals experience even larger Simon effect than bilinguals!
One cognitive benefit of bilingualism
Cultural influence on cognition
Is everything in our cognition influenced by our culture?
Cultural relativism
cognitive processes influenced by culture (e.g., categorization, cognitive styles)
Cultural universality
cognitive processes independent of culture (e.g. sensory processing)
How culture influences cognition
To name just a few:
Cognitive styles
Object recognition
Perception and categorization
Counting…etc.
Cultural differences in categorization
-
Categorization
Knowledge-based categorization
Cultural and educational influence on
knowledgeHow do you categorize “Hat, gloves, sunglasses”?
Prototype and exemplars
What’s your prototype of sea cucumber if
you’ve never seen it?
Cultural influence on counting
But Oksapmin (a language spoken in Papua New Guinea) uses 27 body parts for counting!!!
Oksapmin children’s development of counting turns out to be later than American children.
Can also be explained by “conditioning”!
Support cultural relativism
And don’t forget…language is also part of our culture!!
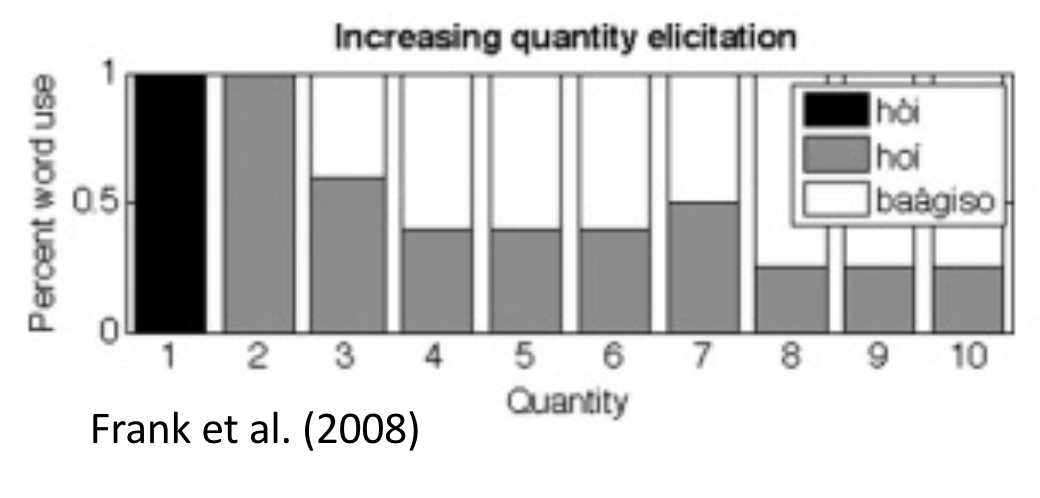
The Pirahã counting system has 3 words: 1, 2 and many
Supports both linguistic relativism and cultural relativism!
Summary: Individual differences
Individual differences can result from cognitive styles, cognitive abilities, cognitive aging, as well as cultural influences.
Simon task: inhibitory control task
Cultural impact on cognition: cultural universality and cultural relativism