Science- Sexual Reproduction
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Meiosis
-Cell division for production of egg or sperm cells for sexual reproduction
-a diploid cell divides twice to produce four haploid cells and the four cells contain half the amount of genetic material
-diploid means two sets of chromosomes (X), haploid means one set of chromosomes (/)
-diploid is 2(n) meaning 2 multiplied by one set of chromosomes or one, haploid is n meaning one set or one and the n is what you multiply by 2 to make it diploid. Haploid also means half the total of chromosomes in the original cell so if there was 4 chromosomes in one cell (diploid) and now in the end there are 2 cells with 2 chromosomes it is haploid.
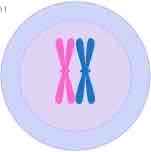
meiosis one, prophase
-chromosomes are shown to be close together, will soon separate
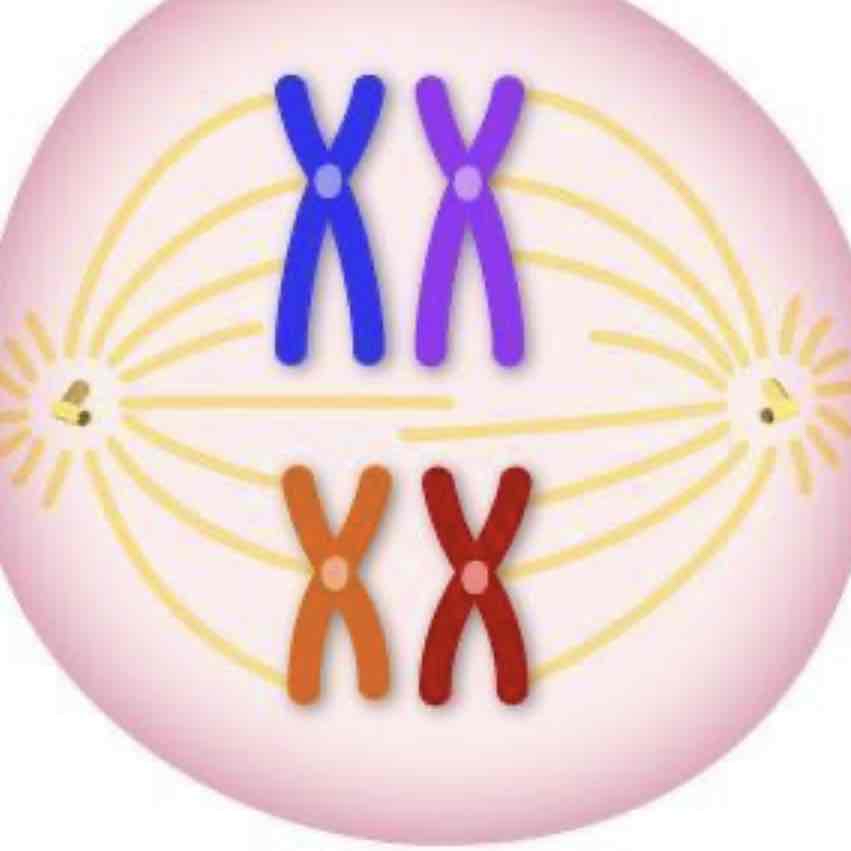
meiosis one, metaphase
-chromosomes are separated and now align with each other or lined up in the middle
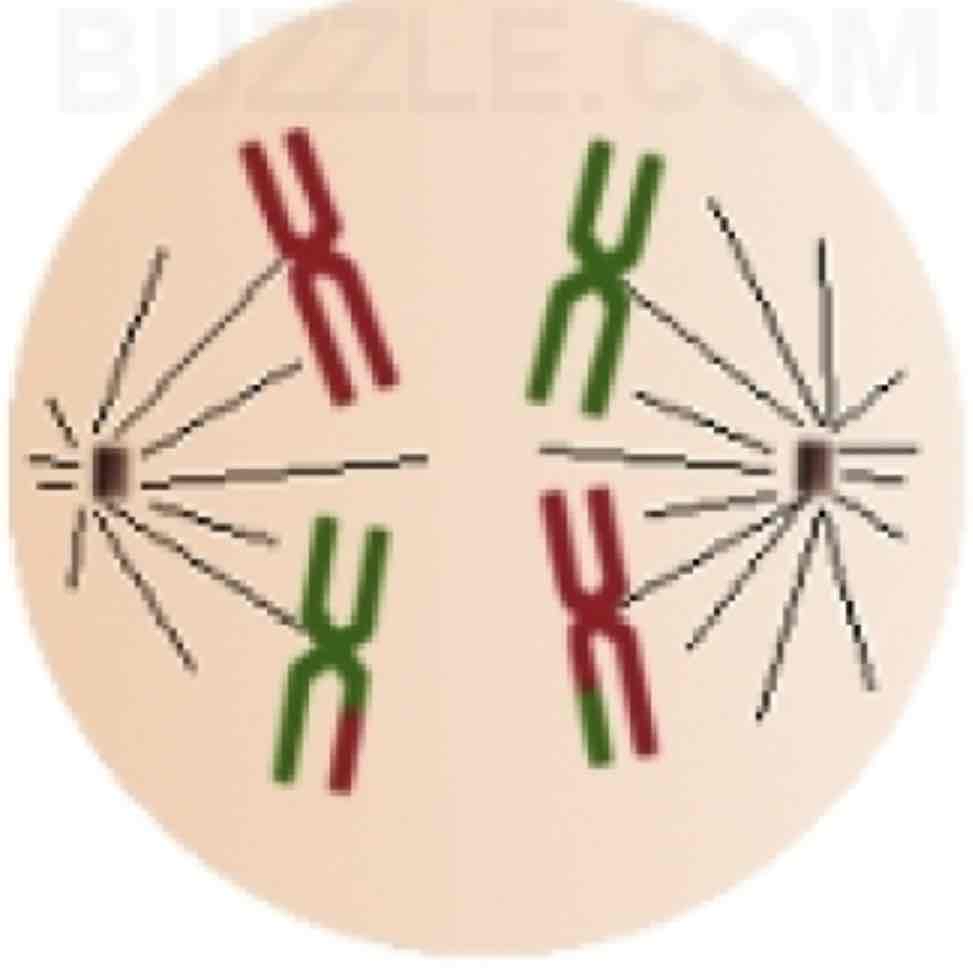
meiosis one, anaphase
-chromosomes are apart and move away from each other to different ends of the cell
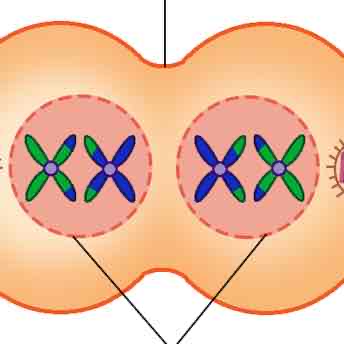
meiosis one, telophase
-nucleus around chromosomes in each side, cell separates into two daughter cells
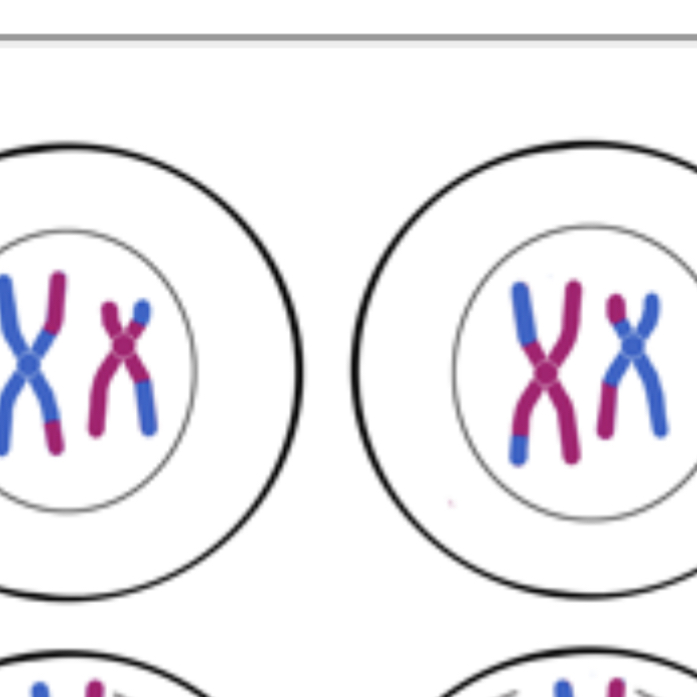
meiosis two, prophase
-shows that there are 2 daughter cells with 2 groups of chromosomes
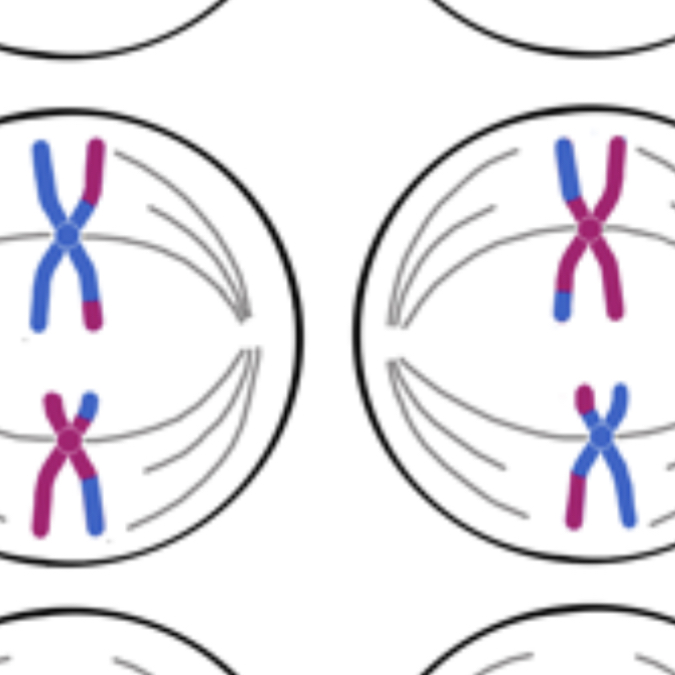
meiosis two, metaphase
-the chromosomes in each cell line up in the middle
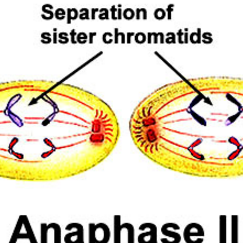
meiosis two, anaphase
-separation of the chromatids (two halves of a chromosome) and each thread goes to different sides of the cells (this goes for both daughter cells)
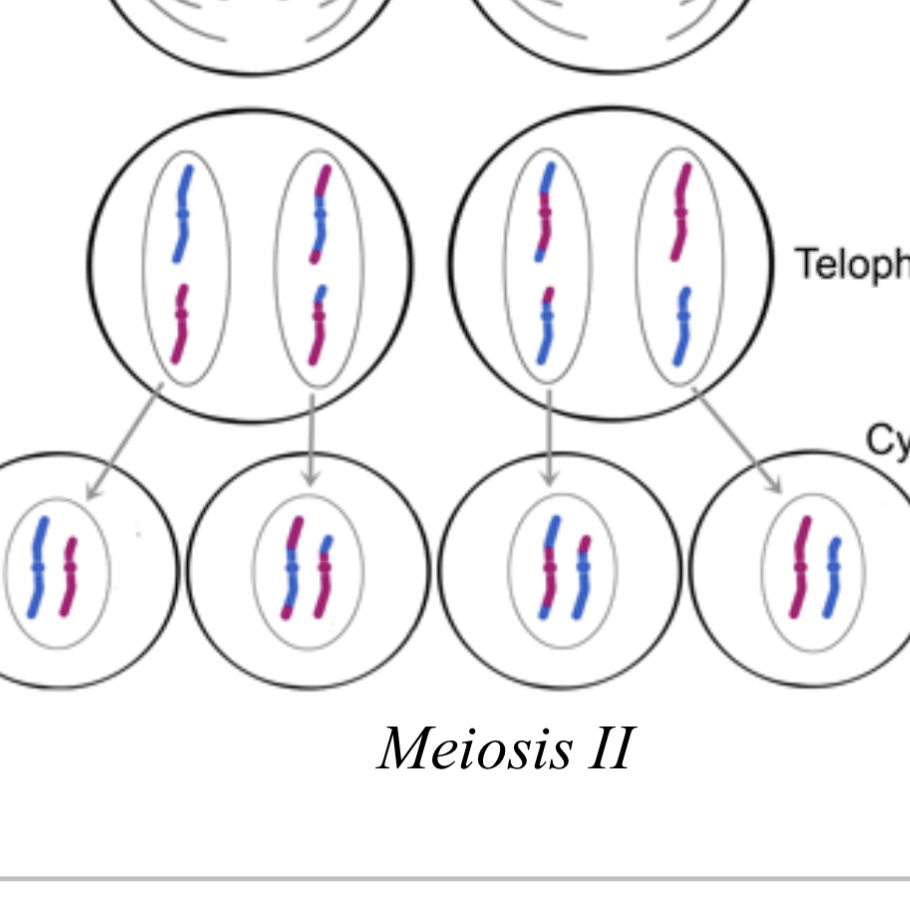
meiosis two, telophase
-cell divides into 4 daughter cells (each haploid cells since it contains half of the original amount of chromosomes)
Gametes
-organism’s reproductive cells
-these cells are haploid because the cells contain one copy of each chromosome
-female gametes=egg cells
-male gametes=sperm cells
-these get produced from meiosis
Development
-sperm and egg cells meet forming a zygote (diploid since sperm and egg cells are haploid and they were joined together)
-Embryonic development takes place during the first eight weeks after fertilization. During this time, the embryo develops. Its cells divide constantly, and tissues and organs form. During the first week, the single fertilized cell, the zygote, develops into a mass of many cells. This mass of cells then hollows out and is called a blastula. The cells of the blastula are embryonic stem cells. All tissues and organs will develop from these cells.
-During the second week, the blastula cells become organized into three distinct layers of cells. The outer layer is called the ectoderm. The middle layer is called the mesoderm. The inner layer is called the endoderm. The illustration on the next page shows which organs and body structures are formed from the cells of these layers. The development of organs and body structures from these cell layers is called differentiation.
-After the first eight weeks of development, the embryo is called a fetus. During fetal development, the organs and parts of the body continue to develop. The body adds a great deal of mass. At birth, the human baby is made up of trillions of cells.
First trimester
-Brain and spinal cord are forming. (4weeks/4mm fetus)
-Digits have appeared. Ears, kidneys, lungs, liver, and muscles are developing. (8weeks/4cm fetus)
-Sexual differentiation almost complete. (12weeks/9cm fetus)
Second trimester
-Fetal movements are felt. (16–18 weeks/20cm fetus)
-Eyelids open. Fetus can survive outside of the mother with specialized care. (24weeks/35cm fetus)
Third trimester
-Rapid weight gain occurs due to the growth and accumulation of fat. (26-38weeks/40-50cm fetus)
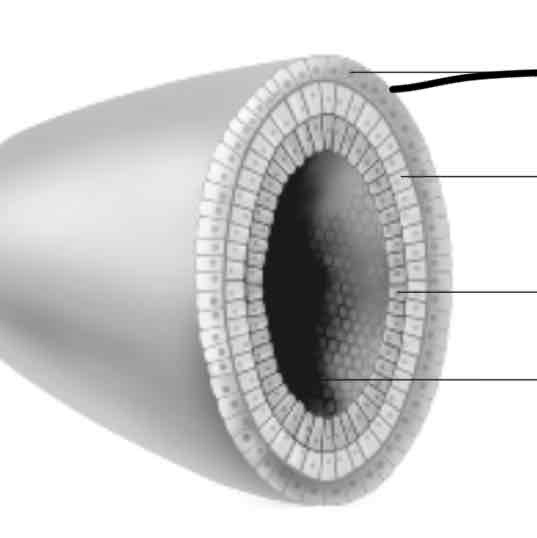
Blastula cells in layers (ectoderm)
-forms the skin and nervous system
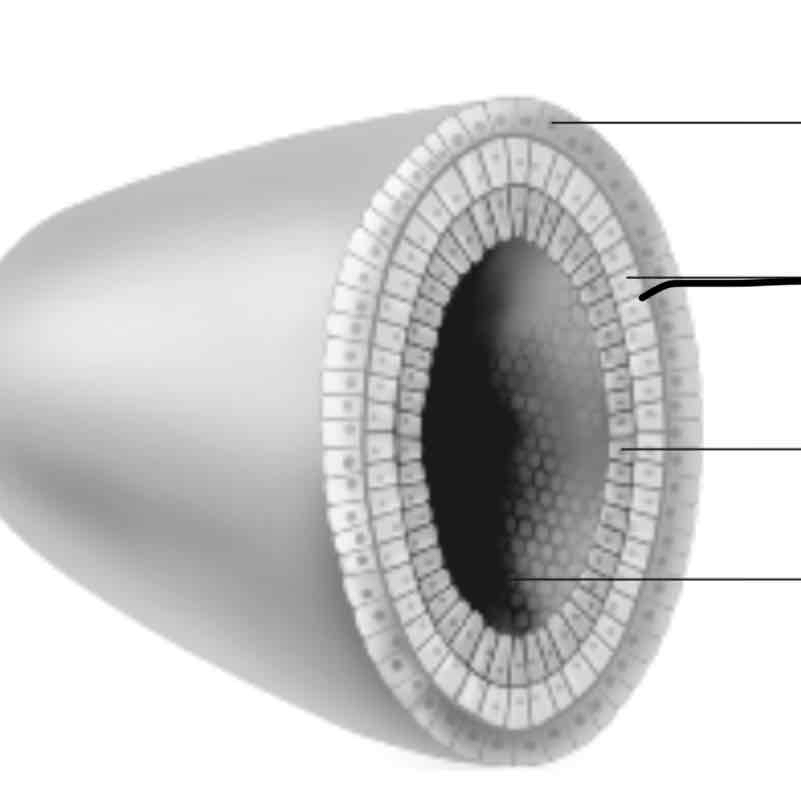
mesoderm
-forms the kidneys, skeleton, muscles, blood vessels, and reproductive organs
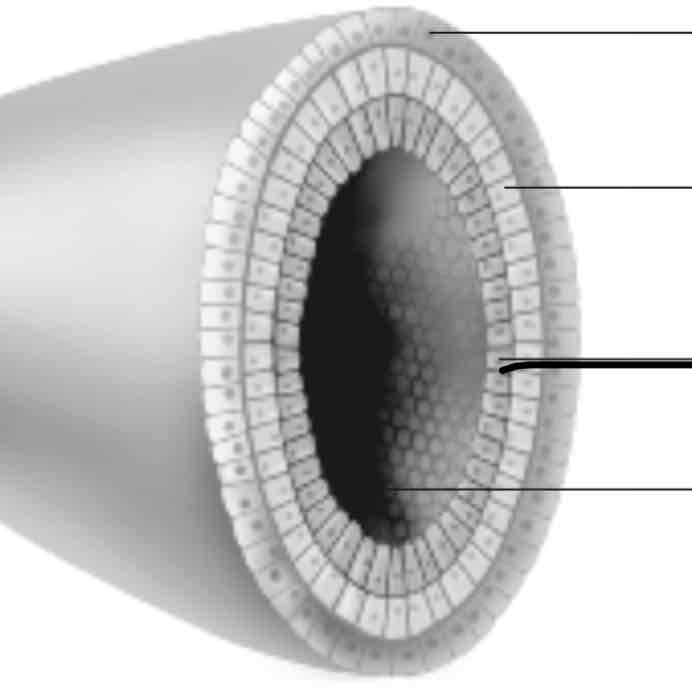
endoderm
-forms the lungs, liver, and lining of the digestive system
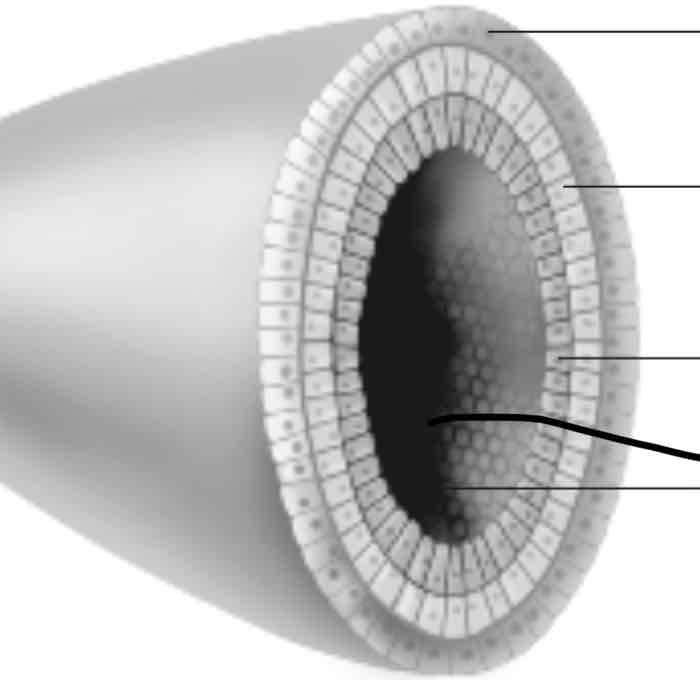
hollow centre
-hollow centre
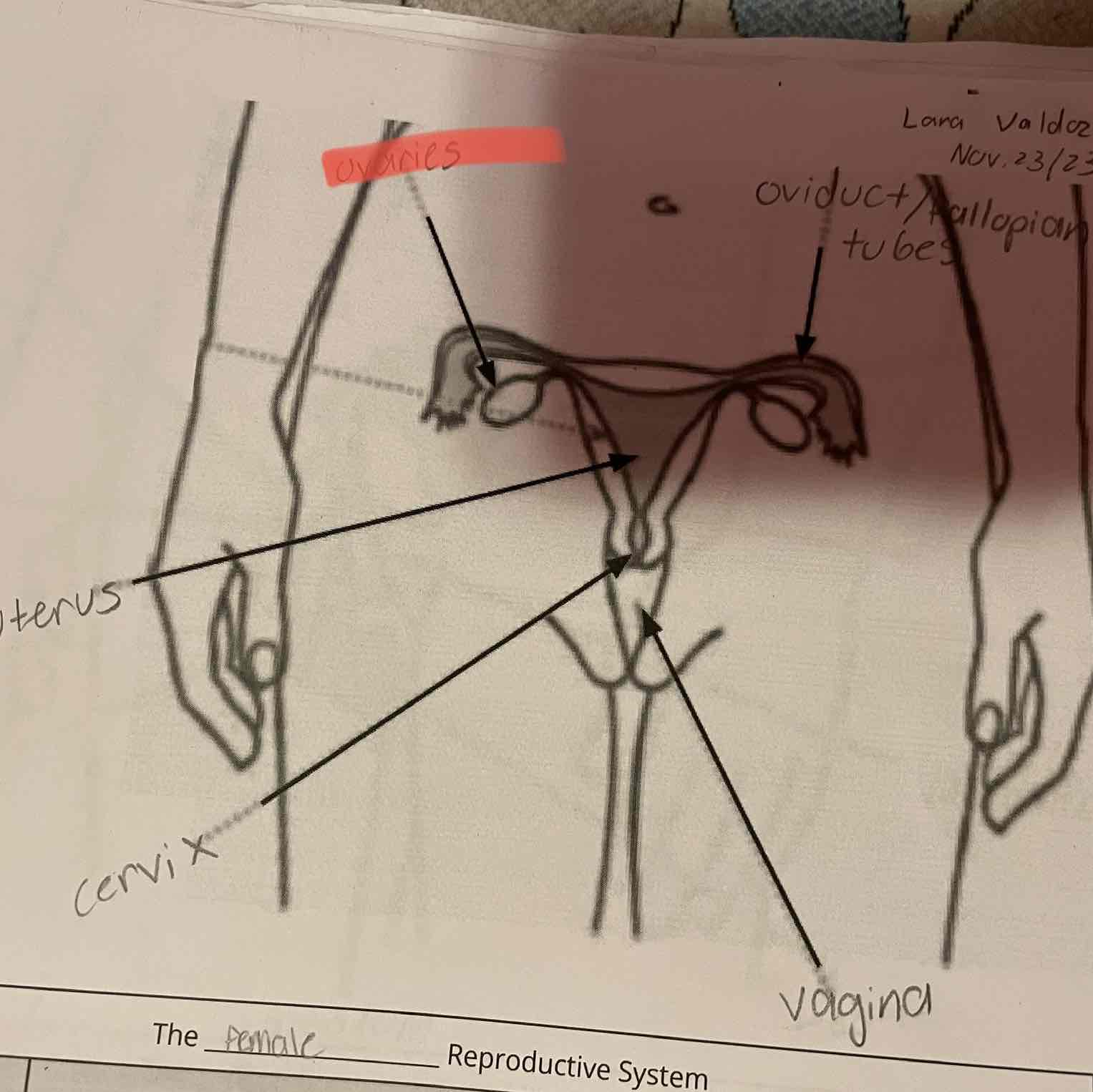
Female reproduction system, ovaries
-Produce eggs (female gametes) by meiosis and release hormones.
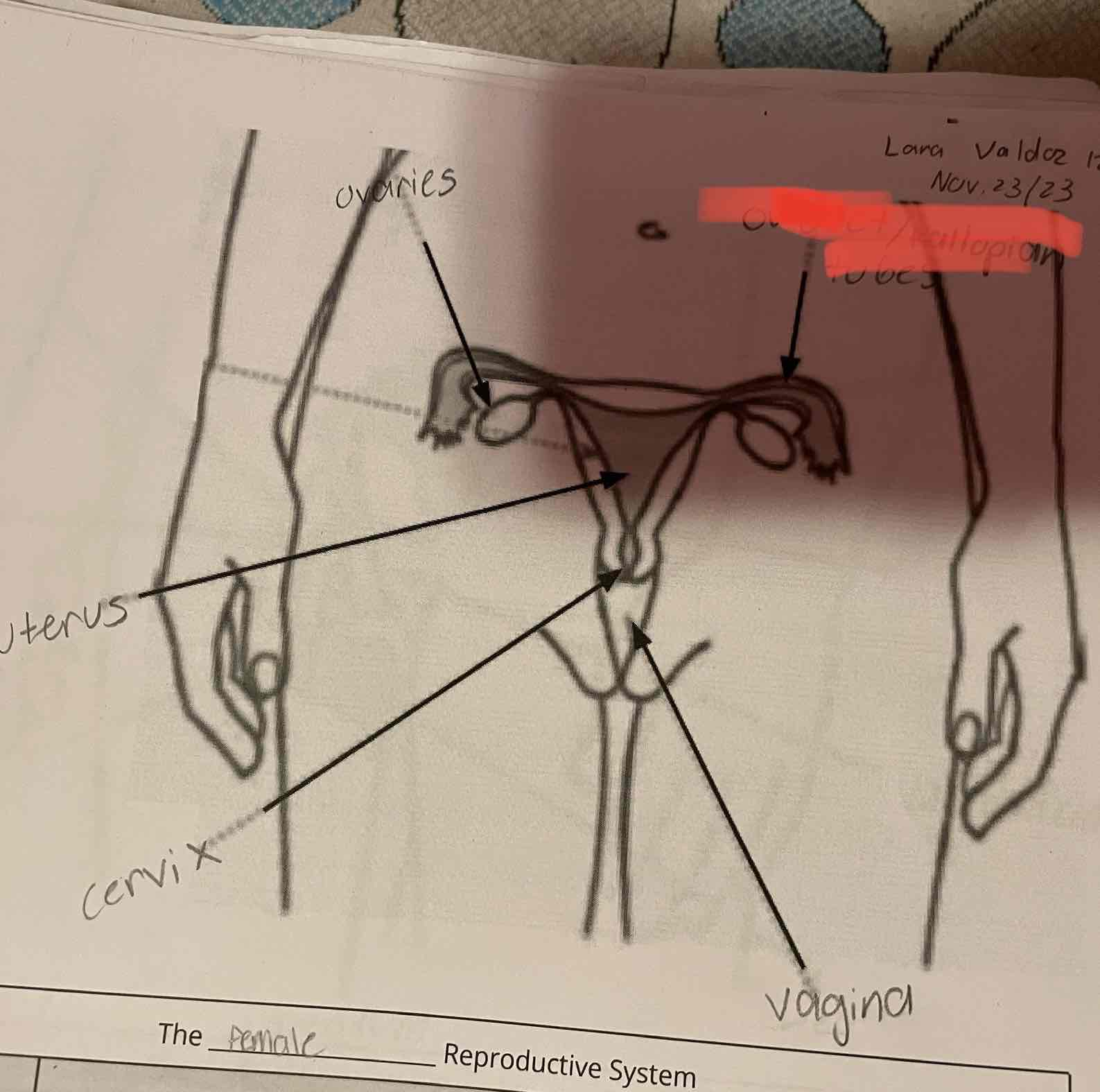
Oviduct/fallopian tubes
-Location of fertilization. Connect the ovaries to the uterus, although the oviducts are not physically connected to the ovaries.
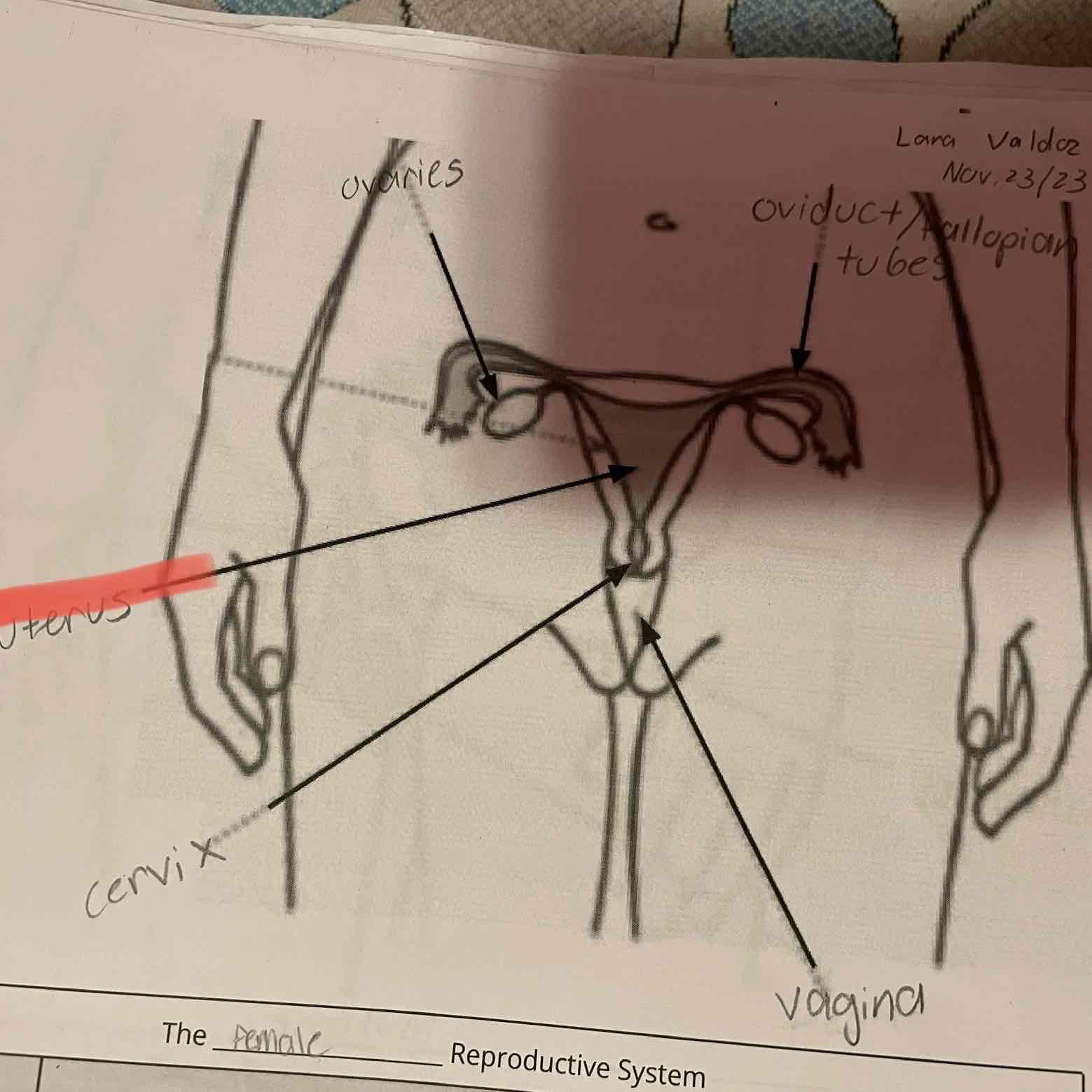
Uterus
-Protects and nourishes the zygote during development.
-Connects the oviducts to the cervix.
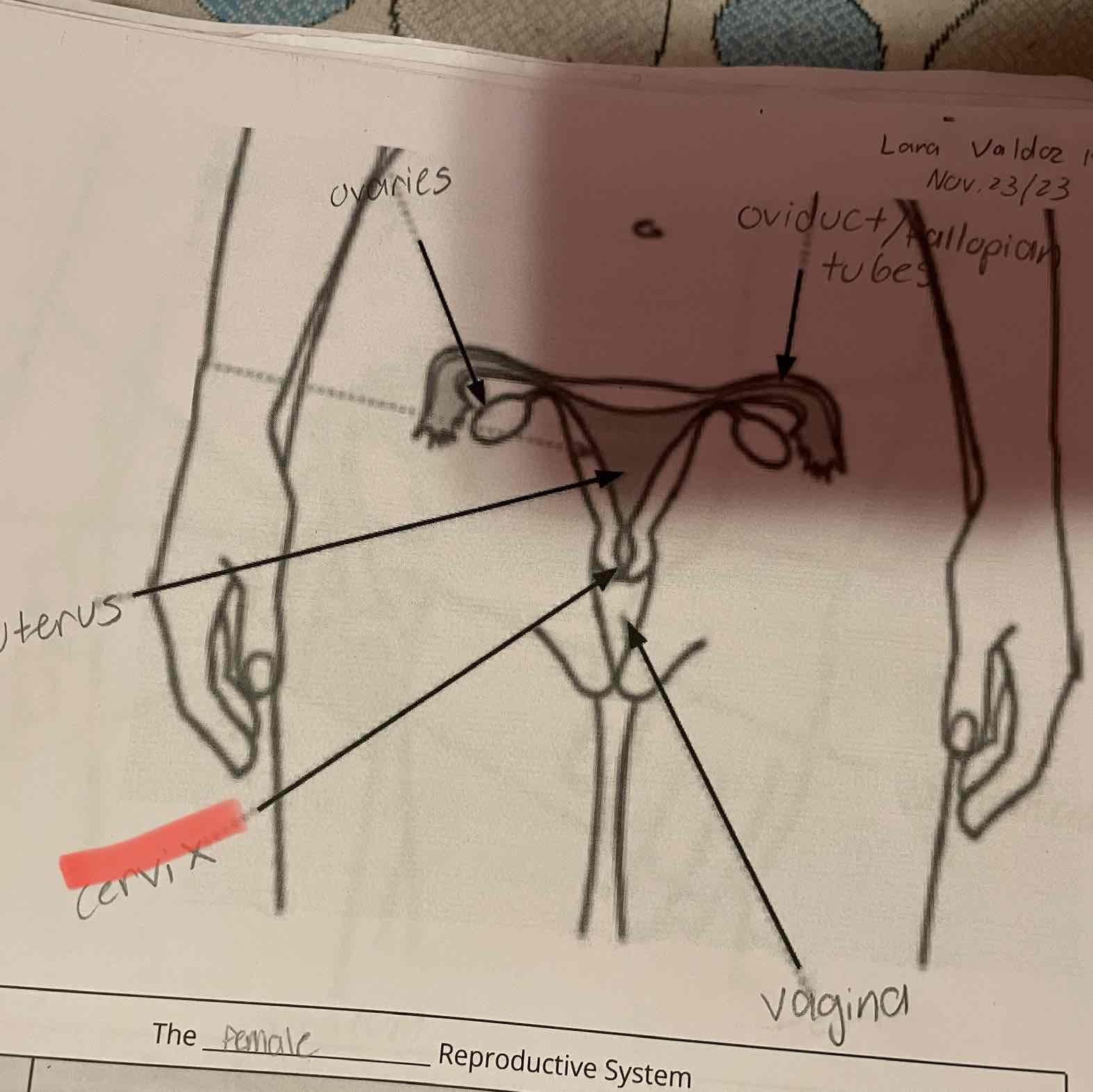
Cervix
-Sperm travel through this opening on the way to the uterus. Dilates (opens) to allow the baby to leave the body during childbirth.
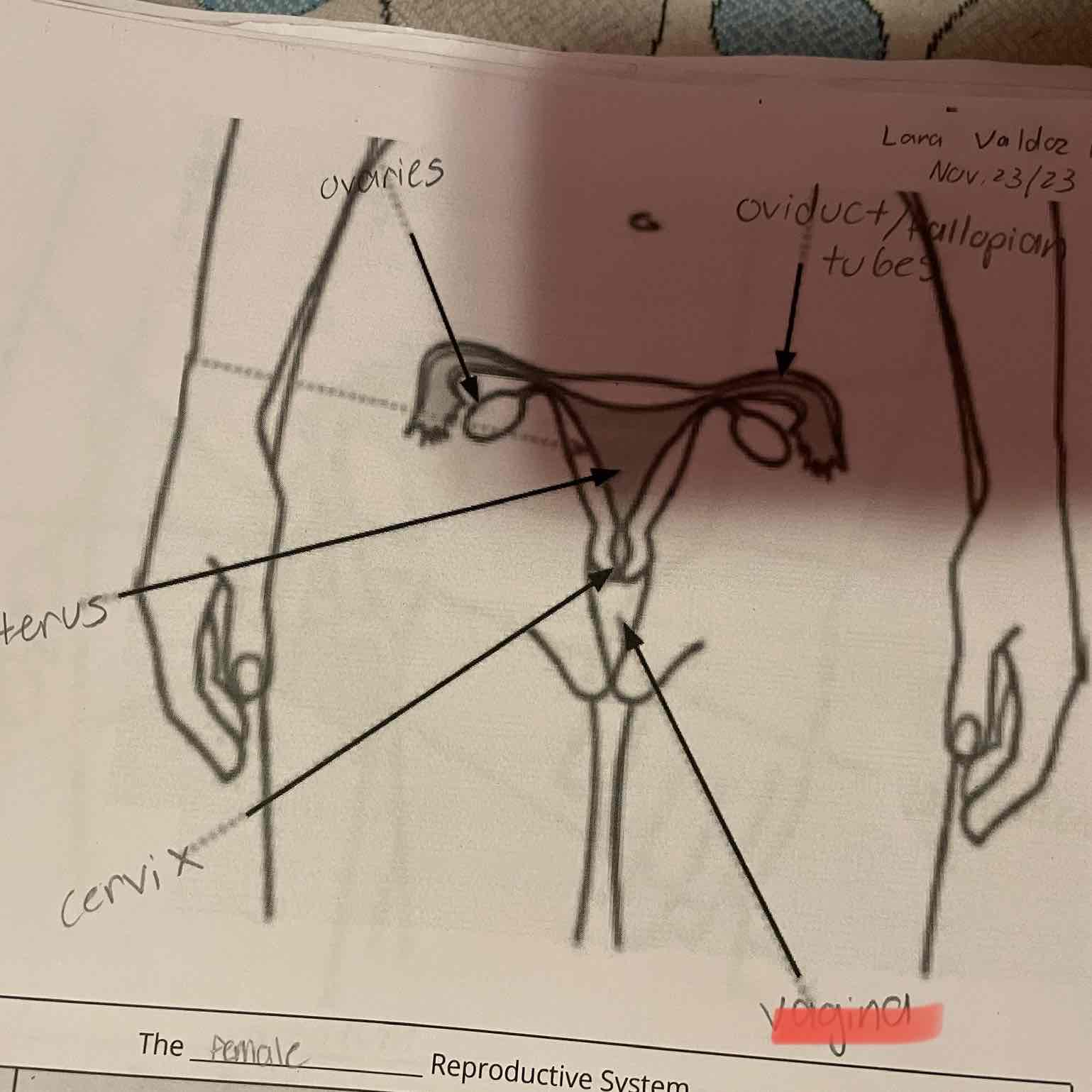
Vagina
-Sperm are deposited here, their first stop on the way to the egg. Opening through which the baby leaves the body, or through which unfertilized eggs leave the body.
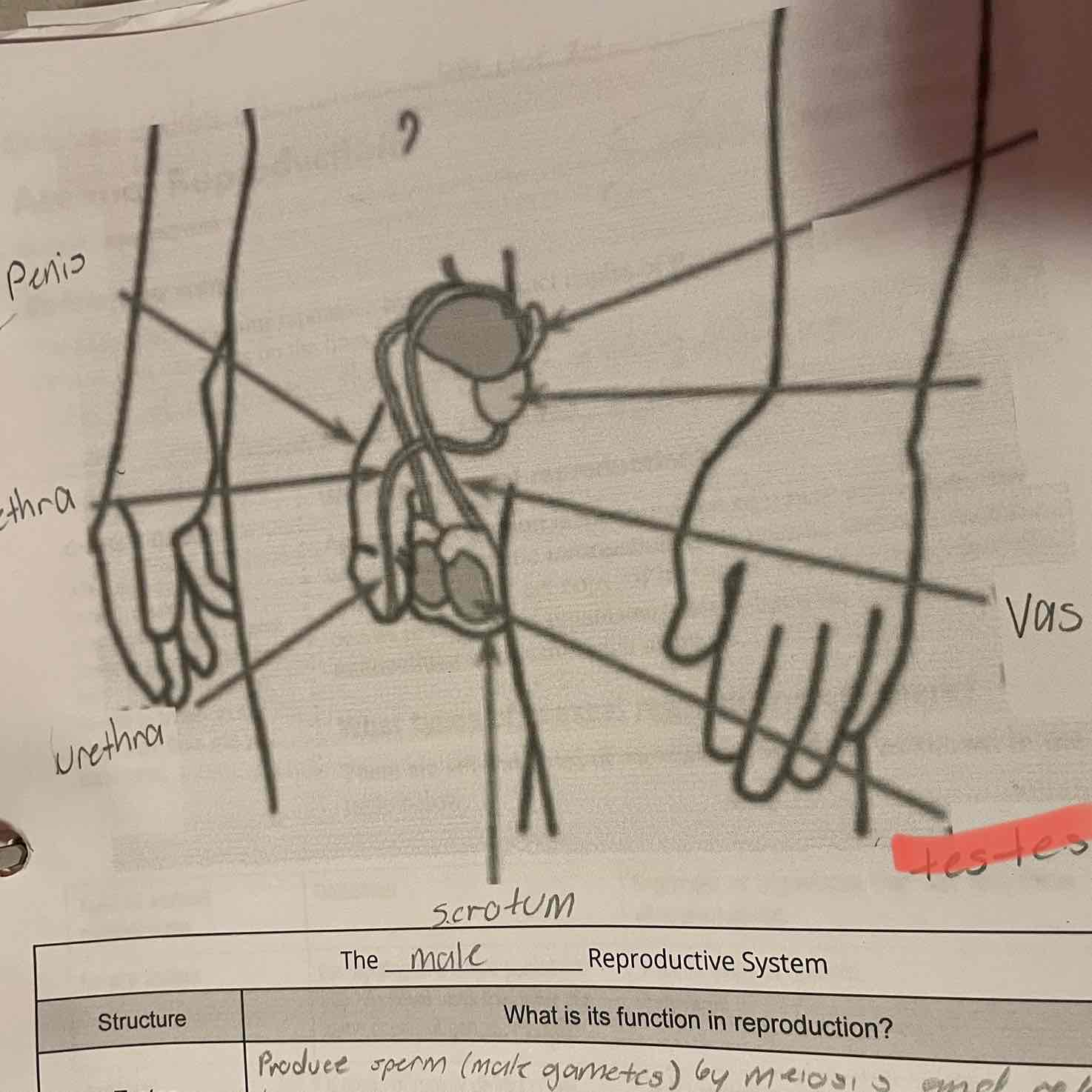
Male reproduction system, testes
-Produce sperm (male gametes) by meiosis and release hormones.
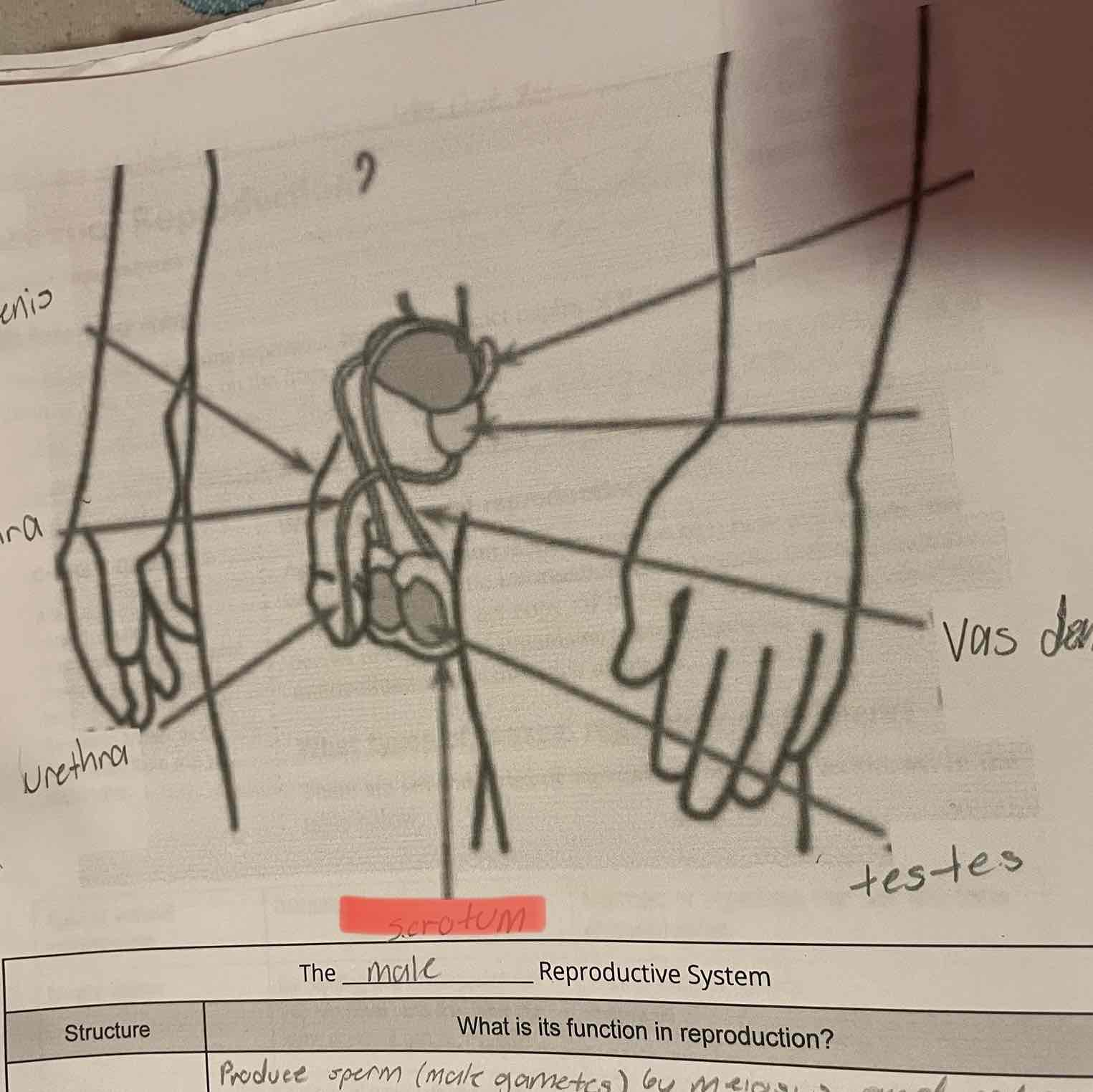
Scrotum
-Protects the testes, maintaining them at a cooler temperature than the body core.
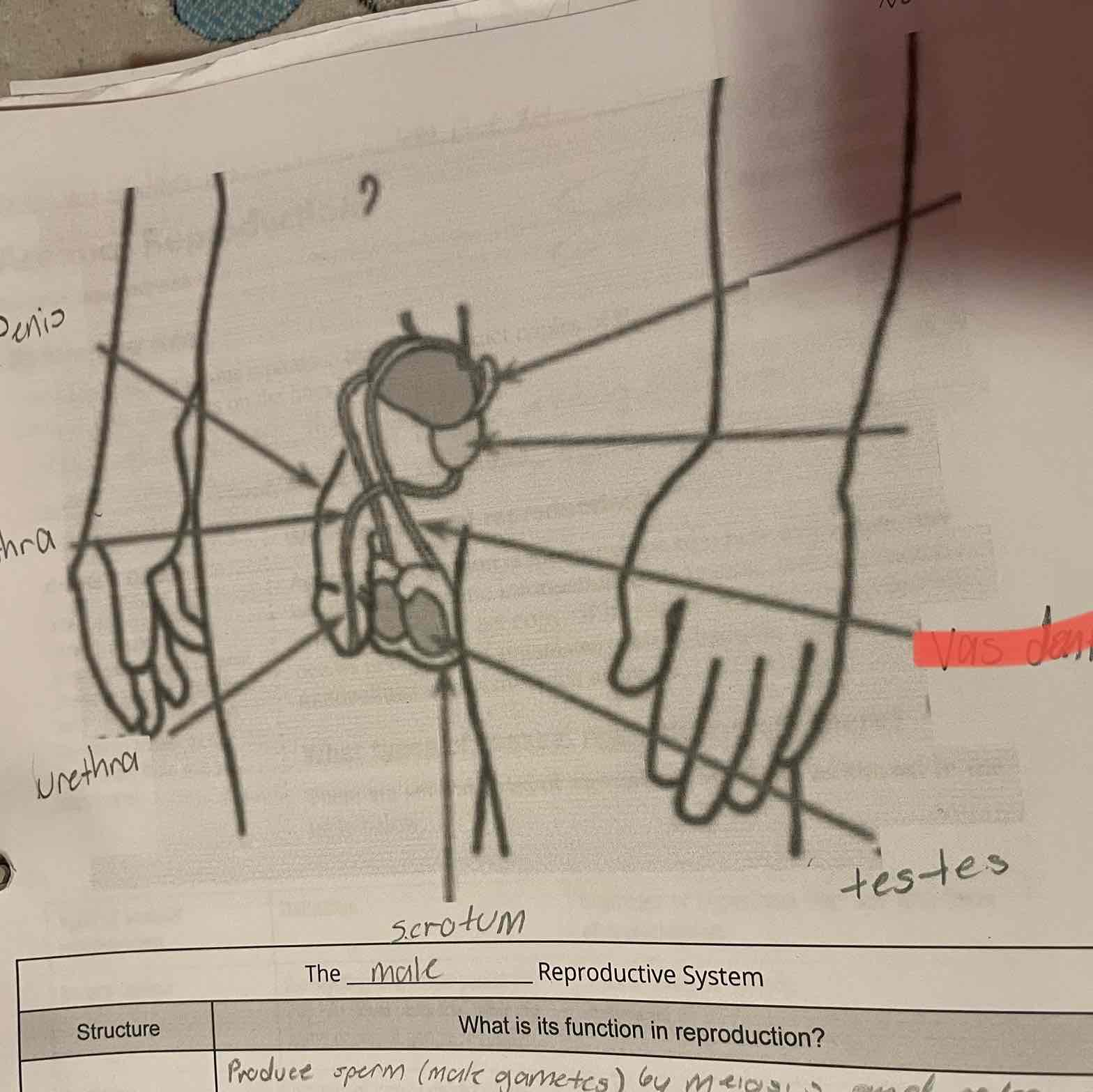
Vas Deferens
-Muscular tubes in which sperm mix with fluids to form semen as the sperm are moved from the testes to the urethra. Can house sperm for several months.
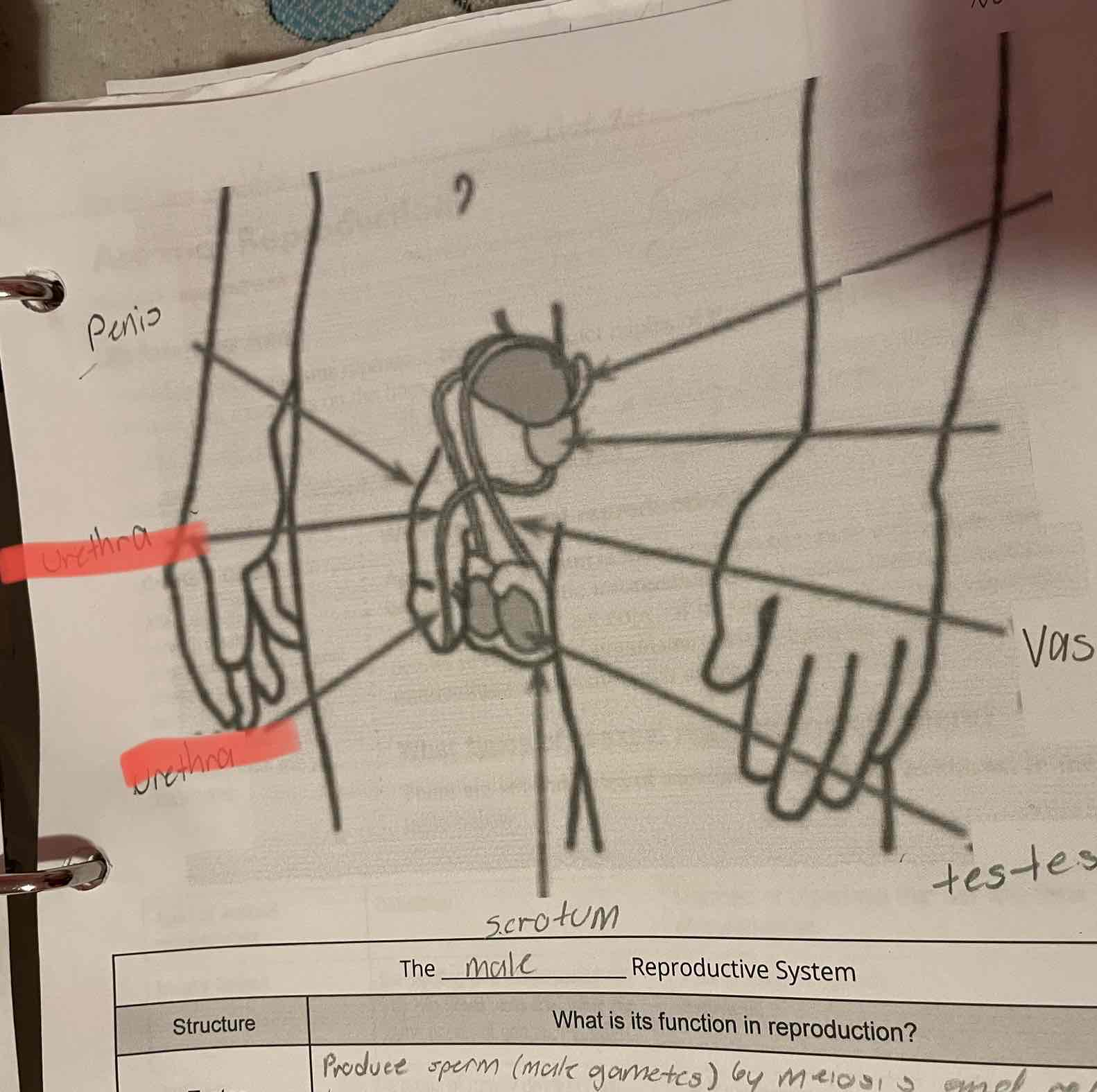
Urethra
-Opening through which sperm leave the body.
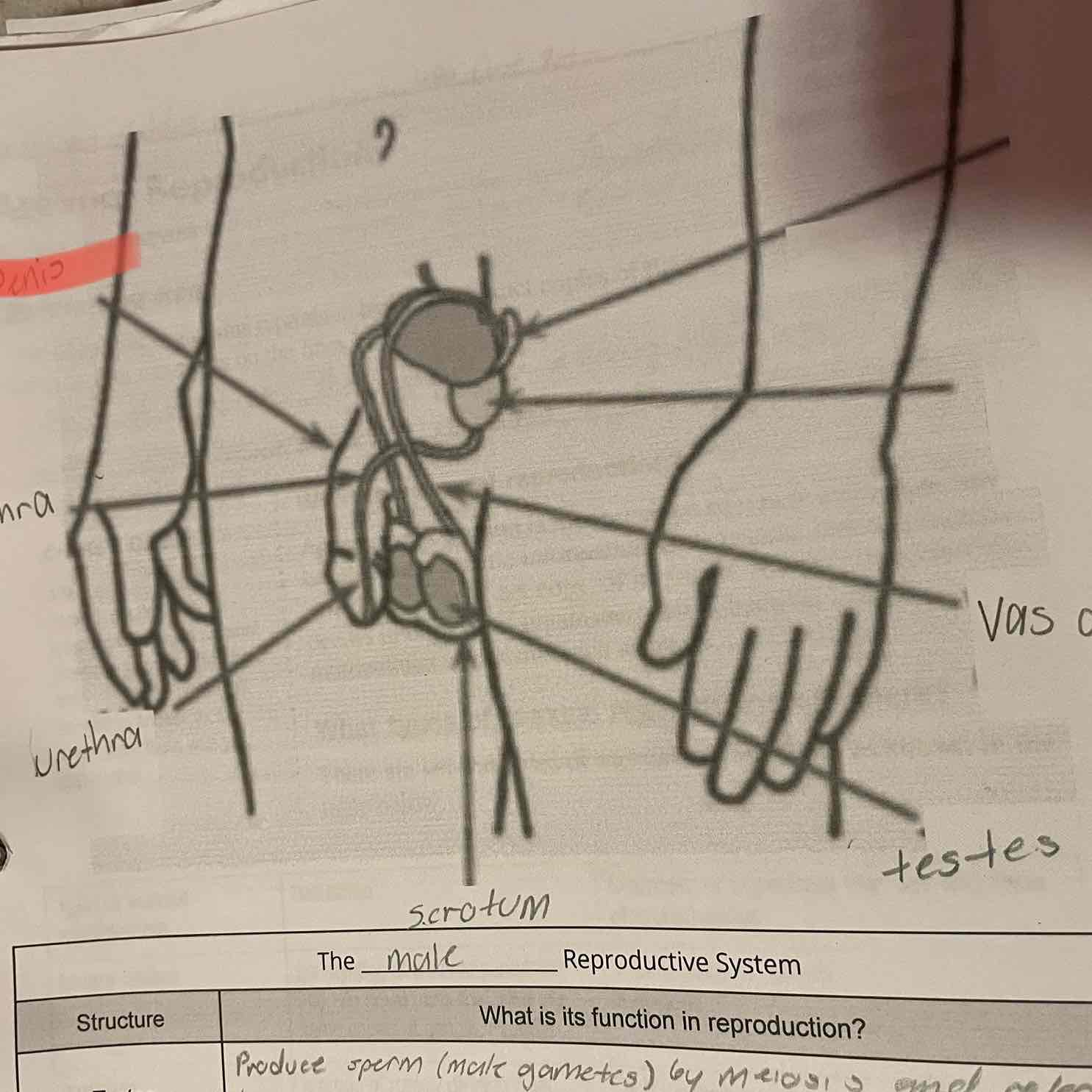
Penis
-Contains the urethra for delivery of sperm.
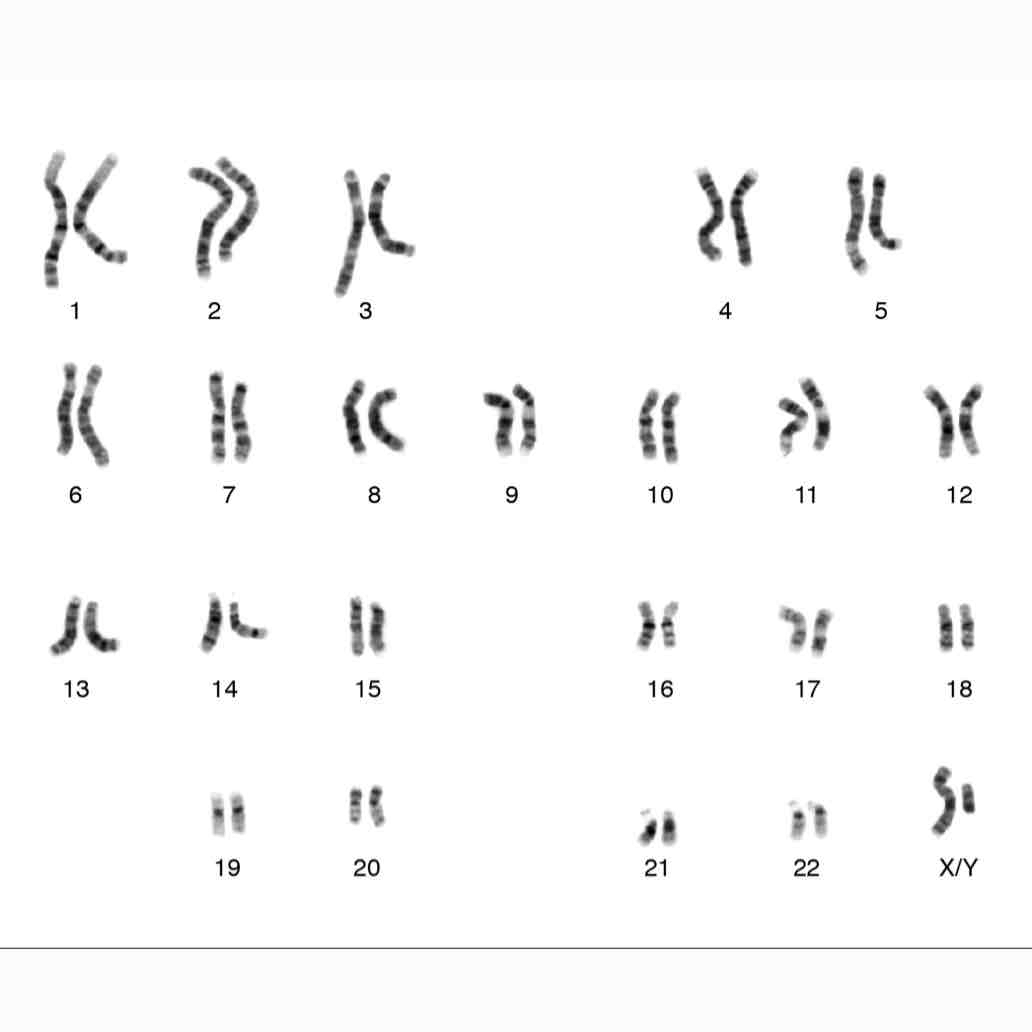
Karyotypes
-A karyotype is a procedure or visual that analyzes size, shape, and number of chromosomes and to find problems.
-to find out gender of organism through a karyotype, remember XY=male XX=female
What gender is this (karyotype)?
-male because XY chromosomes
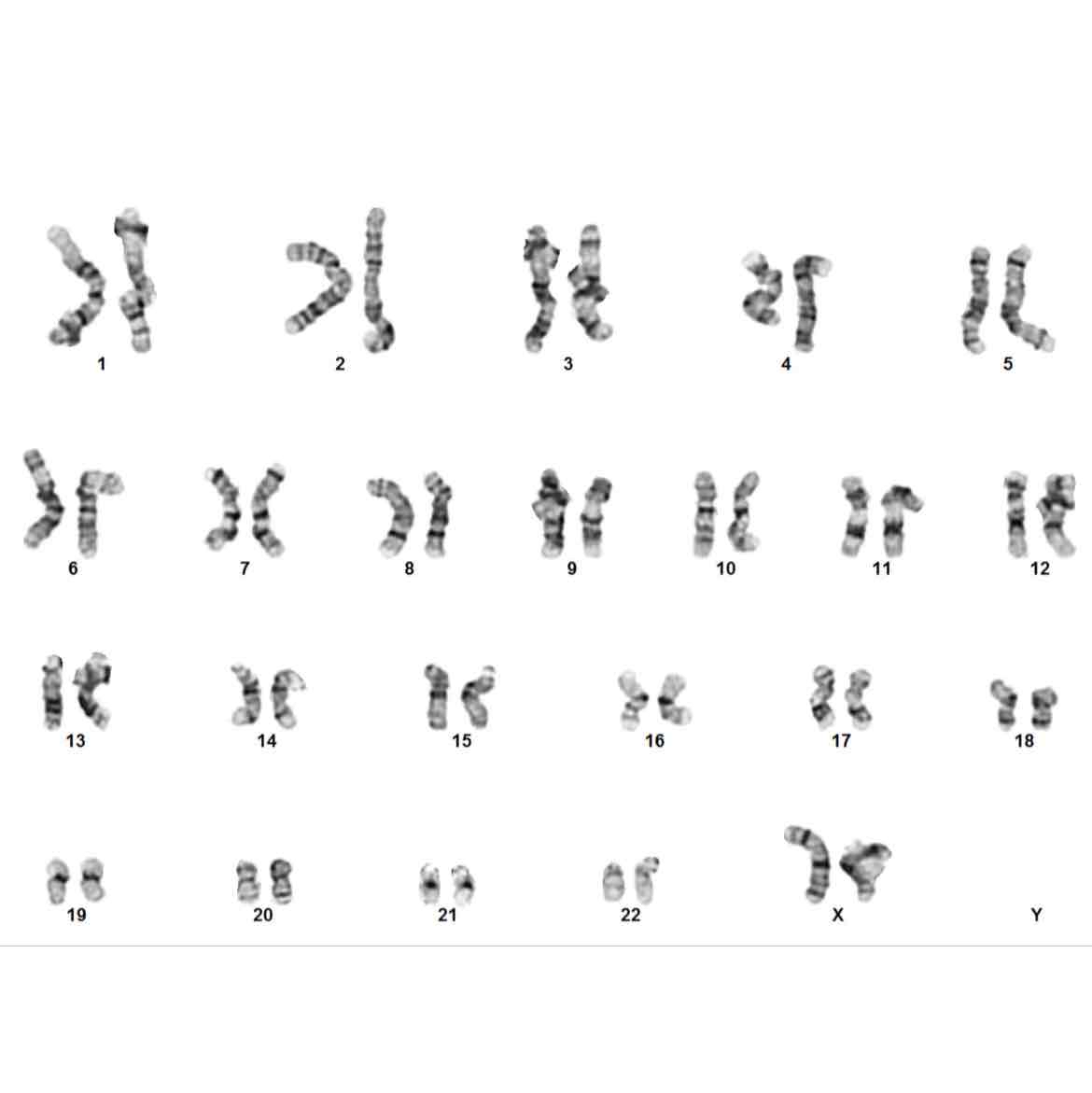
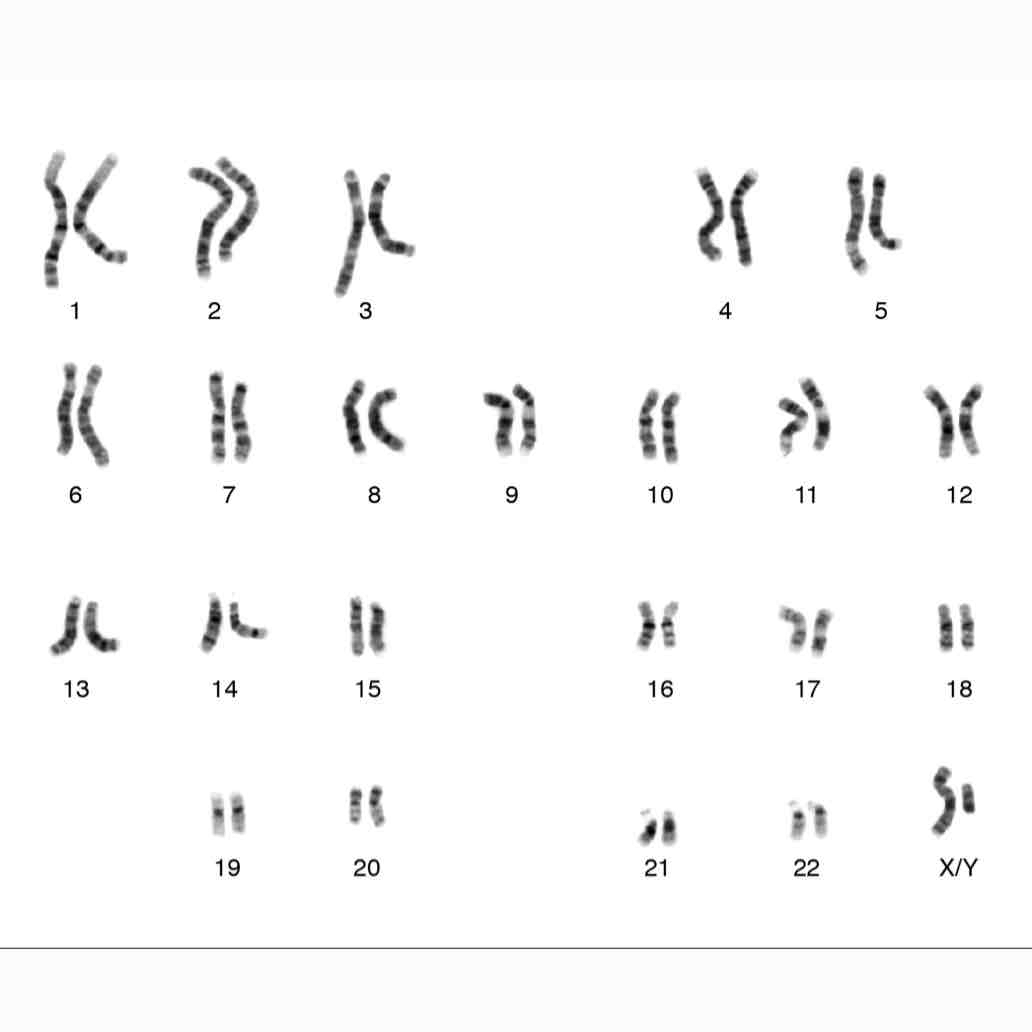
What gender is this (karyotype)?
-female because 2 X chromosomes
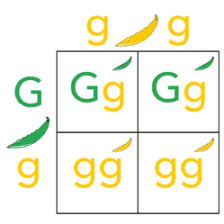
Punnet square and genotypes and phenotypes
-The Punnett square is a table in which all of the possible outcomes for a genetic cross between two individuals with known genotypes are given. In its simplest form, the Punnett square consists of a square divided into four quadrants.
-A person's genotype is their unique sequence of DNA. More specifically, this term is used to refer to the two forms a person has inherited from their mother and father, for a particular gene. Phenotype is the observable expression of this genotype, a person's presentation.
-each square in the punnet square is 25% when calculating percentage
What is the possibility?
Let's say that in seals, the gene for the length of the whiskers has two alleles.
The dominant allele (W) codes long whiskers and the recessive allele (w) codes for short whiskers.
What is the probability of producing offspring that have short whiskers from a cross of two long-whiskered seals, one that is homozygous dominant and one that is heterozygous? Show your work on the punnett square.
-50% short whiskers
-50% long whiskers
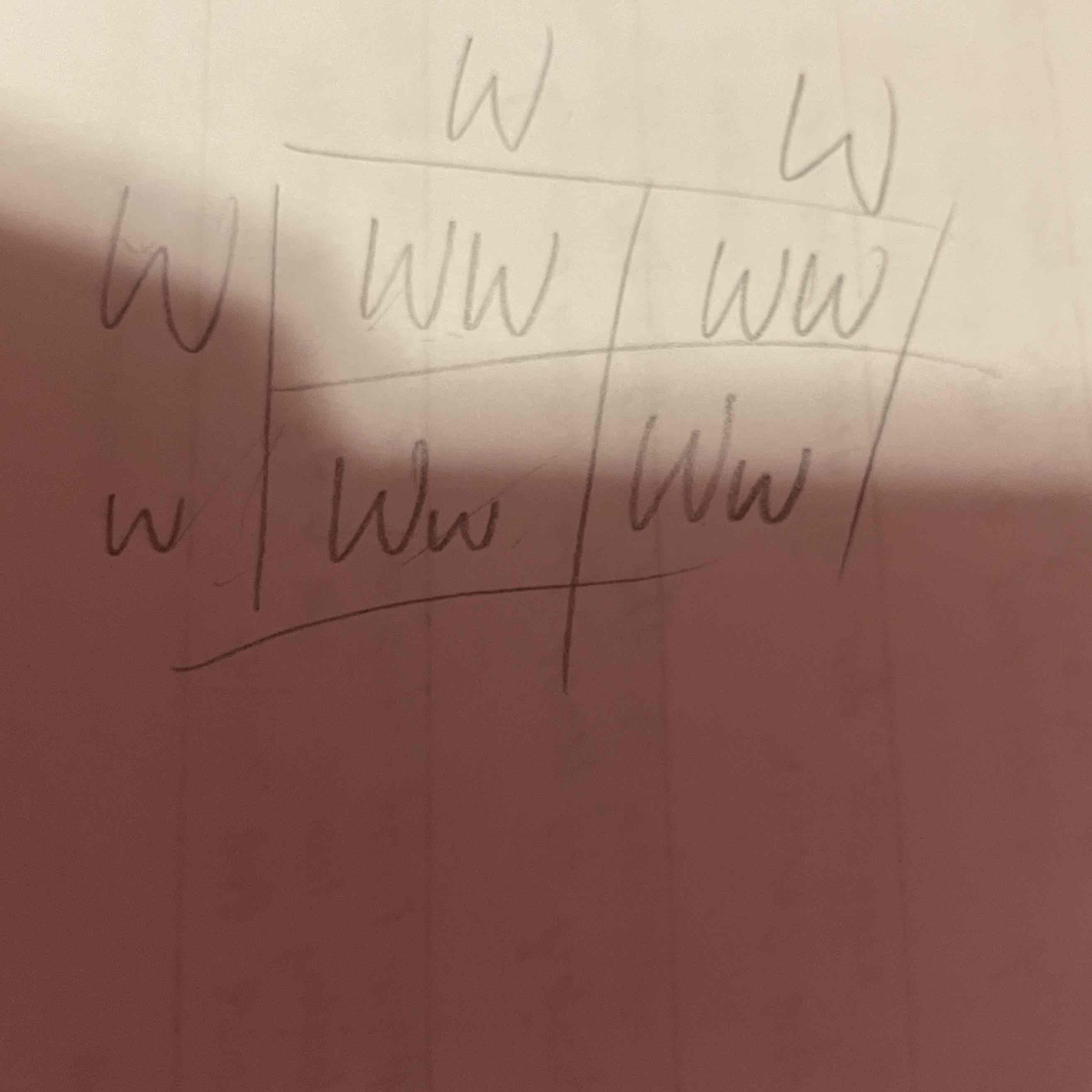
Homozygous vs Heterozygous
-If a genotype is said to be homozygous for a specific trait, then it has the same (identical) version of the allele.
-If the organism has one copy of two different alleles, for example Aa, it is heterozygous
Alleles
-are variations from our mom and dad’s genes (so one allele from mom and one allele from dad so alleles are pairs), leading to diverse traits such as eye color.
What is the possibility?
If one parent seal is a heterozygous long-whisker and the other is short: whiskered, what is the probability that the offspring will have short whiskers?
-50% long whiskers
-50% short whiskers
