Unit 9: Molecular Biology/Protein synthesis & gene expression
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Protein synthesis
The process of creating new little protein guys trhiugh transcription and translation
DNA → mRNA → Protein
Translation
The synthesis of a polypeptide using genetic info encoded in an mRNA pal.
There is a change in the langue from nucelotides into amino acids
mRNA= proteins
this happens outside of the cell in the cytoplasm
This is where codons are read and made into little protein pals.
Transcription
This is when DNA goes to mRNA.
This happens inside the nucles or nuclear envolope.
The DNA spits into RNA, they make another RNA on the otherside but instead of using T’s they use U’s
The broken DNA is then put back together and the mRNA is yeeted out of the cell.
Messenger RNA
mRNA that carries the code for making protein to a ribosome.
They just drop info off at a ribosome to make synthesis proteins (Make proteins)
Transfer RNA
tRNA carries an amino acid to a ribosome to join together to from a protein.
The anti-codon attaches to the tRNA as well as your amino acids, (which you consume) they connect together to make your polypeptide chains which make a protein.
Amino acid
Make the proteins or smth
Gene regulation
turning genes on and off depending on what the cell needs in order to maintain homeostasis.
Gene expression
gene gets turned on in cell to make RNA and proteins = Gene “Expressed”
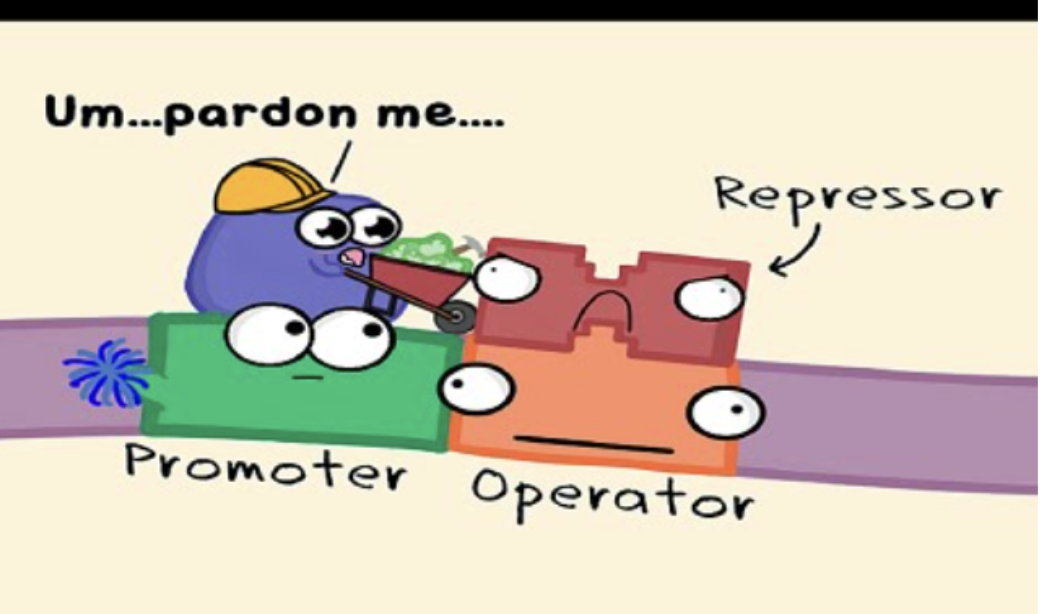
Operon
The genetic switch that turns genes on and off. It is a main part in green regulation
Thay are located on the gene
They control gene expression and stick onto a gene to make it either stop or start gene expression (aka making mRNA to make proteins)
It is a group of portions consisting of an operator, promoter, and repressed that control a group of genes.
Lac operon
The example we used in class, it creates the enzyme that produces enzymes to break down lactase.
Sugar binds to the repressor to allow the operator to let the promoter through and create an enzyme
AraC operon
A rpressor that sits on top of the Lac operon when there is now arabinose sugar present.
Example used in class
Regulatory gene
a gene to code for a protein (maybe a repressor or something else) and controls the transcription of another gene.
Repressor protein
proteins that turn off/reduce gene expression
RNA polymerase
proteins that turn off/reduce gene expression
promoter
region of DNA where RNA polymerase begins to transcribe a gene
They “promote” or start an RNA polymerase.
They also act as a primer
terminator
genetic parts that usually occur at the end of a gene or operon and cause transcription to stop
They make mRNA polymerase stop
codon
3 nucleotides of an mRNA strand that tells a ribosome what nucleic acid to make.
anticodon
The opposite code of a codon
ex: Codon =ACU, Anticodon = UGA
start codon
The first codon that tells a ribosome to “start” reading
stop codon
The last codon that tells a ribosome to “stop” reading
codon chart
Chart to identify a nucleic acid based on a codon or anti-codno+translation.
plasmid
circular pieces of DNA found naturally in bacteria
only in prokaryotic organisms
Recombinant DNA
not natural
genetically engineered in labs
recombined when a gene from one organism is combined with DNA from another = pGOL Lab
introns/exons
on/off switches
Introns a slipced out before the mRNA enters cytoplasm
Exons code for stuff
Introns have the operons on them.
translocation
genetic change in which a piece of chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome
ribosome
the organelles that protein synthesis
nucleus
where DNA is stored in Eu.
The equvilent to this is a
cytoplasm
Space/gellys in the cell
This is where mRNA goes into after leaving the nucleus and binds with ribosomes in order to produce proteins
mutations
a change in the DNA sequence during DNA replication
Base Substitution, deletion, translocation.
can result in change in the amino acid sequence so protein structure
reading frame
a way of dividing the sequence of nucleotides in a nucleic acid into a set of codons
frame shift
enetic mutation caused by a deletion or insertion in a DNA sequence that shifts the way the sequence is read
EX: normal - The dog has a bone.
Base sub- The Dog tas a bone.
Deletion -
silent mutation
a mutation that’s silent
base substitution
An oopsie in the process of changing DNA into mRNA where a base is substituted with another back accident.
Ex: An A is supposed to be paired with a U, but is paired with a C instead.
point mutation
occurs in a genome when a single base pair is added, deleted, or changed
base insertion
the addition of one or more nucleotide base pairs into a DNA sequence
missense mutations
a DNA change that results in different amino acids being encoded at a particular position in the resulting protein
Ampicillin
one of the cillins, I’m allergic to amoxicillin
mutagen
the addition of one or more nucleotide base pairs into a DNA sequence
operator
on/off switch for a gene in an operon
Silent mutation
a type of substitution mutation wherein the change in the DNA sequence of the gene has no effect on the amino acid sequence