Atmospheric Properties
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
1
New cards
what are some atmospheric hazard?
* blizzard
* hurricane
* flood
* hurricane
* flood
2
New cards
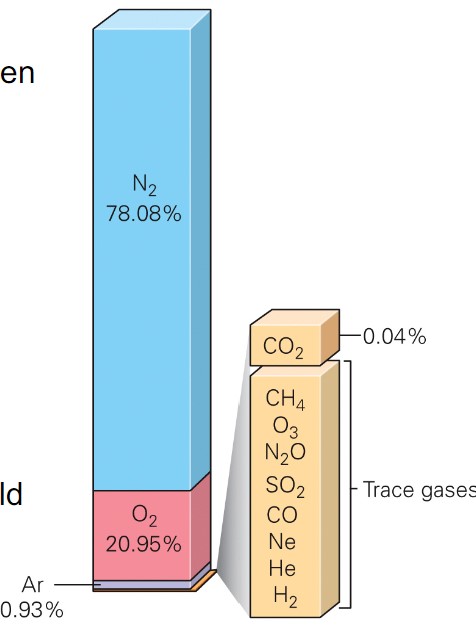
what is atmospheric composition?
* dry air:
* Mostly 78% nitrogen (N2)
* 21% oxygen (O2)
* water:
* percent varies depending on time and place
* constantly changes phase to liquid and solid
* aerosols:
* liquid or solid particles
* dust, soil, salt, ash, pollen, bacteria, mold
* create haze when present with water vapor
* Mostly 78% nitrogen (N2)
* 21% oxygen (O2)
* water:
* percent varies depending on time and place
* constantly changes phase to liquid and solid
* aerosols:
* liquid or solid particles
* dust, soil, salt, ash, pollen, bacteria, mold
* create haze when present with water vapor
3
New cards
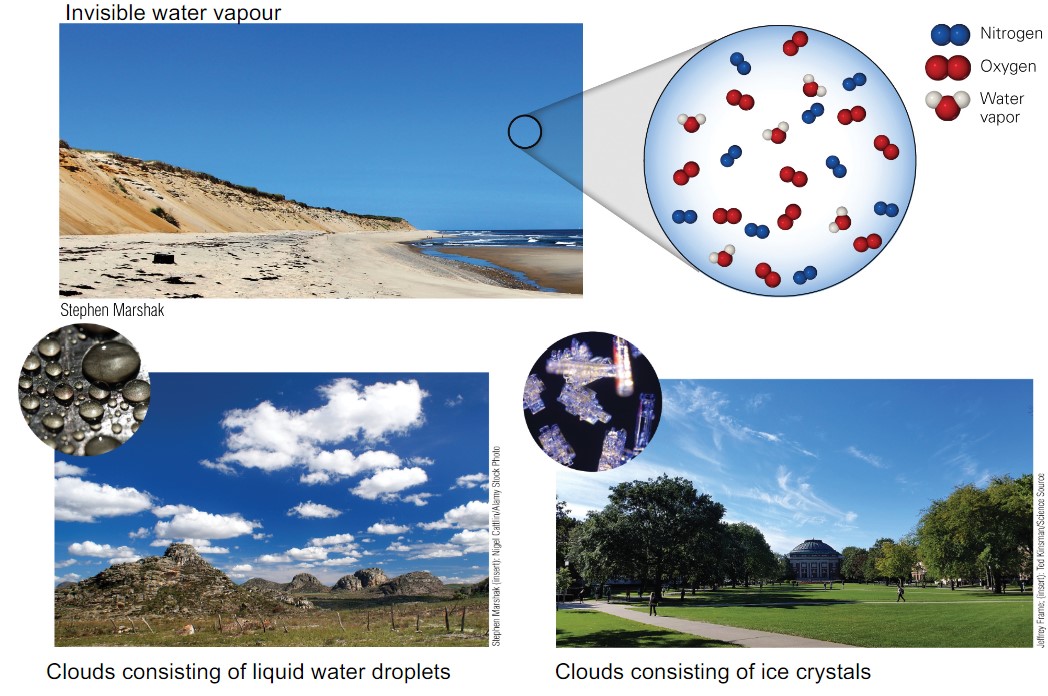
water in atmosphere?
* invisible water vapour
* clouds consisting of liquid water droplets
* clouds consisting of ice crystals
* clouds consisting of liquid water droplets
* clouds consisting of ice crystals
4
New cards
aerosols in the atmos
* volcanic ash
* pollen
* sea salt
* soot
* Aerosols that capture water molecules can produce haze
* pollen
* sea salt
* soot
* Aerosols that capture water molecules can produce haze
5
New cards
what is weather?
* refers to the day-to-day changes in atmos conditions: temperature, precipitation
6
New cards
what is climate?
* is long-term statistical avg of weather conditions
* assessed using at least 30-yrs of data
* assessed using at least 30-yrs of data
7
New cards
what is temperature?
* air molec’s avg speed
* faster molecs results in higher temperature
* measured in ºF and ºC
* faster molecs results in higher temperature
* measured in ºF and ºC
8
New cards
pressure refers to?
* the force applied by air on a specified surface area
* the weight of a column of air
* molecules move apart in hot air:
* hotter air is less dense → lower p
* molecs mover closer tgt in cool air
* cool air is more dense → higher p
* air p varies daily n seasonally
* the weight of a column of air
* molecules move apart in hot air:
* hotter air is less dense → lower p
* molecs mover closer tgt in cool air
* cool air is more dense → higher p
* air p varies daily n seasonally
9
New cards
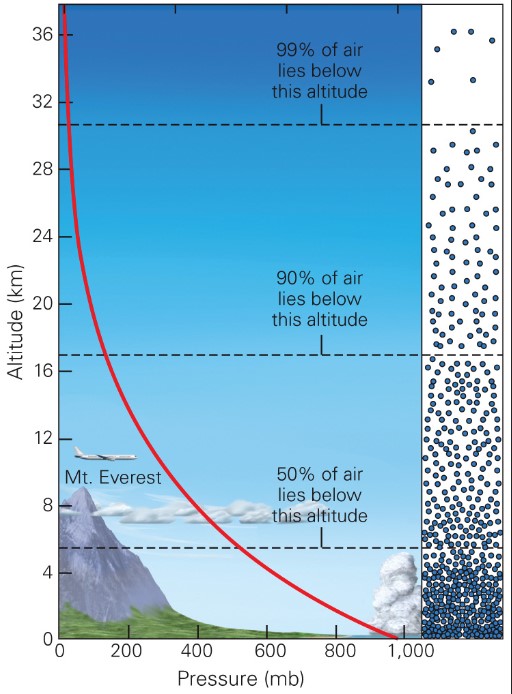
atmospheric p
* air p and density decreases as altitude increases
* \~99.9% of atmos lies below 50 km
* \~99.9% of atmos lies below 50 km
10
New cards
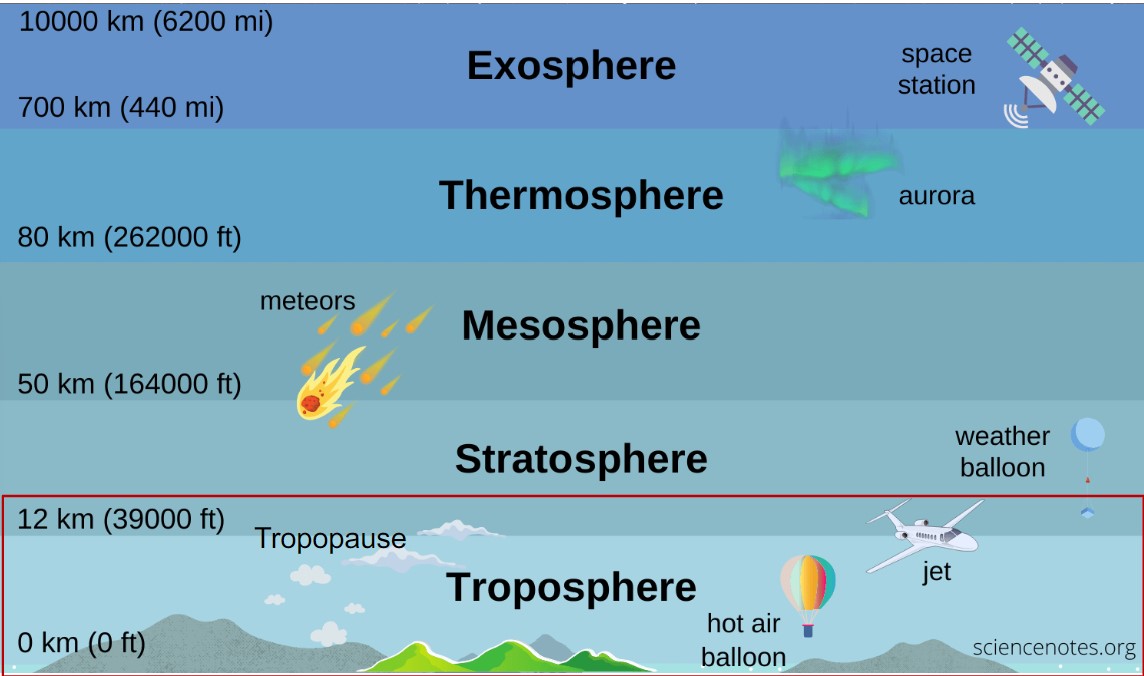
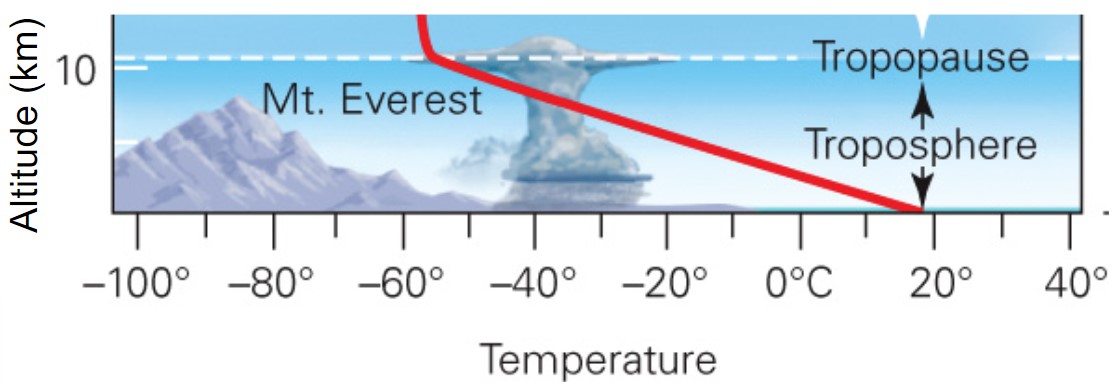
layers of the atmosphere
* tropopause is layer focused
11
New cards
what is enviro lapse rate?
* the change of temperature w/ altitude \~6.5ºC/km
* troposphere temperature decreases w/ increasing altitude
* troposphere temperature decreases w/ increasing altitude
12
New cards
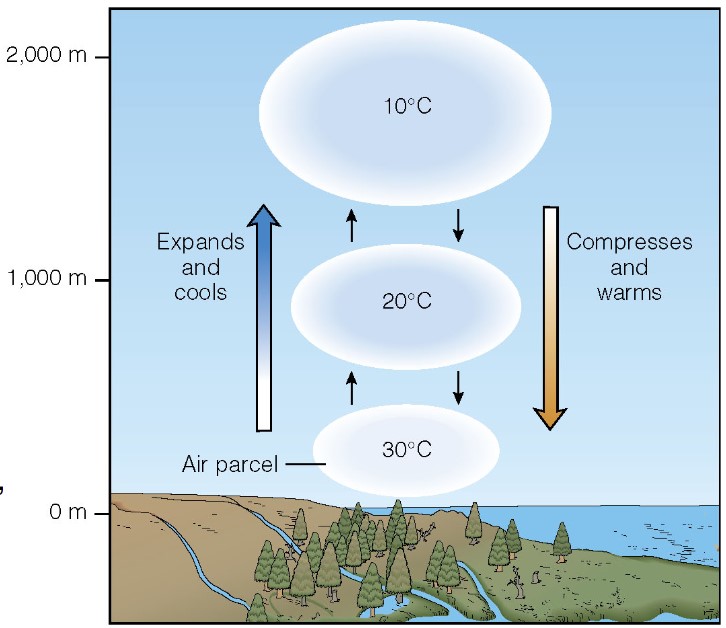
adiabatic cooling
* air that is lifted experiences a drop in pressure, allowing it to expand
* expansion of air uses energy, so the air mass becomes cooler
* initially, it is warm
* as the air mass cools, water vapour condenses, the air mass becomes supersaturated n clouds form
* as becomes warm again, goes down
* expansion of air uses energy, so the air mass becomes cooler
* initially, it is warm
* as the air mass cools, water vapour condenses, the air mass becomes supersaturated n clouds form
* as becomes warm again, goes down
13
New cards
when does adiabatic cooling occur?
* when rising air cools
14
New cards
what is dry adiabatic lapse rate?
* rate of cooling of a parcel of dry air (\~ 10ºC/km)
15
New cards
what is saturated (moist) adiabatic lapse rate?
* rate of cooling of a parcel of saturated air (\~6ºC/km)
16
New cards
what are clouds?
* visible water droplets and/or ice crystals w
17
New cards
when do clouds form?
* when saturated air becomes supersaturated
* water condenses on aerosol condensation nuclei
* water condenses on aerosol condensation nuclei
18
New cards
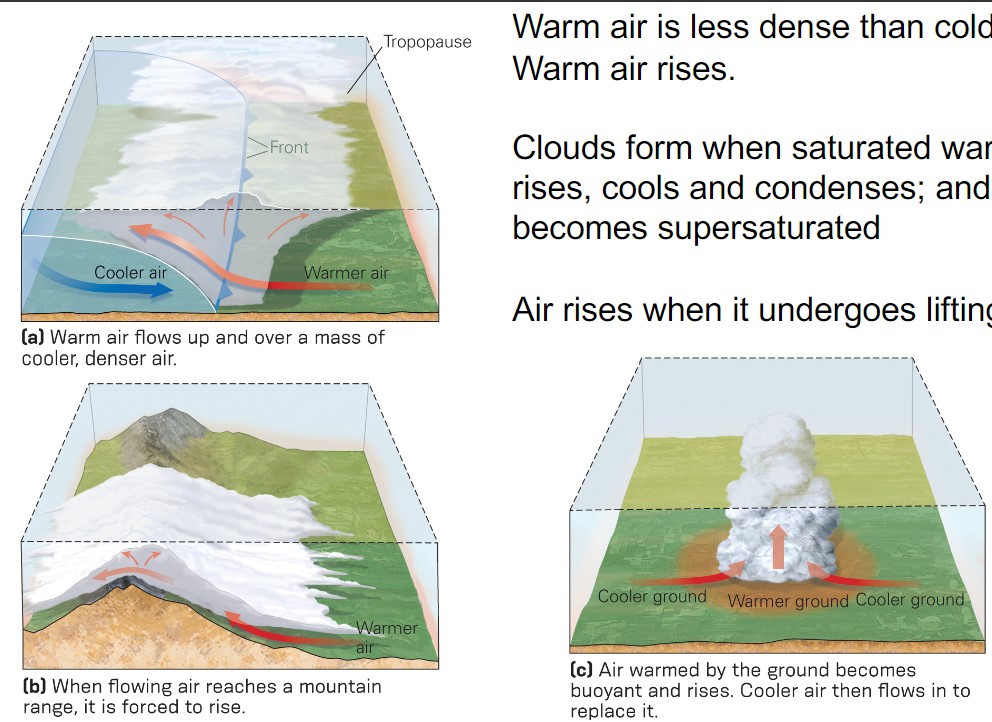
cloud formation
* warm air is less dense that cold air → warm air rises
* clouds form when saturated warm air rises, cools and condenses; and becomes supersaturated
* air rises when it undergoes lifting
* clouds form when saturated warm air rises, cools and condenses; and becomes supersaturated
* air rises when it undergoes lifting
19
New cards
what are the 3 types of cloud formation relating to lifting?
1. warm + cool air come tgt → front
2. has to go over → forced to rise, thus forming cloud
3. localized heating
20
New cards
what is the temperature of warm clouds?
* they have consistent temperature > 0ºC
* liquid state
* liquid state
21
New cards
if water droplets consolidate to ________ mm diameter, they will fall
>0.5
22
New cards
how do raindrops grow?
* as they fall by colliding w/ other droplets
* can grow to \~4 mm diameter.
* can grow to \~4 mm diameter.
23
New cards
cold clouds temperature?
* consistent temperatures < 0ºC.
24
New cards
what are the 2 ways ice crystals may grow?
1. snowflakes: when liquid water gradually freezes to ice nuclei
2. rime: when supercooled droplets instantly freeze to ice nuclei
* when don’t have aerosols, latch onto other crystals
25
New cards
how do graupel and hail dev?
* when rime ice crystals keep growing
26
New cards
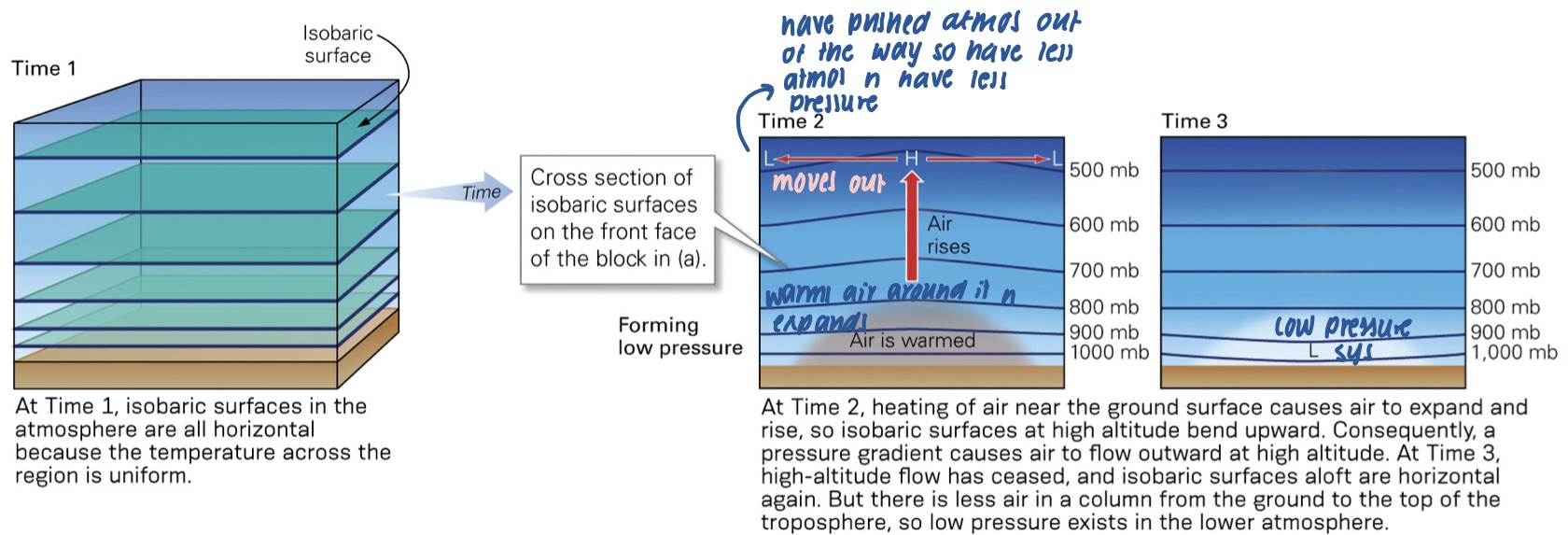
how do low pressure systems work?
* as air at Earth’s surface expands and rises w/ local heating it pushes air up above it
* air then starts to flow outward in the upper atmos
* the total vol of air decreases, low p devs
* air then starts to flow outward in the upper atmos
* the total vol of air decreases, low p devs
27
New cards
how do high pressure systems work?
* as air at Earth’s surface cools and contracts, air in the upper atmos flows inward
* the total vol of air increases, high p devs
* the total vol of air increases, high p devs
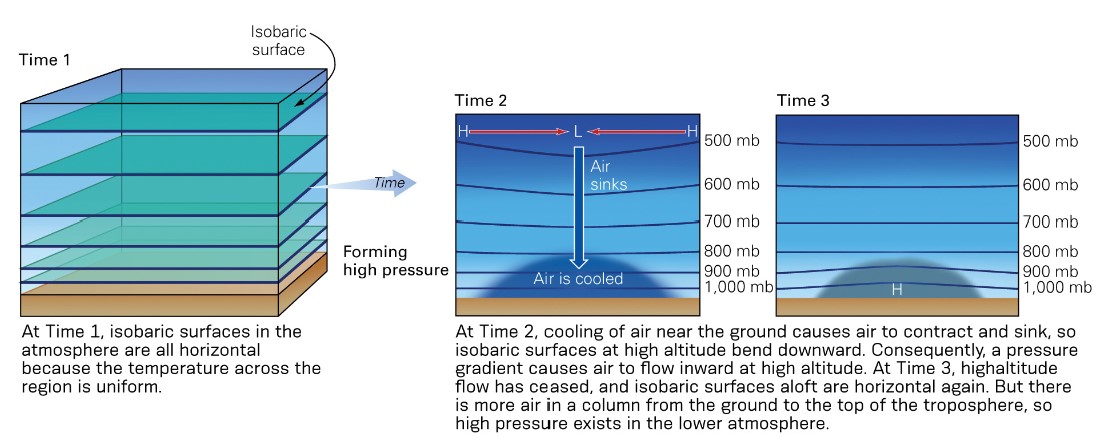
28
New cards
what is a pressure gradient?
* pressure change divided by distance
* air always moves from higher to lower p; represented on maps w/ isobars; lines of equal pressure
* this air is wind
* high p gradient → faster wind
* air always moves from higher to lower p; represented on maps w/ isobars; lines of equal pressure
* this air is wind
* high p gradient → faster wind
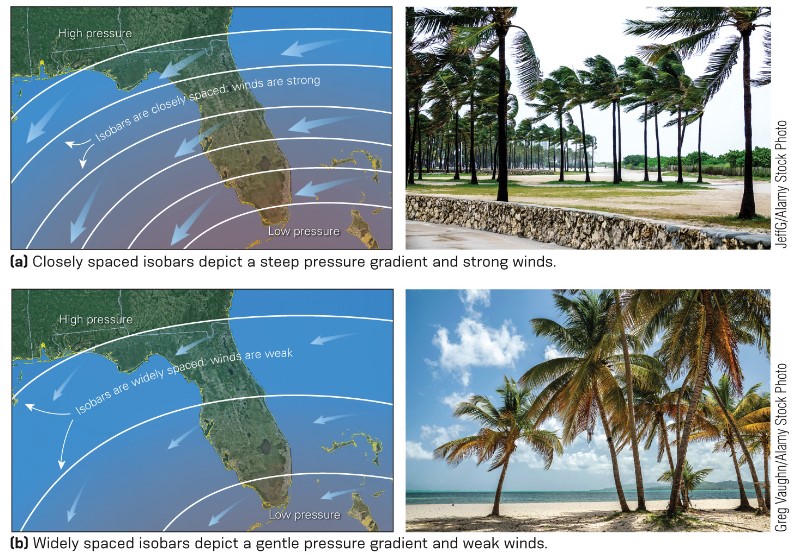
29
New cards
what is the Coriolis effect?
* air’s apparent deflection relative to the spinning Earth
* air veers right in N hemis, left in S hemis
* Coriolis Effect increases as air speed increases
* axis rotation speed at Earth’s equator = 1,670 km/ hr
* Axis rotation speed at Earth’s poles = 0 km/hr
* air veers right in N hemis, left in S hemis
* Coriolis Effect increases as air speed increases
* axis rotation speed at Earth’s equator = 1,670 km/ hr
* Axis rotation speed at Earth’s poles = 0 km/hr
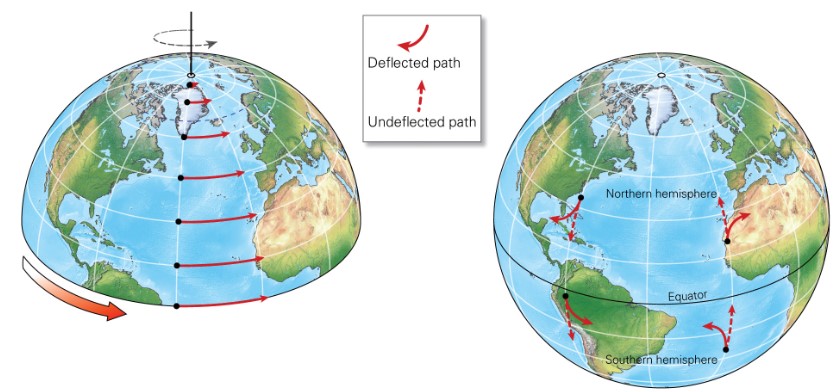
30
New cards
winds in the northern hemis
* northern hemis low p
* wind spirals from higher p into a low p, counterclockwise
* wind spirals from higher p into a low p, counterclockwise
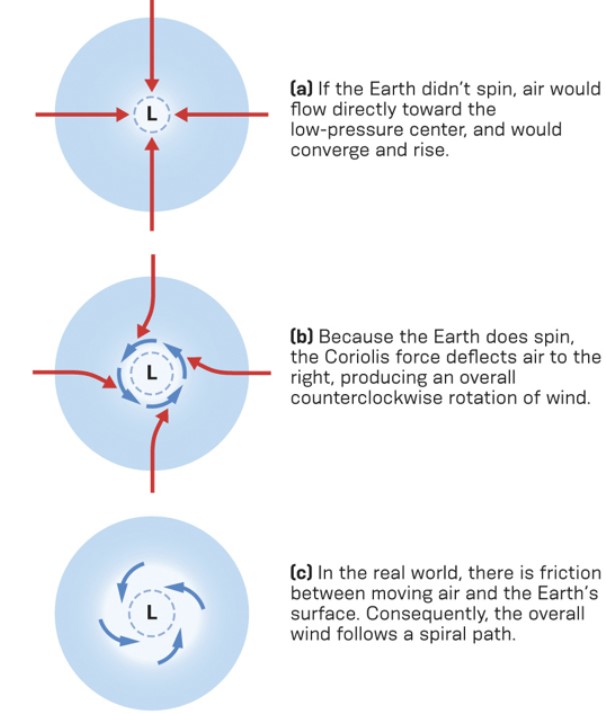
31
New cards
when do hurricanes form?
* between 5 -30º latitude
32
New cards
what is the Ferrel cell?
* region where cold polar air and warm tropical air converge
* steep p gradient creates polar jet stream
* can produce parge storms called mid-latitude cyclones
* steep p gradient creates polar jet stream
* can produce parge storms called mid-latitude cyclones
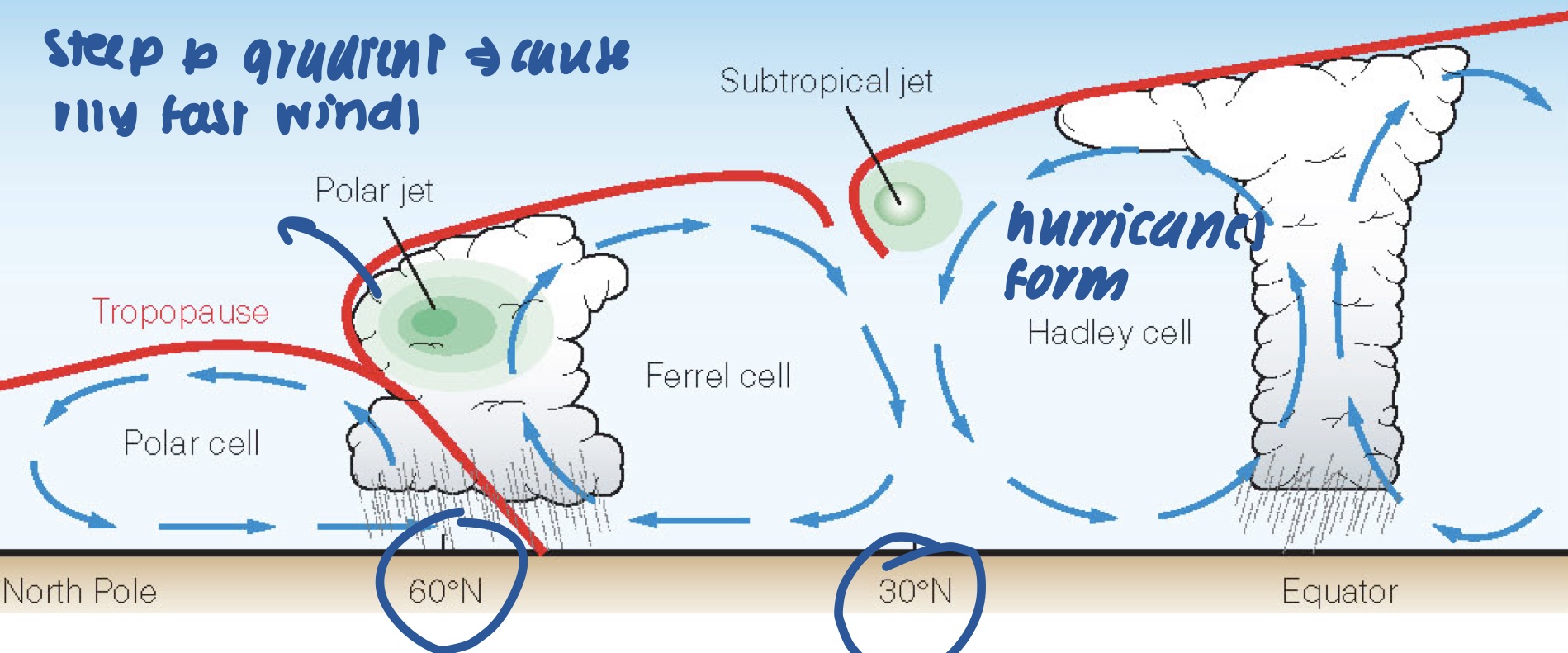
33
New cards
what is a polar front?
* the boundary between warm, tropical and cold, polar air
34
New cards
what do steep pressure gradient generate?
* polar front jet stream
35
New cards
what is a polar-front jet stream?
* very fast wind, 10km high, flowing over the polar front
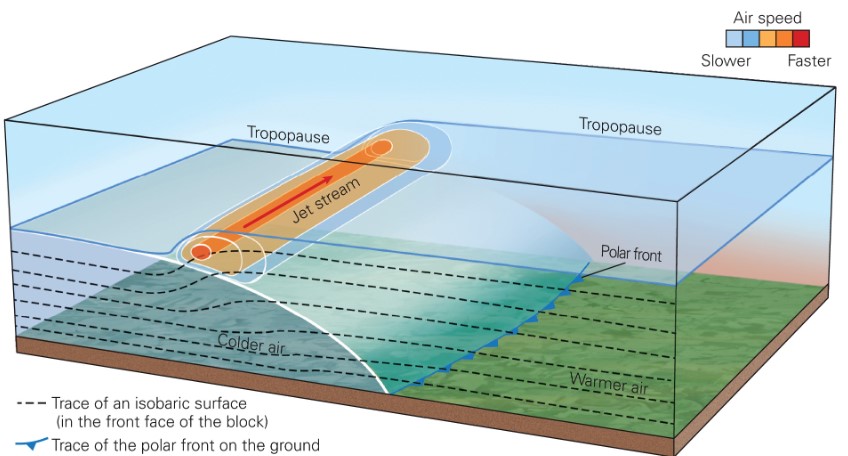
36
New cards
polar front and jet stream flow in __________ undulations
wave-like
37
New cards
how does jet stream air flow?
* uneven manner
* speed is not the same → more air can flow out of a region than into it
* speed is not the same → more air can flow out of a region than into it