Neuro Lab Practical Cerebellum and Spinal Cord and some brain functions
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
vermis of cerebellum
Name this structure (be specific).
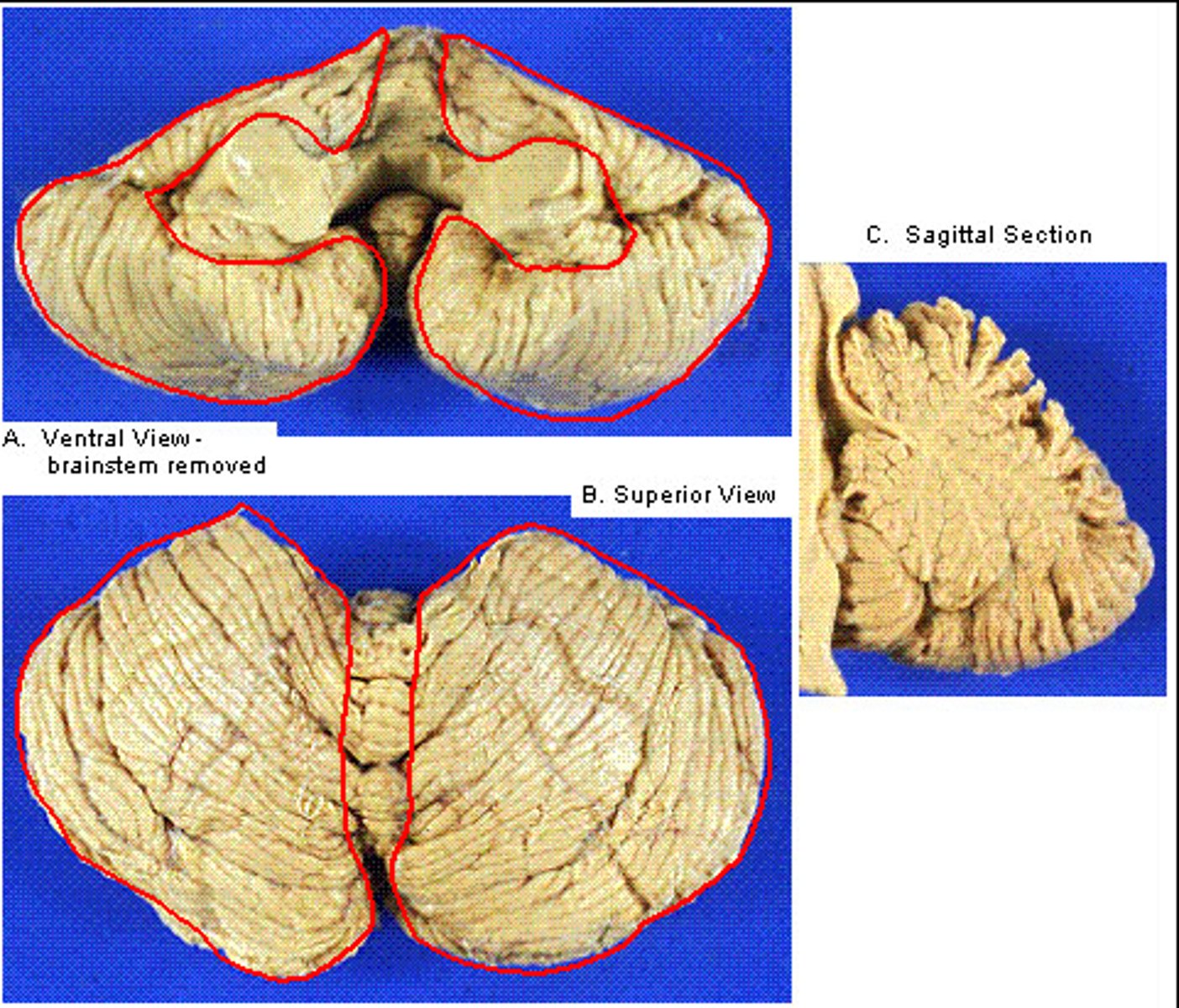
hemispheres of cerebellum
Name this structure (be specific).
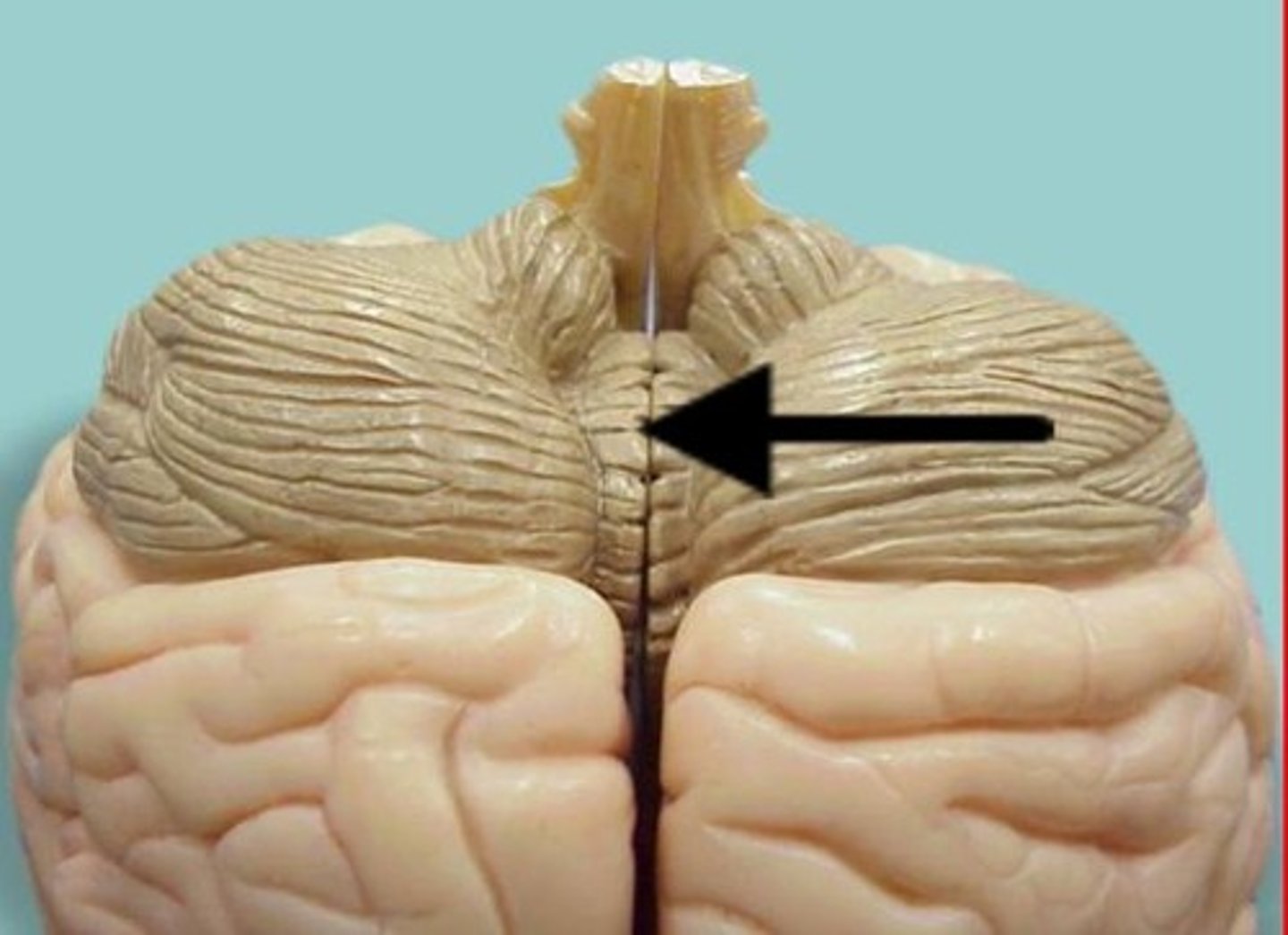
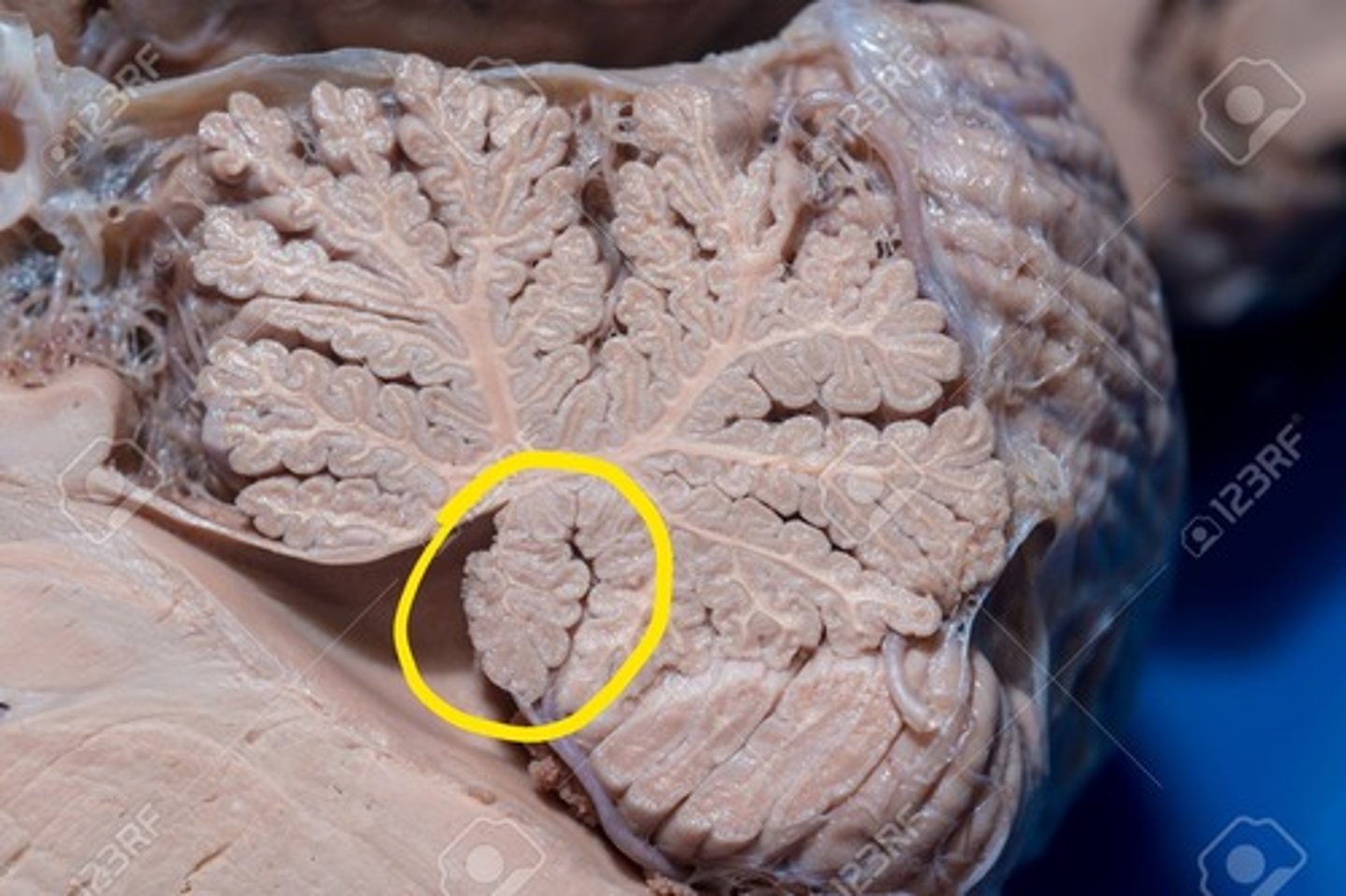
flocculonodular lobe of cerebellum
Name this structure (be specific).
flocculonodular lobe of cerebellum
Name this structure (be specific).
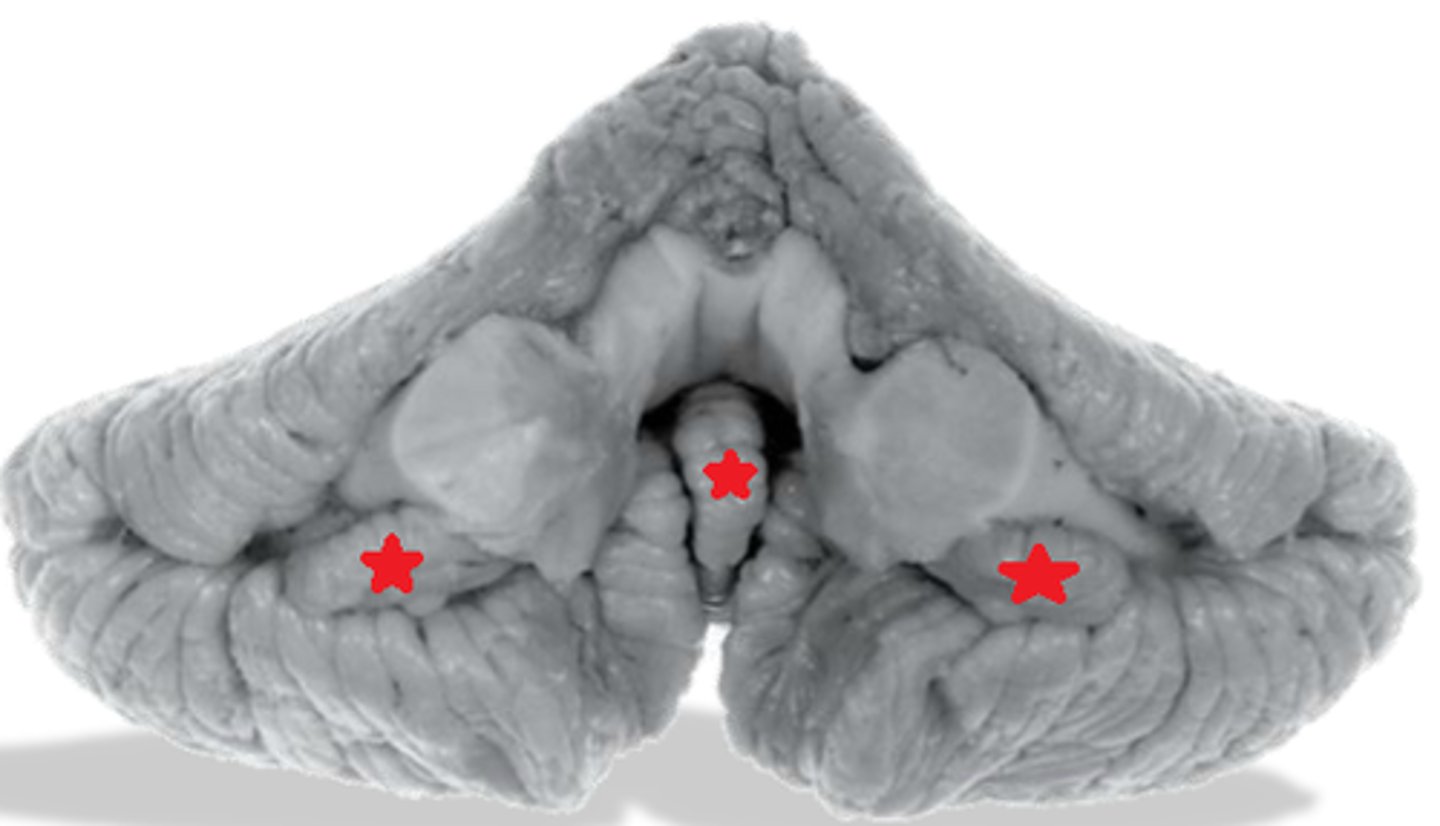
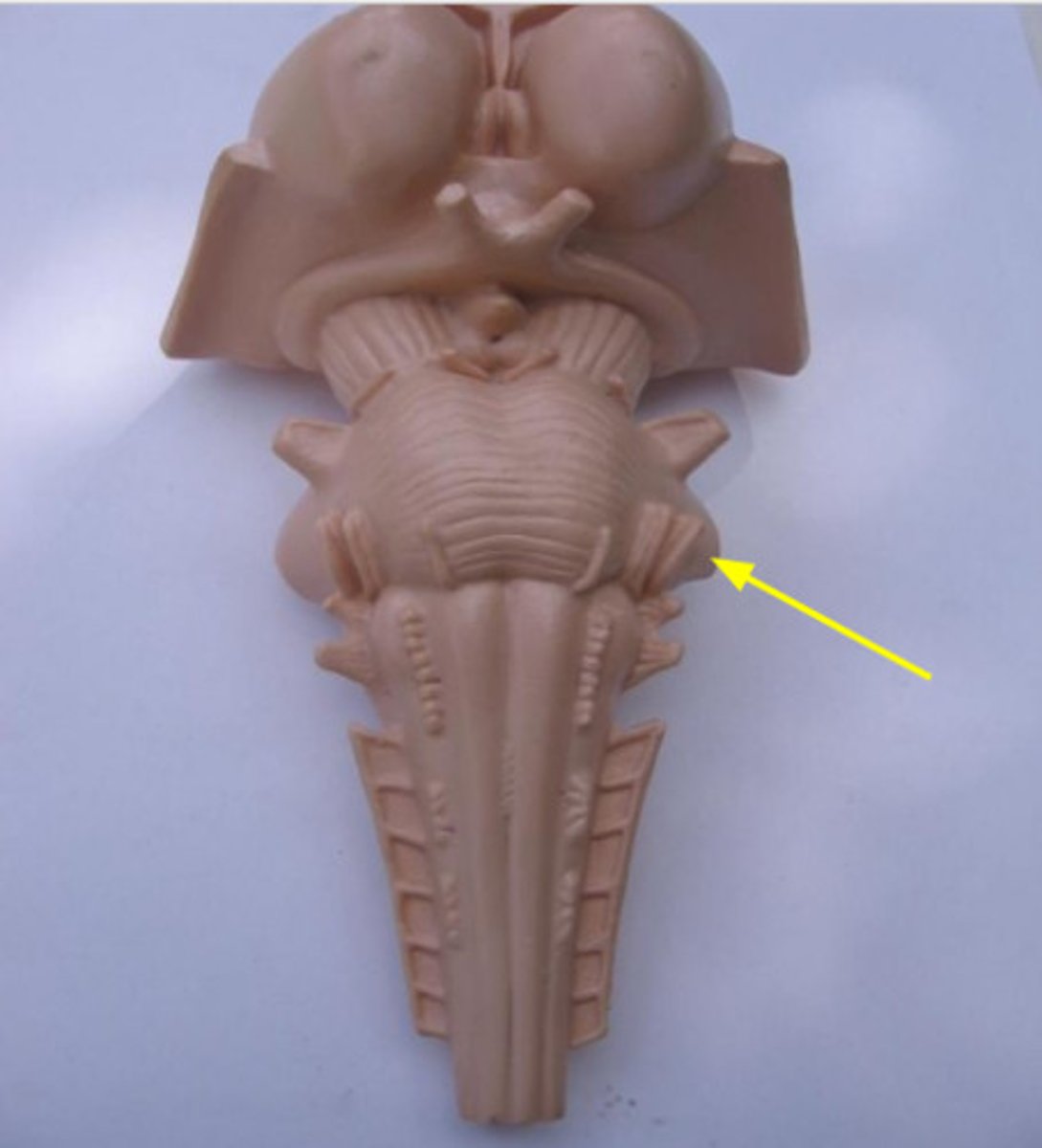
cerebellar peduncles
Name this structure (be specific).
white matter of spinal cord
Name this tissue.
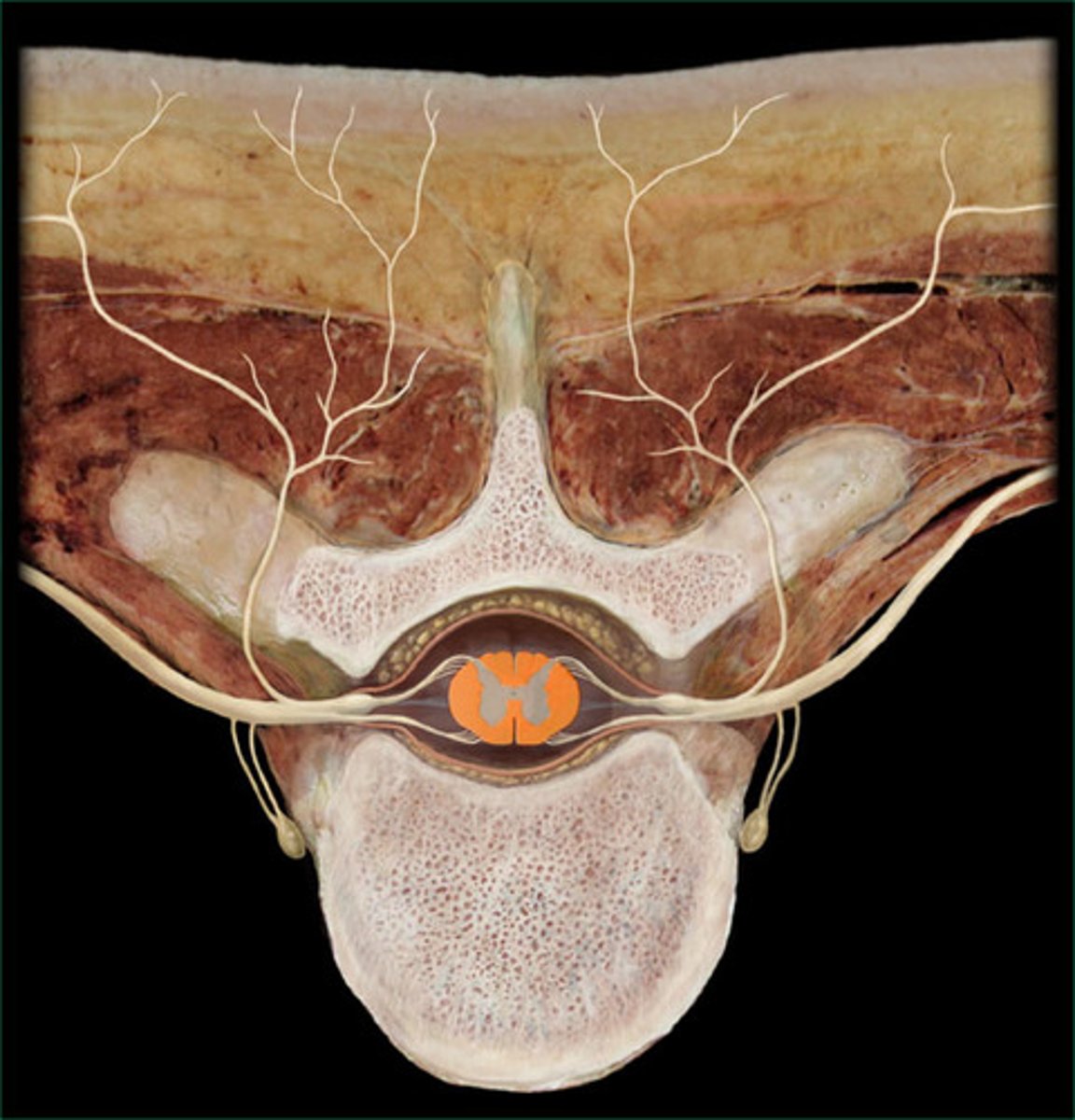
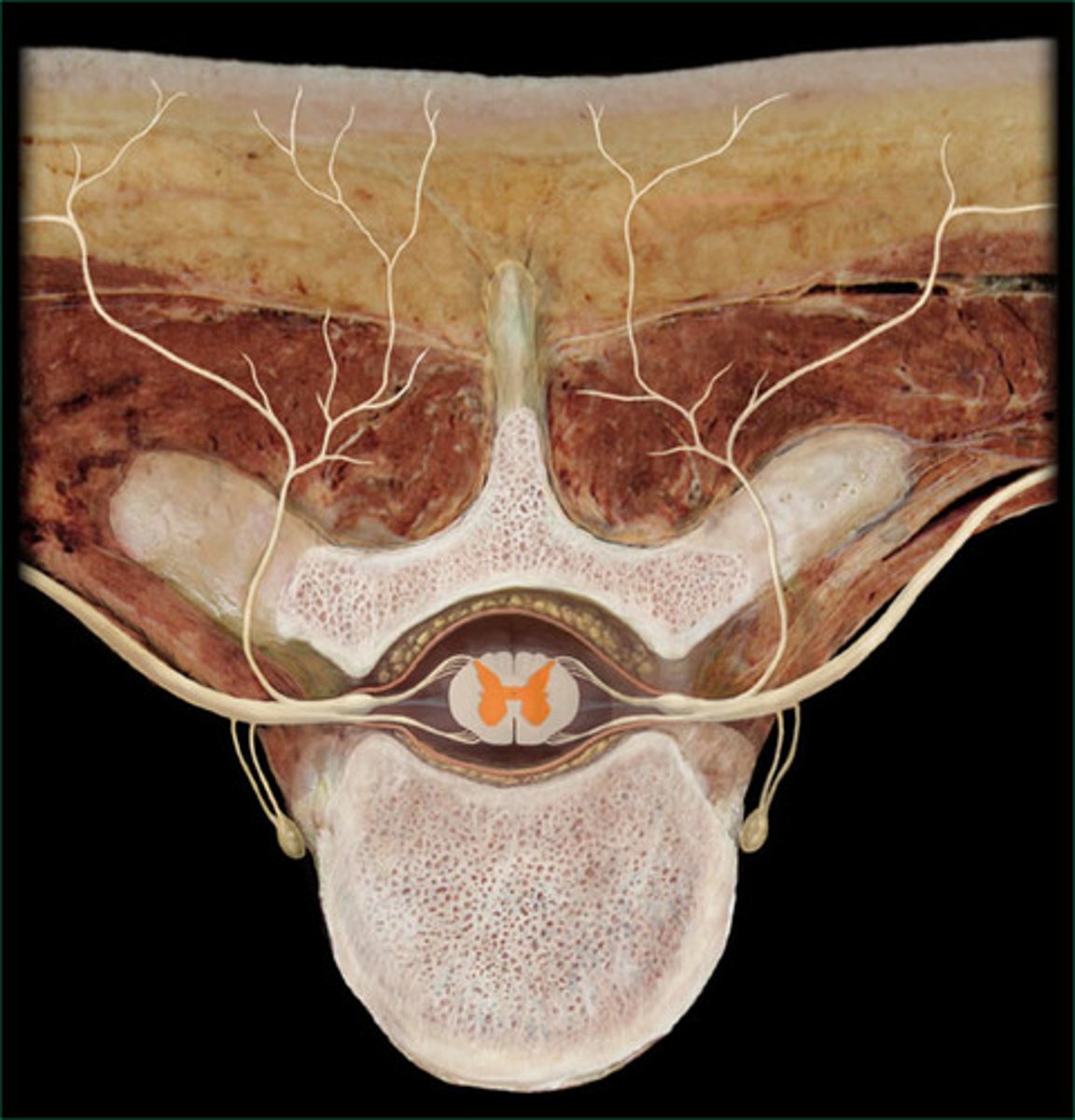
gray matter of spinal cord
Name this tissue.
dorsal rootlets of spinal nerve
Name this structure.
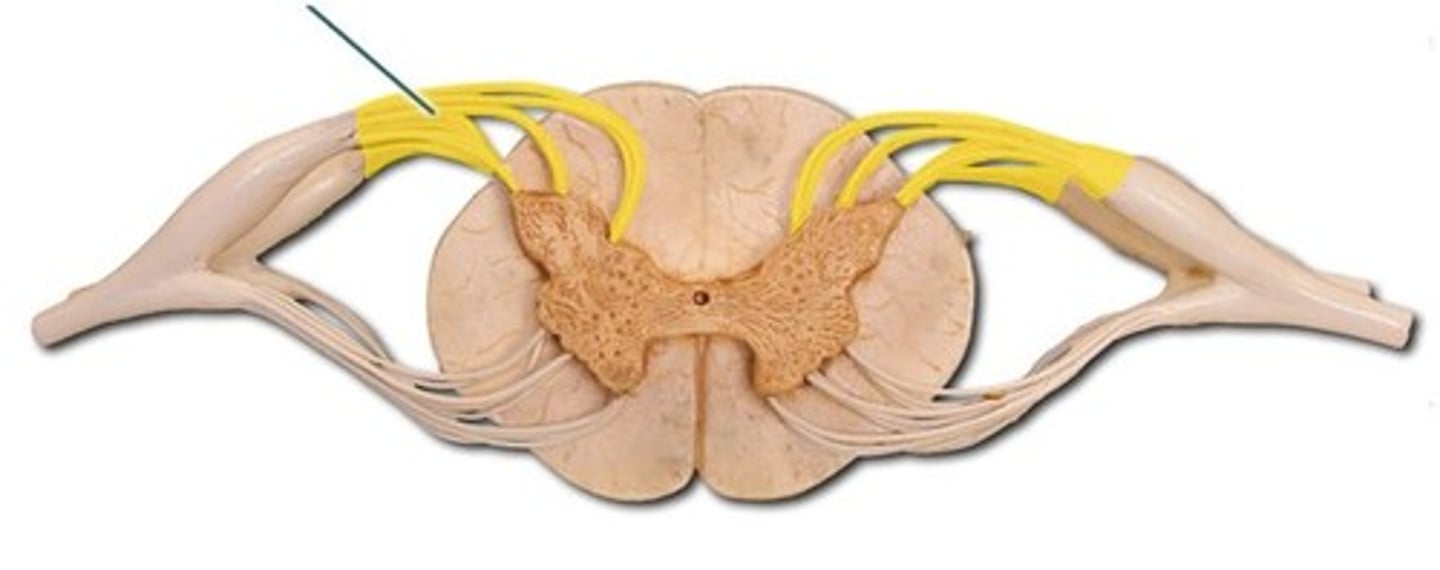
ventral rootlets of spinal nerve
Name this structure.
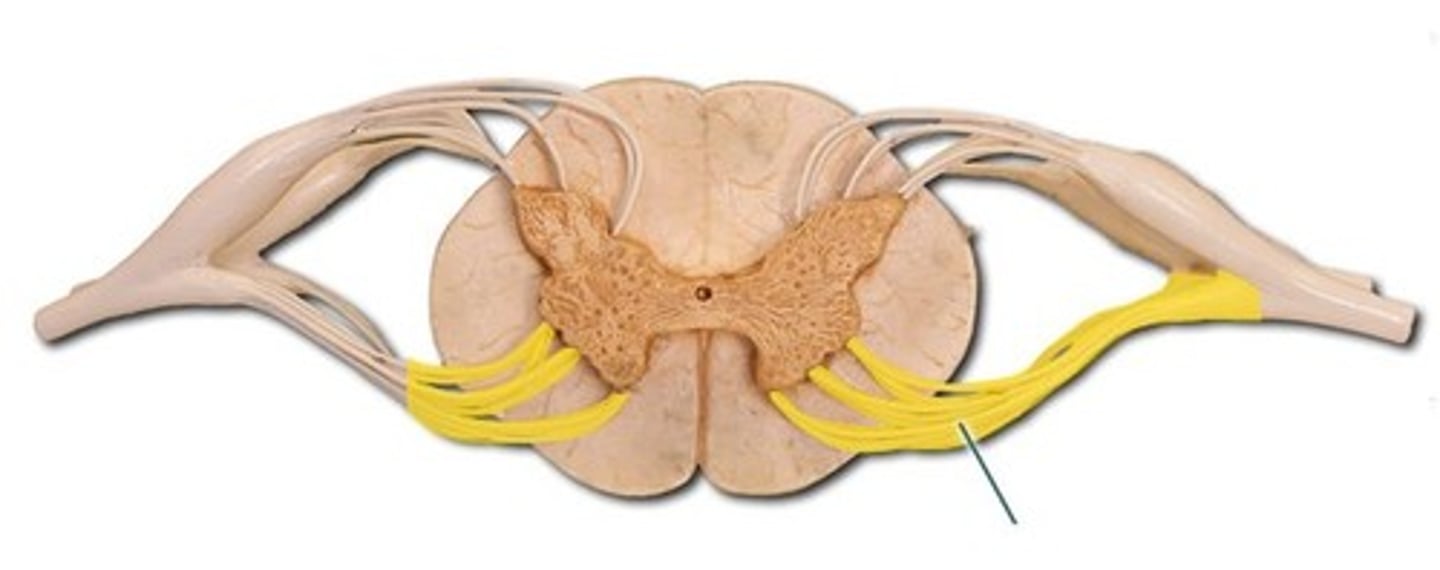
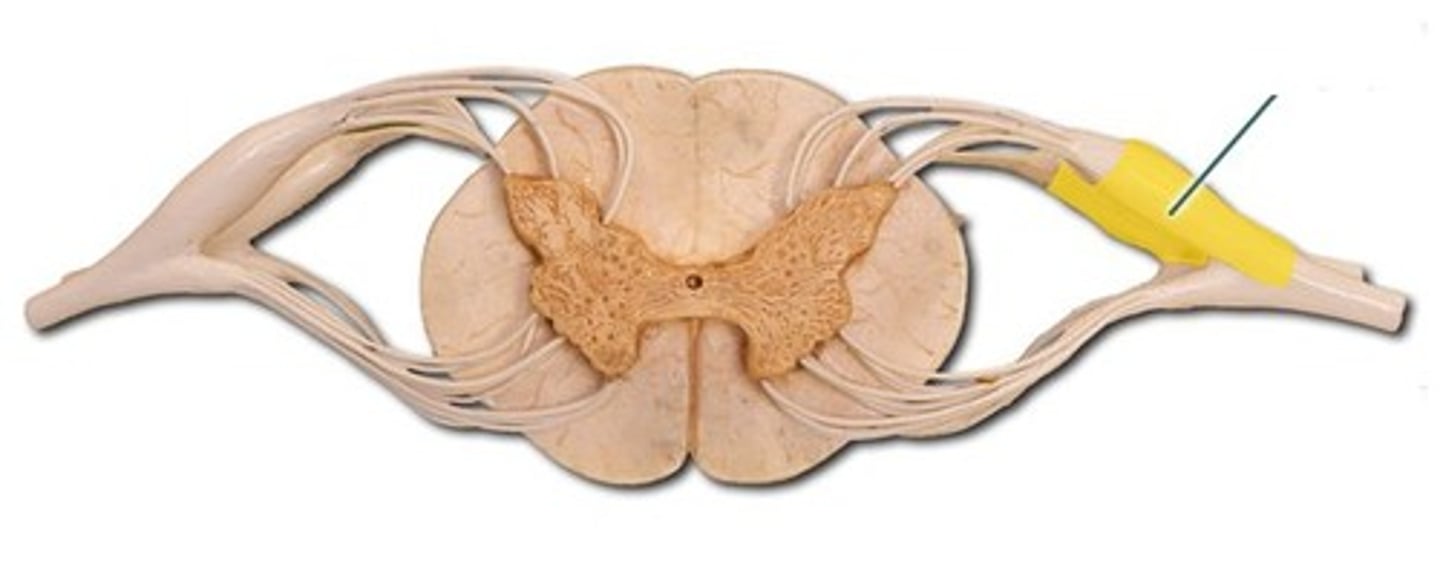
dorsal root ganglion
Name this structure.
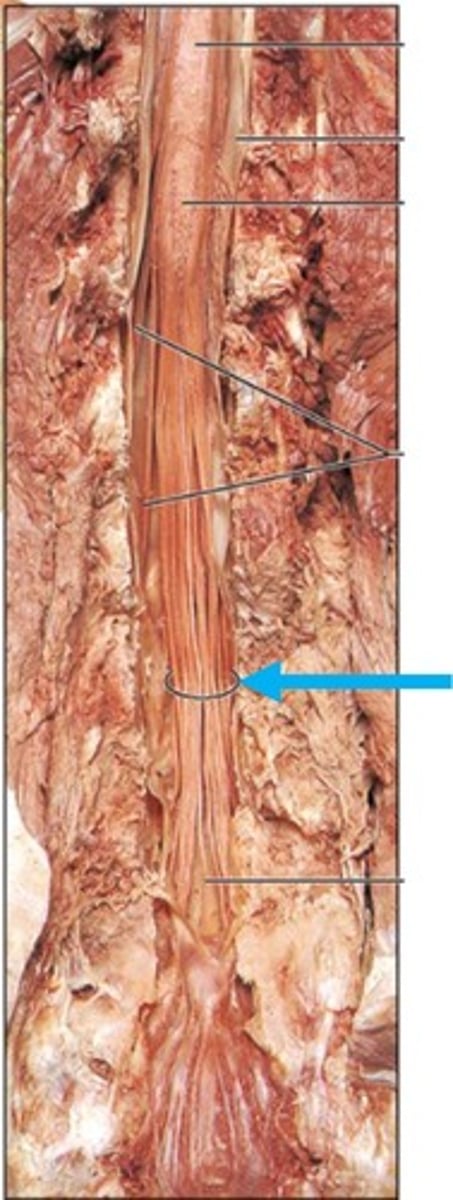
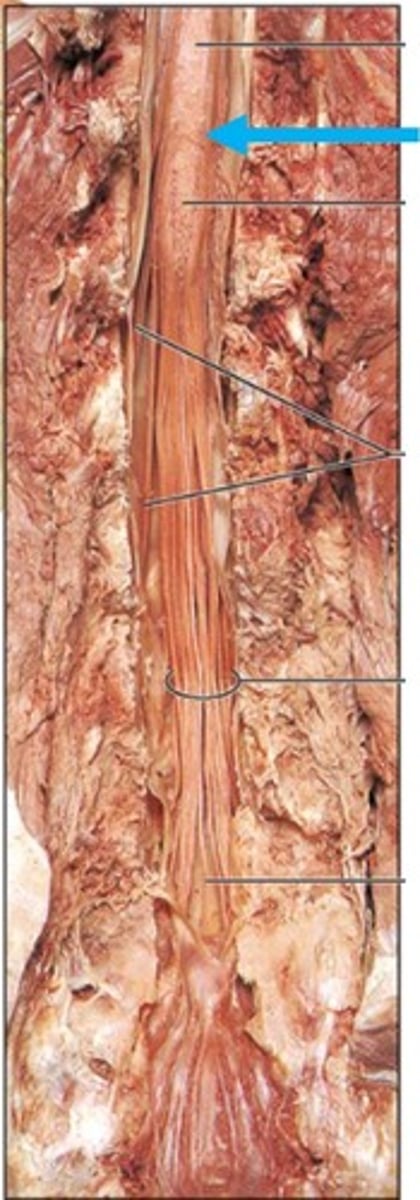
cauda equina
Name this structure.
lumbosacral enlargement of spinal cord
Name this structure.
conus medullaris
Name this structure.
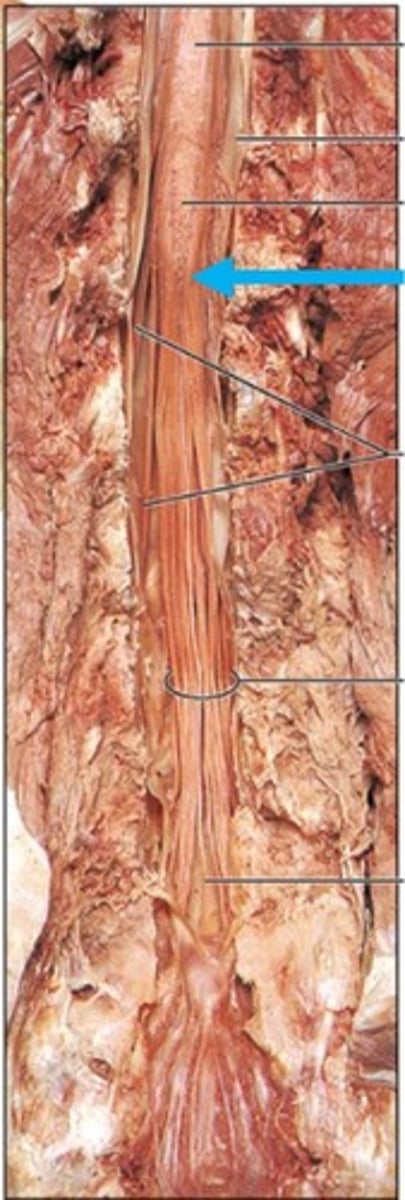
filum terminale
Name this structure.
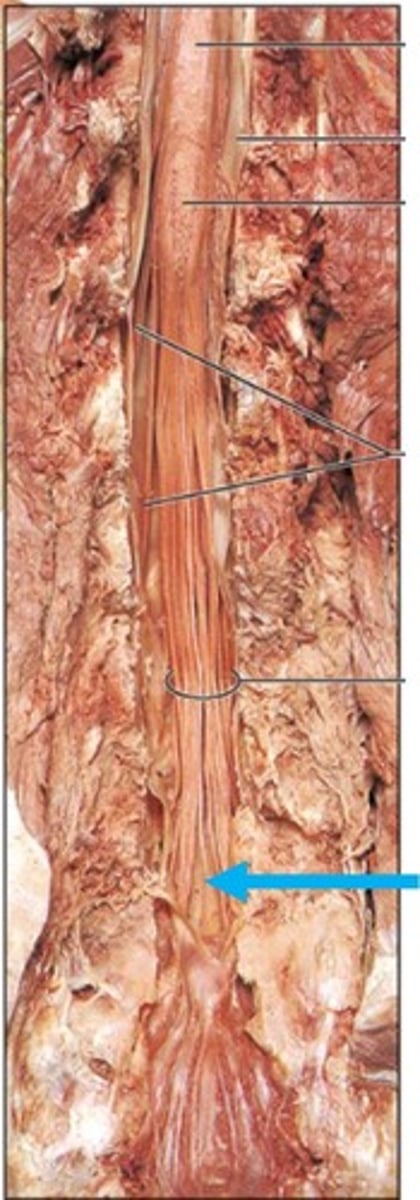
denticulate ligaments
Name this structure.
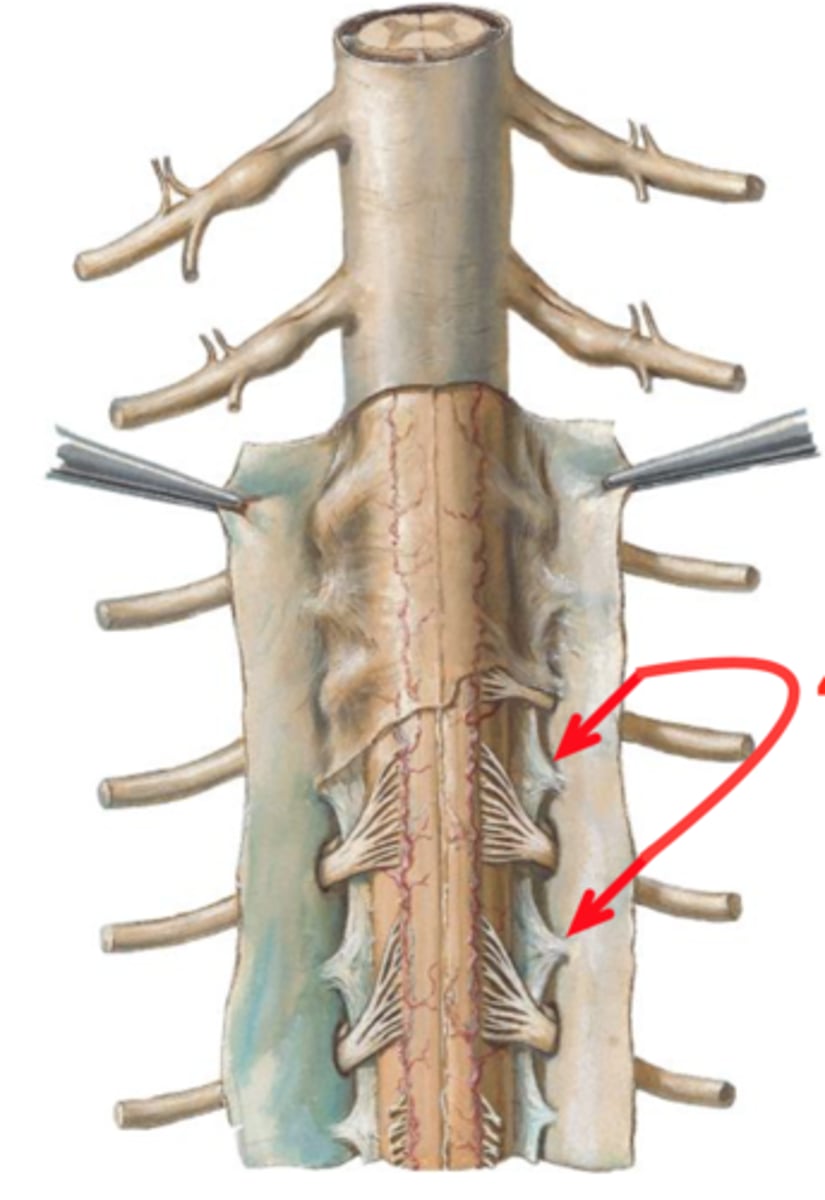
central canal of spinal cord
Name this opening.
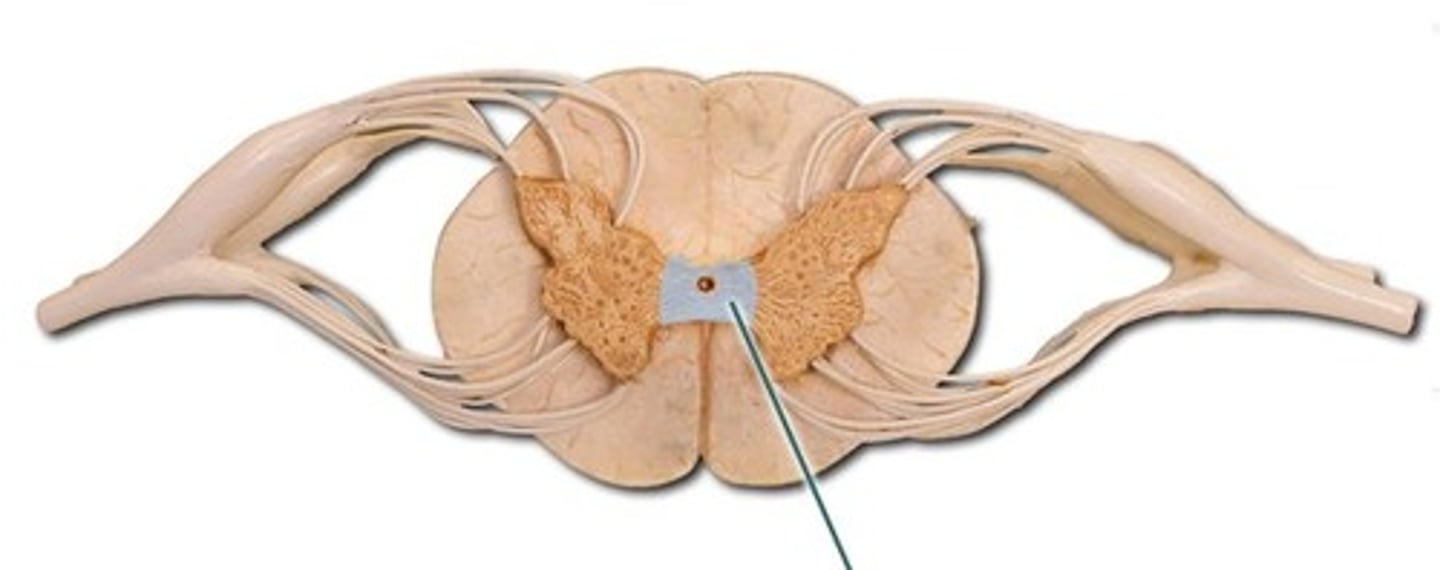
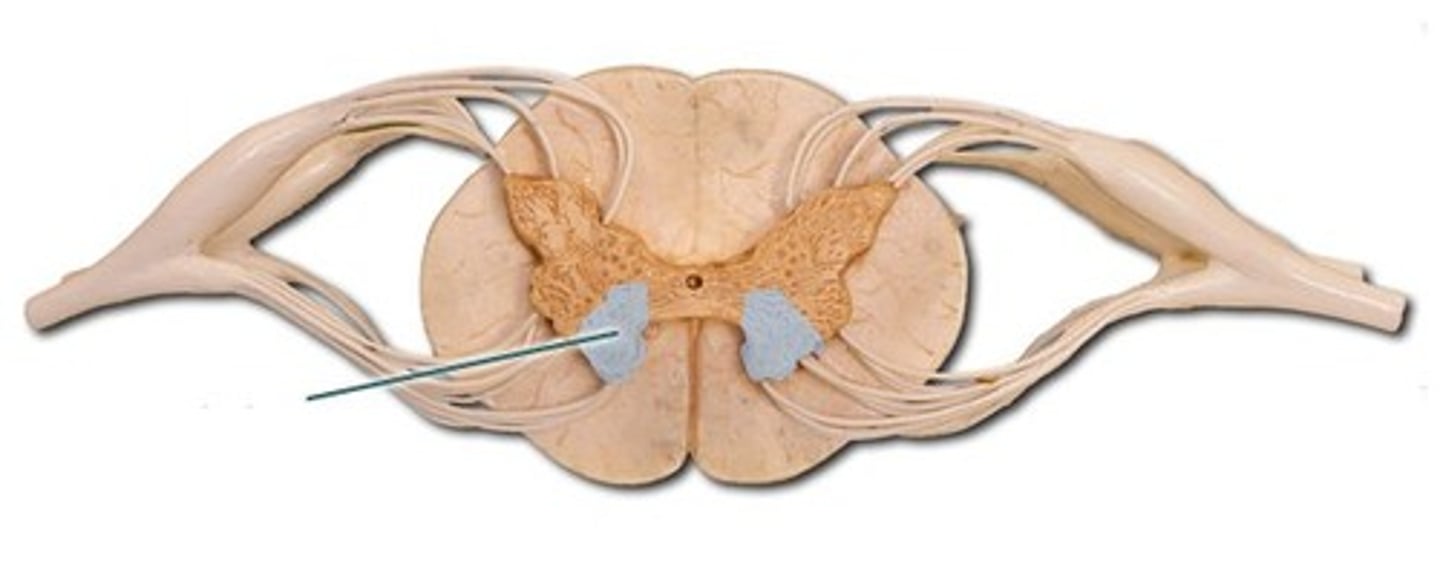
dorsal horn of spinal cord
Name this structure.
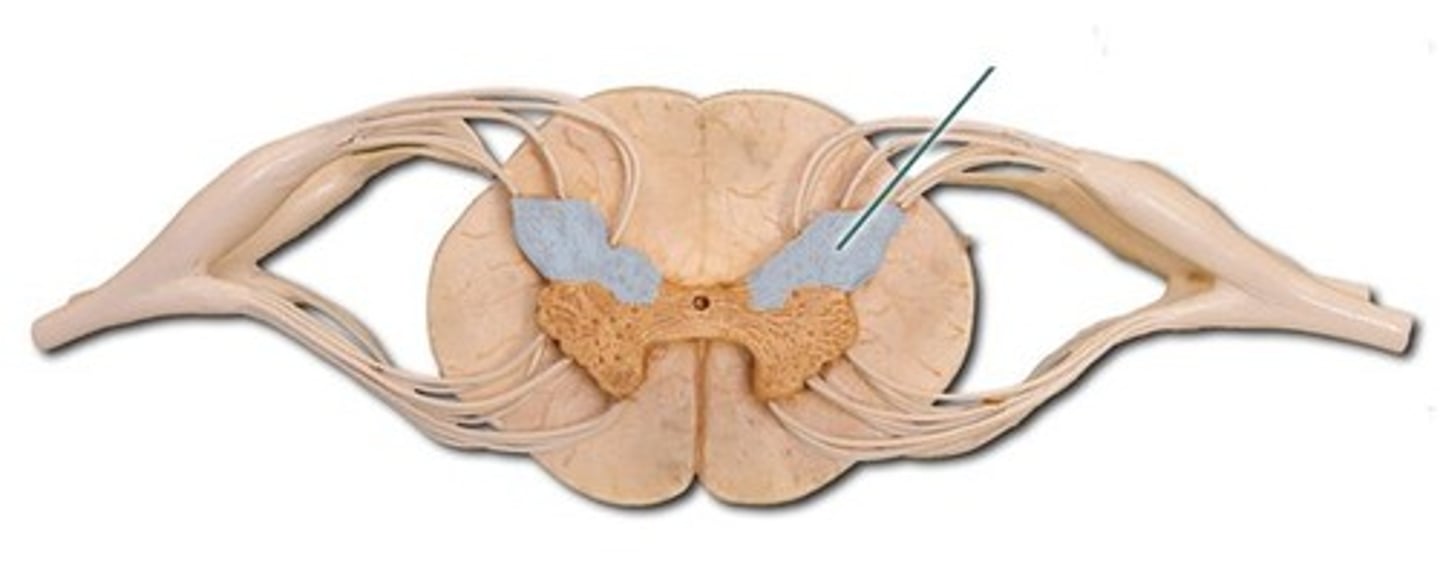
ventral horn of spinal cord
Name this structure.
8
Number of cervical nerves.
12
Number of thoracic nerves.
5
Number of lumbar nerves.
5
Number of sacral nerves.
basal ganglia function
Direct input from frontal lobe, facilitates motor movements, inhibits unneeded movements
Spatial-temporal aspects of speech
Damage: unusual body postures, dysarthria, change in body tone, involuntary uncontrolled movements interfere with voluntary speech, walk or other movements (dyskinesias)
amygdala function
Responsible for the response and memory of emotions, especially fear
thalamus function
relay station for sensory impulses, pain
hypothalamus function
water balance/bp/temp regulation/hunger/thirst/sex.
subthalamus function
Interacts with the basal ganglia to control movements.
superior colliculi function
visual reflexes
inferior colliculi function
auditory reflexes
insula function
Contains the Gustatory Cortex which is responsible for taste; interpretation of music
Wernicke's area function
controls language reception - a brain area involved in language comprehension and expression; usually in the left temporal lobe
vermis function
integration of information between the two cerebellar lobes; gross motor coordination timing, posture, locomotion
Broca's area function
Speech production area found in dominant hemisphere-> left; verbal expression of language
post-central gyrus function
sensory strip
receives pain, temperature and touch information from the body
pre-central gyrus function
primary motor cortex
mamillary bodies function
limbic system such as emotions
anterior cerebellar lobe function
- Receives information from the spinocerebellar tracts.
- Sends inhibitory fibers with the lateral vestibular tract.
Primarily associated with GAIT ATAXIA
Partially works with vermis
frontal lobe function
involved in motor function: problem solving, memory, judgment, impulse control
temporal lobe function
auditory
parietal lobe function
somatic sensory processing
occipital lobe function
visual processing
pineal body function
Secrete melatonin and is involved in regulation of sleep and sex behavior
substantia nigra function
secretes dopamine
Infundibulum function
Small funnel-like stalk that connects the pituitary to the brain and is the passage which pituitary hormones are delivered to the deeper parts of the brain
medulla oblongata function
regulating vital function (breathing, digestion, heart rate)
caudate nucleus function
learning and memory from feedback
filum terminale function
anchors spinal cord to coccyx
corpus callosum function
Connects the right and left hemispheres of the brain
olfactory nerve function
sensory, smell
optic nerve function
sensory, vision
occulomotor nerve function
Motor, Eye movement and pupillary constriction
vestibulocochlear nerve function
hearing, equillibrium (balance)
trochlear nerve function
motor, eye movement
facial nerve function
facial expression, taste
trigeminal nerve function
1. Ohpthalmic--Sensory--orbital
2. Maxillary--Sensory--upper teeth
3. Mandibular--Mixed--
Sensory--muscles for swallowing and anterior 2/3 of tongue
Motor--opening jaw, chewing (mastication)
hypoglossal nerve function
Movement of the tongue and for speech
glossopharyngeal nerve function
Sensory-Taste, respiration, blood pressure
Motor- Swallowing & gagging
abducens nerve function
lateral eye movement
vagus nerve function
Visceral muscle movement (heart, lungs, intestines)
accessory nerve function
swallowing, head, neck, and shoulder movements